
Ulna
By : Sara OthmanOverview
The ulna is the stabilizing bone of the forearm and the longer, thinner and medial bone in the forearm , it doesn’t reach to the wrist,)
Type:- is long bone
Location:- in the forearm medial and parallel to the radius ( the other bone on the forearm ).
The characteristic of the bone is the proximal hook-shaped end.
Type:- is long bone
Location:- in the forearm medial and parallel to the radius ( the other bone on the forearm ).
The characteristic of the bone is the proximal hook-shaped end.
Bony parts
From the proximal
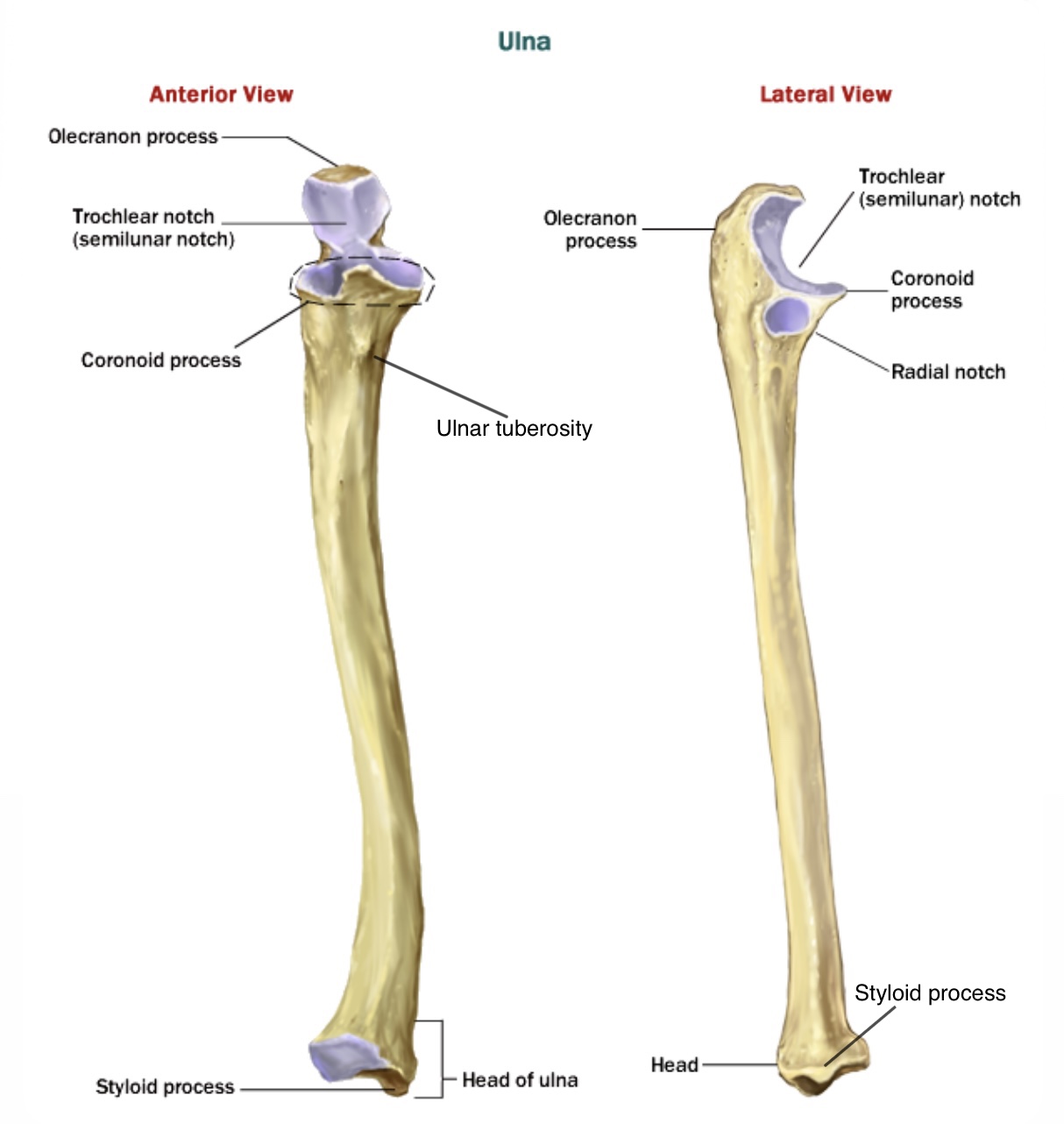
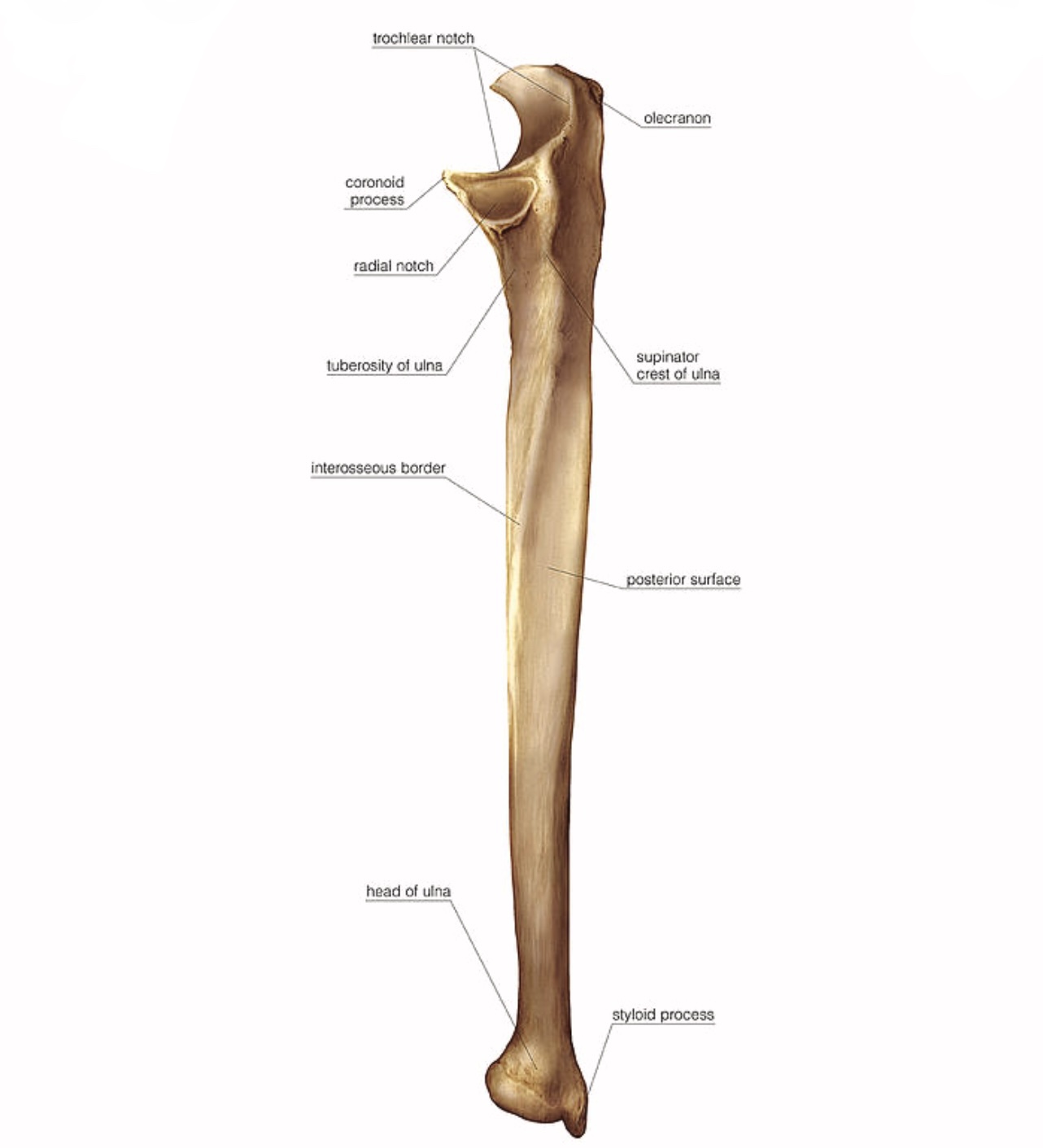
1- it has two processes , the first is the olecranon process which is large , thick , curvet eminence ( forms the point of the elbow ) found on the posterior aspect of the bone that articulates with the olecranon fossa of humerus , the olecranon process is the area where the triceps muscle is inserted .
The second one is the coronoid process on the anterior surface of ulna has a triangular form that fits into the coronoid fossa of the humerus , the two processes form the wall of the trochlear notch and their articulation with the humerus forms part of the elbow joint.
2- the trochlear notch ( semilunar notch ) is a crescent structure in which the trochlea of the humerus lies , its upper end is the olecranon process and the lower end is the coronoid process.
3- the radial notch is the shallow smooth notch for the head of radius on the lateral surface of ulna immediately below the trochlear notch to form the ( proximal radioulnar joint )
4- the supinator crest is the prominent ridge inferior to the radial notch from which part of the supinator m. is arised.
5- the ulnar tuberosity on the anterior surface just inferior to the coronoid process , it forms the insertion site of the brachialis m.
6- the shaft is elongated and extended to the small head of ulna , it has three surfaces:-
a) the posterior surface is rounded and subcutaneous broad above and narrow at the middle and below.
b) its anterior surface is smooth and concave at the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone ,is the nutrient canal directed obliquely upward.
*the nutrient canal is the canal with nutrient foramina for the vessels that supply the bone , usually it extends into the medullary cavity from the growing end of the bone.
*the growing end of the ulna is the lower end of the ulna
c) the medial surface is broad and concave above , narrow and convex below , its lower fourth is subcutaneous.
also it has three borders:-
a) the volar ( anterior ) border extends from the coronoid process above to styloid process below.
b) the dorsal ( posterior ) border extends from the olecranon process above to the back of styloid process below.
c) the interosseous border is sharp border on the lateral side of ulna for the attachment of interosseous membrane ( between the ulna and radius ).
7- the head is a small rounded and forms the distal end of the ulna , it has an articular surface on the lateral side to articulate with ulnar notch of radius and form ( the distal radioulnar joint )
8- the styloid process is the small conical projection on the posteromedial surface of the head and separated from it by a small depression and groove.
1- it has two processes , the first is the olecranon process which is large , thick , curvet eminence ( forms the point of the elbow ) found on the posterior aspect of the bone that articulates with the olecranon fossa of humerus , the olecranon process is the area where the triceps muscle is inserted .
The second one is the coronoid process on the anterior surface of ulna has a triangular form that fits into the coronoid fossa of the humerus , the two processes form the wall of the trochlear notch and their articulation with the humerus forms part of the elbow joint.
2- the trochlear notch ( semilunar notch ) is a crescent structure in which the trochlea of the humerus lies , its upper end is the olecranon process and the lower end is the coronoid process.
3- the radial notch is the shallow smooth notch for the head of radius on the lateral surface of ulna immediately below the trochlear notch to form the ( proximal radioulnar joint )
4- the supinator crest is the prominent ridge inferior to the radial notch from which part of the supinator m. is arised.
5- the ulnar tuberosity on the anterior surface just inferior to the coronoid process , it forms the insertion site of the brachialis m.
6- the shaft is elongated and extended to the small head of ulna , it has three surfaces:-
a) the posterior surface is rounded and subcutaneous broad above and narrow at the middle and below.
b) its anterior surface is smooth and concave at the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone ,is the nutrient canal directed obliquely upward.
*the nutrient canal is the canal with nutrient foramina for the vessels that supply the bone , usually it extends into the medullary cavity from the growing end of the bone.
*the growing end of the ulna is the lower end of the ulna
c) the medial surface is broad and concave above , narrow and convex below , its lower fourth is subcutaneous.
also it has three borders:-
a) the volar ( anterior ) border extends from the coronoid process above to styloid process below.
b) the dorsal ( posterior ) border extends from the olecranon process above to the back of styloid process below.
c) the interosseous border is sharp border on the lateral side of ulna for the attachment of interosseous membrane ( between the ulna and radius ).
7- the head is a small rounded and forms the distal end of the ulna , it has an articular surface on the lateral side to articulate with ulnar notch of radius and form ( the distal radioulnar joint )
8- the styloid process is the small conical projection on the posteromedial surface of the head and separated from it by a small depression and groove.
How to know the bone is right or left
1- the olecranon process should be posteriorly.
2- the trochlear notch should be anteriorly.
3-the radial notch should be on the lateral side.
4- the styloid process should be on the medial side.
2- the trochlear notch should be anteriorly.
3-the radial notch should be on the lateral side.
4- the styloid process should be on the medial side.
The articulation
1- the ulna articulates with the humerus to form the elbow joint through ( olecranon process , coronoid process , trochlear notch ).
2- the ulna articulates with radius through the radial notch with the head of radius to form the proximal radioulnar joint and through the articular surface of the head and the ulnar notch of radius to form the distal radioulnar joint.
* it doesn’t have an articulation for the wrist .
*the radioulnar joints are synovial pivot joints , they allow pronation and supination movements of the forearm ( the radius rotates around the ulna ).
*Pivot joint allows only rotary movement around a single axis .
2- the ulna articulates with radius through the radial notch with the head of radius to form the proximal radioulnar joint and through the articular surface of the head and the ulnar notch of radius to form the distal radioulnar joint.
* it doesn’t have an articulation for the wrist .
*the radioulnar joints are synovial pivot joints , they allow pronation and supination movements of the forearm ( the radius rotates around the ulna ).
*Pivot joint allows only rotary movement around a single axis .

Muscles attached to the bone
The ulna gives origion to
1- humeroulnar head of flexor digitorum superficialis , deep head of flexor carpi ulnaris , one head of pronator teres at processes of ulna.
2- flexor digitorum profundus at the shaft.
3- supinator at supinator crest and fossa.
4- pronator quadratus at distal third of the ulna.
5- abductor pollicis longus at posterior surface of ulna.
6- parts of ( extensor carpi ulnaris , extensor pollicis longus , extensor indicis ) at posterior of ulna.
And receive the insertion of
1- triceps barchii & anconeus at the olecranon process.
2- brachialis at coronoid process.
1- humeroulnar head of flexor digitorum superficialis , deep head of flexor carpi ulnaris , one head of pronator teres at processes of ulna.
2- flexor digitorum profundus at the shaft.
3- supinator at supinator crest and fossa.
4- pronator quadratus at distal third of the ulna.
5- abductor pollicis longus at posterior surface of ulna.
6- parts of ( extensor carpi ulnaris , extensor pollicis longus , extensor indicis ) at posterior of ulna.
And receive the insertion of
1- triceps barchii & anconeus at the olecranon process.
2- brachialis at coronoid process.

Attachments of ulna
Fractures of the ulna
The fracture of the shaft of ulna may be associated with the fracture of the shaft of radius and may not , the fracture of only ulnar bone is associated with the dislocation of the radius ( because they are enclosed by the interosseous membrane ) and that will affect the pronation and supination of the forearm.
Monteggia fracture:- refers to the fracture of ulna and dislocation of the head of radius ( proximal radioulnar joint ) , the dislocation is happened anteriorly for 70% and sometimes posteriorly or laterally, the fracture of the ulna is happened in the shaft or metaphysis , rarely happened that the anterior dislocation of the head of radius with fracture of the shaft (diaphysis) of the ulna and radius , These fractures are rarely happened in adults and more common in children with peak incidence between 4 and 10 years of age.
Galeazzi fracture:- is the isolated fracture of the junction between the middle and distal third of radius accompanied with the dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint , can be caused by direct wrist trauma and falling onto outstretched hand with pronated forearm.
The fracture of the olecranon process:- is the fracture of the pointy bone of the elbow and may be displaced by the triceps m. ( make insertion on it ) , can be caused by a landing on the elbow or a direct impact from an object or indirect blow , this fracture is more common and usually occurs in isolation (there are no other injuries) but can also be a part of a more complex elbow injuries .
Monteggia fracture:- refers to the fracture of ulna and dislocation of the head of radius ( proximal radioulnar joint ) , the dislocation is happened anteriorly for 70% and sometimes posteriorly or laterally, the fracture of the ulna is happened in the shaft or metaphysis , rarely happened that the anterior dislocation of the head of radius with fracture of the shaft (diaphysis) of the ulna and radius , These fractures are rarely happened in adults and more common in children with peak incidence between 4 and 10 years of age.
Galeazzi fracture:- is the isolated fracture of the junction between the middle and distal third of radius accompanied with the dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint , can be caused by direct wrist trauma and falling onto outstretched hand with pronated forearm.
The fracture of the olecranon process:- is the fracture of the pointy bone of the elbow and may be displaced by the triceps m. ( make insertion on it ) , can be caused by a landing on the elbow or a direct impact from an object or indirect blow , this fracture is more common and usually occurs in isolation (there are no other injuries) but can also be a part of a more complex elbow injuries .



Monteggia fracture
Blood supply of the ulna
The ulna receive its blood supply from the branch of the anterior interosseous a. ( a branch of ulnar a. ) where it enters the nutrient canal which located in the shaft through the nutrient foramen.

Nutrient foramen of the ulna
References
1- Moore's Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition / pp.677-678 , pp.685-686
2- LAWRENCE E. WINESKI Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions /10th Edition (2018 ) / pp.94-95-96
3- the ulna , Author: Oliver Jones , source: Teachme Anatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/bones/ulna/
4- Radius and Ulna , Author: Edwin Ocran MBChB, MBc , source: kenhub , https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-radius-and-the-ulna
5- Monteggia fractures , Authors: Neal P. Johnson , Michael Silberman , source: NCBI Bookshelf , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470575/
2- LAWRENCE E. WINESKI Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions /10th Edition (2018 ) / pp.94-95-96
3- the ulna , Author: Oliver Jones , source: Teachme Anatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/bones/ulna/
4- Radius and Ulna , Author: Edwin Ocran MBChB, MBc , source: kenhub , https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-radius-and-the-ulna
5- Monteggia fractures , Authors: Neal P. Johnson , Michael Silberman , source: NCBI Bookshelf , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470575/
References of images
_Cover image : mammoth memory , https://images.app.goo.gl/RqbsARCDDYKFdKJ17
_Figure1 : parts of the bone , source: Anantomy-medicine.come , https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fanatomy-medicine.com%2Fuploads%2Fposts%2F2015-09%2F1443248504_02ulna.png&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fanatomy-medicine.com%2Fmusculoskeletal-system%2F75-the-ulna.html&tbnid=mpNCT8KkMwIoeM&vet=1&docid=QIMMMbwjcX6A7M&w=611&h=677&hl=ar&source=sh%2Fx%2Fim
_Figure2 : parts of the bone , sorce: pixels , https://images.app.goo.gl/UM4nPWKPLNvGXLNH7
_Figure3 : Netter Atlas of Anatomy / plate 425
_Figure4 : attachments , source: Anatomy QA , https://images.app.goo.gl/iE2bWEVSWdGWhKjM9
_Figure5 : Monteggia fracture , source: Don’t forget the Bubbles , https://images.app.goo.gl/Jm7YmhMN59tjrYRL6
_Figure6 : Galeazzi fracture , source: hotcore.info , https://images.app.goo.gl/4t698srfss4MKcqT6
_Figure7 : Olecranone fracture , source: Don’t forget the Bubbles , https://images.app.goo.gl/WqUP11rfwnALAG9b8
_Figure8 : Nutrient foramen , source: Vedantu , https://images.app.goo.gl/8zw25wedx7v36AzG6
_Figure1 : parts of the bone , source: Anantomy-medicine.come , https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fanatomy-medicine.com%2Fuploads%2Fposts%2F2015-09%2F1443248504_02ulna.png&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fanatomy-medicine.com%2Fmusculoskeletal-system%2F75-the-ulna.html&tbnid=mpNCT8KkMwIoeM&vet=1&docid=QIMMMbwjcX6A7M&w=611&h=677&hl=ar&source=sh%2Fx%2Fim
_Figure2 : parts of the bone , sorce: pixels , https://images.app.goo.gl/UM4nPWKPLNvGXLNH7
_Figure3 : Netter Atlas of Anatomy / plate 425
_Figure4 : attachments , source: Anatomy QA , https://images.app.goo.gl/iE2bWEVSWdGWhKjM9
_Figure5 : Monteggia fracture , source: Don’t forget the Bubbles , https://images.app.goo.gl/Jm7YmhMN59tjrYRL6
_Figure6 : Galeazzi fracture , source: hotcore.info , https://images.app.goo.gl/4t698srfss4MKcqT6
_Figure7 : Olecranone fracture , source: Don’t forget the Bubbles , https://images.app.goo.gl/WqUP11rfwnALAG9b8
_Figure8 : Nutrient foramen , source: Vedantu , https://images.app.goo.gl/8zw25wedx7v36AzG6
