CUBITAL FOSSA
By : Karam AlanazIntroduction
Definition :
The cubital fossa is superficially apparent as a depression on the anterior aspect of the elbow region.
Site :
it is an intermuscular space in front of the elbow.
Shape :
It is triangular in shape, its base above & apex below.
The cubital fossa is superficially apparent as a depression on the anterior aspect of the elbow region.
Site :
it is an intermuscular space in front of the elbow.
Shape :
It is triangular in shape, its base above & apex below.
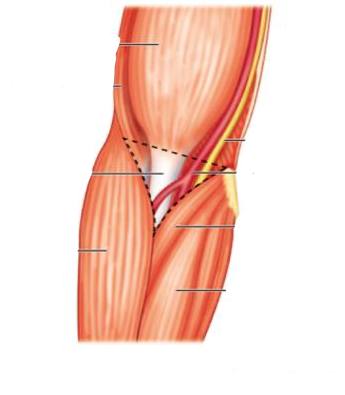
Boundaries
(1) base: an imaginary line between the 2 humeral epicondyles.
(2) medial border: pronator teres m.
(3) lateral border: brachioradialis m.
(4) apex: is formed by the meeting of the medial &lateral borders (brachioradialis overlapping pronator teres).
Floor
formed by:
(1) brachialis (above &medially)
(2) supinator (below &laterally)
Roof
formed by:
(1) skin.
(2) superficial fascia containing :
(a) basilic v. with anterior branch of medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (medially)
(b) cephalic v. with anterior-branch of lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm (laterally)
(c) median cubital v. :Connecting the basilic & cephalic veins.
(3) deep fascia (reinforced by the bicipital aponeurosis).
(2) medial border: pronator teres m.
(3) lateral border: brachioradialis m.
(4) apex: is formed by the meeting of the medial &lateral borders (brachioradialis overlapping pronator teres).
Floor
formed by:
(1) brachialis (above &medially)
(2) supinator (below &laterally)
Roof
formed by:
(1) skin.
(2) superficial fascia containing :
(a) basilic v. with anterior branch of medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (medially)
(b) cephalic v. with anterior-branch of lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm (laterally)
(c) median cubital v. :Connecting the basilic & cephalic veins.
(3) deep fascia (reinforced by the bicipital aponeurosis).
Content
arranged from medial to lateral as follows:
(1) Median n.: leaves the fossa by passing between the heads of pronator teres m.
(2) the terminal part of the brachial artery &the beginning of both radial &ulnar arteries:
(a) the radial a. leaves the fossa by passing deep to its apex. (b) ulnar a. "it leaves by pronator teres m.
(3) Biceps tendon passes backward to reach its insertion in the radial tuberosity.
(4) Radial nerve &its posterior Interosseous branch(deep branch), the radial nerve leaves the fossa by passing deep to the brachioradialis m. , the posterior interosseous n. leaves the fossa by piercing the supinator m.
*the cubital fossa contains one lymph node (epitrochlear) lying in front of the medial epicondyle of the humerus.
(1) Median n.: leaves the fossa by passing between the heads of pronator teres m.
(2) the terminal part of the brachial artery &the beginning of both radial &ulnar arteries:
(a) the radial a. leaves the fossa by passing deep to its apex. (b) ulnar a. "it leaves by pronator teres m.
(3) Biceps tendon passes backward to reach its insertion in the radial tuberosity.
(4) Radial nerve &its posterior Interosseous branch(deep branch), the radial nerve leaves the fossa by passing deep to the brachioradialis m. , the posterior interosseous n. leaves the fossa by piercing the supinator m.
*the cubital fossa contains one lymph node (epitrochlear) lying in front of the medial epicondyle of the humerus.
Clinical Notes
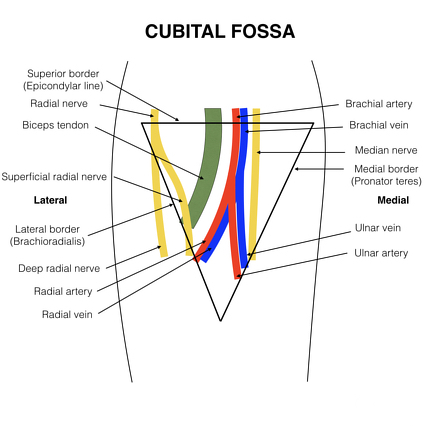
1- Bicipital Myotatic Reflex
The biceps reflex is one of several deep tendon reflexes that are routinely tested during physical examinations. The relaxed limb is passively pronated and partially extended at the elbow. The examiner’s thumb is firmly placed on the biceps tendon, and the reflex hammer is briskly tapped at the base of the nail bed of the examiner’s thumb. A normal (positive) response is an involuntary contraction of the biceps, felt as a momentarily tensed tendon, usually with a brief jerk-like flexion of the elbow. A positive response confirms the integrity of the musculocutaneous nerve and the C5 and C6 spinal cord segments. Excessive, diminished, or prolonged (hung) responses may indicate central or peripheral nervous system disease, or metabolic disorders (e.g., thyroid disease).
2- Venipuncture :
the veins in the cubital fossa varies greatly. In approximately 20% of people, a median antebrachial vein (median vein of the forearm) divides into a median basilic vein, which joins the basilic vein of the arm, and a median cephalic vein, which joins the cephalic vein of the arm. Once the vein is punctured to receive blood that needed for CBC TEST ( Complete blood test )
3- The median cubital vein in the cubital fossa is also a site for the introduction of cardiac catheters to examine the great vessels and chambers of the heart
The biceps reflex is one of several deep tendon reflexes that are routinely tested during physical examinations. The relaxed limb is passively pronated and partially extended at the elbow. The examiner’s thumb is firmly placed on the biceps tendon, and the reflex hammer is briskly tapped at the base of the nail bed of the examiner’s thumb. A normal (positive) response is an involuntary contraction of the biceps, felt as a momentarily tensed tendon, usually with a brief jerk-like flexion of the elbow. A positive response confirms the integrity of the musculocutaneous nerve and the C5 and C6 spinal cord segments. Excessive, diminished, or prolonged (hung) responses may indicate central or peripheral nervous system disease, or metabolic disorders (e.g., thyroid disease).
2- Venipuncture :
the veins in the cubital fossa varies greatly. In approximately 20% of people, a median antebrachial vein (median vein of the forearm) divides into a median basilic vein, which joins the basilic vein of the arm, and a median cephalic vein, which joins the cephalic vein of the arm. Once the vein is punctured to receive blood that needed for CBC TEST ( Complete blood test )
3- The median cubital vein in the cubital fossa is also a site for the introduction of cardiac catheters to examine the great vessels and chambers of the heart

Referances
1-Anatomy of upper limb by Sameh Doss , p.56
2- Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition , p.514,p.517,p.521,p.539,p.540,p542
Figures:
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition , Figure B3.19 - median vein of forearm.
color Atlas of anatomy seventh edition,p.416,p417,p.418
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition, figure 3.55 surface anatomy of cutiba fossa .
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition , figure B3.14 method of eliciting and biceps reflex.
Cubital fossa - Quizlet ,https://images.app.goo.gl/KnwzxhUVjNKEzxNF8
2- Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition , p.514,p.517,p.521,p.539,p.540,p542
Figures:
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition , Figure B3.19 - median vein of forearm.
color Atlas of anatomy seventh edition,p.416,p417,p.418
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition, figure 3.55 surface anatomy of cutiba fossa .
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition , figure B3.14 method of eliciting and biceps reflex.
Cubital fossa - Quizlet ,https://images.app.goo.gl/KnwzxhUVjNKEzxNF8
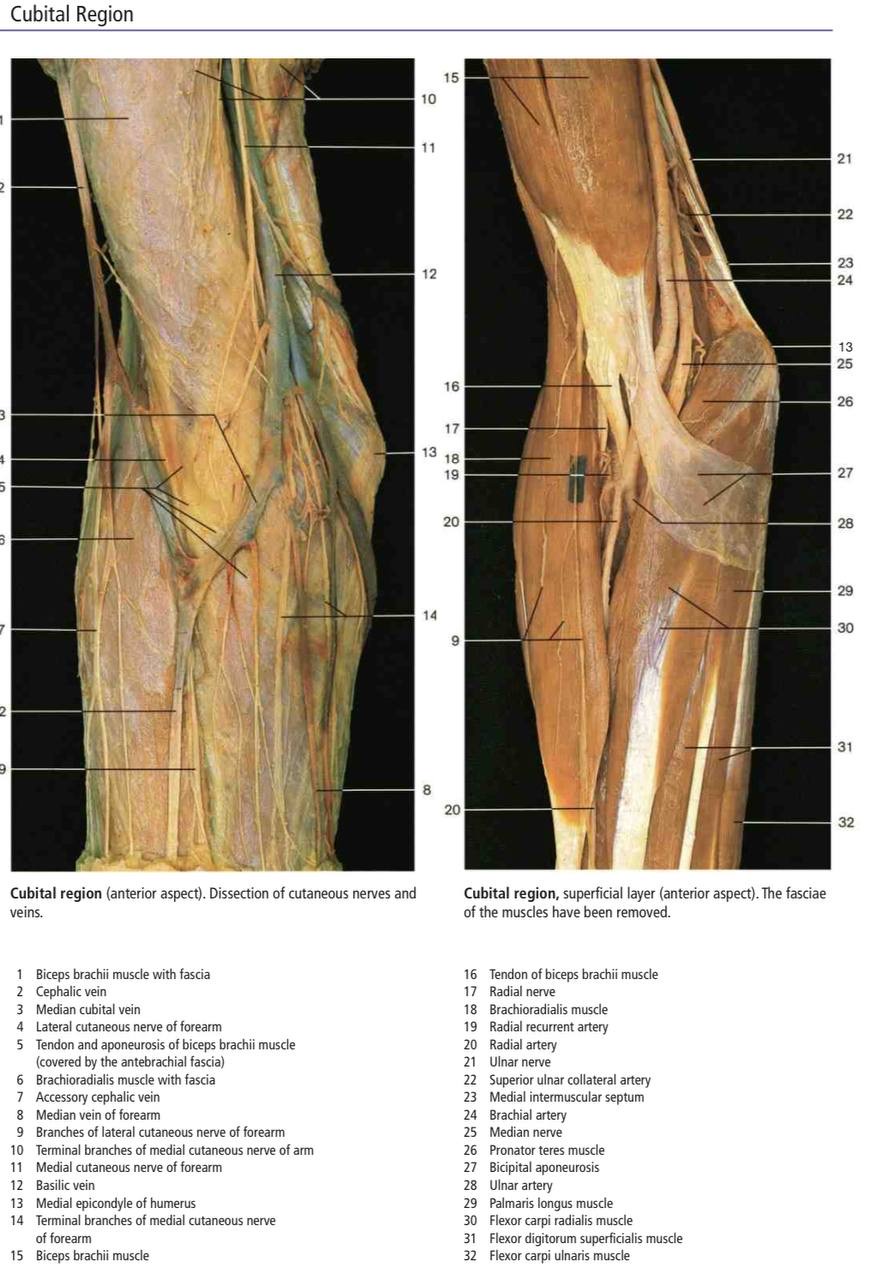
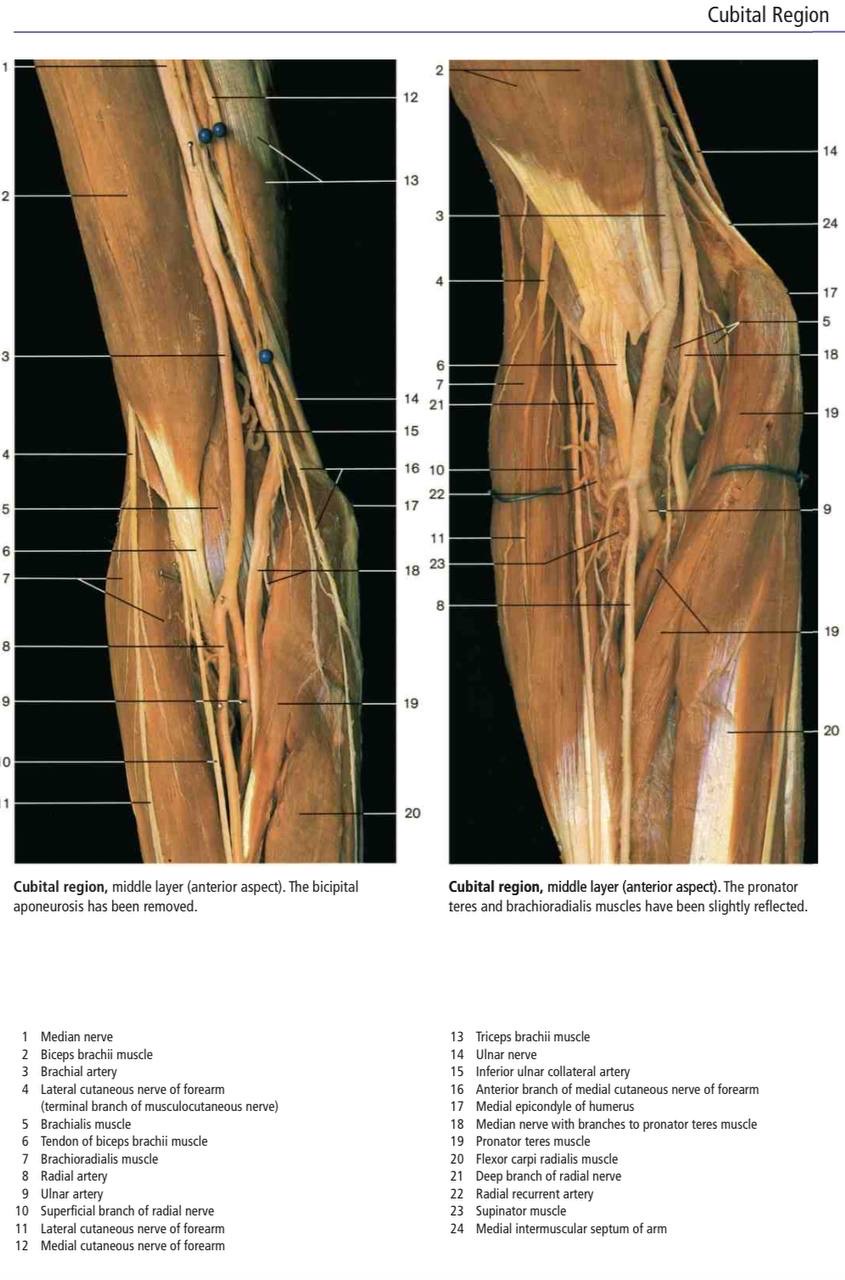
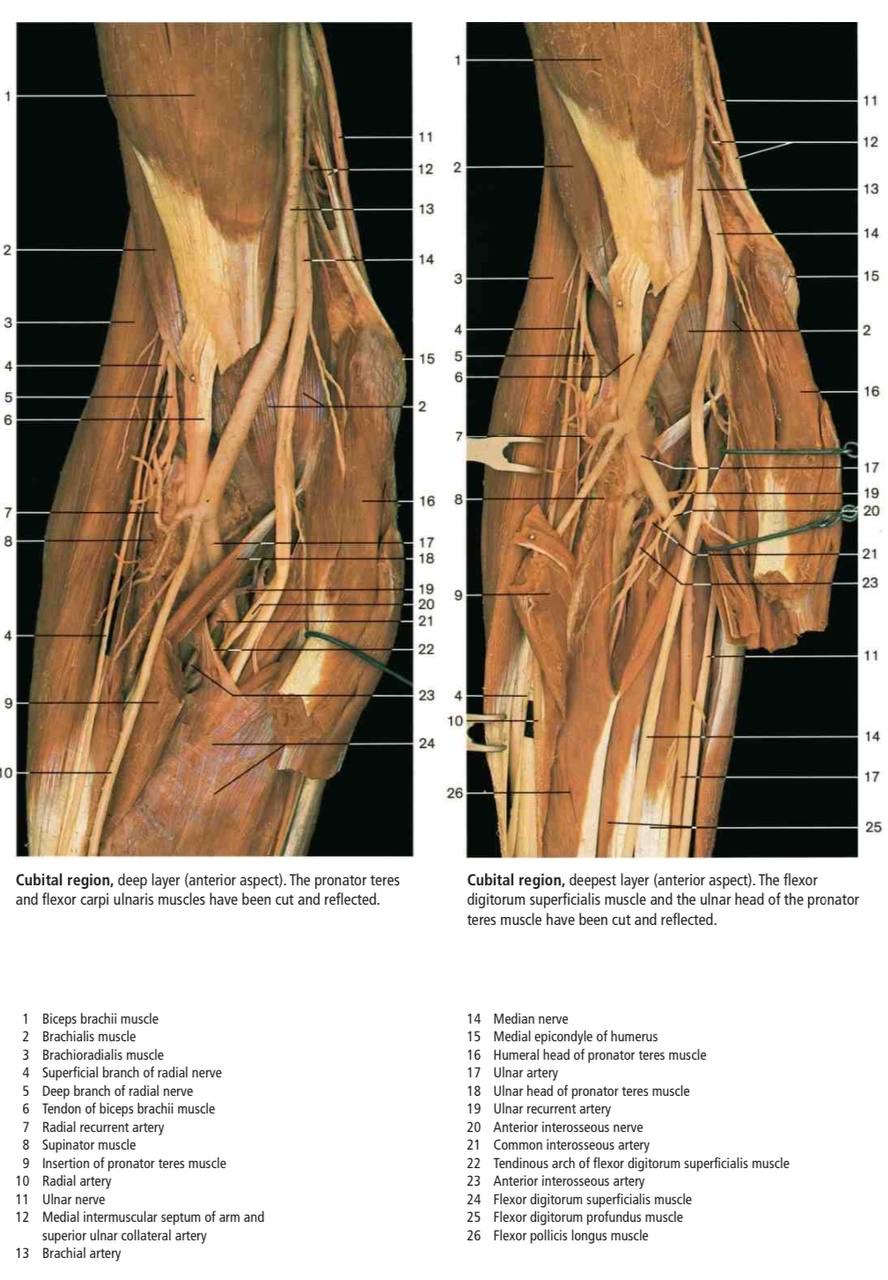
Real Images of Cubital fossa
