
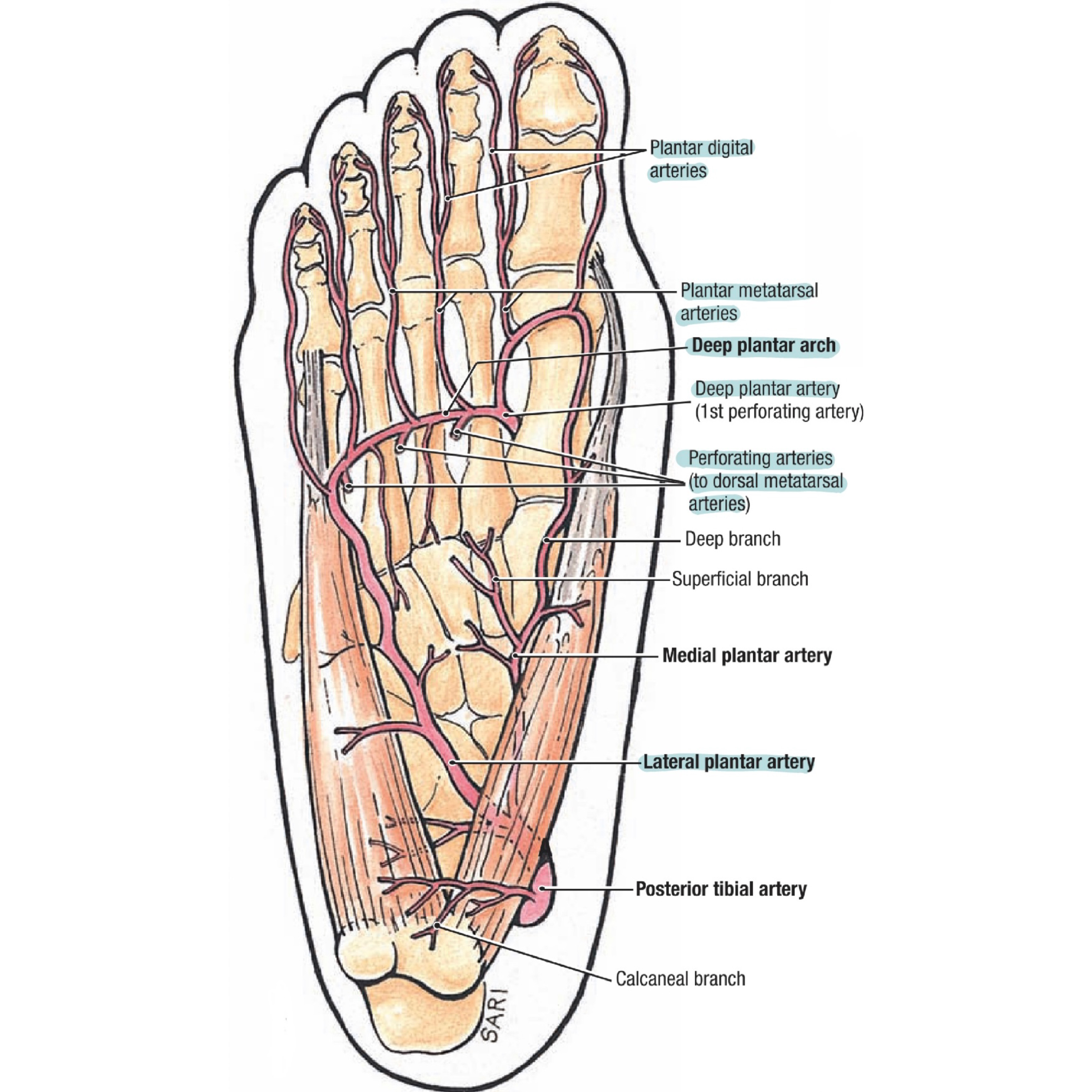
Deep plantar arch
By : Aisha MohammedDefinition
It is one of the small arteries of the lower limb located at the sole of foot and provides its blood supply. It is formed by union of the lateral plantar artery and the dorsalis pedis artery (deep plantar branch).
Origin
The deep plantar arch is the direct continuation the lateral plantar artery which is a terminal branch of the posterior tibial artery. The posterior tibial artery is the posterior branch of the popliteal artery. The popliteal artery, which is the continuation of the femoral artery which is the continuation of external iliac artery ,which is one of the branches of the common iliac artery, which is a division of the abdominal aorta.
(Abdominal Aorta > Right / Left Common Iliac Artery > Right External Iliac Artery > Femoral Artery >
Popliteal Artery > Posterior Tibial Artery > lateral Plantar Artery > Deep plantar arch)
(Abdominal Aorta > Right / Left Common Iliac Artery > Right External Iliac Artery > Femoral Artery >
Popliteal Artery > Posterior Tibial Artery > lateral Plantar Artery > Deep plantar arch)

Course
It's deeply situated, extending laterally from the 5th metatarsal base as a direct continuation of the lateral plantar artery to the proximal end of the 1st
intermetatarsal space medially when it’s completed medially by the deep plantar artery of dorsalis pedis.
intermetatarsal space medially when it’s completed medially by the deep plantar artery of dorsalis pedis.
Relations
Plantar to: bases of the 2nd to 4th metatarsals and corresponding interossei.
Dorsal to: the oblique part of adductor hallucis muscle.
Accompanied by: venae comitantes.
Note: The deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve lies in the concavity of the plantar arch.
Dorsal to: the oblique part of adductor hallucis muscle.
Accompanied by: venae comitantes.
Note: The deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve lies in the concavity of the plantar arch.
Branches
1-Three perforating branches: which ascend through the proximal ends of the 2nd to 4th intermetatarsal spaces, between the heads of the dorsal interossei, and anastomose with the dorsal metatarsal arteries.
2-Four plantar metatarsal arteries: which distally extend between the metatarsals in contact with the interossei . Each plantar metatarsal artery divides into two plantar digital arteries to supply the adjacent digital aspects. Near its division place, each plantar metatarsal artery dorsally sends a distal perforating branch to join a dorsal metatarsal artery. The most medial metatarsal arteries are joined by the superficial digital branches of the medial plantar artery. Typically, the plantar digital arteries provide most of the blood that reaches the distal toes, including the nail bed, via perforating and arrangement that also occurs in the fingers.
3-Numerous branches: that supply the skin, fasciae and muscles in the
sole.
2-Four plantar metatarsal arteries: which distally extend between the metatarsals in contact with the interossei . Each plantar metatarsal artery divides into two plantar digital arteries to supply the adjacent digital aspects. Near its division place, each plantar metatarsal artery dorsally sends a distal perforating branch to join a dorsal metatarsal artery. The most medial metatarsal arteries are joined by the superficial digital branches of the medial plantar artery. Typically, the plantar digital arteries provide most of the blood that reaches the distal toes, including the nail bed, via perforating and arrangement that also occurs in the fingers.
3-Numerous branches: that supply the skin, fasciae and muscles in the
sole.
It supplies
Muscles:
1- The lumbricals muscles (by plantar metatarsal arteries)
2- Flexor hallucis brevis muscle (by first plantar metatarsal artery)
3- Abductor hallucis muscle (by first plantar metatarsal artery)
4- Plantar interossei muscles (by plantar metatarsal arteries)
Joints:
It supplies the interphalangeal joints by the digital branches of the plantar arch.
1- The lumbricals muscles (by plantar metatarsal arteries)
2- Flexor hallucis brevis muscle (by first plantar metatarsal artery)
3- Abductor hallucis muscle (by first plantar metatarsal artery)
4- Plantar interossei muscles (by plantar metatarsal arteries)
Joints:
It supplies the interphalangeal joints by the digital branches of the plantar arch.
Clinical section
Hemorrhaging Wounds of Sole of Foot
Usually, the wounds that are caused by the puncturing of the foot sole involves the damage of the deep plantar arch and its branches result in severe bleeding, typically from both ends of the cut artery because of its anastomoses.
The bleeding is difficult to control because of :
1. Depth of the vessel
2. Its important close relations
Usually, the wounds that are caused by the puncturing of the foot sole involves the damage of the deep plantar arch and its branches result in severe bleeding, typically from both ends of the cut artery because of its anastomoses.
The bleeding is difficult to control because of :
1. Depth of the vessel
2. Its important close relations
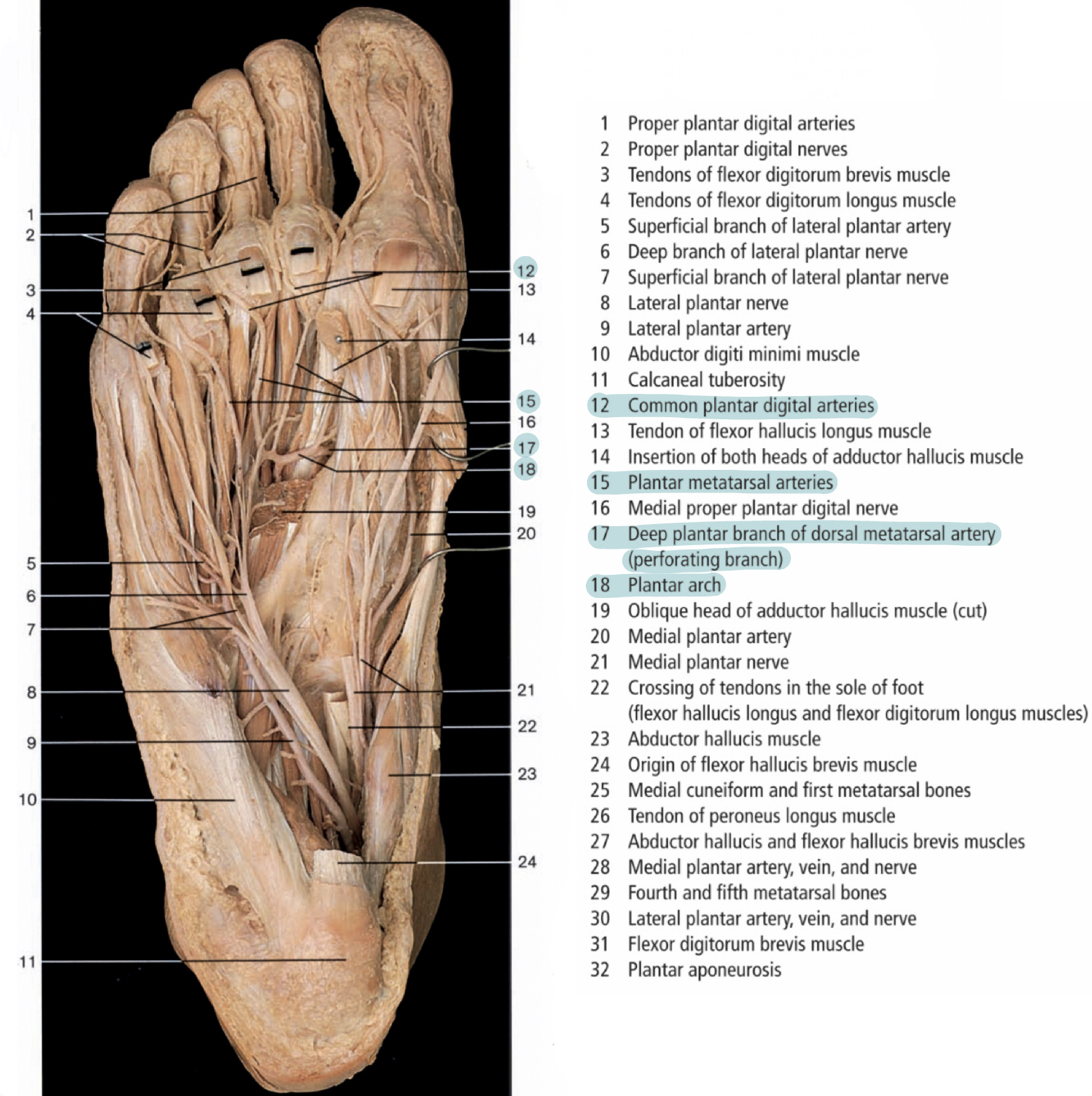
Cadavers
Refrences
• Susan Standring, Neel Anand, Rolfe Birch, Patricia Collins, Alan R Crossman, Michael
Gleeson , Girish Jawaheer, Ariana L Smith, Jonathan D Spratt, Mark D Stringer, R
Shane Tubbs, Richard Tunstall, Alan J Wein, Caroline B Wigley ‘s Gray's Anatomy The
Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. copyright © 2016, Elsevier Limited. Forty-first
edition. Pages(1445)
• Anne MR Agur, Arthur F Dalley, and Keith L. Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy 8th
edition/ Copyright © 2018 Wolters Kluwer / pages (779-784-811)
• Kenneth Prakash Moses, John C. Banks, Jr., Pedro B. Nava, Darrell K. Petersen, ‘ s
ATLAS OF CLINICAL GROSS ANATOMY.Copyright © 2013, 2005, by Saunders, an
imprint of Elsevier Inc.second eidtion.pages(605)
• Byas Deb Ghosh‘s Human Anatomy for Students.copyright© 2013, Jaypee Brothers
Medical Publishers.second edition.pages(349)
• Johannes W.Rohen, Chihiro Yokochi, Elke Lütjen-Drecoll ‘s Anatomy: A Photographic
Atlas.Copyright © 2016 Schattauer GmbH and Wolters Kluwer.8th edition.pages(512)
Gleeson , Girish Jawaheer, Ariana L Smith, Jonathan D Spratt, Mark D Stringer, R
Shane Tubbs, Richard Tunstall, Alan J Wein, Caroline B Wigley ‘s Gray's Anatomy The
Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. copyright © 2016, Elsevier Limited. Forty-first
edition. Pages(1445)
• Anne MR Agur, Arthur F Dalley, and Keith L. Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy 8th
edition/ Copyright © 2018 Wolters Kluwer / pages (779-784-811)
• Kenneth Prakash Moses, John C. Banks, Jr., Pedro B. Nava, Darrell K. Petersen, ‘ s
ATLAS OF CLINICAL GROSS ANATOMY.Copyright © 2013, 2005, by Saunders, an
imprint of Elsevier Inc.second eidtion.pages(605)
• Byas Deb Ghosh‘s Human Anatomy for Students.copyright© 2013, Jaypee Brothers
Medical Publishers.second edition.pages(349)
• Johannes W.Rohen, Chihiro Yokochi, Elke Lütjen-Drecoll ‘s Anatomy: A Photographic
Atlas.Copyright © 2016 Schattauer GmbH and Wolters Kluwer.8th edition.pages(512)
