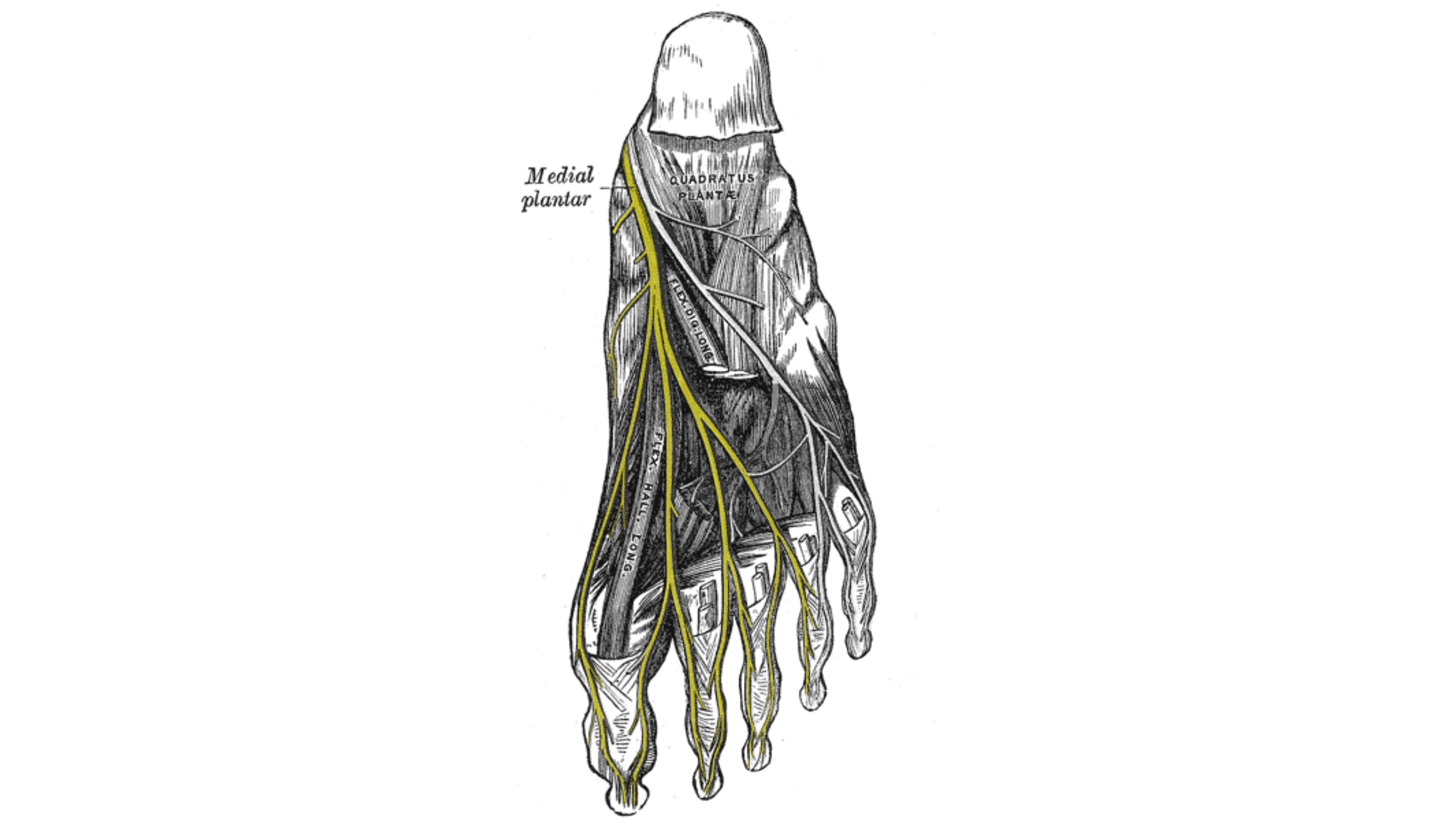
Medial plantar nerve
By : Aisha MohammedDefinition
It is one of the small nerves of the lower limb located at the sole of foot and supplies it. It is the major sensory nerve supply in the sole of the foot and the largest and the most anterior of the two terminal branches of the tibial nerve. It accompanies the medial plantar artery.
The medial plantar nerve supplies more skin area (more cutaneous) and less muscles, comparingly to its counterpart (the lateral plantar nerve). Its resembles the median nerve of the hand in its distribution to both skin and muscles but to the foot.
The medial plantar nerve supplies more skin area (more cutaneous) and less muscles, comparingly to its counterpart (the lateral plantar nerve). Its resembles the median nerve of the hand in its distribution to both skin and muscles but to the foot.
Origin
The medial plantar nerve is the largest terminal division of the tibial nerve. The tibial nerve is the larger component of the sciatic nerve(L4 -S3).
(Spinal cord > Lumbosacral plexus > Sciatic nerve > Tibial nerve > Medial plantar nerve)
(Spinal cord > Lumbosacral plexus > Sciatic nerve > Tibial nerve > Medial plantar nerve)
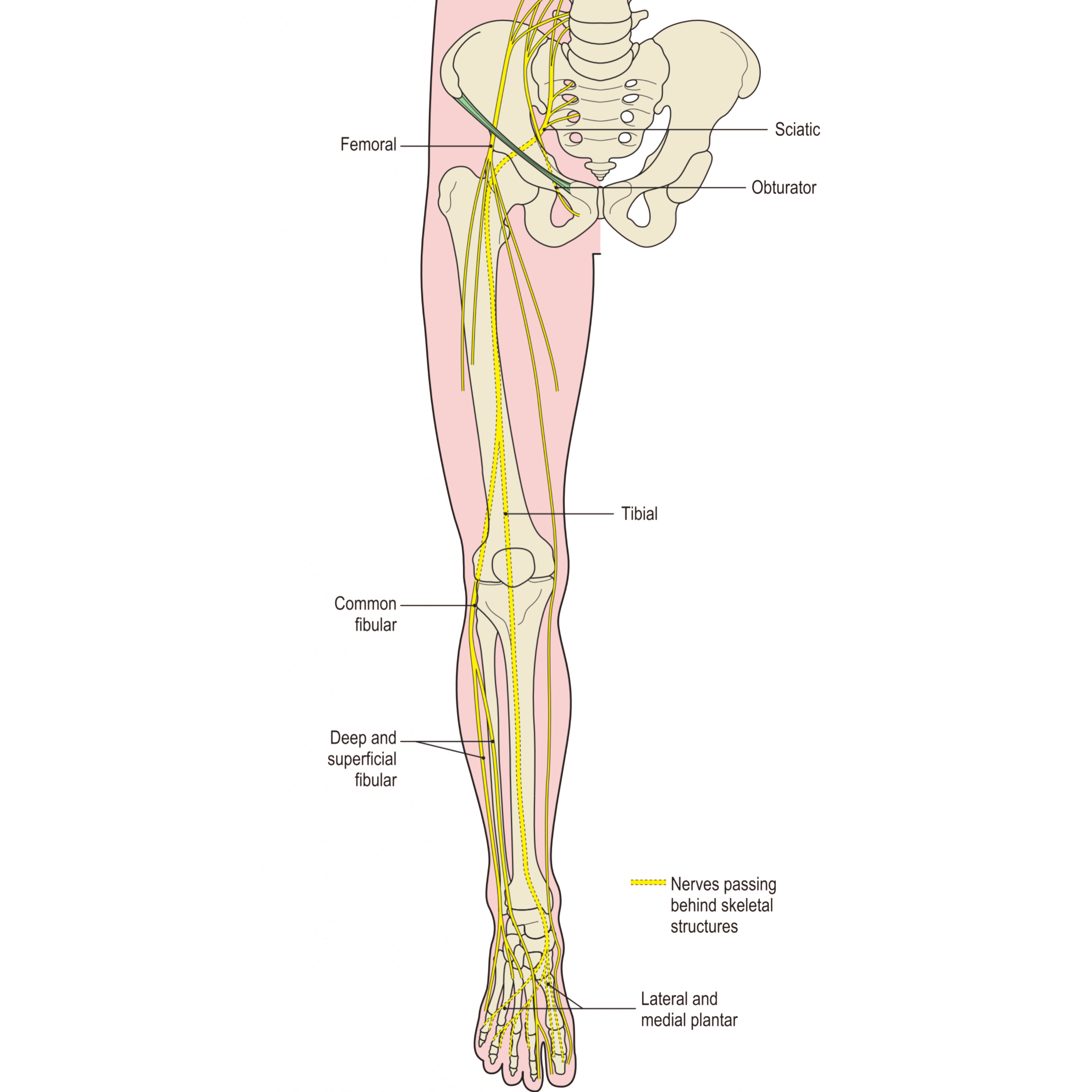
Course
The medial plantar nerve passes behind the ankle and curves under the medial border of the foot. Entering a tunnel behind a bony prominence, (the navicular) bordered by the abductor hallucis muscle. When it enters the sole of foot, it passes forward firstly deep to this abductor hallucis. Then, it goes between the abductor hallucis muscle and the flexor digitorum brevis muscle supplying both muscles, then it gives off a medial proper digital nerve to the great toe . At the base of the metatarsals, it divides into three common plantar digital nerves and each one of them divides into two proper digital branches.
Branches
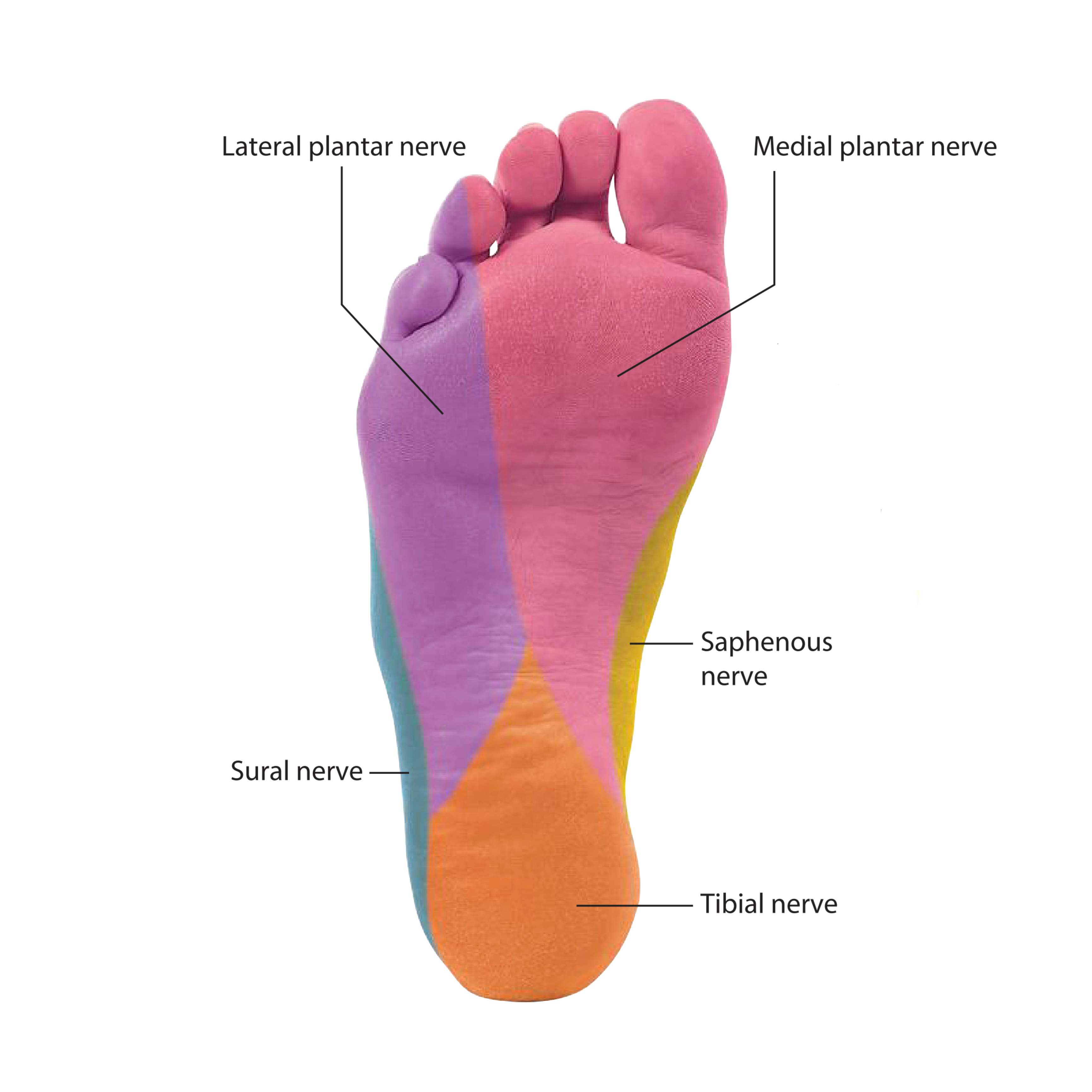
A)Cutaneous branches
Which pierce the plantar aponeurosis between the flexor digitorum brevis and the abductor hallucis muscles to supply the skin of the most of the medial anterior two-thirds of the sole by four branches:
1.The first proper digital nerve (medial proper digital nerve) : which supplies the medial side of great toe.
2.The first common plantar digital nerve : which divides into two proper digital branches to supply the adjacent sides of the great and the second toes.
3.The second common plantar digital nerve : which divides into two proper digital branches to supply the adjacent sides of the second and the third toes.
4.The third common plantar digital nerve : which divides into two proper digital branches to supply the adjacent sides of the third and fourth toes.
B)Muscular branches
1.Two branches originate just near the origin of the nerve and enter the deep surfaces of the muscles supply the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis muscles.
2.Branch from the hallucal medial digital nerve to supply the flexor hallucis brevis muscle.
3.Branch from the first common plantar digital nerve to supply the first lumbrical muscle.
1.Two branches originate just near the origin of the nerve and enter the deep surfaces of the muscles supply the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis muscles. 2.Branch from the hallucal medial digital nerve to supply the flexor hallucis brevis muscle. 3.Branch from the first common plantar digital nerve to supply the first lumbrical muscle.
C)Articular branches
Which supply the joints of the tarsus and metatarsus.
Which pierce the plantar aponeurosis between the flexor digitorum brevis and the abductor hallucis muscles to supply the skin of the most of the medial anterior two-thirds of the sole by four branches:
1.The first proper digital nerve (medial proper digital nerve) : which supplies the medial side of great toe.
2.The first common plantar digital nerve : which divides into two proper digital branches to supply the adjacent sides of the great and the second toes.
3.The second common plantar digital nerve : which divides into two proper digital branches to supply the adjacent sides of the second and the third toes.
4.The third common plantar digital nerve : which divides into two proper digital branches to supply the adjacent sides of the third and fourth toes.
B)Muscular branches
1.Two branches originate just near the origin of the nerve and enter the deep surfaces of the muscles supply the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis muscles.
2.Branch from the hallucal medial digital nerve to supply the flexor hallucis brevis muscle.
3.Branch from the first common plantar digital nerve to supply the first lumbrical muscle.
1.Two branches originate just near the origin of the nerve and enter the deep surfaces of the muscles supply the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis muscles. 2.Branch from the hallucal medial digital nerve to supply the flexor hallucis brevis muscle. 3.Branch from the first common plantar digital nerve to supply the first lumbrical muscle.
C)Articular branches
Which supply the joints of the tarsus and metatarsus.
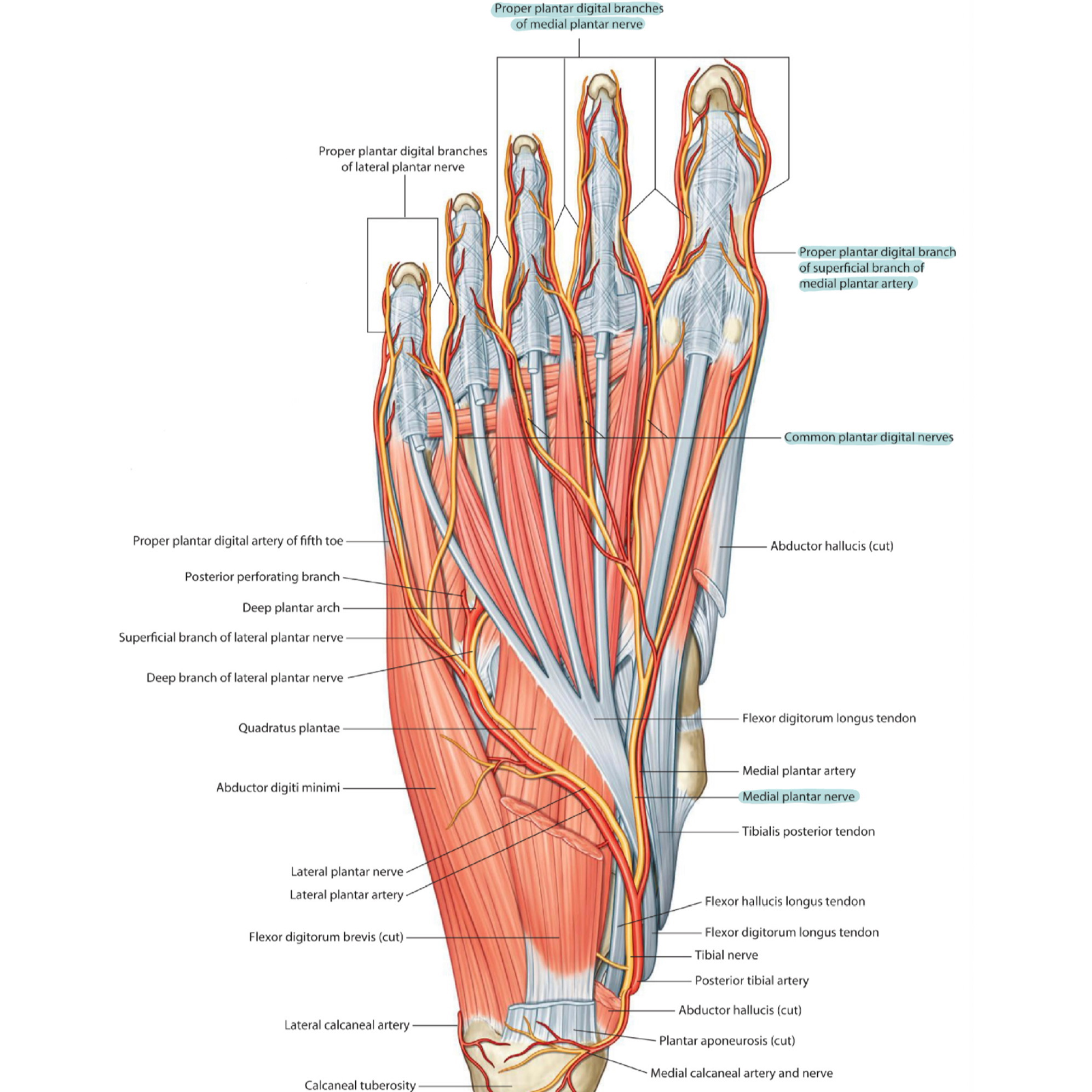
Clinical notes
1.Medial plantar nerve entrapment
It’s the compression of medial plantar nerve or its branches between bone, ligaments, and other connective tissues when passing deep to the flexor retinaculum of foot or deep to abductor hallucis. It can occur during repetitive eversion of the foot or any other compression leading classically to a burning sensation in the distribution of that nerve and causing pain. The pain gets worse when the ankle is moving and some conditions(as wearing certain inappropriate shoes or doing some exercises as running) could create additional pressure on the affected nerves.
Note : Because of its frequency in runners, these symptoms are called "jogger's foot”
2.Jogger's foot (Medial Plantar Neuropraxia)
It’s a chronic medial plantar nerve entrapment syndrome in the long distance-runners. Flat feet runners are more exposed to get injured than people with more obvious longitudinal arch of their foot, because in flat foot there is more pressure is exerted on the nerve, and this is because the foot has more contraction with the ground and the force.
Repetitive trauma and inflammation could cause:
1.Swelling
2.Compression of the medial plantar nerve at the tunnel behind the navicular bone.
The patient also could show:
1.Occasional weakness of the foot or toes.
2.Increased burning at the deep aspect of the heel.
Treatment:
It can consist of many steps including:
1.Resting
2.Changing the mechanical forces at play that lead to the nerve irritation
3.Manual therapy (ART nerve release) In severe cases, the surgical release of the nerve entrapment is neede.
3.Morton's neuroma
It is one of the most common form of nerve entrapment in the foot. Which is a condition of thickening of the tissue around a nerve in the foot. Most commonly , it affects the third common plantar digital nerve at the third interspace between the third and fourth toes because it is the region where the nerve is joined by the common plantar digital nerve of lateral plantar nerve, so the resulting nerve will be larger in diameter than other nerves. When the patient enters the push-off phase of walking, the forces tend to compress the common plantar nerve (which is sandwiched between the ground and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament) which can be irritated. Usually in such cases, there is some associated inflammatory changes and the thickening factor could cause sharp, burning pain at the ball of the foot.
Treatment : It may include an injection of the anti-inflammatory drugs, or it may be necessary to a surgical removal of the lesion.
It’s the compression of medial plantar nerve or its branches between bone, ligaments, and other connective tissues when passing deep to the flexor retinaculum of foot or deep to abductor hallucis. It can occur during repetitive eversion of the foot or any other compression leading classically to a burning sensation in the distribution of that nerve and causing pain. The pain gets worse when the ankle is moving and some conditions(as wearing certain inappropriate shoes or doing some exercises as running) could create additional pressure on the affected nerves.
Note : Because of its frequency in runners, these symptoms are called "jogger's foot”
2.Jogger's foot (Medial Plantar Neuropraxia)
It’s a chronic medial plantar nerve entrapment syndrome in the long distance-runners. Flat feet runners are more exposed to get injured than people with more obvious longitudinal arch of their foot, because in flat foot there is more pressure is exerted on the nerve, and this is because the foot has more contraction with the ground and the force.
Repetitive trauma and inflammation could cause:
1.Swelling
2.Compression of the medial plantar nerve at the tunnel behind the navicular bone.
The patient also could show:
1.Occasional weakness of the foot or toes.
2.Increased burning at the deep aspect of the heel.
Treatment:
It can consist of many steps including:
1.Resting
2.Changing the mechanical forces at play that lead to the nerve irritation
3.Manual therapy (ART nerve release) In severe cases, the surgical release of the nerve entrapment is neede.
3.Morton's neuroma
It is one of the most common form of nerve entrapment in the foot. Which is a condition of thickening of the tissue around a nerve in the foot. Most commonly , it affects the third common plantar digital nerve at the third interspace between the third and fourth toes because it is the region where the nerve is joined by the common plantar digital nerve of lateral plantar nerve, so the resulting nerve will be larger in diameter than other nerves. When the patient enters the push-off phase of walking, the forces tend to compress the common plantar nerve (which is sandwiched between the ground and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament) which can be irritated. Usually in such cases, there is some associated inflammatory changes and the thickening factor could cause sharp, burning pain at the ball of the foot.
Treatment : It may include an injection of the anti-inflammatory drugs, or it may be necessary to a surgical removal of the lesion.
Cadavers
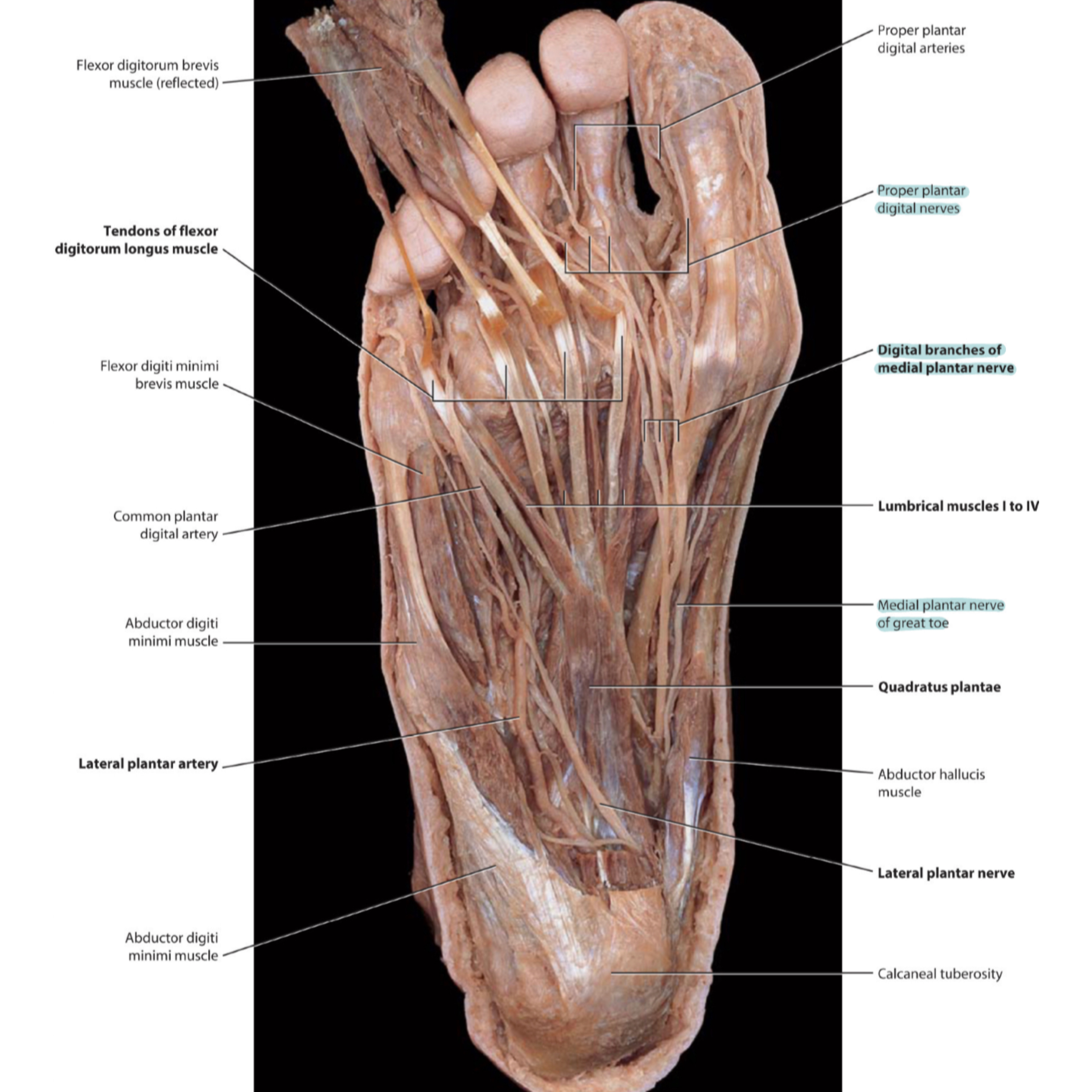
Cadaver shows the medial plantar nerve (sole of foot)
References
• Anne MR Agur, Arthur F Dalley, and Keith L. Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy 8th edition/ Copyright © 2018 Wolters Kluwer / pages (776-784)
• Susan Standring, Neel Anand, Rolfe Birch, Patricia Collins, Alan R Crossman, Michael Gleeson , Girish Jawaheer, Ariana L Smith, Jonathan D Spratt, Mark D Stringer, R Shane Tubbs, Richard Tunstall, Alan J Wein, Caroline B Wigley ‘s Gray's Anatomy The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. copyright © 2016, Elsevier Limited. Forty-first
edition. Pages(1447)
• Adam W. M. Mitchell, Richard L. Drake, and Wayne Vogl’s Gray's Anatomy for Students. 4th edition/ Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. / pages (656-657)
• What is Jogger’s Foot (Medial Plantar Neuropraxia) By Scott Kaar for sportsmd https://www.sportsmd.com/sports-injuries/foot-ankle-injuries/joggers-foot/
• Jogger’s foot - another cause od Heel and foot pain common in distance runners by Mark
Hawkins for In Motion Spine and Joint Center ( IMSJC) https://www.imsjc.com/articles/joggers-foot-another-cause-of-heel-and-foot-pain-common- in-distance-runners
• Kenneth Prakash Moses, John C. Banks, Jr., Pedro B. Nava, Darrell K. Petersen, ‘ s ATLAS OF CLINICAL GROSS ANATOMY.Copyright © 2013, 2005, by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.second eidtion.pages(604.FIGURE 47.12)
• Morton's neuroma by mayo clinic staff for Mayoclinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases conditions/mortons-neuroma/symptoms-causes/ syc20351935#:~:text=Morton's%20neuroma%20involves%20a%20thickening,numbness% 20in%20the%20affected%20toes.
• Adam W. M. Mitchell, Richard L. Drake, Richard M. Tibbitts, Paul E. Richardson ,and Wayne Vogl’s Gray's atlas of Anatomy 2nd edition/ Copyright © 2015, 2008 by Churchill Livingstone, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. / pages (361)
• Susan Standring, Neel Anand, Rolfe Birch, Patricia Collins, Alan R Crossman, Michael Gleeson , Girish Jawaheer, Ariana L Smith, Jonathan D Spratt, Mark D Stringer, R Shane Tubbs, Richard Tunstall, Alan J Wein, Caroline B Wigley ‘s Gray's Anatomy The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. copyright © 2016, Elsevier Limited. Forty-first
edition. Pages(1447)
• Adam W. M. Mitchell, Richard L. Drake, and Wayne Vogl’s Gray's Anatomy for Students. 4th edition/ Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. / pages (656-657)
• What is Jogger’s Foot (Medial Plantar Neuropraxia) By Scott Kaar for sportsmd https://www.sportsmd.com/sports-injuries/foot-ankle-injuries/joggers-foot/
• Jogger’s foot - another cause od Heel and foot pain common in distance runners by Mark
Hawkins for In Motion Spine and Joint Center ( IMSJC) https://www.imsjc.com/articles/joggers-foot-another-cause-of-heel-and-foot-pain-common- in-distance-runners
• Kenneth Prakash Moses, John C. Banks, Jr., Pedro B. Nava, Darrell K. Petersen, ‘ s ATLAS OF CLINICAL GROSS ANATOMY.Copyright © 2013, 2005, by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.second eidtion.pages(604.FIGURE 47.12)
• Morton's neuroma by mayo clinic staff for Mayoclinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases conditions/mortons-neuroma/symptoms-causes/ syc20351935#:~:text=Morton's%20neuroma%20involves%20a%20thickening,numbness% 20in%20the%20affected%20toes.
• Adam W. M. Mitchell, Richard L. Drake, Richard M. Tibbitts, Paul E. Richardson ,and Wayne Vogl’s Gray's atlas of Anatomy 2nd edition/ Copyright © 2015, 2008 by Churchill Livingstone, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. / pages (361)
