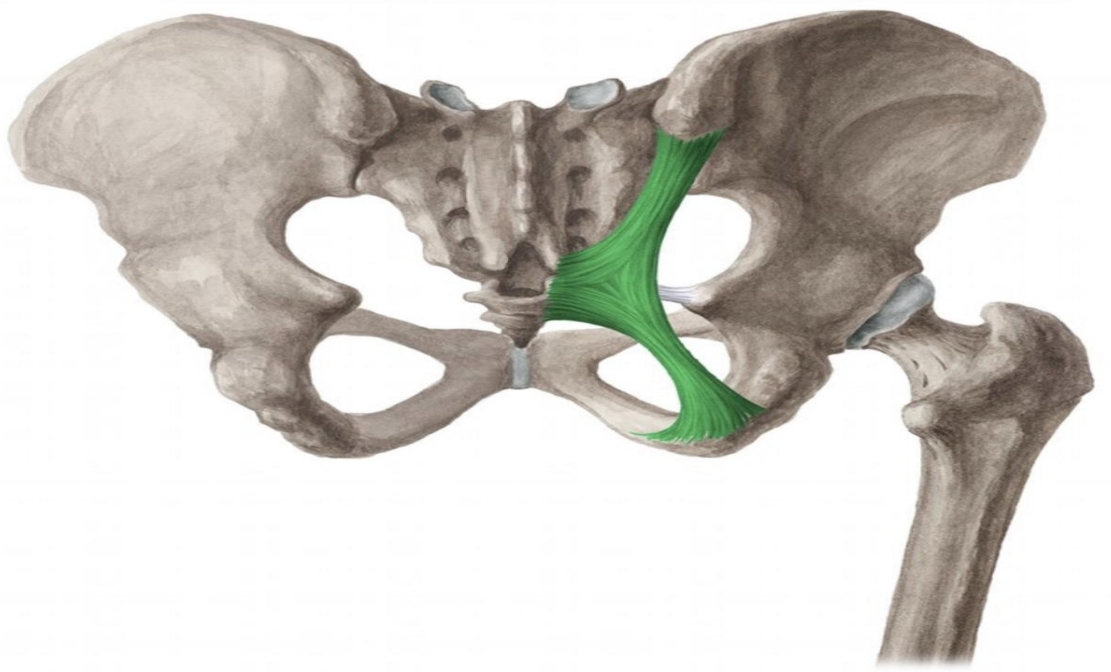
Sacrotuberous ligament
By : Banan AlzubaidiDefinition :
. Sacrotuberous ligament : It is a thick ..flexible fibrous band (from living tissue) ..
mainly composed from the collagen fibers.
. shape: it is flat .. slender .. triangular like fan
shaped .
. It converts the sciatic notches (part of the pelvic bone)to the
sciatic foramina and forms the boundaries to these foramina.
mainly composed from the collagen fibers.
. shape: it is flat .. slender .. triangular like fan
shaped .
. It converts the sciatic notches (part of the pelvic bone)to the
sciatic foramina and forms the boundaries to these foramina.
Function:
1) The main function of the sacrotuberous ligament is providing stabilization to
the pelvic bone and sacroiliac joint.
2) It is strong enough to support the
sacrum bone and prevent the sacrum bone moving from its position under the
body weight.
3) it is stabilizes the sacrum from twisting or rotating with the
pelvis and prevents it from turning forward when the pressure is descending on
the spine, especially during these sports, gymnastics, golf, high jump and
volleyball.
4) it strengths
connecting the the vertebral columnar(sacrum) to the ischial tuberosity of the
pelvis bone .
the pelvic bone and sacroiliac joint.
2) It is strong enough to support the
sacrum bone and prevent the sacrum bone moving from its position under the
body weight.
3) it is stabilizes the sacrum from twisting or rotating with the
pelvis and prevents it from turning forward when the pressure is descending on
the spine, especially during these sports, gymnastics, golf, high jump and
volleyball.
4) it strengths
connecting the the vertebral columnar(sacrum) to the ischial tuberosity of the
pelvis bone .
Origin and insertion :
.Origin : from the posterior ilium bone ..lateral sacrum and coccyx
bone...and sacroiliac joint capsule.
.Insertion: medial ischial tuberosity and addition fibers (falciform
ligament)extend to ischial ramus.
. (Varation) /NOTE: falciform process (falciform ligament) of the sacrotuberous
ligament it is found to be absent in the 13% of the cadavers.
bone...and sacroiliac joint capsule.
.Insertion: medial ischial tuberosity and addition fibers (falciform
ligament)extend to ischial ramus.
. (Varation) /NOTE: falciform process (falciform ligament) of the sacrotuberous
ligament it is found to be absent in the 13% of the cadavers.
Located :
. in the posterior border of the pelvis bone(in the lower and
back of the pelvic bone)(On the either sides of the body).
. this ligament arises midway down the posterior border of the sacrum
which is located at the spinal base...it passes obliquely
.. downward .. forward .... and lateralward .
back of the pelvic bone)(On the either sides of the body).
. this ligament arises midway down the posterior border of the sacrum
which is located at the spinal base...it passes obliquely
.. downward .. forward .... and lateralward .
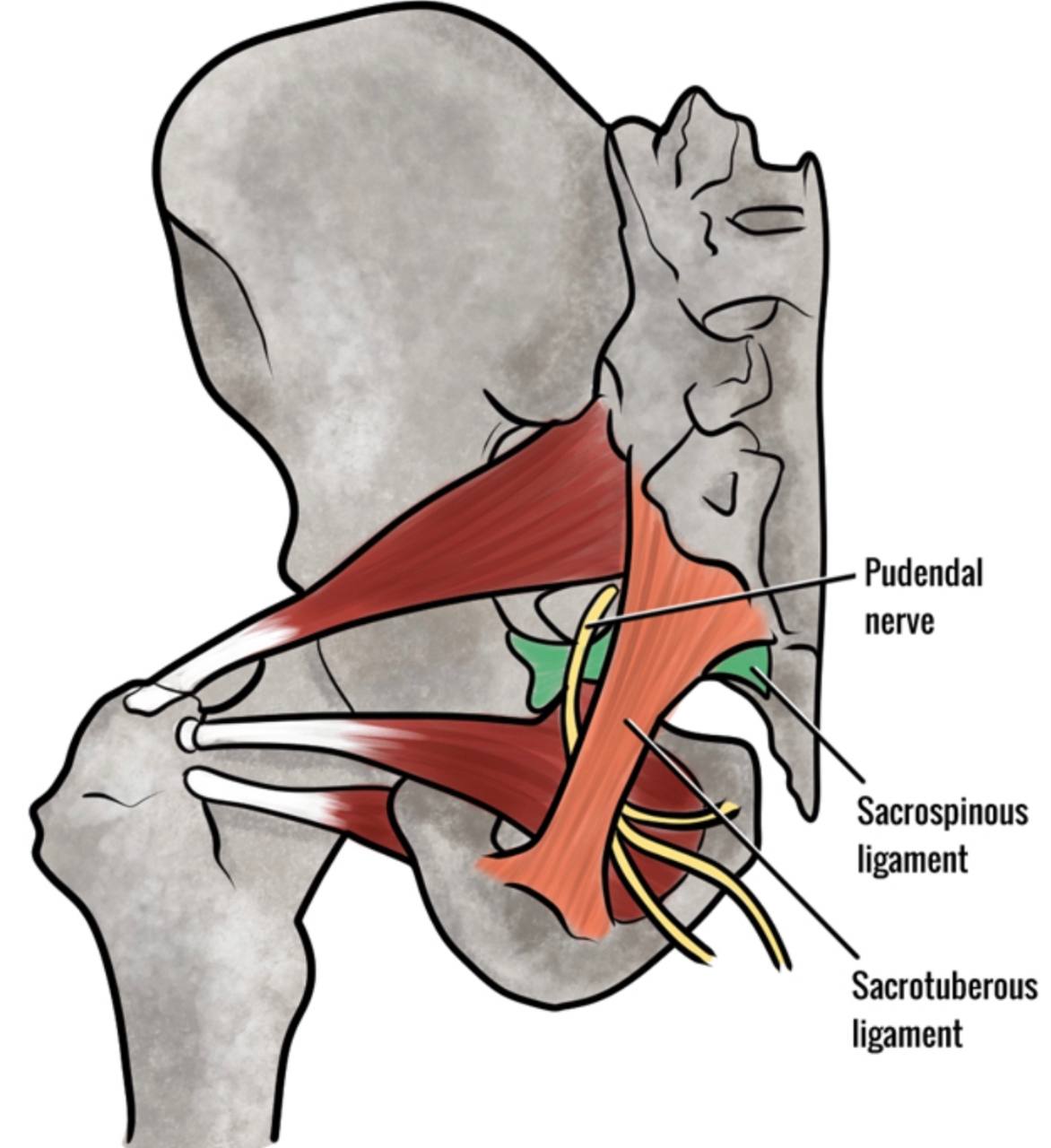
Relations :
. Anteriorly : part united to the sacrospinous ligament.
. posteriorly : gluteal maximus.
. Superiorly: posterior boundary of the
greater sciatic foramen.
. Inferiorly: posterior boundary of the lesser sciatic foramen.
. posteriorly : gluteal maximus.
. Superiorly: posterior boundary of the
greater sciatic foramen.
. Inferiorly: posterior boundary of the lesser sciatic foramen.
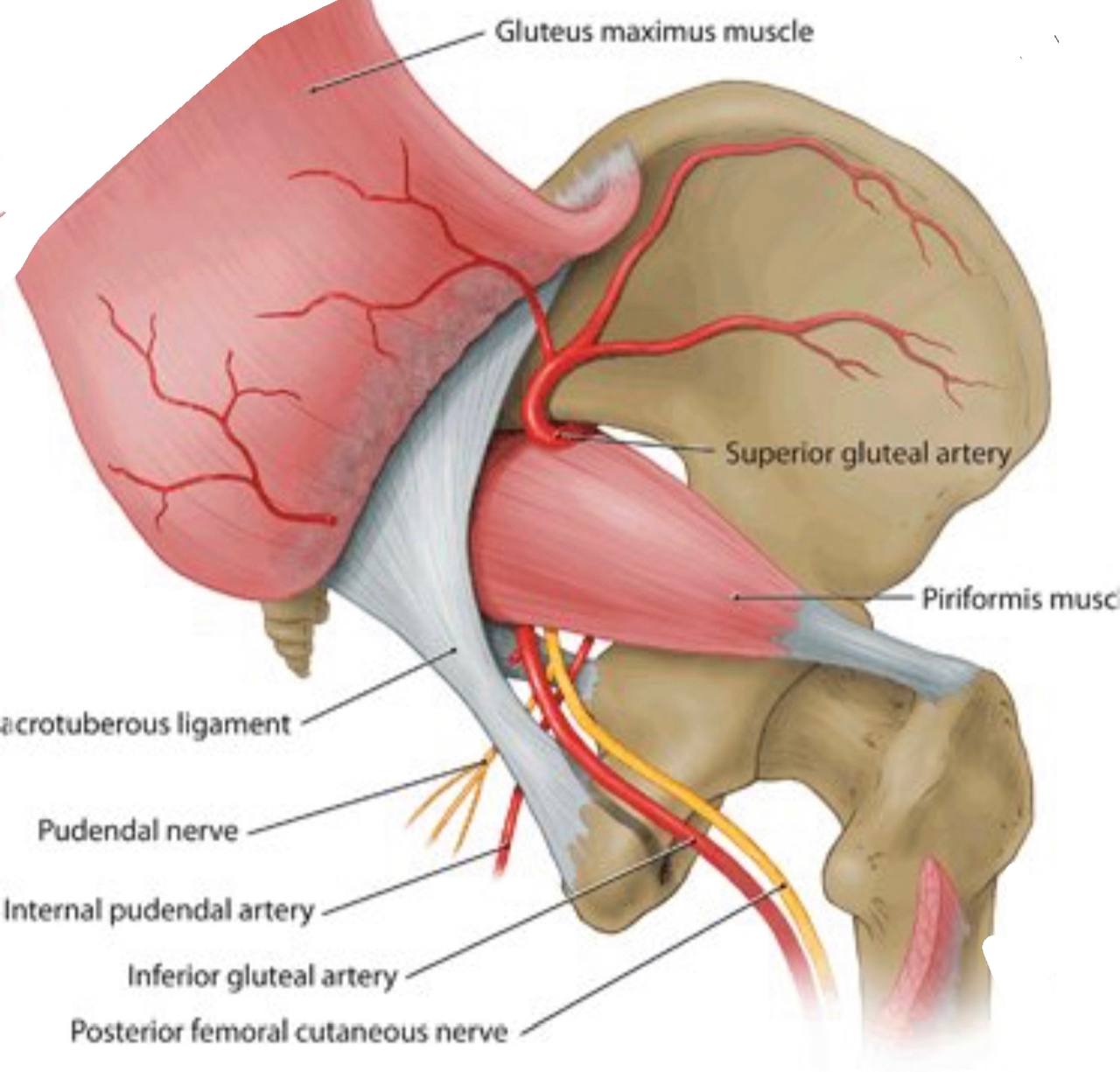
Blood and nerve supply :
. Blood supply : coccygeal branches of the inferior gluteal artery.
. Nerve supply : perforating cutaneous nerves and branches of the
coccygeal plexus.
. Nerve supply : perforating cutaneous nerves and branches of the
coccygeal plexus.
Clinical note :
. Most of the time, the sacrotuberous ligament is thin and cannot be touched
externally, but when the ligament is stressed by an injury or an aggressive
physical activity, it can become tight and thick, and this can lead to the
ossification of the ligaments or pressure on the pudendal nerve syndrome.
. When the ligament becomes more tight than usual , pain will occur in the
central side of the back of the thigh and in cases ( severe injuries ) it may
go down to the calf and into the heal ( this may interfere with pain in the
hamstrings if the pain is in the back thigh only ).
. The straight leg raise test is used to evaluate the neurological
disorders and to differentiate whether the pain is caused by the
pudendal nerve syndrome or by the pain in the hamstrings.
externally, but when the ligament is stressed by an injury or an aggressive
physical activity, it can become tight and thick, and this can lead to the
ossification of the ligaments or pressure on the pudendal nerve syndrome.
. When the ligament becomes more tight than usual , pain will occur in the
central side of the back of the thigh and in cases ( severe injuries ) it may
go down to the calf and into the heal ( this may interfere with pain in the
hamstrings if the pain is in the back thigh only ).
. The straight leg raise test is used to evaluate the neurological
disorders and to differentiate whether the pain is caused by the
pudendal nerve syndrome or by the pain in the hamstrings.
Treatment :
. The goal of physical therapy is to reduce the pain by reducing the injury
irritation, spasm and inflammation :
1) Proper rest, such as stopping sports activities that cause discomfort.
2) Ice, to relieve pain.
3) Exercises, to increase strength and stability in the lower back and the sacrum to
reduce injury to the sacrotuberous ligaments.
irritation, spasm and inflammation :
1) Proper rest, such as stopping sports activities that cause discomfort.
2) Ice, to relieve pain.
3) Exercises, to increase strength and stability in the lower back and the sacrum to
reduce injury to the sacrotuberous ligaments.
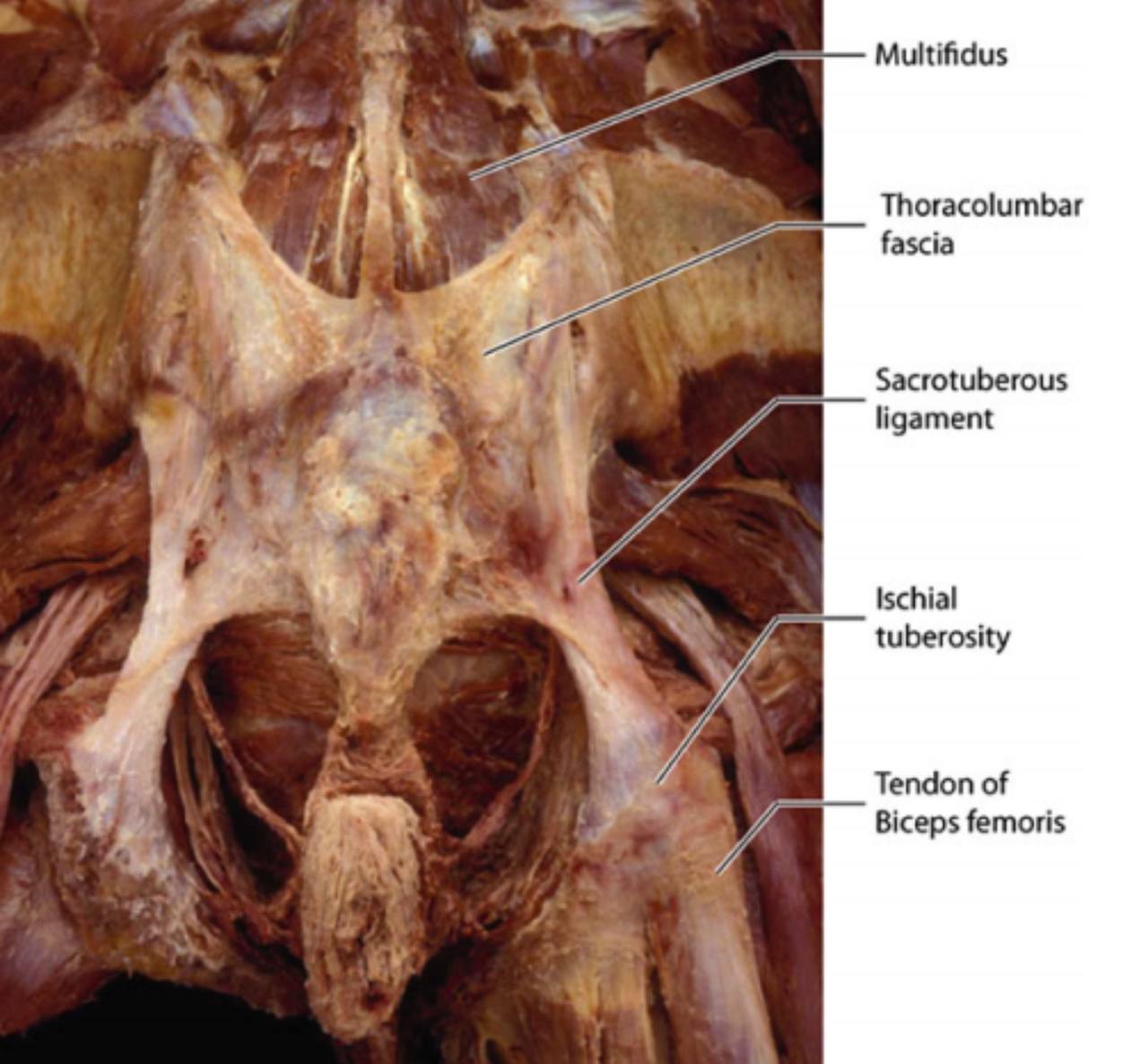
NOTE :
. Many fibers of the sacrotuberous ligament mix with other muscle fibers :
1) Provide extensive insertion for the gluteal maximus muscle.
2) Distal fibers of this ligament part-way blend with the proximal
tendon of the long head of the biceps femoris( which is associated
with important muscles of the hamstring compartment on the
posterior aspect of the thigh)(so this muscle can stabilize the
sacroiliac joint through the sacrotuberous ligament ).
3) Sacrospinous ligament.
4) Posterior sacroiliac ligament and sacroiliac joint capsule.
5) The bottom of the sacrotuberous ligament connects to the
thoracolumbar fascia that further connects into the multifidus and
erector spinae ..this plays an important role in walking and running.
. the ossification of the sacrotuberous ligament mostly seen in men and never seen
in children.
. occurring the bilateral ossification of the sacrotuberous ligament is rare.
. When this ligament is flexible, it gives way during the fetal expulsion reflex,
when the sacrum is move outward, making the fetal path more wide for
childbirth (during natural childbirth).
. NOTE : The pudendal nerve may become involved between the sacrotuberous
ligament and sacrospinous ligament (this the inner space of these ligaments)...
This causes chronic perineal pain ..the sacrotuberous ligamemt is a major factor
in the undiagnosed chronic perineal pain.
. Treat that condition: the sacrotuberous ligament is surgically removed
to reduce pain .
1) Provide extensive insertion for the gluteal maximus muscle.
2) Distal fibers of this ligament part-way blend with the proximal
tendon of the long head of the biceps femoris( which is associated
with important muscles of the hamstring compartment on the
posterior aspect of the thigh)(so this muscle can stabilize the
sacroiliac joint through the sacrotuberous ligament ).
3) Sacrospinous ligament.
4) Posterior sacroiliac ligament and sacroiliac joint capsule.
5) The bottom of the sacrotuberous ligament connects to the
thoracolumbar fascia that further connects into the multifidus and
erector spinae ..this plays an important role in walking and running.
. the ossification of the sacrotuberous ligament mostly seen in men and never seen
in children.
. occurring the bilateral ossification of the sacrotuberous ligament is rare.
. When this ligament is flexible, it gives way during the fetal expulsion reflex,
when the sacrum is move outward, making the fetal path more wide for
childbirth (during natural childbirth).
. NOTE : The pudendal nerve may become involved between the sacrotuberous
ligament and sacrospinous ligament (this the inner space of these ligaments)...
This causes chronic perineal pain ..the sacrotuberous ligamemt is a major factor
in the undiagnosed chronic perineal pain.
. Treat that condition: the sacrotuberous ligament is surgically removed
to reduce pain .
References of images :
Cover image /sacrotuberous ligament /kenhub/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjJysbl0KX7AhVvX_EDHQlrCiAQFnoECCQQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.kenhub.com%2Fen%2Flibrary%2Fanatomy%2Fsacrotuberous-ligament&usg=AOvVaw2a9yjSRhigno3Kp8hnIU_J
Fig. 1/sacrotuberous ligament and pudendal nerve /William E. Morgan, DC/http://drmorgan.info/clinicians-corner/sacrotuberous-ligament-pudendal-nerve/
Fig. 2)The vascular supply of the sacrotuberous ligament/ researchgate/ https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-vascular-supply-of-the -sacrotuberous-ligament-STL-and-surrounding-anatomy-as-viewed_fig1_314297382
Fig. 3/sacrotuberous ligament /brookbushinstitute/https://brookbushinstitute.com/articles/the-effect-of-sacroiliac-joint-pain-on-muscle-recruitment
Fig. 1/sacrotuberous ligament and pudendal nerve /William E. Morgan, DC/http://drmorgan.info/clinicians-corner/sacrotuberous-ligament-pudendal-nerve/
Fig. 2)The vascular supply of the sacrotuberous ligament/ researchgate/ https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-vascular-supply-of-the -sacrotuberous-ligament-STL-and-surrounding-anatomy-as-viewed_fig1_314297382
Fig. 3/sacrotuberous ligament /brookbushinstitute/https://brookbushinstitute.com/articles/the-effect-of-sacroiliac-joint-pain-on-muscle-recruitment
