Nail Unit
By : Malak AlsammanDefinition
The nail unit : is a group of distal digital structures that located on the dorsal surface of the fingers and toes.
The Functions of the Nail Unit :
•It protects the digits from cuts and traumas.
•It increases the dexterity and the sensitivity, because they stop the otherwise potentially fleshy skinny bit of the tip of the finger from moving around too much so, all the sensors and receptors stay in place during touching things and picking up things.
The Nail Unit components
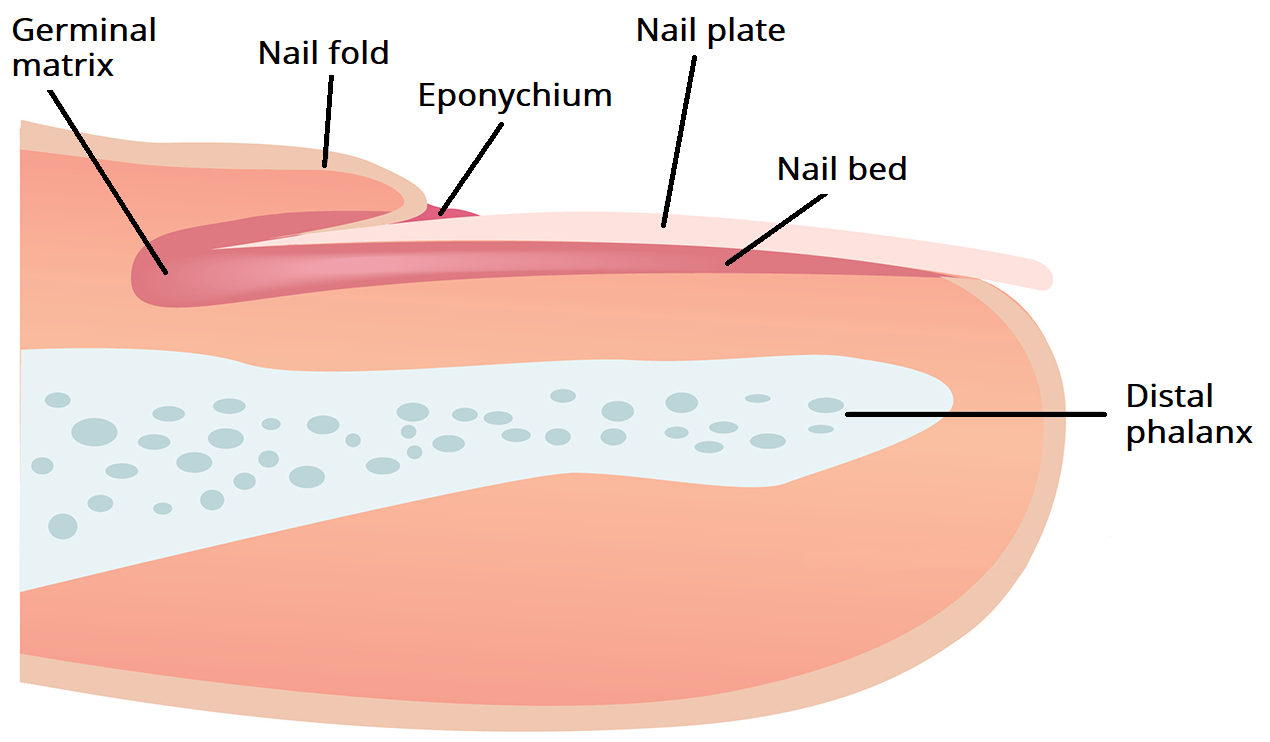
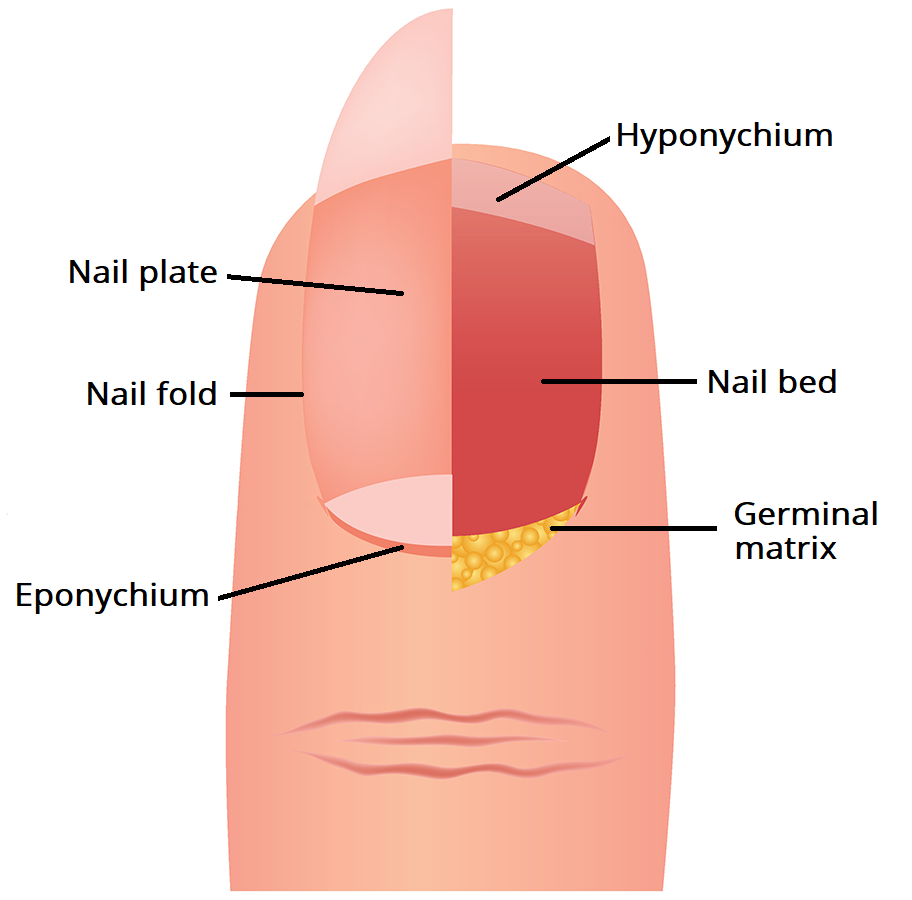
Nail plate : or nail body ( it is the thing that we call a nail ) ,
•Distally, it has a free edge
• It is anchored to the nail bed
•It is translucent , hard and flexible ( it appears pink due to the colour of the nail bed below it)
•It is made of keratin ( which it’s a fibrous protein that it’s hard , structural , insoluble and waterproof ).
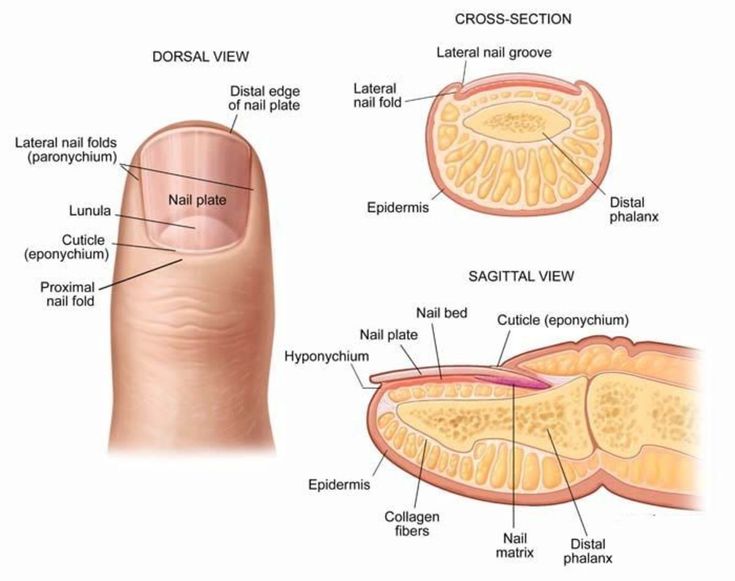
Nail folds : skin that surrounds and protects the proximal and lateral borders
of the nail plate.
Nail bed : which also called as sterile matrix (it’s the skin deep to nail plate )
•It’s epithelium, like the skin
•It is located deep to the nail plate and attaching it to the distal phalanx, it is well anchored to stop the nail from moving around
•It provides a smooth area for growing the nail plate, but it doesn’t help in the plate growth itself
•It has a lot of capillaries so, it has a really good blood supply and this gives the pink colour
Note : when you flex your nail or squeeze the nail bed, it turns white because the blood is pushed out from that area then when you release it, it returns pink and this is kind of helpful to indicate the peripheral blood flow so, if you see bluing or slowing you will figure out that the blood supply is not that good right now.
Nail Matrix : or germinal matrix
•It is an area of soft tissue which is located proximal to the nail bed
•The cells of the nail matrix divide , keratinize , and their cytoplasm is replaced by keratin and protein filaments and then the cells die to form the nail plate and the continuous of divisions pushes the nail plate over the nail bed as it matures
•It produces about 90% of the new nail.
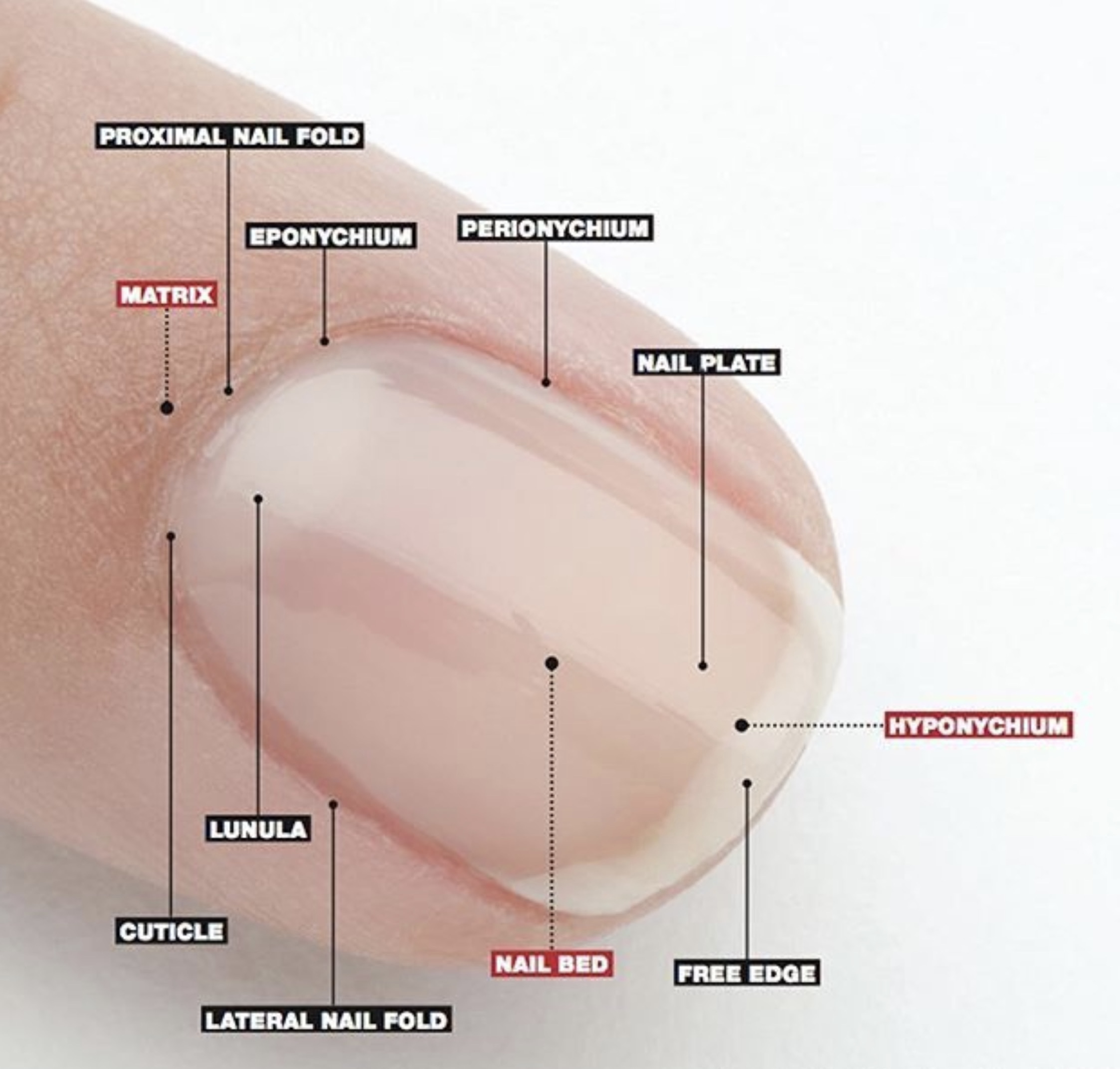
Lunula : it’s a white half moon appearance of the nail matrix ( lunula is the visible part of the nail matrix ) that appears at the proximal ends of the nail and it is different from the rest of the nail.
Eponychium (cuticle) : it’s where the lunula meets the skin.
Hyponychium : it’s the area that located under the free edge of the nail plate ( distal end ).....distal to the nail bed.
Paronychium ; it’s where the nail plate meets the skin on the each sides laterally.
•Distally, it has a free edge
• It is anchored to the nail bed
•It is translucent , hard and flexible ( it appears pink due to the colour of the nail bed below it)
•It is made of keratin ( which it’s a fibrous protein that it’s hard , structural , insoluble and waterproof ).
Nail folds : skin that surrounds and protects the proximal and lateral borders
of the nail plate.
Nail bed : which also called as sterile matrix (it’s the skin deep to nail plate )
•It’s epithelium, like the skin
•It is located deep to the nail plate and attaching it to the distal phalanx, it is well anchored to stop the nail from moving around
•It provides a smooth area for growing the nail plate, but it doesn’t help in the plate growth itself
•It has a lot of capillaries so, it has a really good blood supply and this gives the pink colour
Note : when you flex your nail or squeeze the nail bed, it turns white because the blood is pushed out from that area then when you release it, it returns pink and this is kind of helpful to indicate the peripheral blood flow so, if you see bluing or slowing you will figure out that the blood supply is not that good right now.
Nail Matrix : or germinal matrix
•It is an area of soft tissue which is located proximal to the nail bed
•The cells of the nail matrix divide , keratinize , and their cytoplasm is replaced by keratin and protein filaments and then the cells die to form the nail plate and the continuous of divisions pushes the nail plate over the nail bed as it matures
•It produces about 90% of the new nail.
Lunula : it’s a white half moon appearance of the nail matrix ( lunula is the visible part of the nail matrix ) that appears at the proximal ends of the nail and it is different from the rest of the nail.
Eponychium (cuticle) : it’s where the lunula meets the skin.
Hyponychium : it’s the area that located under the free edge of the nail plate ( distal end ).....distal to the nail bed.
Paronychium ; it’s where the nail plate meets the skin on the each sides laterally.
Fun Facts
•Your nails are part of your integumentary system which also includes the skin...... and hair ( this system’s job is to protect deeper tissues ).
•Your nails are fixed in place because they are adherent to the nail bed, which it has a dermis that is tightly adherent to the periosteum of the bone (which is the connective tissue covering the bone ) so, the nail is kind of fixed to the bone and to these all different layers …..this is why your nail doesn’t move around very easily.
•Your nails grow about half a millimetres a week (fingernails grow faster than toenails ).
•Your nails on your fingers grow faster than those on your toes , the nails on longer fingers also grow faster so do nails that get bitten , nails also grow faster in summer than in winter .
•The white colour of the lunula is because that its cells haven’t keratinized yet ( haven’t lost their nucleus yet) in the nail producing process .
•Your nails are fixed in place because they are adherent to the nail bed, which it has a dermis that is tightly adherent to the periosteum of the bone (which is the connective tissue covering the bone ) so, the nail is kind of fixed to the bone and to these all different layers …..this is why your nail doesn’t move around very easily.
•Your nails grow about half a millimetres a week (fingernails grow faster than toenails ).
•Your nails on your fingers grow faster than those on your toes , the nails on longer fingers also grow faster so do nails that get bitten , nails also grow faster in summer than in winter .
•The white colour of the lunula is because that its cells haven’t keratinized yet ( haven’t lost their nucleus yet) in the nail producing process .
Nail bed injury
• Nail bed injury : it’s a damage to the soft tissue below the nail plate ( nail bed and nail matrix ) it could happen when you get your fingers or toes hit , crush or cut by something and it's a common thing to happen .
There are three types of nail bed injury:
• Subungual hematomas
It happens when a small blood vessel beneath your nail bed leak ...and blood gather between you nail and nail bed ,
this could happen when you get your tip of the fingers or toes crushed by something , also when you wear a tight shoes CUZ it can put pressure on the blood vessels and causes leakage .
Fact the colour of hematomas can change from red or purple to brown or black .
Laceration
It happens when a cut or laceration pierces the nail and nail bed . This can cause large Subungual hematomas.
Avulsions
This happens when your nail and part of your nail bed pulling a way partly or entirely from the rest of your nail bed.
Treatment
• Treatment depends on the injury severity and the degree of injury .
So if you have a minor nail bed injury you can treat it at home ....By washing the injured area , bandaging it , applying some ice , or lifting the injured hand or foot or applying gentle compression to reduce any throbbing .
If you found that you have a severe Subungual hematomas , first of all, you need to have an x-ray of the affected finger or toe to make sure that there is no bony injury ( because these injuries are usually related to the distal phalanx injury)
and the doctor may treat this by making a small hole in the nail and draining the gathering blood ....
If the nail is damaged or the blood covers more than half of the nail the doctor may remove the nail and repair the nail bed and matrix
If the nail is badly damaged the doctor may attach a synthetic nail .
There are three types of nail bed injury:
• Subungual hematomas
It happens when a small blood vessel beneath your nail bed leak ...and blood gather between you nail and nail bed ,
this could happen when you get your tip of the fingers or toes crushed by something , also when you wear a tight shoes CUZ it can put pressure on the blood vessels and causes leakage .
Fact the colour of hematomas can change from red or purple to brown or black .
Laceration
It happens when a cut or laceration pierces the nail and nail bed . This can cause large Subungual hematomas.
Avulsions
This happens when your nail and part of your nail bed pulling a way partly or entirely from the rest of your nail bed.
Treatment
• Treatment depends on the injury severity and the degree of injury .
So if you have a minor nail bed injury you can treat it at home ....By washing the injured area , bandaging it , applying some ice , or lifting the injured hand or foot or applying gentle compression to reduce any throbbing .
If you found that you have a severe Subungual hematomas , first of all, you need to have an x-ray of the affected finger or toe to make sure that there is no bony injury ( because these injuries are usually related to the distal phalanx injury)
and the doctor may treat this by making a small hole in the nail and draining the gathering blood ....
If the nail is damaged or the blood covers more than half of the nail the doctor may remove the nail and repair the nail bed and matrix
If the nail is badly damaged the doctor may attach a synthetic nail .
References
The Nail Unit - Plate - Germinal Matrix - Bed - TeachMeAnatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/misc/nail-unit/
Nail bed injury: Pictures, types, and treatments - Medical News Today
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/nail-bed-injury
Lateral view of the nail unit , TeachMeAnatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/wp-content/uploads/Lateral-view-of-the-Nail-Unit-Anatomy-1024x598.png
Anterior view of the nail unit , TeachMeAnatomy ,https://teachmeanatomy.info/wp-content/uploads/Anterior-Aspect-of-the-Nail-Unit-Anatomy.png
Nail anatomy , Nailpro , https://www.nailpro.com/health/article/21157886/nail-anatomy-a-professional-primer-on-the-parts-of-the-nail
Nail bed injury: Pictures, types, and treatments - Medical News Today
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/nail-bed-injury
Lateral view of the nail unit , TeachMeAnatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/wp-content/uploads/Lateral-view-of-the-Nail-Unit-Anatomy-1024x598.png
Anterior view of the nail unit , TeachMeAnatomy ,https://teachmeanatomy.info/wp-content/uploads/Anterior-Aspect-of-the-Nail-Unit-Anatomy.png
Nail anatomy , Nailpro , https://www.nailpro.com/health/article/21157886/nail-anatomy-a-professional-primer-on-the-parts-of-the-nail
