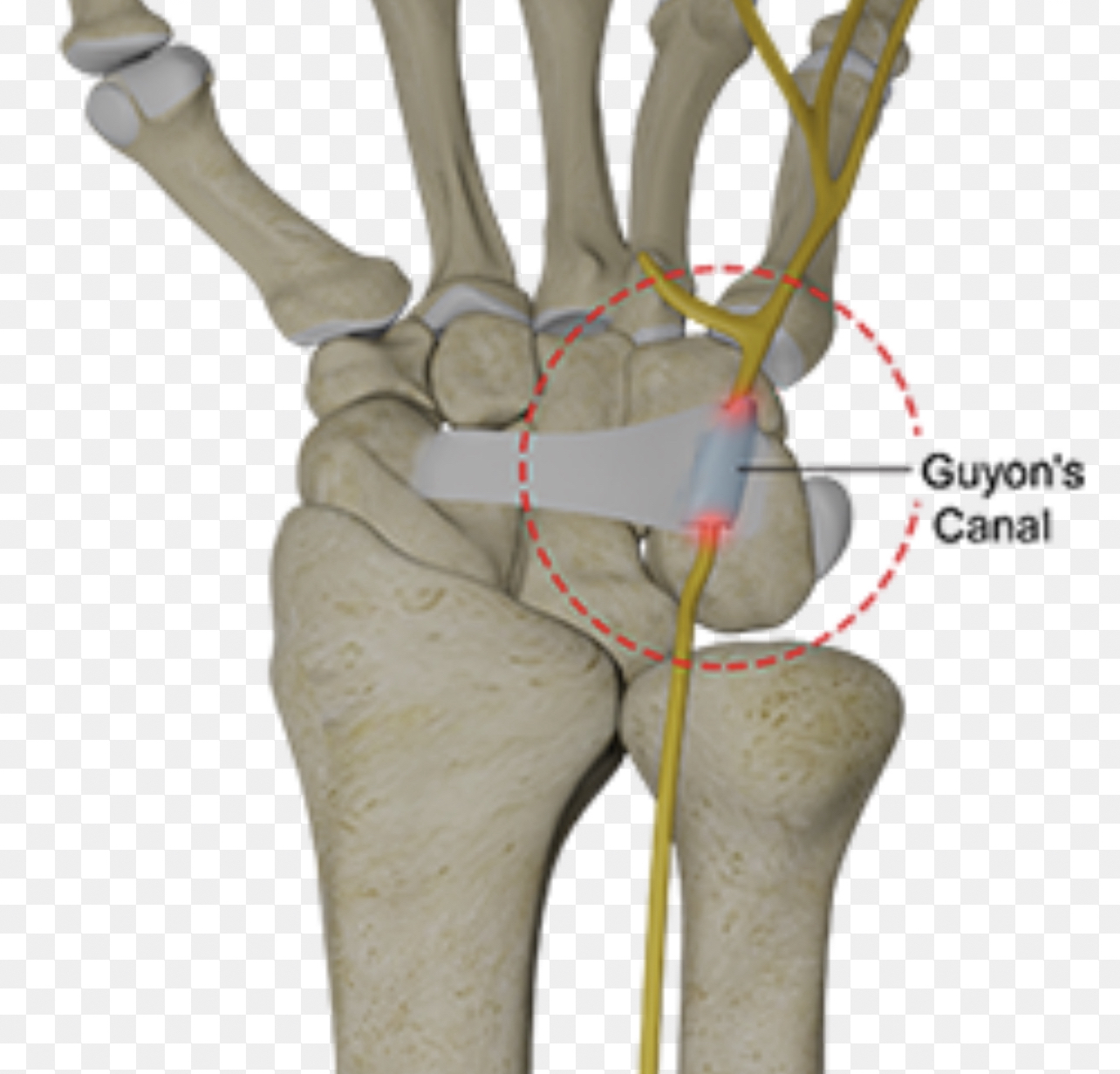
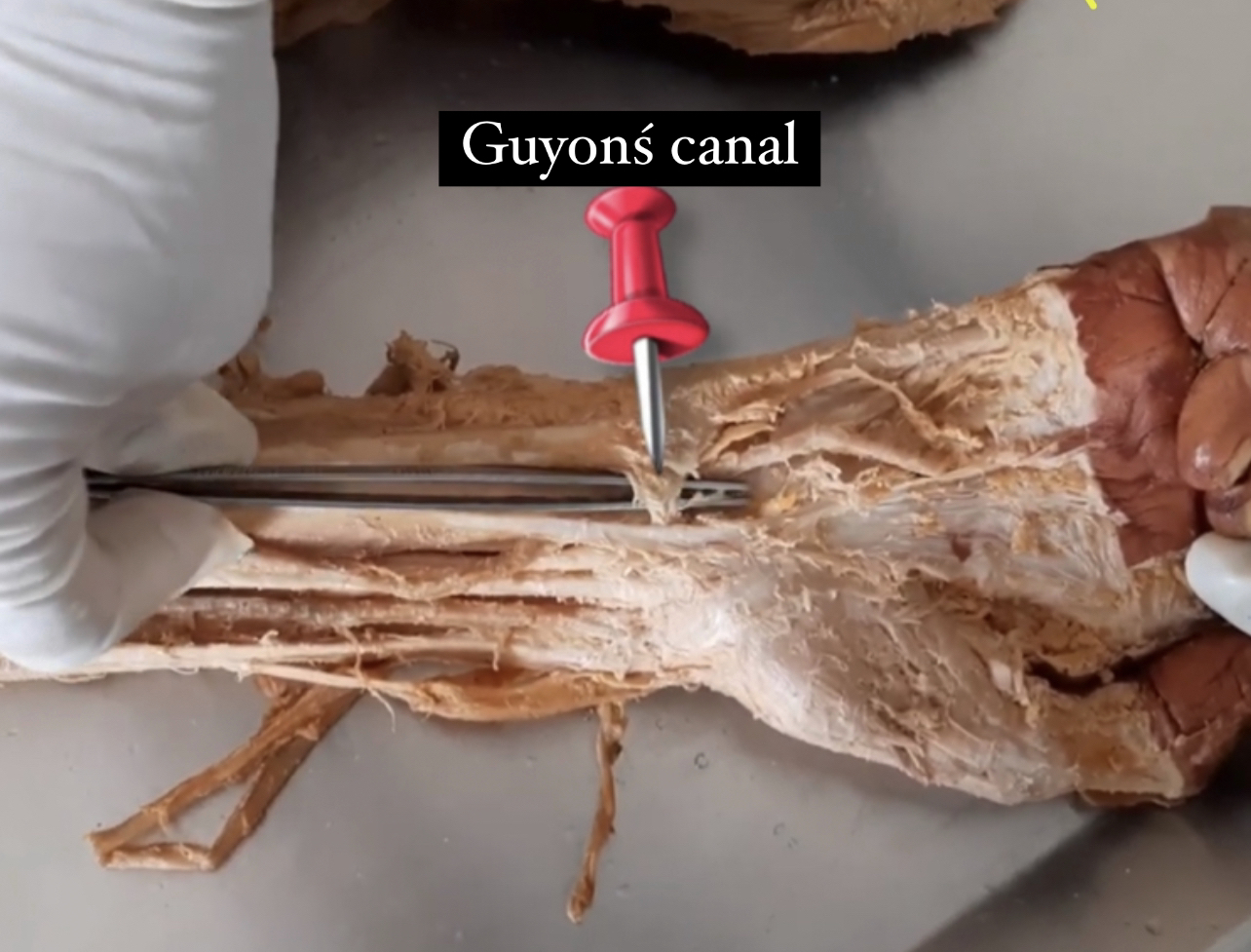
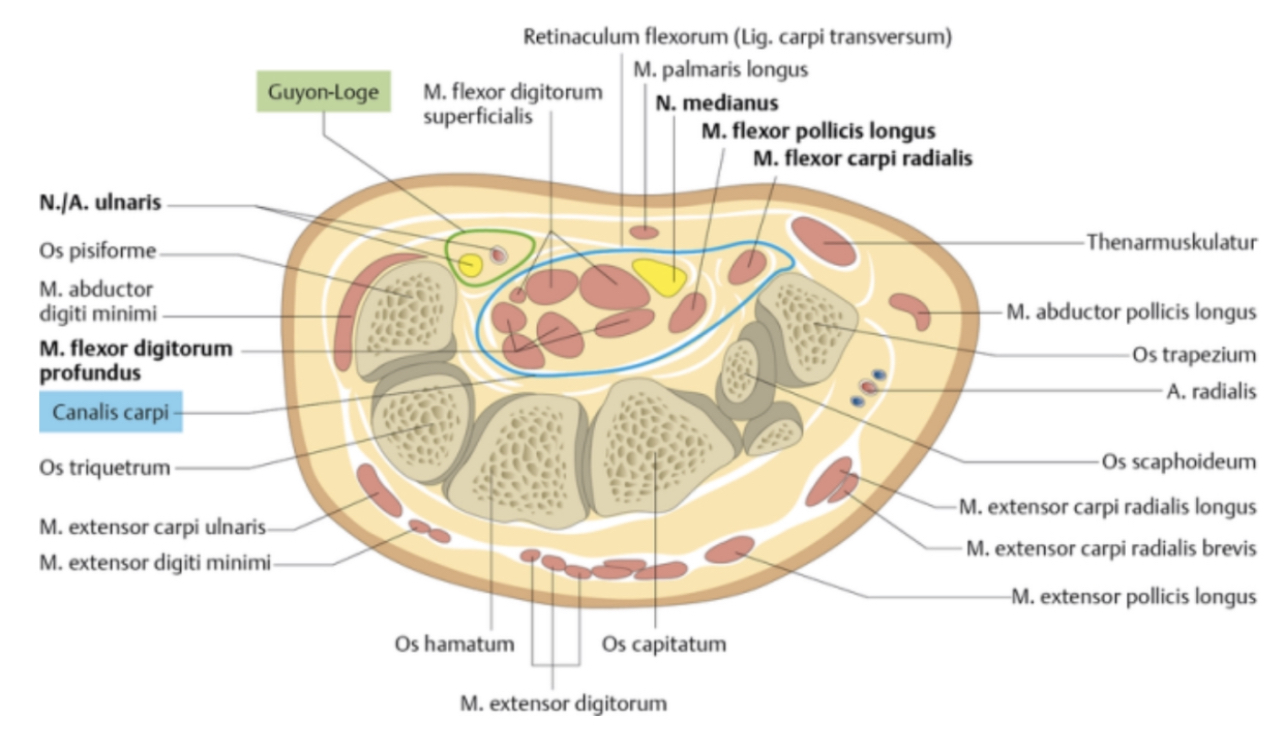
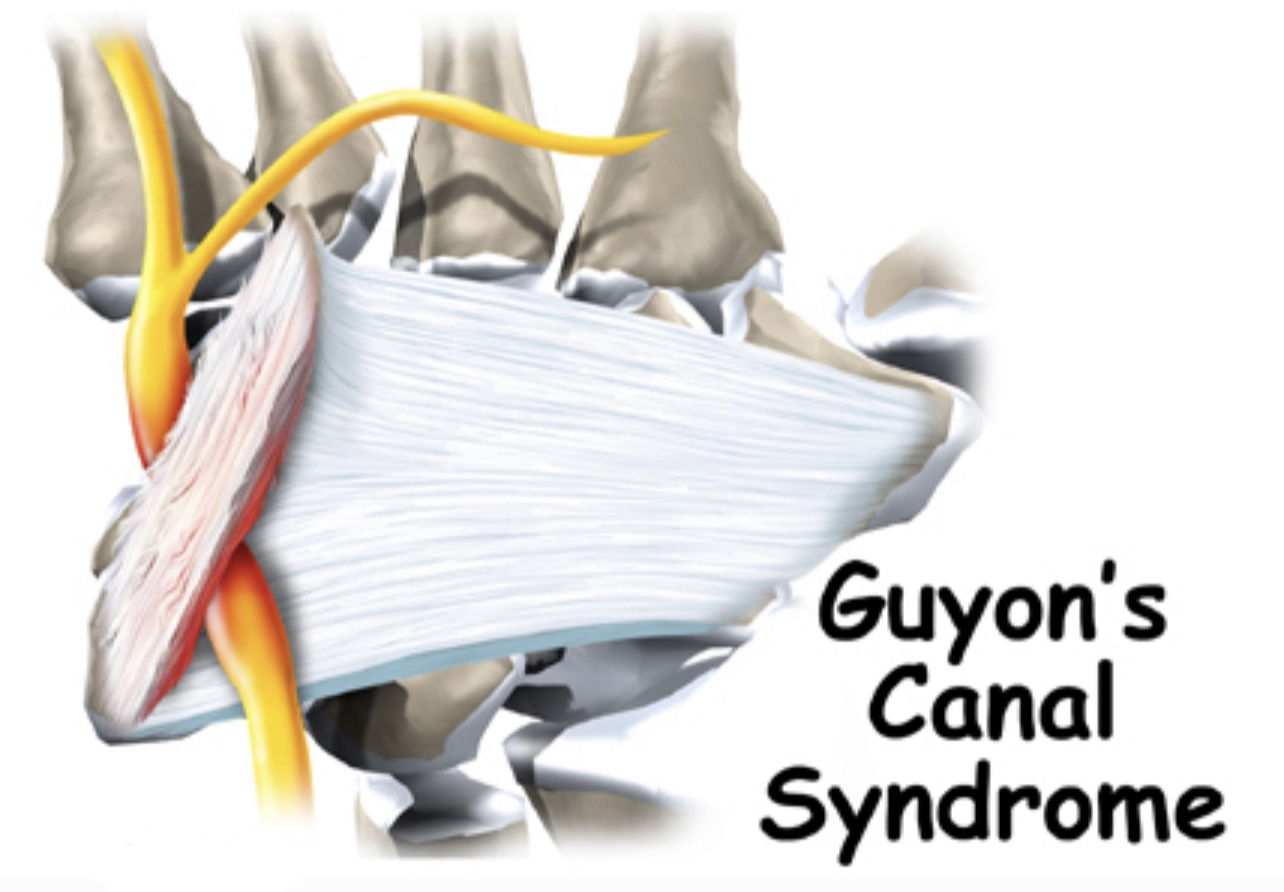
Ulnar (Guyonś) Canal
By : Banan AlzubaidiDefinition :
•It is a fibro-osseous tunnel ..longitudinal canal .
•Derived from the superficial part of the flexor retinaculum .
•In the wrist at the level of the palm (medially ) ..extend from the proximal border of the pisiform bone to the origin of the hypothenar muscles
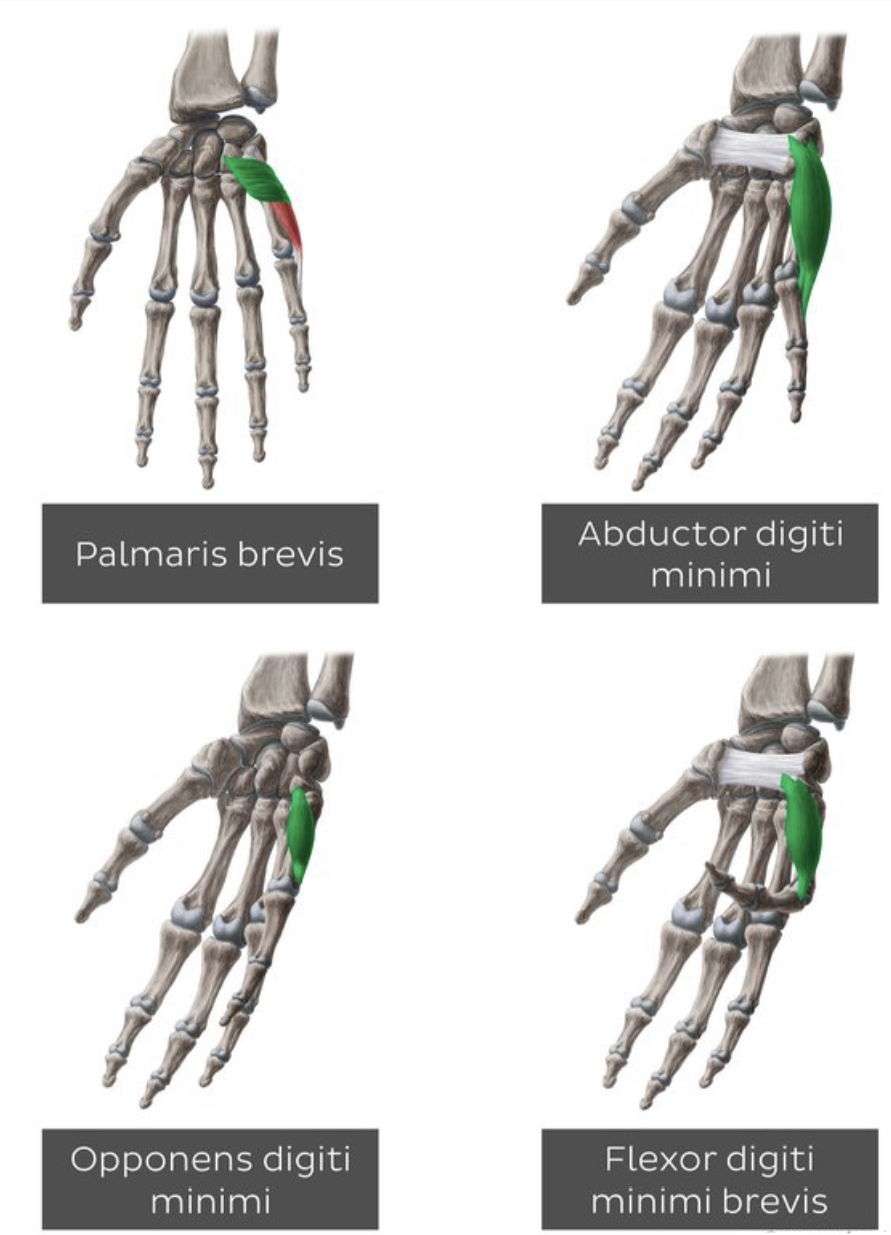
1)abductor digiti minimi
2)opponens digiti minimi
3)Flexor digiti minimi
4)palmaris brevisat the hook of the hamate .
•It is approximately 4cm long.
•It is allows the passage of the ulnar nerve,artery and vein from the forearm to the hand.
•Derived from the superficial part of the flexor retinaculum .
•In the wrist at the level of the palm (medially ) ..extend from the proximal border of the pisiform bone to the origin of the hypothenar muscles
Note
Are intrinsic muscles at the medial side of the hand : 1)abductor digiti minimi
2)opponens digiti minimi
3)Flexor digiti minimi
4)palmaris brevis
•It is approximately 4cm long.
•It is allows the passage of the ulnar nerve,artery and vein from the forearm to the hand.
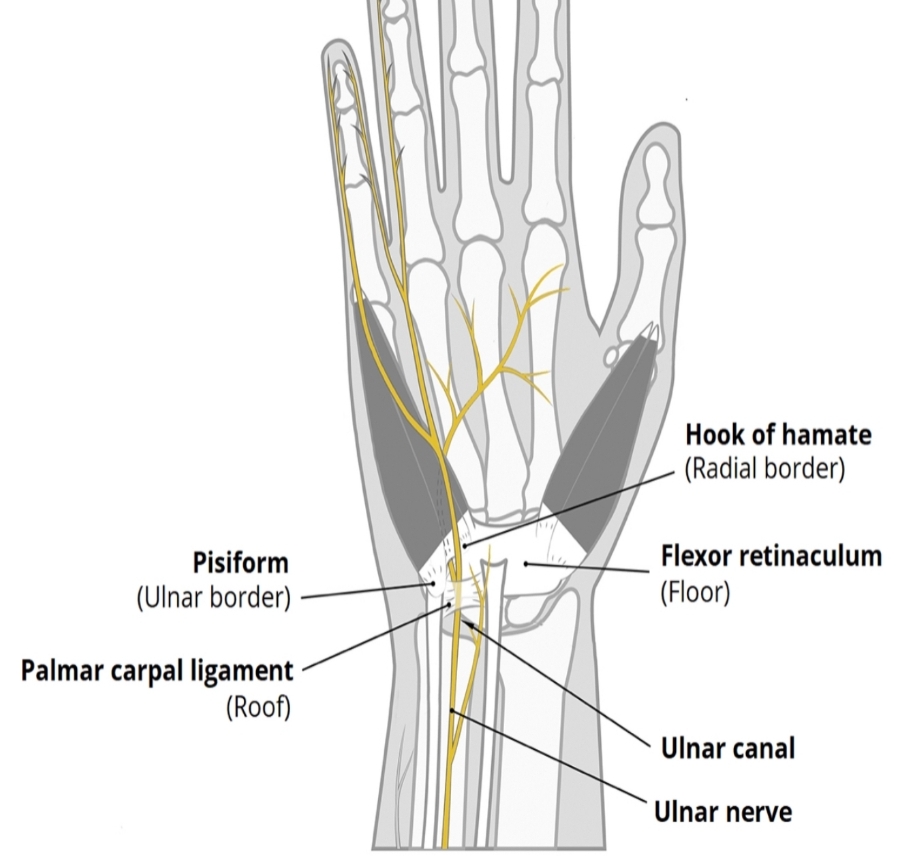
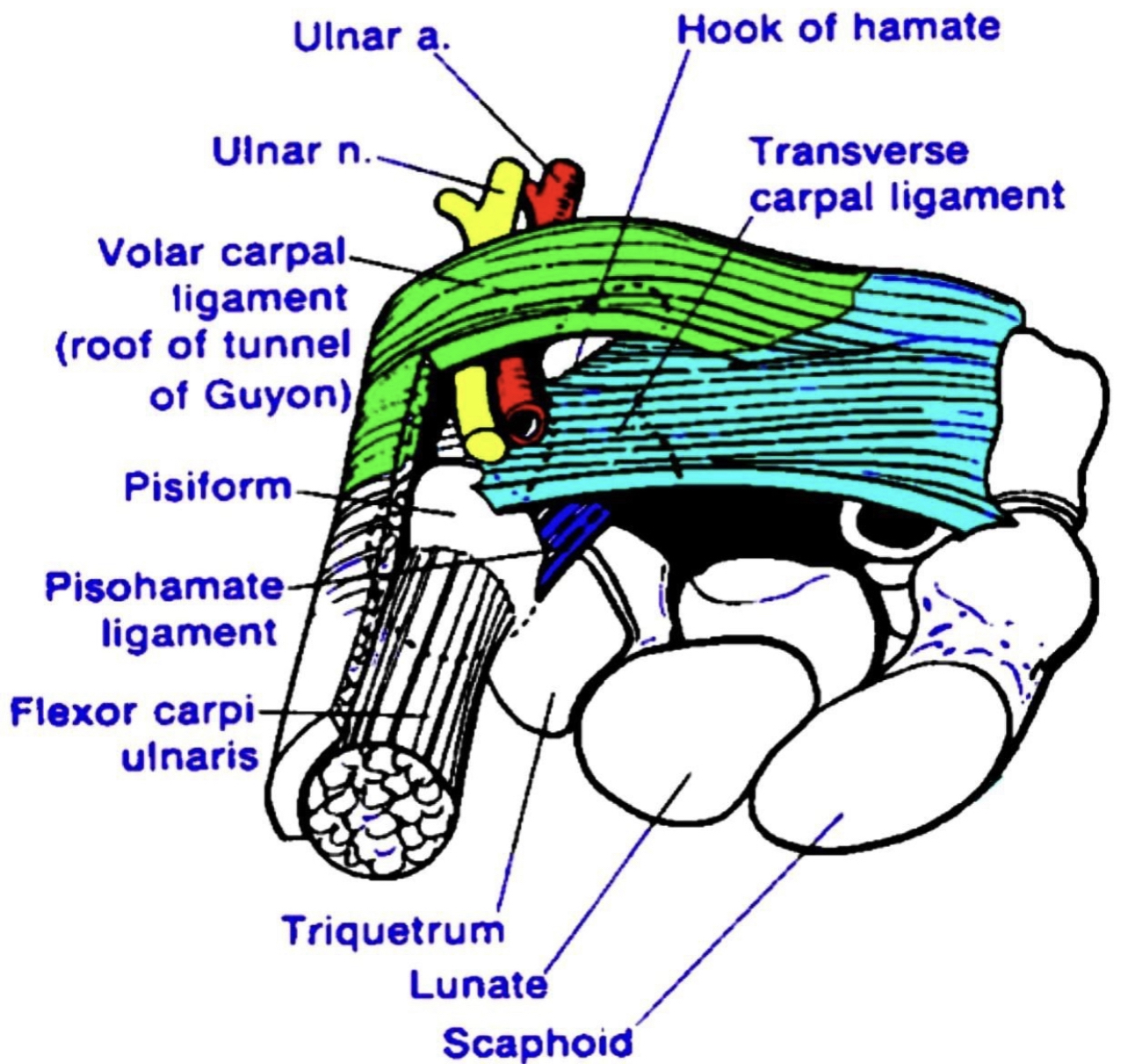
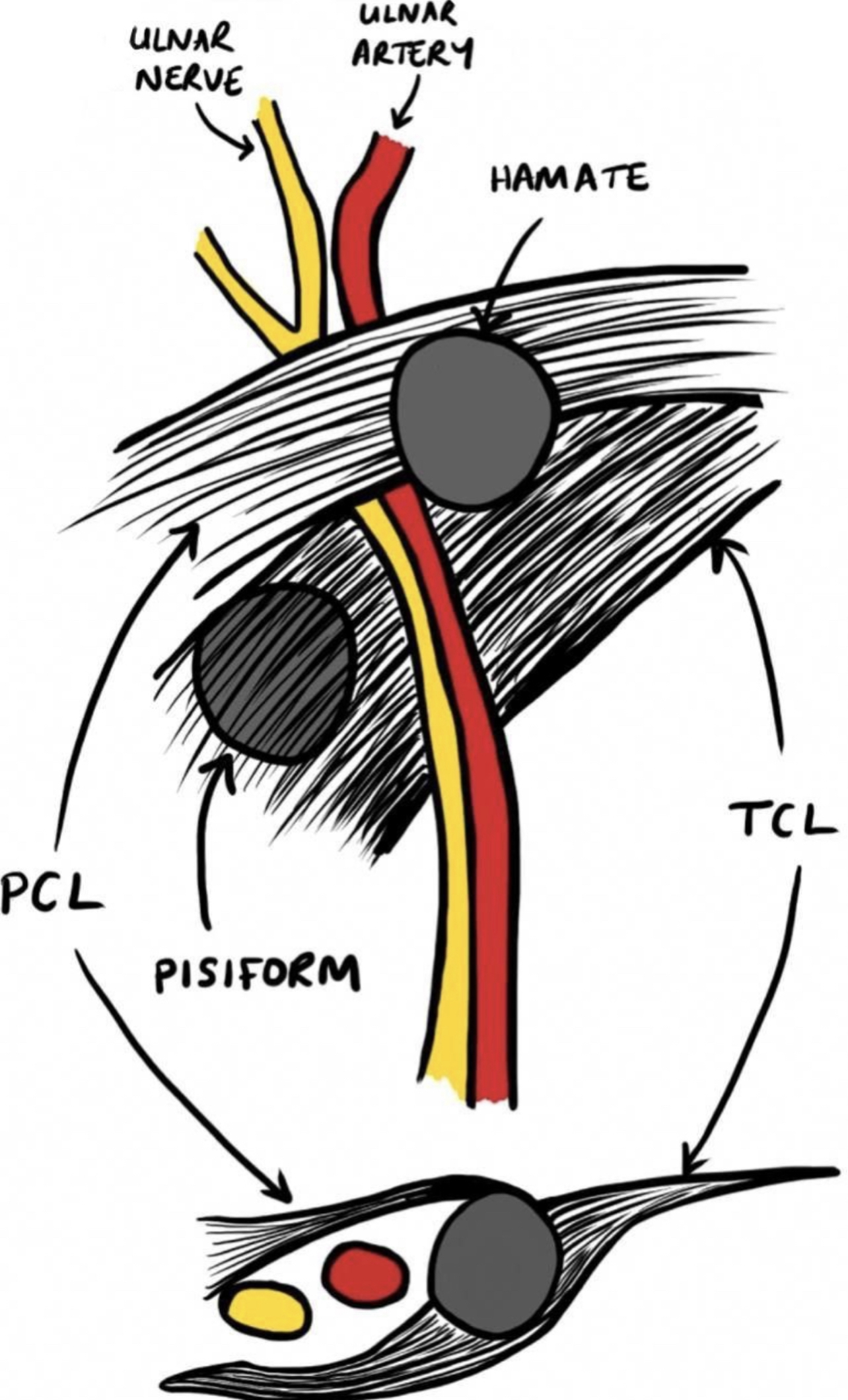
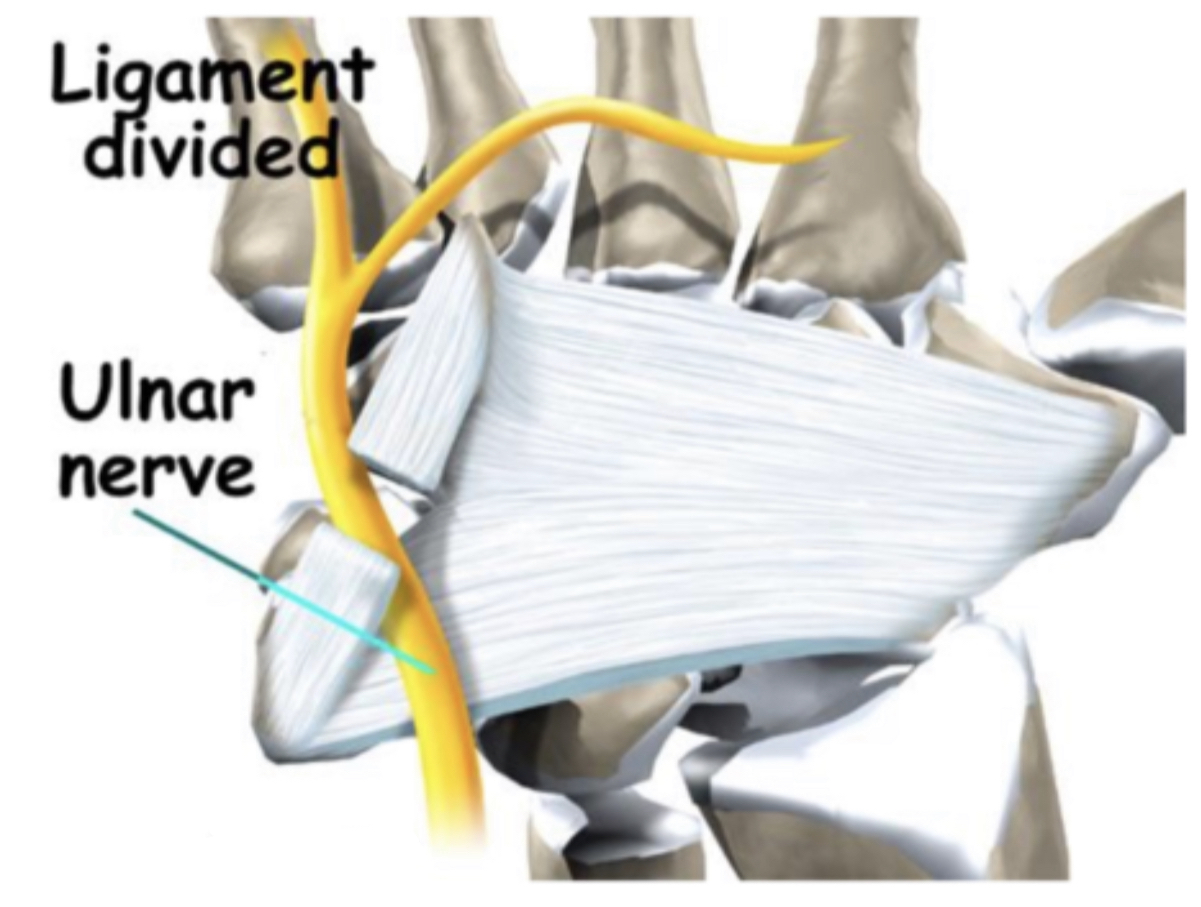
Borders :
• Medial side (ulnar side):
1 )pisiform bone(more proximally).
2 )flexor carpi ulnaris tendon.
3 )abductor digiti minimi muscle.
4 )pisohamate ligament
• Lateral side (radial side):
1)hook of the hamate bone (more distally).
2 )transverse carpal ligament.
• Floor:
1 )transverse carpal ligament.
2 )pisohamate ligament.
3 )pisometacarpal ligament.
4)flexor retinaculum : it is thick band of the deep fascia in the front of the wrist converting the concavity of the wrist to the tunnel (carpal tunnel).
5 ) hypothenar muscles .
• Roof:
1)palmar carpal ligament(volar carpal ligament ).
2)fascia..and skin.
1 )pisiform bone(more proximally).
2 )flexor carpi ulnaris tendon.
3 )abductor digiti minimi muscle.
4 )pisohamate ligament
• Lateral side (radial side):
1)hook of the hamate bone (more distally).
2 )transverse carpal ligament.
• Floor:
1 )transverse carpal ligament.
2 )pisohamate ligament.
3 )pisometacarpal ligament.
4)flexor retinaculum : it is thick band of the deep fascia in the front of the wrist converting the concavity of the wrist to the tunnel (carpal tunnel).
5 ) hypothenar muscles .
Note
Are intrinsic muscles at the medial side of the hand : 1)abductor digiti minimi 2)opponens digiti minimi 3)Flexor digiti minimi 4)palmaris brevis• Roof:
1)palmar carpal ligament(volar carpal ligament ).
2)fascia..and skin.

Contents :
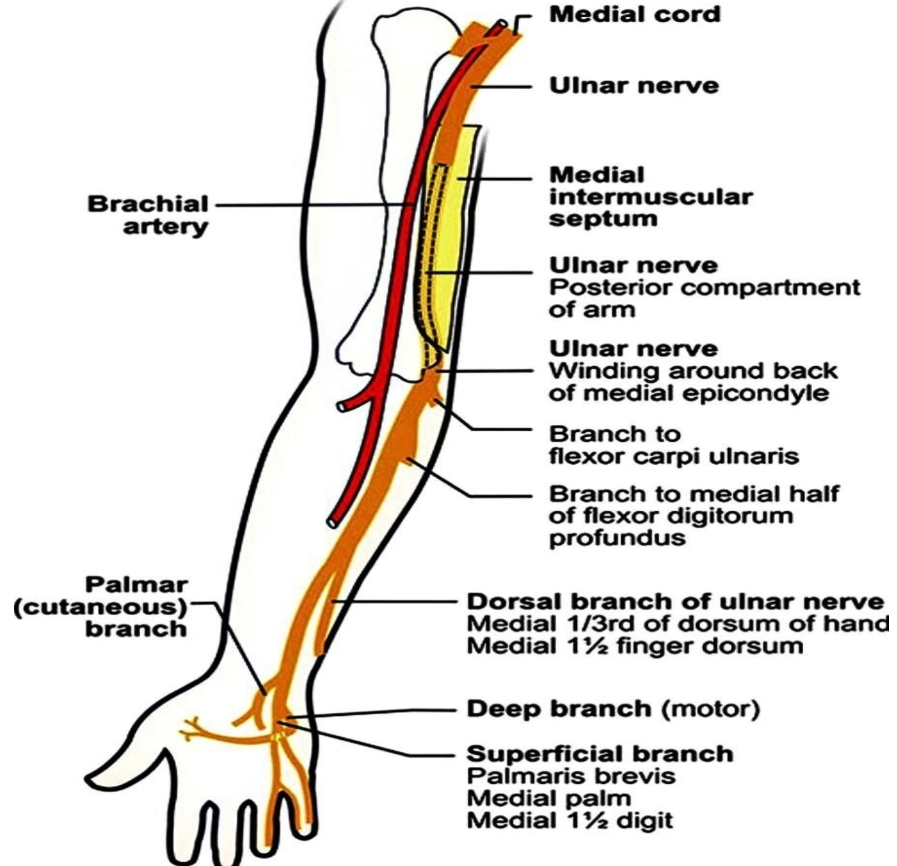
1 ) ulnar nerve (where the ulnar nerve divides into two branches:
•( 1)superficial branches )(sensory) of the ulnar nerve ..(that gives:
1)palmar digital branch that supply the skin of the medial one and half fingers (little finger and adjacent side between little and ring fingers ) of the palmar aspect only of the hand and the distal phalange of the medial one and half fingers of the dorsum of the hand.
2)branches to the palmaris brevis muscle .
• 2 ) deep branches (motor) of the ulnar nerve : supply the hypothenar muscle …interosseous muscle ….3-4lumbricals muscle and both head of the adductor pollicis muscle .. Deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis (when present)
2 )ulnar artery.
3 )ulnar vein.
4 )lymphatic vessels .
5 )fat.
● NOTE :in the guyonś canal ,the ulnar nerve is medial to the ulnar artery.
● NOTE :the proximal and middle phalanges of the medial one and half fingers of the dorsum of the hand are supplied by the dorsal digital branch of the ulnar nerve which arises from the dorsal cutaneous of the ulnar nerve .
•( 1)superficial branches )(sensory) of the ulnar nerve ..(that gives:
1)palmar digital branch that supply the skin of the medial one and half fingers (little finger and adjacent side between little and ring fingers ) of the palmar aspect only of the hand and the distal phalange of the medial one and half fingers of the dorsum of the hand.
2)branches to the palmaris brevis muscle .
• 2 ) deep branches (motor) of the ulnar nerve : supply the hypothenar muscle …interosseous muscle ….3-4lumbricals muscle and both head of the adductor pollicis muscle .. Deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis (when present)
2 )ulnar artery.
3 )ulnar vein.
4 )lymphatic vessels .
5 )fat.
● NOTE :in the guyonś canal ,the ulnar nerve is medial to the ulnar artery.
● NOTE :the proximal and middle phalanges of the medial one and half fingers of the dorsum of the hand are supplied by the dorsal digital branch of the ulnar nerve which arises from the dorsal cutaneous of the ulnar nerve .

Clinical notes :
• ulnar (guyonś)canal syndrome ..also known(handlebars palsy):
•it is the compression of the ulnar nerve when passes through the ulnar (guyonś)canal in the wrist.
•It is common in people who ride bicycles regularly ….weightlifters or when using crutches because to prolonged pressure on the guyonś canal against bicycle handlebars.
•it is the compression of the ulnar nerve when passes through the ulnar (guyonś)canal in the wrist.
•It is common in people who ride bicycles regularly ….weightlifters or when using crutches because to prolonged pressure on the guyonś canal against bicycle handlebars.
The causes :
1 )Ganglion cysts:it is most common to occur in this syndrome.
2 )fractures or dislocation of the hook of the hamate bone (one bone of the carpal bones).
3 )ulnar artery thrombosis or aneurysm (hypothenar hammer syndrome) (this syndrome can cause compression and inflammation to the ulnar nerve in the guyonś canal)(in this syndrome the blood flow of the fingers is reduced )the cause of this syndrome similar to the cause of the guyonś canal syndrome.
4 )Repetitive trauma caused by external factors.
5 )Tumor (lipoma).
6 )arthritis in the wrist joint :it is refer to inflammation ...swelling tenderness in the joint ...the major symptoms of the arthritis stiffness and pain in the joint.
7 )synovitis in the wrist joint :refers to the inflammation of the synovial membrane the lining the wrist joint.
8 )anatomical anomalies (can be hypertrophic muscle of the normal anatomy …or unusual location.
9 )Carpal tunnel syndrome :it is may cause a change in the wrist joint leads to damage the ulnar nerve in the guyonś canal.
2 )fractures or dislocation of the hook of the hamate bone (one bone of the carpal bones).
3 )ulnar artery thrombosis or aneurysm (hypothenar hammer syndrome) (this syndrome can cause compression and inflammation to the ulnar nerve in the guyonś canal)(in this syndrome the blood flow of the fingers is reduced )the cause of this syndrome similar to the cause of the guyonś canal syndrome.
4 )Repetitive trauma caused by external factors.
5 )Tumor (lipoma).
6 )arthritis in the wrist joint :it is refer to inflammation ...swelling tenderness in the joint ...the major symptoms of the arthritis stiffness and pain in the joint.
7 )synovitis in the wrist joint :refers to the inflammation of the synovial membrane the lining the wrist joint.
8 )anatomical anomalies (can be hypertrophic muscle of the normal anatomy …or unusual location.
9 )Carpal tunnel syndrome :it is may cause a change in the wrist joint leads to damage the ulnar nerve in the guyonś canal.
The symptoms :
1 )Feeling of the pins ..needles ..tingling (paraesthesia)in the medial one and half fingers (little finger and adjacent side between little and ring fingers)of the palmar aspect of the hand.
2 )Burning pain in the wrist.
3 )sensation decrease in the little finger and adjacent side between the ring and little fingers.
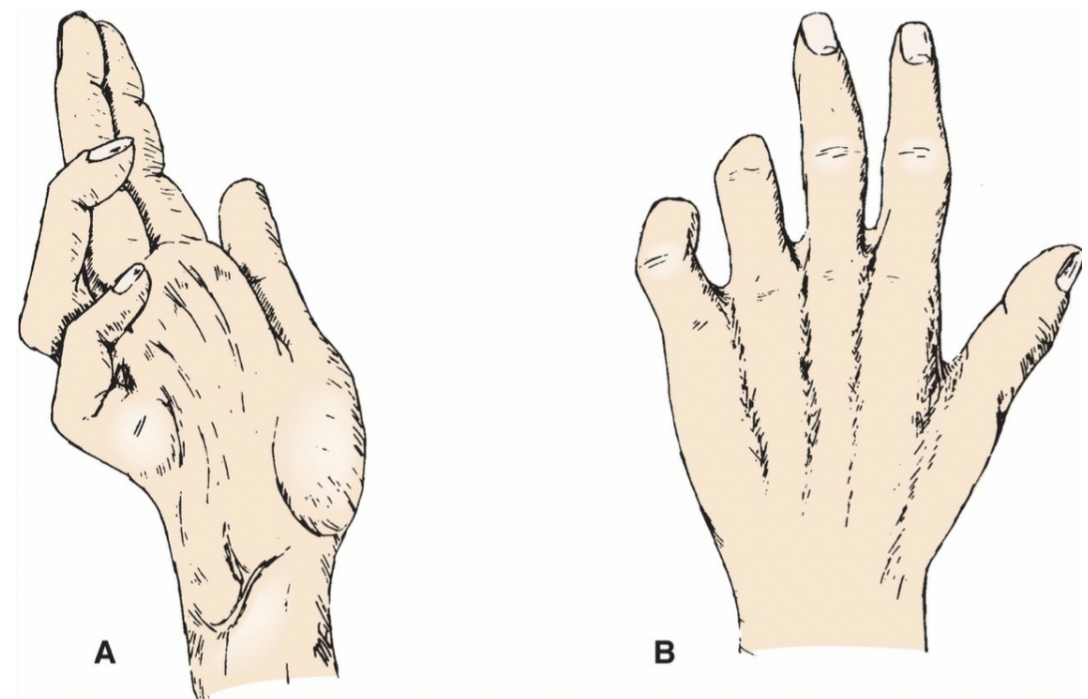
4 )Claw hand in the little and ring fingers ..when the muscles in the hand that are controlled by the ulnar nerve become weak.
5 )Weakness in the small muscles(interosseous muscle) in the palm of the hand and muscles that pull the thumb into the palm can make it hard to spread finger and pinch with the thumb.
6 )Difficulty in grasping.
7 )Difficulty in carrying things.
8 )Difficulty in doing complex things like writing.
2 )Burning pain in the wrist.
3 )sensation decrease in the little finger and adjacent side between the ring and little fingers.
4 )Claw hand in the little and ring fingers ..when the muscles in the hand that are controlled by the ulnar nerve become weak.
5 )Weakness in the small muscles(interosseous muscle) in the palm of the hand and muscles that pull the thumb into the palm can make it hard to spread finger and pinch with the thumb.
6 )Difficulty in grasping.
7 )Difficulty in carrying things.
8 )Difficulty in doing complex things like writing.
The diagnosis :
By physical examination :
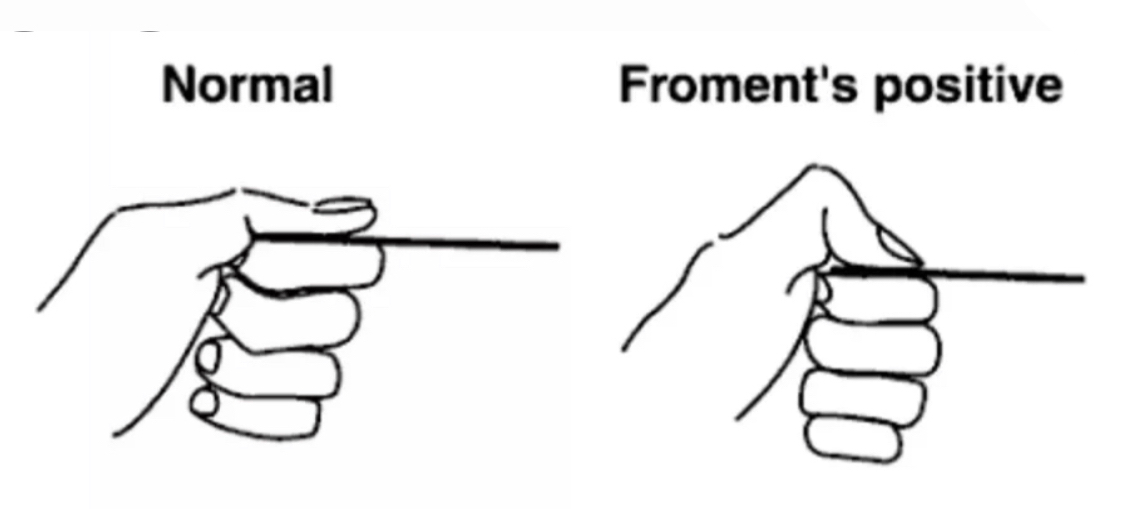
1)Froment's sign :is a physical examination of the hand to test for palsy of the ulnar nerve which results in reduced functionality and muscle weakness of the pinch grip. It tests the strength of the adductor pollicis of the thumb ..the nerve that supply this muscle is the ulnar nerve ..so this muscle become weak when the ulnar nerve is paralyzed.
2)Wartenberg's Sign :refers to the slightly greater abduction of the fifth digit because ofweakness or paralysis of the adducting palmar interosseous muscle and unopposed action of the extensor muscles (digiti minimi...digitorum communis )which are innervated by the radial nerve.
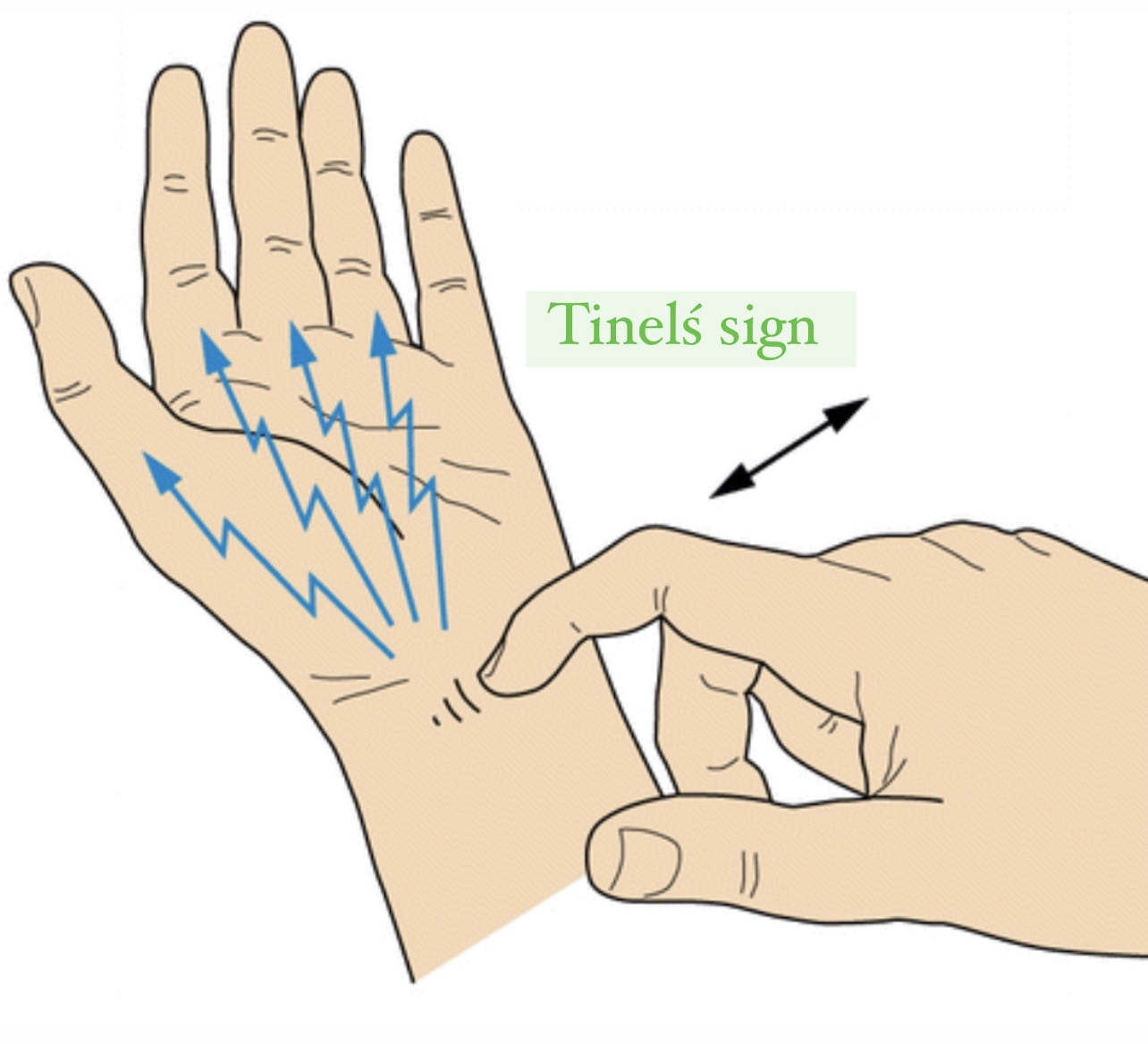
3)Tinelś sign :it is to detect nerve irritation and is performed by tapping lightly on the nerve.
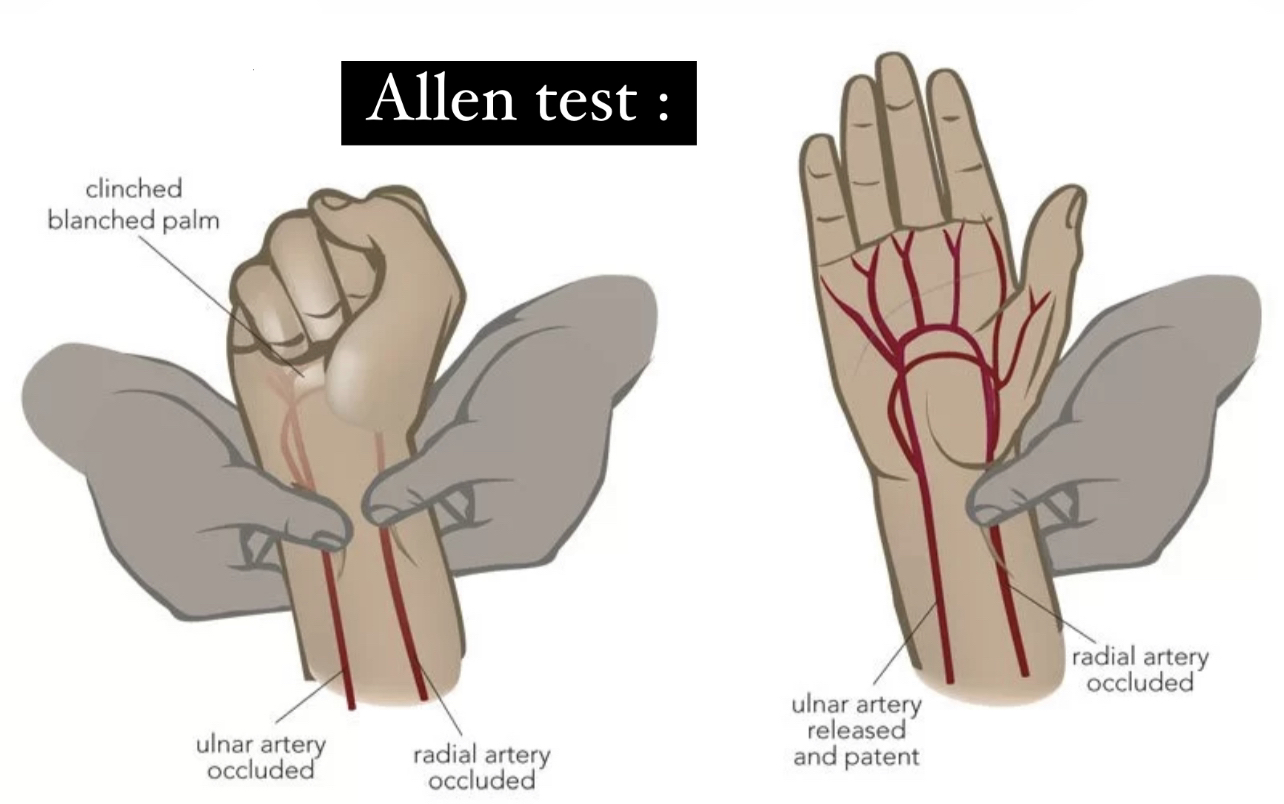
4)allen test :valuation the arterial supply of hand which is useful when ulnar artery thrombosis is suspected.
1)Froment's sign :is a physical examination of the hand to test for palsy of the ulnar nerve which results in reduced functionality and muscle weakness of the pinch grip. It tests the strength of the adductor pollicis of the thumb ..the nerve that supply this muscle is the ulnar nerve ..so this muscle become weak when the ulnar nerve is paralyzed.
2)Wartenberg's Sign :refers to the slightly greater abduction of the fifth digit because ofweakness or paralysis of the adducting palmar interosseous muscle and unopposed action of the extensor muscles (digiti minimi...digitorum communis )which are innervated by the radial nerve.
3)Tinelś sign :it is to detect nerve irritation and is performed by tapping lightly on the nerve.
4)allen test :valuation the arterial supply of hand which is useful when ulnar artery thrombosis is suspected.

by using the medical devices:
1 ) hand x-ray or computed tomography(CT) scan can be used to value the bones fractures (especially hook of the hamate bone).
2 ) angiography can be used for the valuation of the ulnar artery aneurysm or thrombosis.
3 ) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hand can show anatomical variation within the guyonś canal valuation for the structure responsible for mechanism compression of the ulnar nerve.
4 ) doppler of the ultrasound used for valuation for ulnar artery thrombosis.
5 ) electromyography (EMG)and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) :are used to valuation peripheral nerve compression ..and location the level at which nerve is effected… for example difference between the compression of the ulnar nerve in guyonś canal in the wrist and in cubital tunnel in the elbow.
6 )study of the nerve conduction are useful in the diagnosis of this syndrome.
1 ) hand x-ray or computed tomography(CT) scan can be used to value the bones fractures (especially hook of the hamate bone).
2 ) angiography can be used for the valuation of the ulnar artery aneurysm or thrombosis.
3 ) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hand can show anatomical variation within the guyonś canal valuation for the structure responsible for mechanism compression of the ulnar nerve.
4 ) doppler of the ultrasound used for valuation for ulnar artery thrombosis.
5 ) electromyography (EMG)and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) :are used to valuation peripheral nerve compression ..and location the level at which nerve is effected… for example difference between the compression of the ulnar nerve in guyonś canal in the wrist and in cubital tunnel in the elbow.
6 )study of the nerve conduction are useful in the diagnosis of this syndrome.

The treatment :
First, the doctor recommends non-surgical treatment if the condition is not severe: including :
1 )Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain (Like :carrying a heavy weight...cycling...avoid movements that put a mechanical load on the wrist ).
2 )Use a brace or hand splint.
3 )Physical therapy –and message therapy.
4 )prescription pain medication.
5 )Anti –inflammatory medications.
6 )Steroid injection.
7 )Additional exercises such as ultrasound and nerve glide exercises.
1 )Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain (Like :carrying a heavy weight...cycling...avoid movements that put a mechanical load on the wrist ).
2 )Use a brace or hand splint.
3 )Physical therapy –and message therapy.
4 )prescription pain medication.
5 )Anti –inflammatory medications.
6 )Steroid injection.
7 )Additional exercises such as ultrasound and nerve glide exercises.
If the case is severe or the non-surgical treatment not affecting the condition, the doctor will resort to surgery :
1 )small incision is made along the ulnar nerve in the palm region.
2 )the surgeon may remove the ganglion cysts or repair of the fracture ..certain ligament may be cut to relieve pressure on the ulnar nerve(the ligament that forms the roof of the guyonś canal.
1 )small incision is made along the ulnar nerve in the palm region.
2 )the surgeon may remove the ganglion cysts or repair of the fracture ..certain ligament may be cut to relieve pressure on the ulnar nerve(the ligament that forms the roof of the guyonś canal.
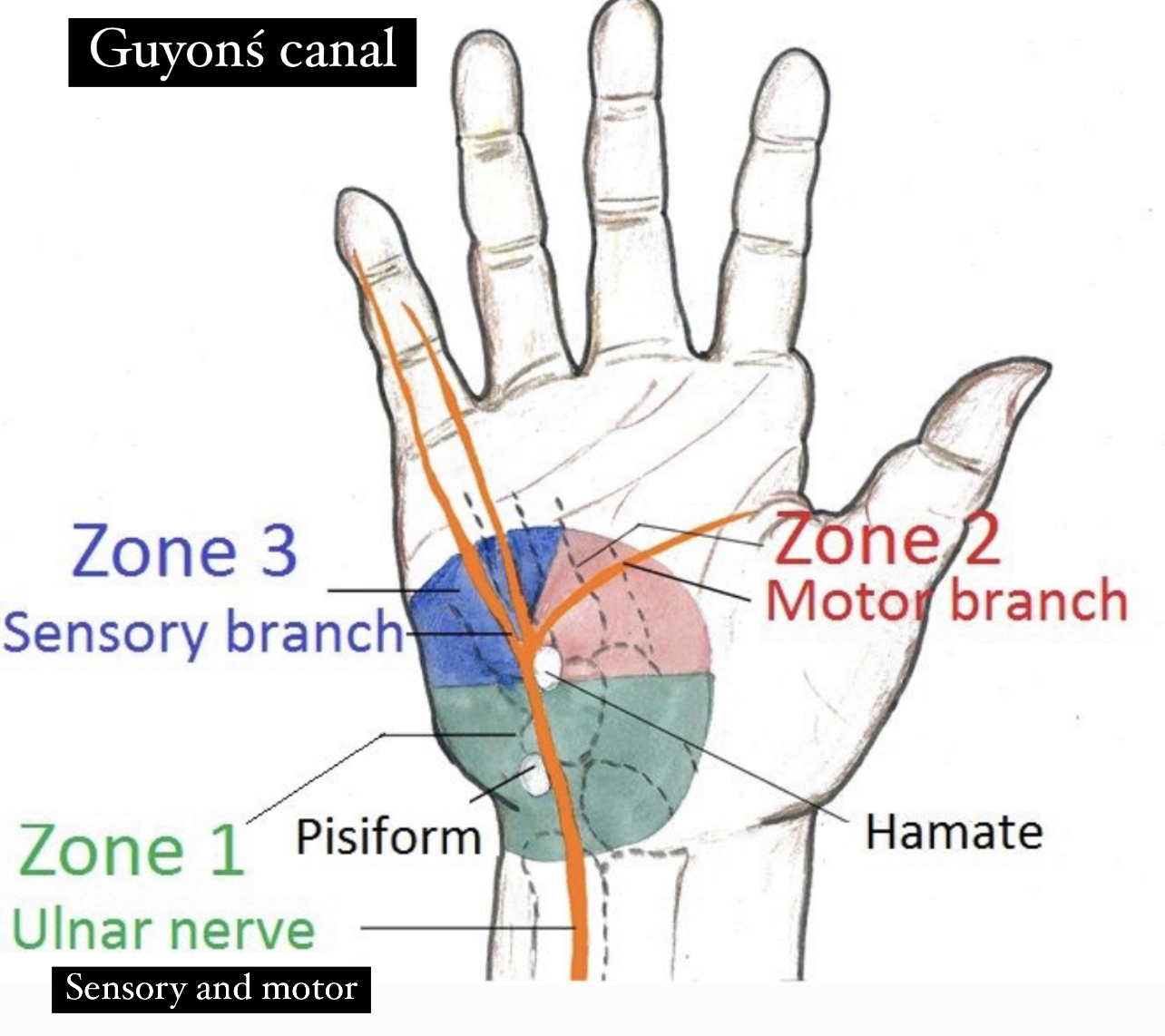
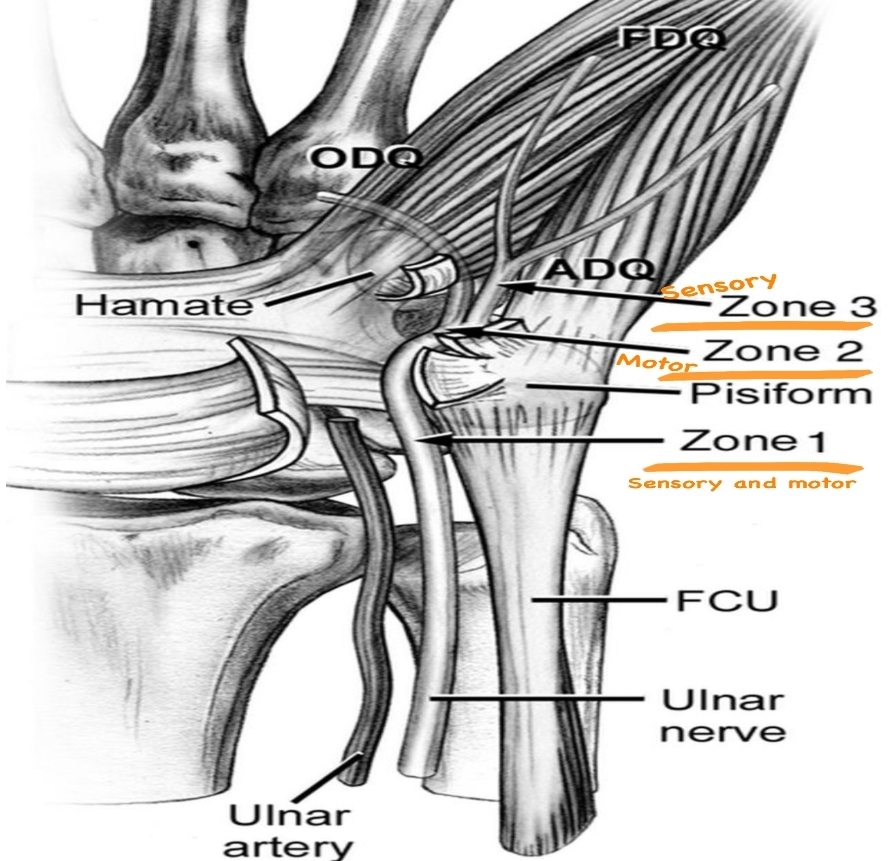
the clinical presentation of the guyonś canal syndrome can be only sensory or only motor or both sensory and motor depending the location of the ulnar nerve compression in the wrist :
1)Zone 1:(motor and sensory ):
• Location :proximal bifurcation of the ulnar nerve(main trunk).
• Symptoms : compression of the ulnar nerve (sensory and motor branches) causes a weakness of the muscles which supplied by the deep branches of ulnar nerve …and the loss of the sensation of the medial one and half fingers of the palmar aspect of the hand.
• Cause :ganglion cysts and hook of the hamate fracture.
2)Zone 2:(more common )motor branch
• Location :deep branch of the ulnar nerve.
• Symptoms :weakness of the muscles in the hand that are supplied by the deep branches of the ulnar nerve.
• Cause :ganglion cysts and hook of the hamate fractures.
3)Zone3:sensory branch
• Location :superficial branch of the ulnar nerve.
• Symptoms :loss of the sensation in the skin of the medial one and half fingers of the palmar aspect of the hand.
• Cause :ulnar artery thrombosis or aneurysm.
References :
1)Guyonś canal /teachmeanatomy/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj11eq12KH6AhXvQ_EDHWI-AvoQFnoECA8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fteachmeanatomy.info%2Fupper-limb%2Fareas%2Fulnar-canal%2F&usg=AOvVaw0mfkI8lqajD0jTE1StYo6S
2)Guyonś canal/physiopedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiLvKGR2aH6AhUXVPEDHaNnAAUQFnoECA8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FGuyon_Canal&usg=AOvVaw02hKWF9NhjBfEAtis5uCxY
3)Guyonś canal syndrome/physiopedia/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiLvKGR2aH6AhUXVPEDHaNnAAUQFnoECBAQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FGuyon_Canal_Syndrome&usg=AOvVaw1hAbK2uW5HrCa07QKTRF72
4)Guyonś canal /ncbi.nlm.nih/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiGpPG83qH6AhViQ_EDHaejBZwQFnoECBIQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fbooks%2FNBK534814%2F&usg=AOvVaw0_6War3FbeDwJhI-MPmA72
5)Guyonś canal syndrome/ncbi.nlm.nih/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjGvf_mo6n6AhWtSPEDHTuLDLIQFnoECAQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fbooks%2FNBK431063%2F&usg=AOvVaw1mBJh5DyfN1UjSJFxwSvdL
6)Guyonś canal /nerveclinic.co/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwig9vir4aH6AhWpXfEDHY8xAnkQFnoECAgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fnerveclinic.co.uk%2Fnerve-conditions%2Fupper-limb%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome&usg=AOvVaw17-hA5Mwo-N1tzH1mL5GVk
7)Guyonś canal/orthowisconsin/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj0vJDa5KH6AhWVSvEDHSmDASYQFnoECAUQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.orthowisconsin.com%2Fulnar-nerve-compression-guyons-canal-orthopaedic-surgeon-wisconsin.html&usg=AOvVaw1GvxjB6HtRWKxaFhQgsG83
8)Guyonś canal syndrome/northcountyomg/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwie2NSf6KH6AhW5X_EDHZk4CQUQFnoECAkQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.northcountyomg.com%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome.php&usg=AOvVaw153nnYIlJQbYSVPkHXPyM3
9)Guyonś canal syndrome/ louiscatalanomd/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiQ3Pm66aH6AhU9XvEDHV8VBbsQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.louiscatalanomd.com%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome-orthopedic-specialist-new-york.html&usg=AOvVaw2NDDXqS5ak2mubQdeInL4k
10)Guyonś canal syndrome/ healthpages/ healthpages.org › guyo...
Guyon's Canal Syndrome, Causes, tingling fingers, Diagnosis, Treatment
11)Guyonś canal /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwimka3IpbX6AhWv_7sIHSi6AI0QFnoECAsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Fguyons-canal&usg=AOvVaw1qTFos3A1mde_NHp_nU0Ng
12)Guyonś canal syndrome /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwimka3IpbX6AhWv_7sIHSi6AI0QFnoECAwQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome&usg=AOvVaw2oHsuhV_Yv7Is_C8vqHGnQ
13)Stanley Hoppenfeld; Michael S. Zeide (1994). Orthopaedic Dictionary. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-397-51311-6.
14)Hatch, Daniel (Aug 20, 2014). "Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome". Orthobullets.
15)James R. Doyle (2003). Surgical Anatomy of the Hand and Upper Extremity. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 682–. ISBN 978-0-397-51725-1.
16)LAWRENCE E. WINESKI / SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Tenth EDITION/Plate(347_348).
2)Guyonś canal/physiopedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiLvKGR2aH6AhUXVPEDHaNnAAUQFnoECA8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FGuyon_Canal&usg=AOvVaw02hKWF9NhjBfEAtis5uCxY
3)Guyonś canal syndrome/physiopedia/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiLvKGR2aH6AhUXVPEDHaNnAAUQFnoECBAQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FGuyon_Canal_Syndrome&usg=AOvVaw1hAbK2uW5HrCa07QKTRF72
4)Guyonś canal /ncbi.nlm.nih/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiGpPG83qH6AhViQ_EDHaejBZwQFnoECBIQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fbooks%2FNBK534814%2F&usg=AOvVaw0_6War3FbeDwJhI-MPmA72
5)Guyonś canal syndrome/ncbi.nlm.nih/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjGvf_mo6n6AhWtSPEDHTuLDLIQFnoECAQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fbooks%2FNBK431063%2F&usg=AOvVaw1mBJh5DyfN1UjSJFxwSvdL
6)Guyonś canal /nerveclinic.co/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwig9vir4aH6AhWpXfEDHY8xAnkQFnoECAgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fnerveclinic.co.uk%2Fnerve-conditions%2Fupper-limb%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome&usg=AOvVaw17-hA5Mwo-N1tzH1mL5GVk
7)Guyonś canal/orthowisconsin/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj0vJDa5KH6AhWVSvEDHSmDASYQFnoECAUQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.orthowisconsin.com%2Fulnar-nerve-compression-guyons-canal-orthopaedic-surgeon-wisconsin.html&usg=AOvVaw1GvxjB6HtRWKxaFhQgsG83
8)Guyonś canal syndrome/northcountyomg/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwie2NSf6KH6AhW5X_EDHZk4CQUQFnoECAkQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.northcountyomg.com%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome.php&usg=AOvVaw153nnYIlJQbYSVPkHXPyM3
9)Guyonś canal syndrome/ louiscatalanomd/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiQ3Pm66aH6AhU9XvEDHV8VBbsQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.louiscatalanomd.com%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome-orthopedic-specialist-new-york.html&usg=AOvVaw2NDDXqS5ak2mubQdeInL4k
10)Guyonś canal syndrome/ healthpages/ healthpages.org › guyo...
Guyon's Canal Syndrome, Causes, tingling fingers, Diagnosis, Treatment
11)Guyonś canal /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwimka3IpbX6AhWv_7sIHSi6AI0QFnoECAsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Fguyons-canal&usg=AOvVaw1qTFos3A1mde_NHp_nU0Ng
12)Guyonś canal syndrome /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwimka3IpbX6AhWv_7sIHSi6AI0QFnoECAwQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Fguyons-canal-syndrome&usg=AOvVaw2oHsuhV_Yv7Is_C8vqHGnQ
13)Stanley Hoppenfeld; Michael S. Zeide (1994). Orthopaedic Dictionary. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-397-51311-6.
14)Hatch, Daniel (Aug 20, 2014). "Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome". Orthobullets.
15)James R. Doyle (2003). Surgical Anatomy of the Hand and Upper Extremity. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 682–. ISBN 978-0-397-51725-1.
16)LAWRENCE E. WINESKI / SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Tenth EDITION/Plate(347_348).
References of images :
Cover image :guyonś canal /orthowisconsin/https://www.orthowisconsin.com/ulnar-nerve-compression-guyons-canal-orthopaedic-surgeon-wisconsin.html
Fig.1)Guyonś canal /teachmeanatomy/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj11eq12KH6AhXvQ_EDHWI-AvoQFnoECA8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fteachmeanatomy.info%2Fupper-limb%2Fareas%2Fulnar-canal%2F&usg=AOvVaw0mfkI8lqajD0jTE1StYo6S
Fig.2)Guyonś canal / Human anatomy academy /https://youtu.be/8s3veJN6lXo
Fig.3)Roof of the guyonś canal /blog.gajidolar
/https://mugoi.online/zhtbvb-nUE0pUZ6Yl9fo3IlMTImLzIlozSlMTkiqUVmYaqyLv5upUNinJ5wY3Wio2Lgo2LgqUIhozIfYJ9zYJq1rJ9hYzu0oJj=
Fig.4)Roof of Tunnel of Guyon canal/i.pinimg/ https://mugoi.online/zhtbvb-nUE0pUZ6Yl9fo3IlMTImLzIlozSlMTkiqUVmYaqyLv5upUNinJ5wY3Wio2Lgo2LgqUIhozIfYJ9zYJq1rJ9hYzu0oJj=
Fig.5)hypothenar muscles /kenhub/https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-hypothenar-muscles
Fig.6)Flexor retinaculum /earthslab/ https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/flexor-retinaculum-hand/
Fig.7)Ulnar nerve /jaypeedigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9789350254974/ch21
Fig.8)Ulnar nerve and artery at the wrist /Cambridge /https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/postgraduate-orthopaedics/drawings-for-the-frcs-tr-orth/91AD39B533188EEA9AB3A570897CB069
Fig.9)flexor retinaculum /Musculoskeletalkey/https://musculoskeletalkey.com/15-the-forearm-fascia-and-retinacula/
Fig.10)Guyonś canal syndrome /Osteopathy.colganosteo / https://osteopathy.colganosteo.com/guyons-canal-syndrome/
Fig.11)SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Figure 3.62/Ulnar nerve palsy/A.anterior view B.posterior view
Fig.12)Fromentś sign/orthofixar/https://orthofixar.com/special-test/froment-sign/
Fig.13)wartenbergś sign /emg-ncv/https://emg-ncv.com/2022/02/14/wartenbergs-syndrome/
Fig.14)Tinelś sign/epomedicine/https://epomedicine.com/medical-students/tinel-sign/
Fig.15)Allens test /mobilephysiotherapyclinic /https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/the-allen-test-for-blood-flow/
Fig.16)Computed tomography/lifescanimaging.sg/https://lifescanimaging.sg/services/computed-tomography-ct-scan/
Fig.17)Doppler of the Ultrasound/medicalnewstoday/https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326824
Fig.18)Electromyography/physimed/https://www.physimed.com/accueil-patients/diagnostic-techniques/emg/?lang=en
Fig.19)Nerve conduction Velocity test /drmncpathlab/https://drmncpathlab.com/what-is-nerve-conduction-velocity-ncv-test/
Fig.20)Guyonś canal syndrome/osteopathy.colganosteo/https://osteopathy.colganosteo.com/guyons-canal-syndrome/
Fig.21)Zone of the guyonś canal /ignatiukplastics /https://www.ignatiukplastics.com/guyon-s-canal
Fig.22)Zone of the guyonś canal /emgsolutions /https://emgsolutions.com/its-all-in-the-wrist-a-primer-on-ulnar-nerve-emg-ncv-evaluation-in-guyons-canal/
Fig.1)Guyonś canal /teachmeanatomy/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj11eq12KH6AhXvQ_EDHWI-AvoQFnoECA8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fteachmeanatomy.info%2Fupper-limb%2Fareas%2Fulnar-canal%2F&usg=AOvVaw0mfkI8lqajD0jTE1StYo6S
Fig.2)Guyonś canal / Human anatomy academy /https://youtu.be/8s3veJN6lXo
Fig.3)Roof of the guyonś canal /blog.gajidolar
/https://mugoi.online/zhtbvb-nUE0pUZ6Yl9fo3IlMTImLzIlozSlMTkiqUVmYaqyLv5upUNinJ5wY3Wio2Lgo2LgqUIhozIfYJ9zYJq1rJ9hYzu0oJj=
Fig.4)Roof of Tunnel of Guyon canal/i.pinimg/ https://mugoi.online/zhtbvb-nUE0pUZ6Yl9fo3IlMTImLzIlozSlMTkiqUVmYaqyLv5upUNinJ5wY3Wio2Lgo2LgqUIhozIfYJ9zYJq1rJ9hYzu0oJj=
Fig.5)hypothenar muscles /kenhub/https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-hypothenar-muscles
Fig.6)Flexor retinaculum /earthslab/ https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/flexor-retinaculum-hand/
Fig.7)Ulnar nerve /jaypeedigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9789350254974/ch21
Fig.8)Ulnar nerve and artery at the wrist /Cambridge /https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/postgraduate-orthopaedics/drawings-for-the-frcs-tr-orth/91AD39B533188EEA9AB3A570897CB069
Fig.9)flexor retinaculum /Musculoskeletalkey/https://musculoskeletalkey.com/15-the-forearm-fascia-and-retinacula/
Fig.10)Guyonś canal syndrome /Osteopathy.colganosteo / https://osteopathy.colganosteo.com/guyons-canal-syndrome/
Fig.11)SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Figure 3.62/Ulnar nerve palsy/A.anterior view B.posterior view
Fig.12)Fromentś sign/orthofixar/https://orthofixar.com/special-test/froment-sign/
Fig.13)wartenbergś sign /emg-ncv/https://emg-ncv.com/2022/02/14/wartenbergs-syndrome/
Fig.14)Tinelś sign/epomedicine/https://epomedicine.com/medical-students/tinel-sign/
Fig.15)Allens test /mobilephysiotherapyclinic /https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/the-allen-test-for-blood-flow/
Fig.16)Computed tomography/lifescanimaging.sg/https://lifescanimaging.sg/services/computed-tomography-ct-scan/
Fig.17)Doppler of the Ultrasound/medicalnewstoday/https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326824
Fig.18)Electromyography/physimed/https://www.physimed.com/accueil-patients/diagnostic-techniques/emg/?lang=en
Fig.19)Nerve conduction Velocity test /drmncpathlab/https://drmncpathlab.com/what-is-nerve-conduction-velocity-ncv-test/
Fig.20)Guyonś canal syndrome/osteopathy.colganosteo/https://osteopathy.colganosteo.com/guyons-canal-syndrome/
Fig.21)Zone of the guyonś canal /ignatiukplastics /https://www.ignatiukplastics.com/guyon-s-canal
Fig.22)Zone of the guyonś canal /emgsolutions /https://emgsolutions.com/its-all-in-the-wrist-a-primer-on-ulnar-nerve-emg-ncv-evaluation-in-guyons-canal/
Reference of the video :
Guyonś canal Release and carpal tunnel Release ..Extended(Feat .Dr.Mackinnon)/WUSTL Learn Surgery/https://youtu.be/RhQwyHUYzVA
