Intermuscular Injections
By : Omar M. Subhi AltaieIntermuscular Injection, How to take them and how do they work?
We use intermuscular injections to install medications in the body quickly, by injecting them in the big muscle masses that have the most blood supply; to reach the blood circulation easily and then to the targeted regions in the body.
● Significance
We use intermuscular injections instead of intravenous injections because these types of injections may disturb the veins or sometimes we cannot easily find the right vein.
In other cases we use IM injections because the oral delivery of that medication cannot happen; the medication might be digested in the stomach.
in comparison to subcutaneous injections, the IM injections are significantly absorbed faster. This is because the muscles we inject in, are a great amount of blood supply than the tissue under the skin. Muscle tissue can also bear larger amount of medications than subcutaneous tissues.
In other cases we use IM injections because the oral delivery of that medication cannot happen; the medication might be digested in the stomach.
in comparison to subcutaneous injections, the IM injections are significantly absorbed faster. This is because the muscles we inject in, are a great amount of blood supply than the tissue under the skin. Muscle tissue can also bear larger amount of medications than subcutaneous tissues.
● Regions
several muscles can be used for injections :
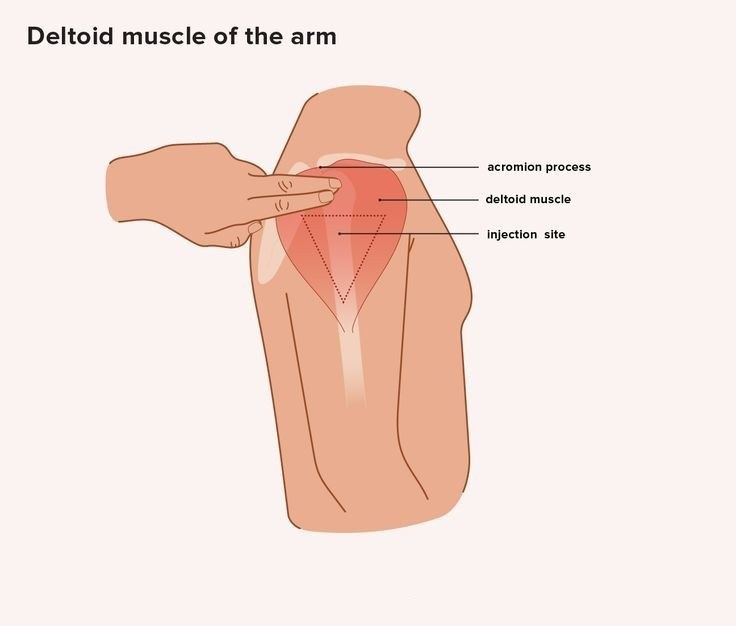
1. deltoid : below the acromion process.
1. deltoid : below the acromion process.
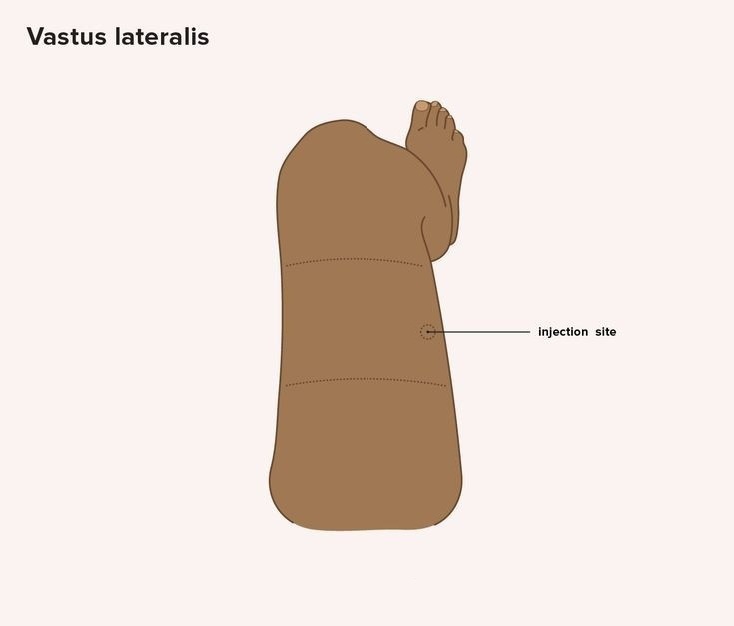
2.Vastus Lateralis: by an imaginary line between the greater trochanter of the femur and the lateral femoral condyle of the knee and giving the injection in the middle third of that line.
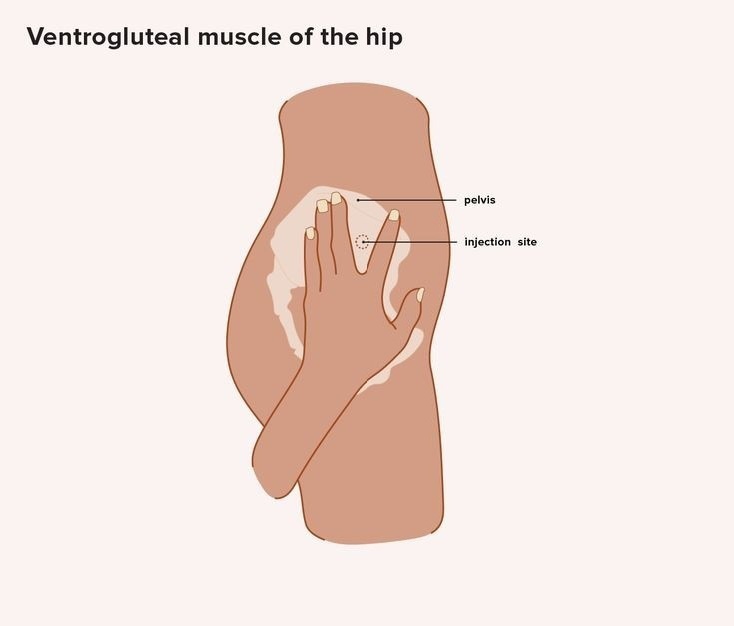
3.Ventrogluteal Region : to make sure that we have chosen the right spot, find the greater trochanter and grip it with the heel of the hand, putting the index finger in the anterior superior iliac spine of the pelvis, and the placing middle finger below the iliac crest - the drug is injected into that triangle formed by the opposite hand, and the iliac crest.
Dorsogluteal Region : the outer upper quadrant of the buttocks, just below the iliac crest.
● Avoiding the sciatic nerve:
By using several landmarks that we discussed in gluteal region article, we can divide the gluteal region into quadrants, to make it easy to avoid particular nerves or vessels.
● the first imagery line is drawn vertically from the highest point of the iliac crest of the pelvis down to the end of the buttock.
● The other line crosses horizontally the first one midway between the highest point of the iliac crest and the horizontal plane through the ischial tuberosity of the pelvis.
The sciatic nerve curves in the lower medial quadrant in its upper lateral corner, then it continues it descending along its lateral margin until the end of that quadrant. Injections can be taken in the anterior corner of the upper lateral quadrant to avoid injury to the sciatic nerve or any other important vessels in the region.
● the first imagery line is drawn vertically from the highest point of the iliac crest of the pelvis down to the end of the buttock.
● The other line crosses horizontally the first one midway between the highest point of the iliac crest and the horizontal plane through the ischial tuberosity of the pelvis.
The sciatic nerve curves in the lower medial quadrant in its upper lateral corner, then it continues it descending along its lateral margin until the end of that quadrant. Injections can be taken in the anterior corner of the upper lateral quadrant to avoid injury to the sciatic nerve or any other important vessels in the region.
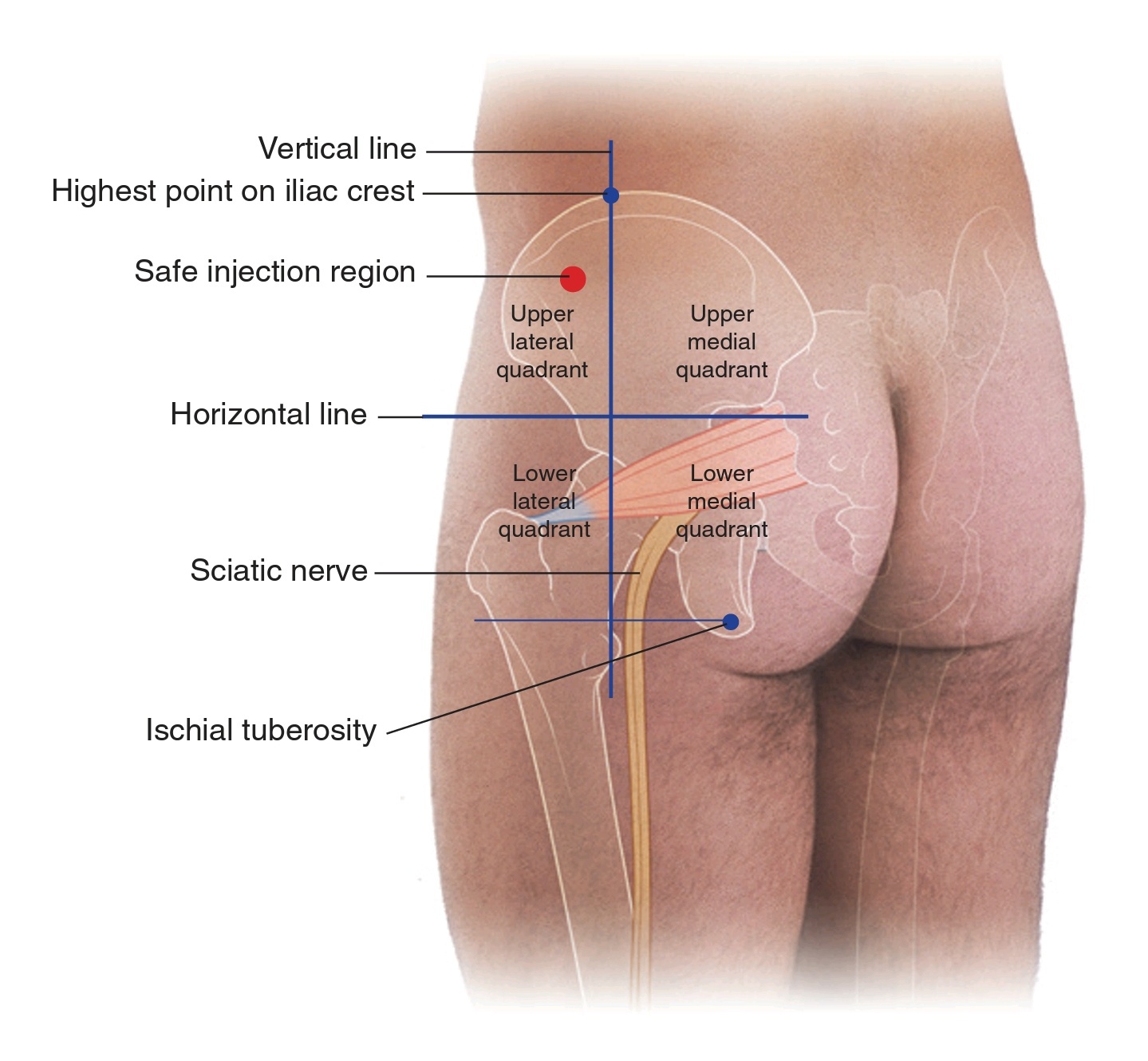
Nerve position in the gluteal region
● Equipment
• syringe : choosing the right size that fits with the needle length; for infants in vastus lateralis muscle the right needle when bunching is (22) and ( 25 mm), and (16-mm) when the skin is stretched.
• For (2-3 years of age) and older children, deltoid, or vastus lateralis muscle is preferred, 25mm to 38mm needle.
• Filter needle that is used to reduce or eliminate particles in medication administered parenterally
• Alcohol-based antiseptic solution (such as isopropyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol)
• The correct drug in an appropriate dose
• Dry cotton buds
• Self-adhesive bandages
• The right size needle and waste disposal unit (trash)
• For (2-3 years of age) and older children, deltoid, or vastus lateralis muscle is preferred, 25mm to 38mm needle.
• Filter needle that is used to reduce or eliminate particles in medication administered parenterally
• Alcohol-based antiseptic solution (such as isopropyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol)
• The correct drug in an appropriate dose
• Dry cotton buds
• Self-adhesive bandages
• The right size needle and waste disposal unit (trash)
● Administration the injections
To achieve the best IM injection process we should follow the following steps:
1. washing the hand : we should make sure to wash our hands carefully for at least 20 seconds by rubbing between our fingers and under the fingernails.
2. wearing the cloves : wearing the cloves to prevent any physical contact with patients, especially if there is sometimes blood in the process if you forget your cloves now you are exposed to bodily fluids.
3. Gathering the right equipment : make sure that you have all the needed supplies at your fingertips. and they are mentioned above.
4. checking the patient : make sure that the patient is lying in a relaxed position and that the muscle that you will inject, is relaxed (extended); because that may obstruct the needle from penetrating the tissue.
5. Cleaning the skin : with 70% isopropyl swab by drawing a circular motion from the center and work your way outward, for 25-30 seconds and let it dry.
2. wearing the cloves : wearing the cloves to prevent any physical contact with patients, especially if there is sometimes blood in the process if you forget your cloves now you are exposed to bodily fluids.
3. Gathering the right equipment : make sure that you have all the needed supplies at your fingertips. and they are mentioned above.
4. checking the patient : make sure that the patient is lying in a relaxed position and that the muscle that you will inject, is relaxed (extended); because that may obstruct the needle from penetrating the tissue.
5. Cleaning the skin : with 70% isopropyl swab by drawing a circular motion from the center and work your way outward, for 25-30 seconds and let it dry.
6. Prepare the syringe with medication:-
• Remove the cap : The rubber stopper on the vial where the syringe is going to penetrate should be cleaned with alcohol.
• Draw air into the syringe : Pull the plunger back to fill the syringe with air that is equal to the volume of the dose that will be injected.
* (We do this; because as we know the vial that contains the medication is a vacuum (it has no air in it) so we put that air from the syringe to the vial to equal amount of air to regulate the pressure).
• Insert air into the vial : without touching the needle remove the cover and penetrate the stopping rubber of the vial and put that air inside it to regulate its pressure.
• Withdraw the medication : turn the supplies you holding upside down at eye level and start to withdraw, observe the fluid coming inside the syringe until you have the right dose, then with small taps on the syringe to remove any bubbles with gentle pressing the plunger.
7. Insert the needle : after the alcohol has dried, use one hand to pull the skin and the fatty tissue on the muscle, an inch away to above or to the side, use the other hand to hold the injection; hold it just like you hold a pen, use your wrist joint to inject the needle in 90-degree angles with a fast and controlled movement.
8. aspiration : after the injection is injected into the muscle the first thing you should do is to aspirate; that means to pull the plunger back a little bit for a few seconds, if you see blood coming in the syringe, should withdraw the syringe and repeat the whole process with another spot, because what happened is that you hit a blood vessel and you don't want to inject the medication straight in it, you can bring damage to that vessel, but if there is no blood, the process continues.
9. Injecting the medication : start injecting the medication slowly (10 seconds for 1 ml) and once the fluid is installed, wait a few more seconds and then withdraw the syringe at the same angle that you injected. After that release, the skin and tissue get back to cover the hole that the syringe made and prevent the fluid from coming back and that is what we called the Z-track .
10. Safe disposal : use the waste disposal unit to dispose of the needle and all other stuff right after the process is done.
To recap the needle the scoop method is recommended; to do that use one hand to hold the uncapped syringe and push the needle through the cap until you cannot push anyone then use a hard surface to recap it completely, now you prevent yourself from getting any inadvertent prick injuries.
11. Apply some pressure on the injected area : you can use gauze to apply small pressure. Note that you should never massage the area that might cause the medication to leak out, and may also cause annoyance and irritation to that area.
● Common complications:
There might be some complications after the injection these are some of them:
○ Noticed pain might be felt at the site of injection by the patient.
○ The abscess might present at the site of the injection.
○ Nerve injury some important nerves in the sites of the injections might be injured if the examiner didn't take care, there is the sciatic nerve in gluteus maximus muscle injection, the femoral nerve in vastus lateralis injections, the superior gluteal nerve in dorsogluteal injection, and there is the radial nerve in deltoid muscle injection.
○ Transmission of the HIV, hepatitis virus through the blood or any bodily fluids that might come out of the patient during the process.
○ Vascular injury is if the needle is injected into one of the vessels in that area.
○ Noticed pain might be felt at the site of injection by the patient.
○ The abscess might present at the site of the injection.
○ Nerve injury some important nerves in the sites of the injections might be injured if the examiner didn't take care, there is the sciatic nerve in gluteus maximus muscle injection, the femoral nerve in vastus lateralis injections, the superior gluteal nerve in dorsogluteal injection, and there is the radial nerve in deltoid muscle injection.
○ Transmission of the HIV, hepatitis virus through the blood or any bodily fluids that might come out of the patient during the process.
○ Vascular injury is if the needle is injected into one of the vessels in that area.
● How do the injections work?
After the medication is injected into the muscle, the blood vessels start the absorption, we use the muscular route when the oral drug absorption is not completely in the right pattern, and when the taken by the patient has a high first-pass effect.
The medication in the muscular injections dissolves much slower than the oral route, and that will provide the right amounts of the dose that will sustain for a long time in the body; the body will be taking small amounts of that dose along that time.
first-pass metabolism or First-pass effect is when an injected medication starts to enter the liver, the liver begins to do its job, the medications undergo extensive biotransformation and thus decreasing its concentration rapidly before it reaches the last target.
The medication in the muscular injections dissolves much slower than the oral route, and that will provide the right amounts of the dose that will sustain for a long time in the body; the body will be taking small amounts of that dose along that time.
first-pass metabolism or First-pass effect is when an injected medication starts to enter the liver, the liver begins to do its job, the medications undergo extensive biotransformation and thus decreasing its concentration rapidly before it reaches the last target.
○ REFERENCES
• Intramuscular Injection Polania Gutierrez JJ, Munakomi S., 2022 Jan., national library of medicine https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556121/
• What Are Intramuscular Injections? Medically reviewed by Avi Varma, MD, MPH, AAHIVS, FAAFP — By Jacquelyn Cafasso — Updated on April 11, 2022, healthline https://www.healthline.com/health/intramuscular-injection#complications
• Z-Track Injections Overview, Medically reviewed by Nicole Galan, RN — By Ann Pietrangelo — Updated on February 8, 2018, healthline https://www.healthline.com/health/z-track-injection#how-to
• Routes of drug administration, first-pass effect WikiLectures https://www.wikilectures.eu/w/Routes_of_drug_administration,_first-pass_effect
• Intramuscular Sedation, In Sedation (Sixth Edition), 2018, ScienceDirect: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/intramuscular-route
• What Are Intramuscular Injections? Medically reviewed by Avi Varma, MD, MPH, AAHIVS, FAAFP — By Jacquelyn Cafasso — Updated on April 11, 2022, healthline https://www.healthline.com/health/intramuscular-injection#complications
• Z-Track Injections Overview, Medically reviewed by Nicole Galan, RN — By Ann Pietrangelo — Updated on February 8, 2018, healthline https://www.healthline.com/health/z-track-injection#how-to
• Routes of drug administration, first-pass effect WikiLectures https://www.wikilectures.eu/w/Routes_of_drug_administration,_first-pass_effect
• Intramuscular Sedation, In Sedation (Sixth Edition), 2018, ScienceDirect: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/intramuscular-route
○ IMAGES REFERENCES
• Cover image from https://www.wikihow.com/Give-a-Newborn-an-IM-Injection?amp=1
• Fig1,2& 3 Illustration by Maya Chastain , healthline website, https://www.healthline.com/health/intramuscular-injection#complications
• Fig4 Posterolateral view of the left gluteal region with gluteal quadrants and the position of the sciatic nerve indicated. Gray's Anatomy for students (4th edition) Fig. 6.129/B page 659
• Fig1,2& 3 Illustration by Maya Chastain , healthline website, https://www.healthline.com/health/intramuscular-injection#complications
• Fig4 Posterolateral view of the left gluteal region with gluteal quadrants and the position of the sciatic nerve indicated. Gray's Anatomy for students (4th edition) Fig. 6.129/B page 659
