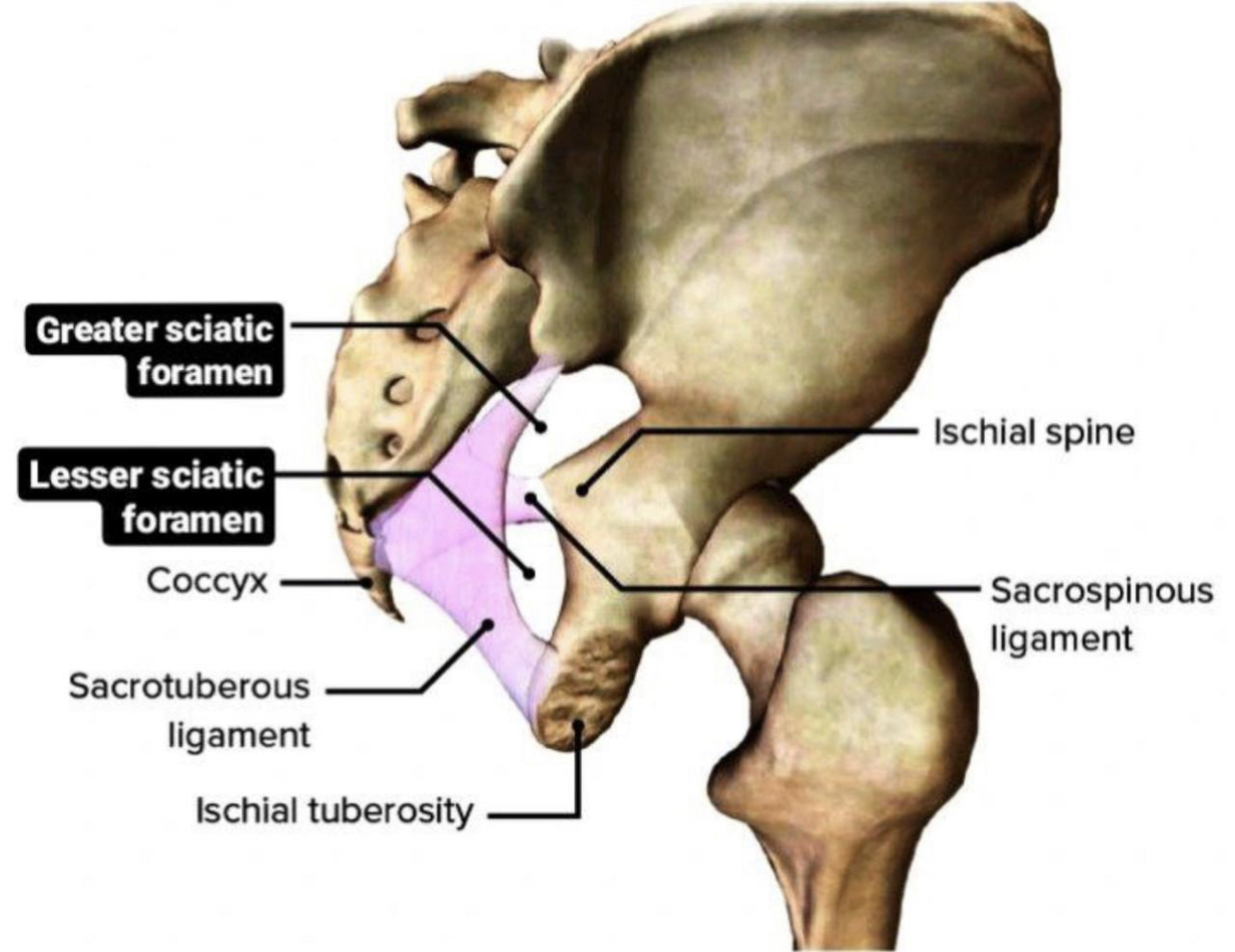
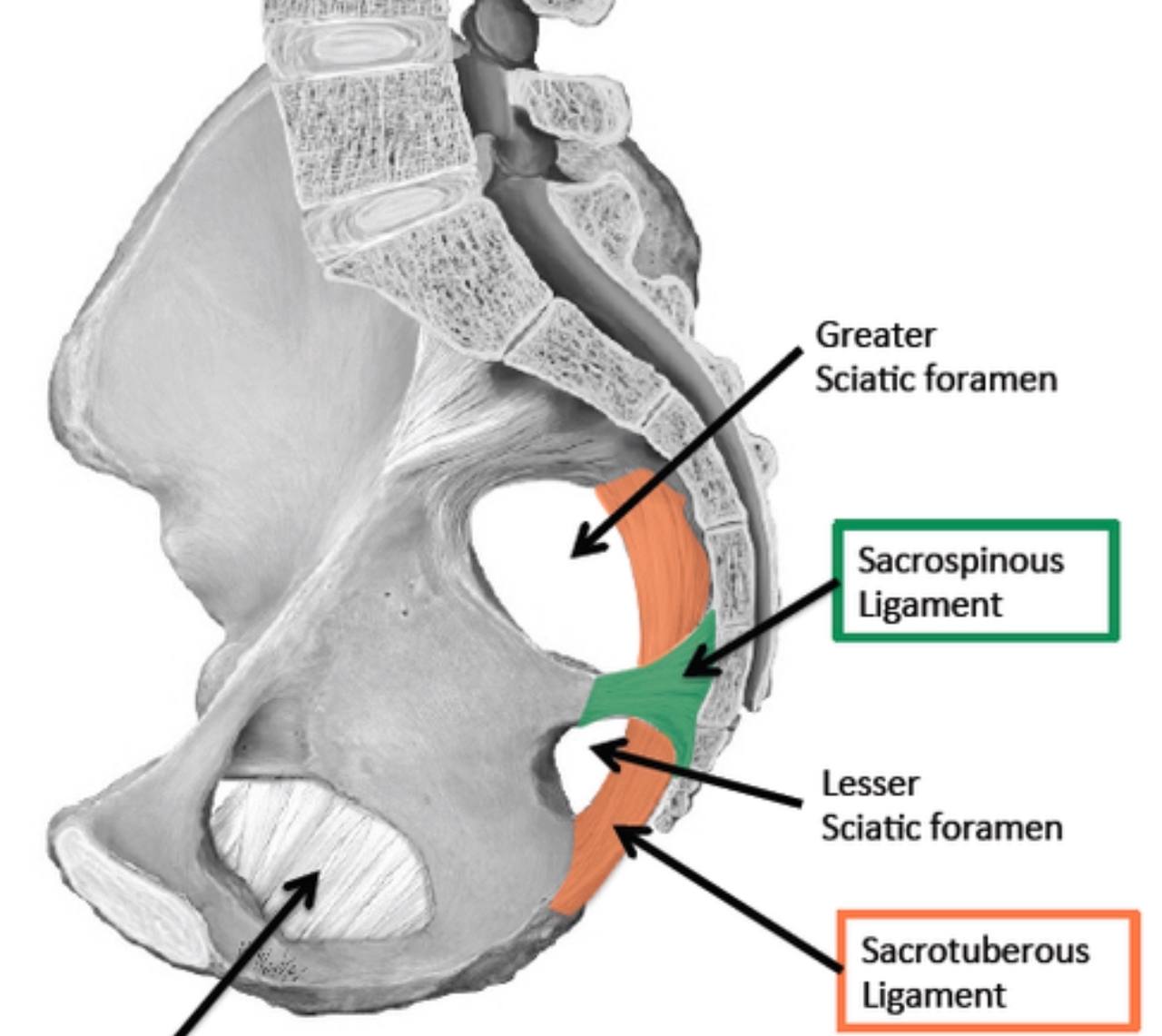
Sciatic foramina
By : Banan AlzubaidiDefinition :
. sciatic foramina : they are two openings( greater sciatic
foramen and lesser sciatic foramen ) in the posterior border
of the human pelvis (it is a part of the hip bone).
. They are like passageway for the structures that entering
and leaving the pelvis.
. They are formed by attaching two ligaments ( sacrospinous
and sacrotuberous ligament ) to the two notches in the hip
bone ( greater sciatic and lesser sciatic notch ).
foramen and lesser sciatic foramen ) in the posterior border
of the human pelvis (it is a part of the hip bone).
. They are like passageway for the structures that entering
and leaving the pelvis.
. They are formed by attaching two ligaments ( sacrospinous
and sacrotuberous ligament ) to the two notches in the hip
bone ( greater sciatic and lesser sciatic notch ).
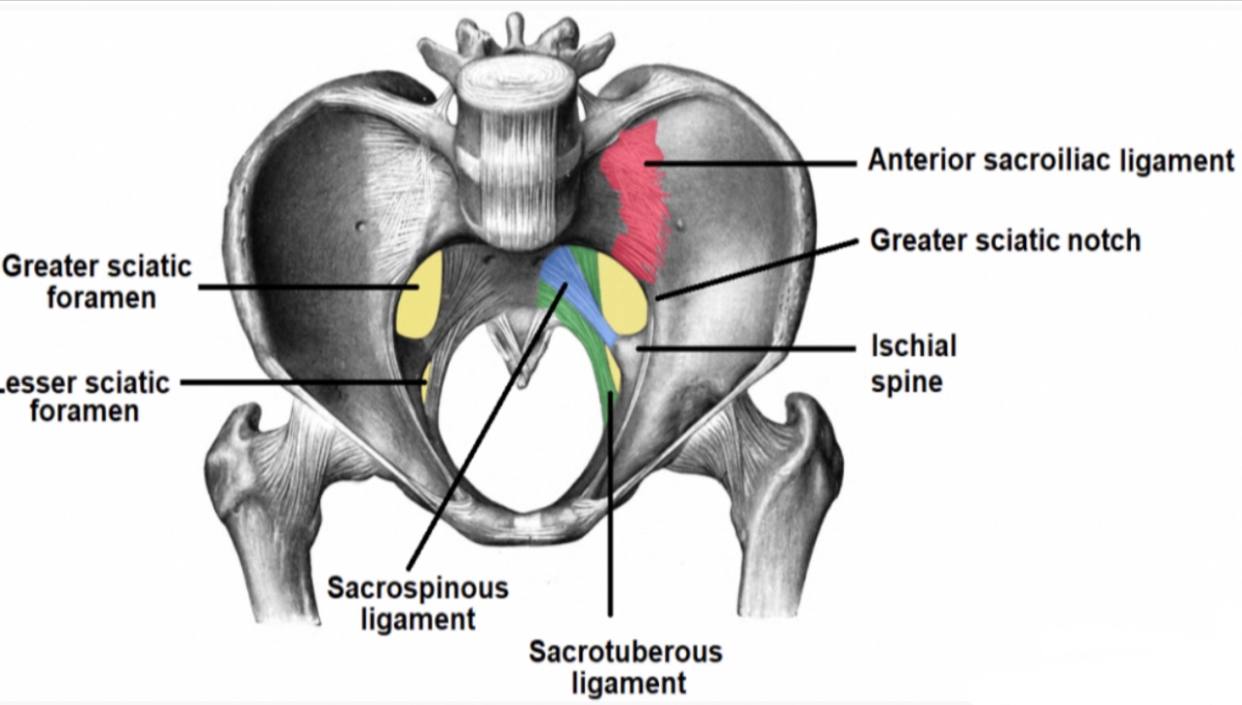
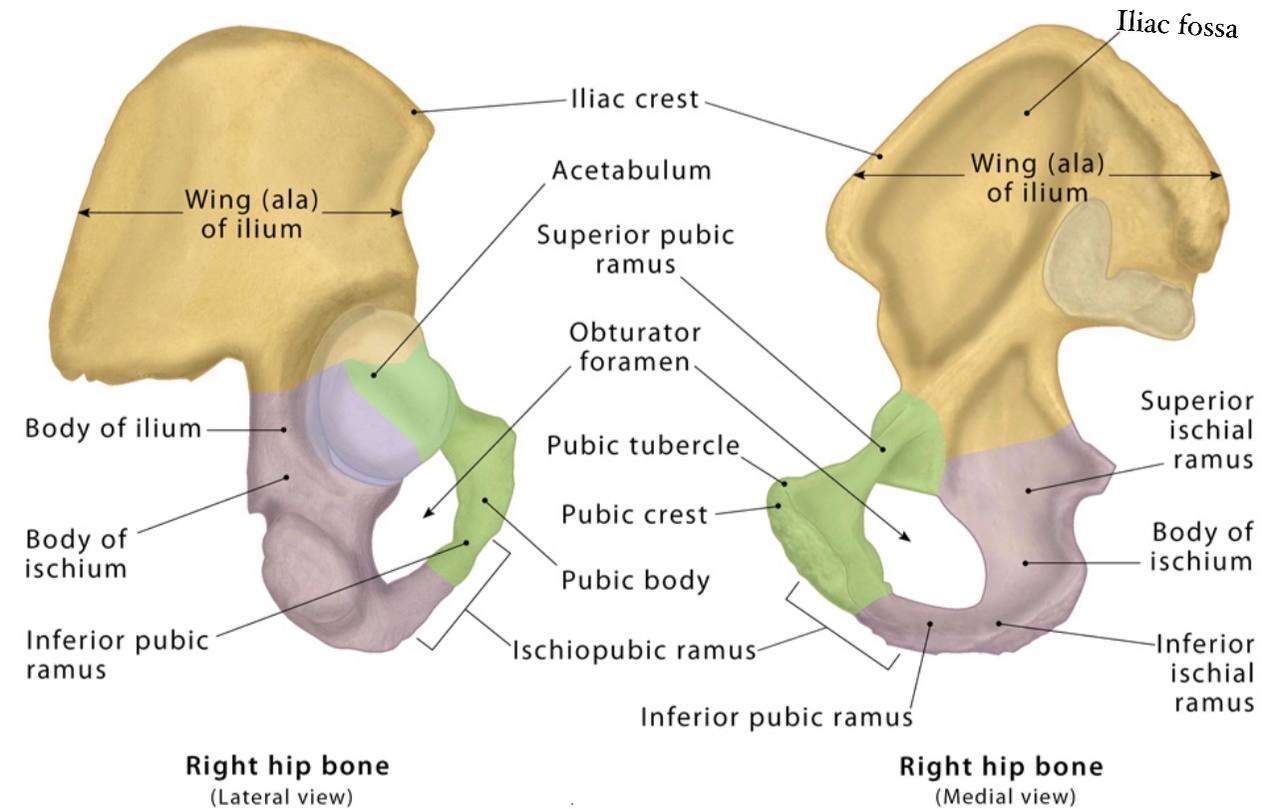
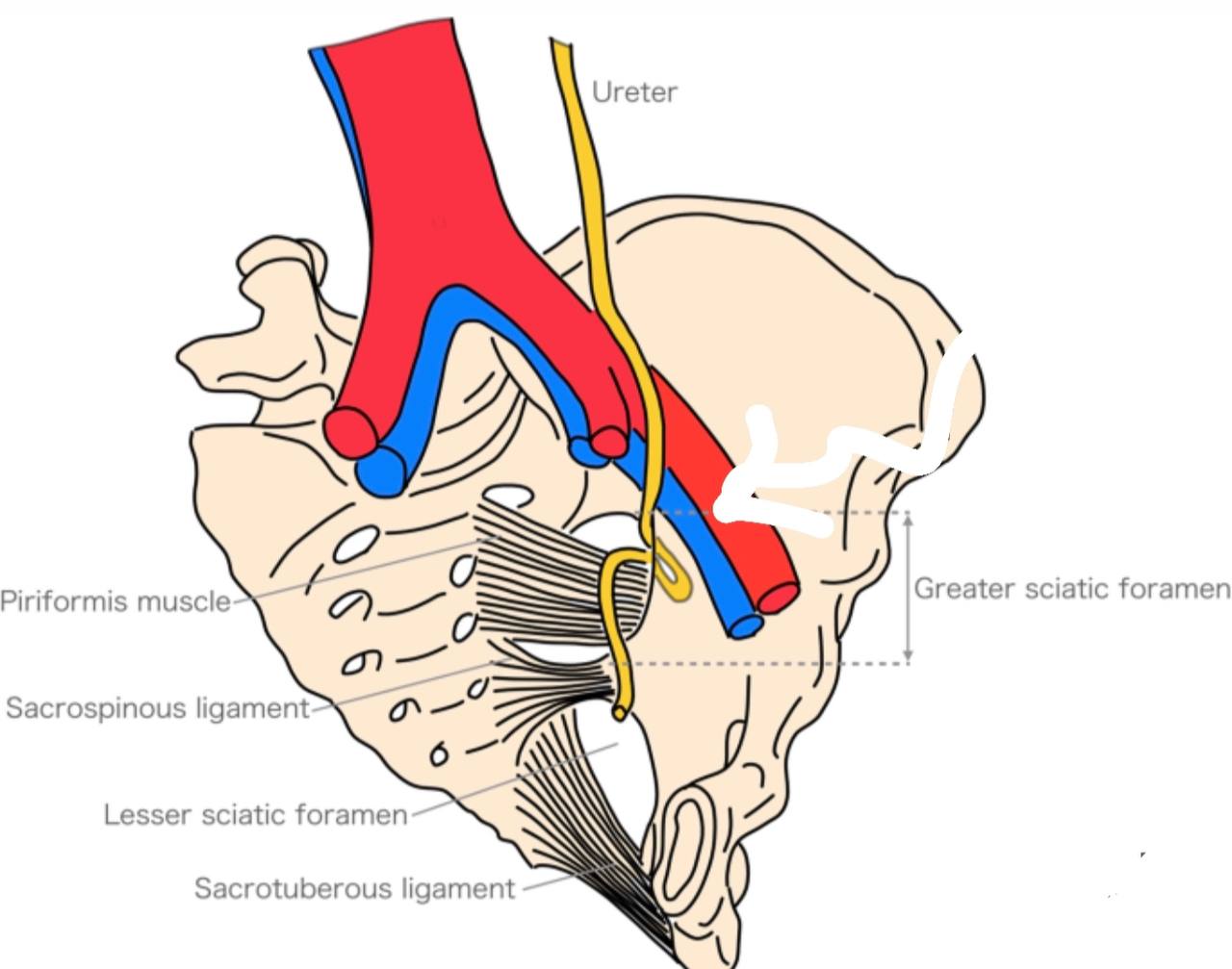
Greater sciatic foramen :
. Greater sciatic foramen : it is a large opening in the ilium
bone (part of the hip bone ) in the pelvis above the lesser
sciatic foramen. It is the major route for structures that
pass between the pelvis and the gluteal region in the lower
limb.
. NOTE : the Greater sciatic foramen is wider in the women pelvis
than in the men pelvis.
. NOTE : the greater sciatic foramen is separated from the lesser
sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament.
. NOTE : the greater sciatic foramem is larger than the lesser sciatic
foramen.
bone (part of the hip bone ) in the pelvis above the lesser
sciatic foramen. It is the major route for structures that
pass between the pelvis and the gluteal region in the lower
limb.
. NOTE : the Greater sciatic foramen is wider in the women pelvis
than in the men pelvis.
. NOTE : the greater sciatic foramen is separated from the lesser
sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament.
. NOTE : the greater sciatic foramem is larger than the lesser sciatic
foramen.
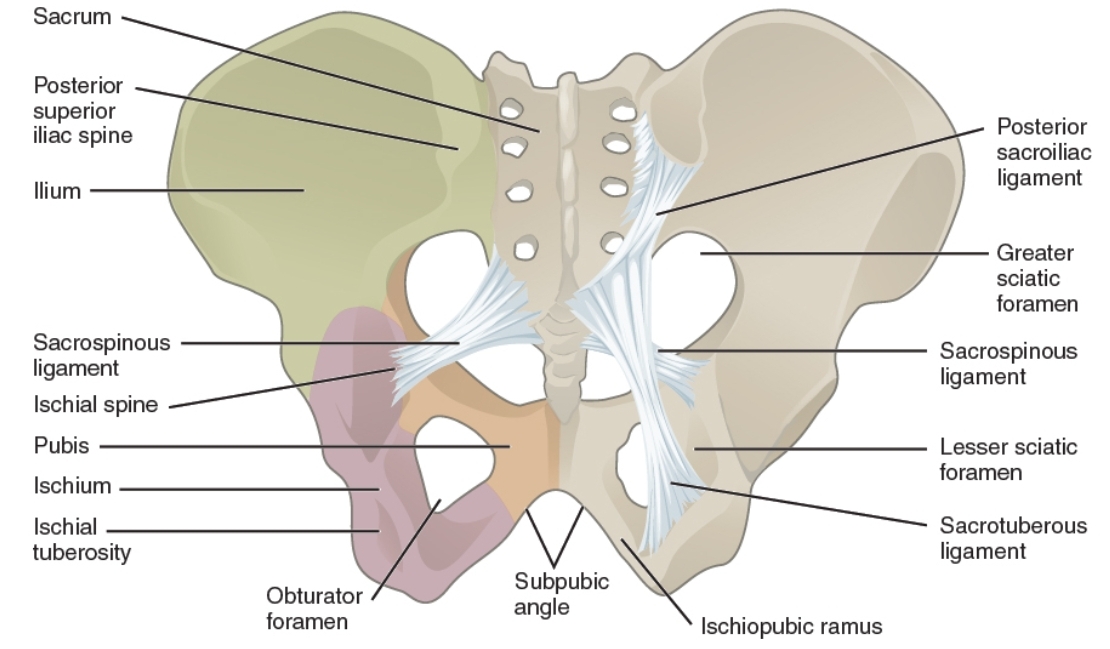
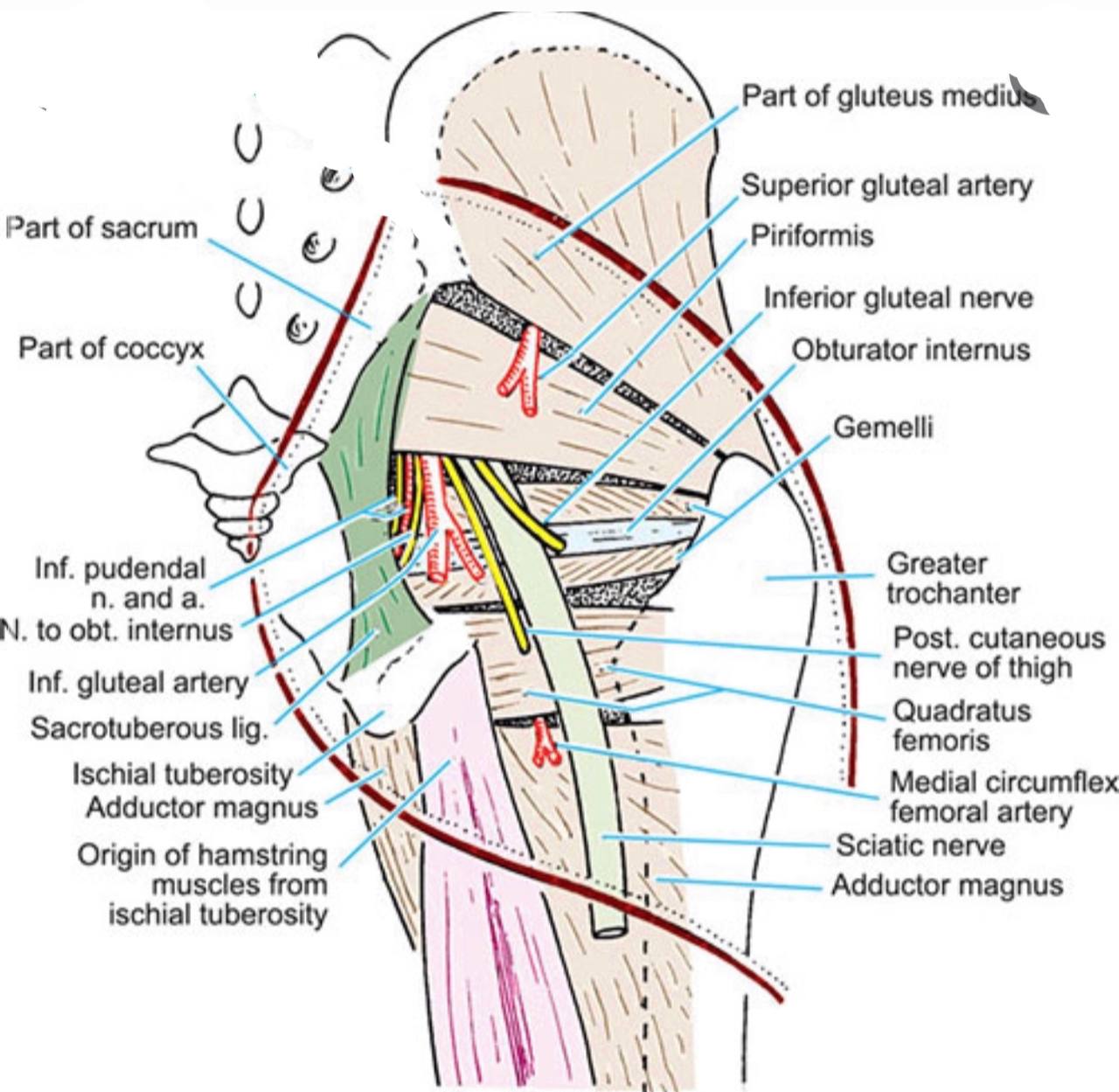
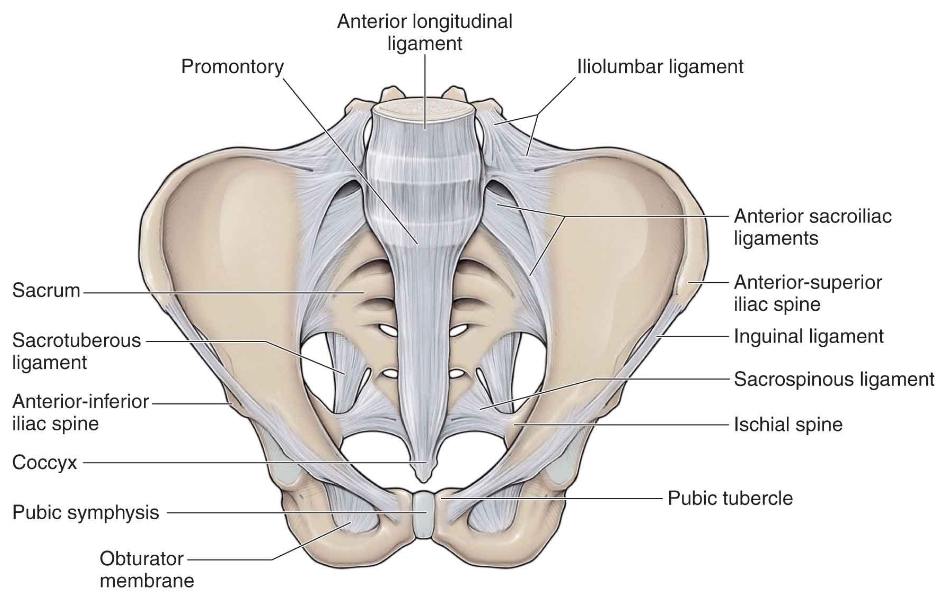
The Borders :
. Anterolaterally : greater sciatic notch of the ilium bone in
the hip bone.
. Posteromedially : sacrotuberous ligament.
. Inferiorly : sacrospinous ligament and ischial spine in the ischium bone (part of the hip bone).
. Superiorly : anterior sacroiliac ligament.
the hip bone.
. Posteromedially : sacrotuberous ligament.
. Inferiorly : sacrospinous ligament and ischial spine in the ischium bone (part of the hip bone).
. Superiorly : anterior sacroiliac ligament
Note
(it is strong ..broad ...and flat ligament formed by the numerous thin bands of the connective tissue ...covers the the front of the sacroiliac joint ..originate from the anterior surface of lateral aspect of the sacrum to the auricular surface of the ilium bone (part of the hip bone))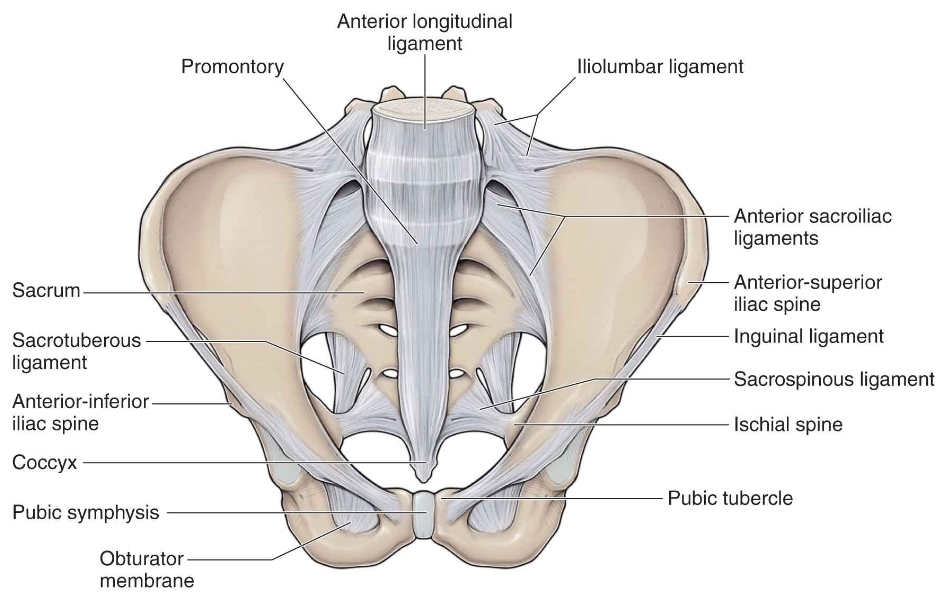
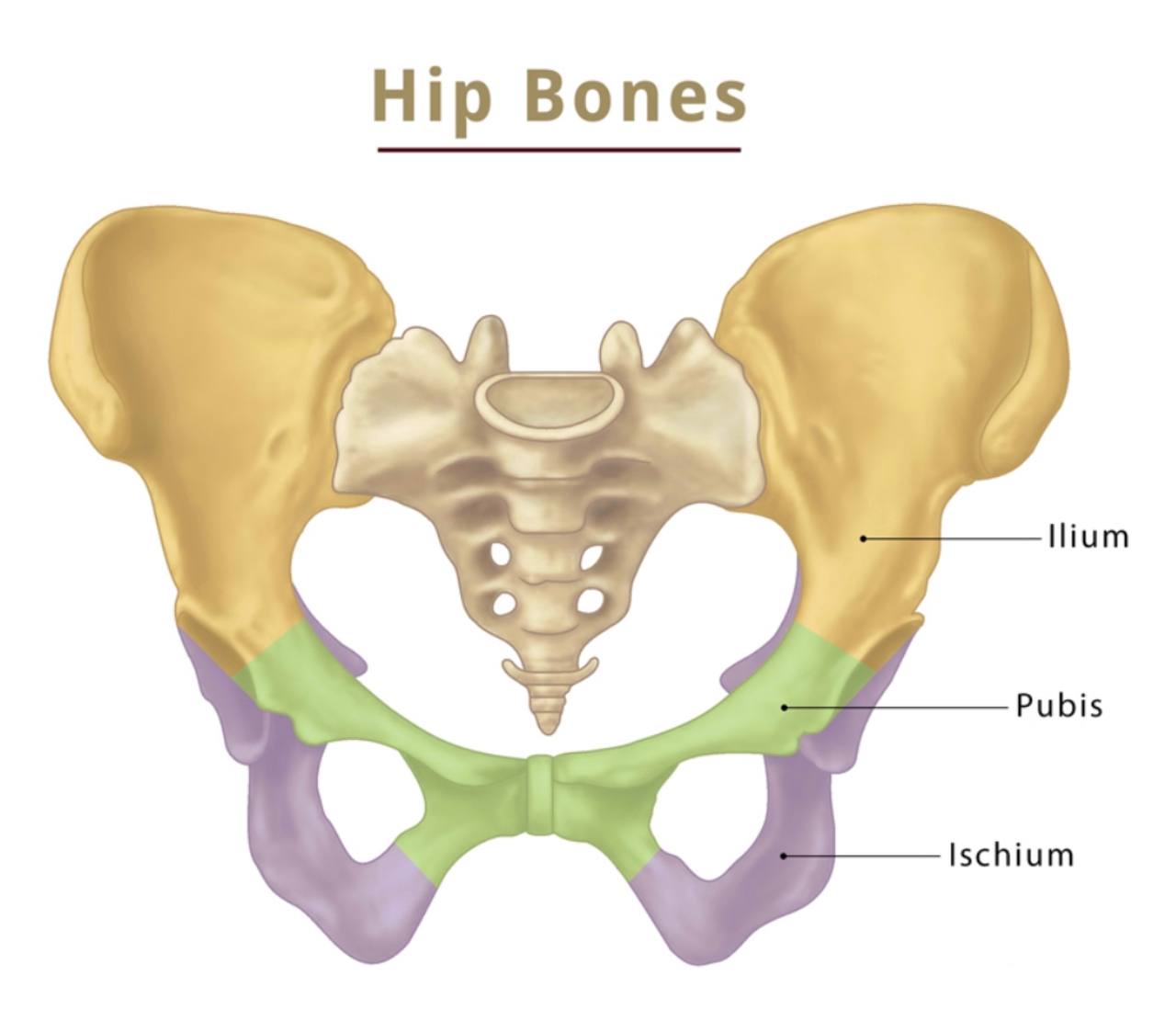
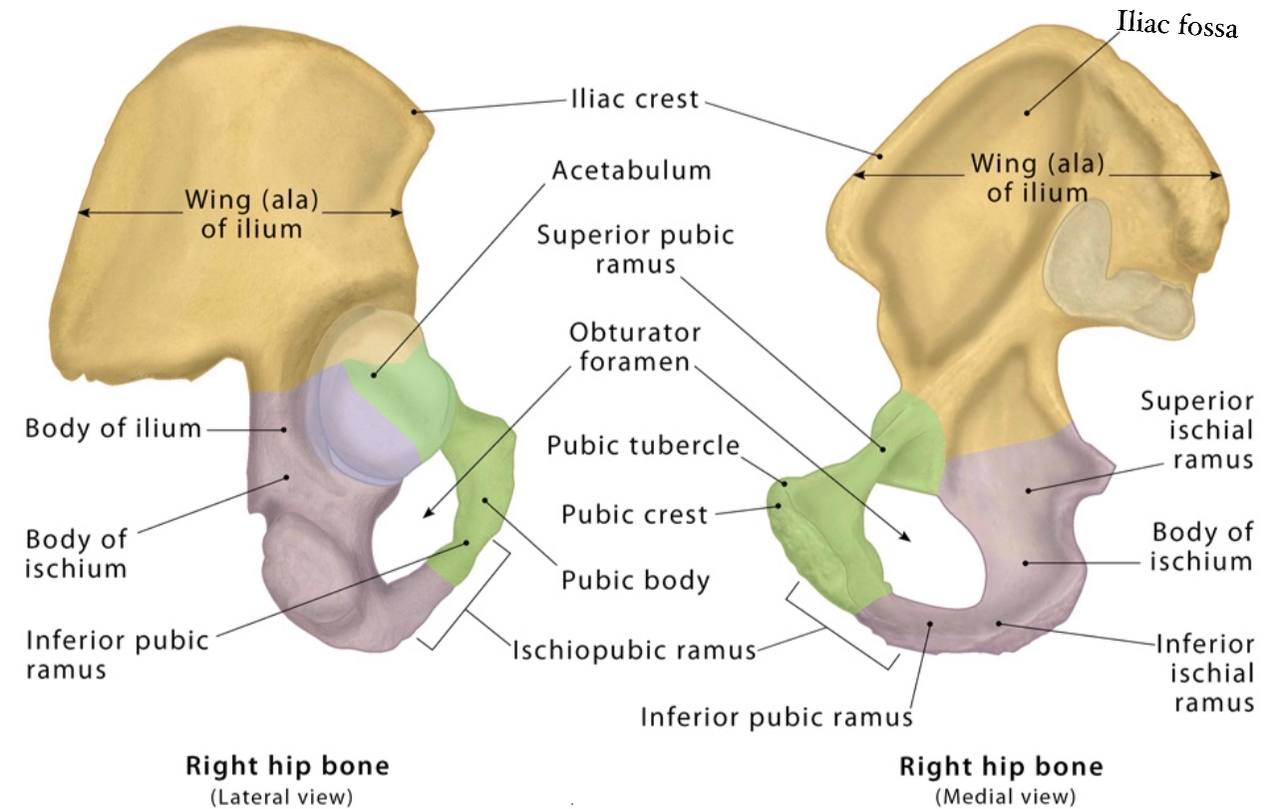
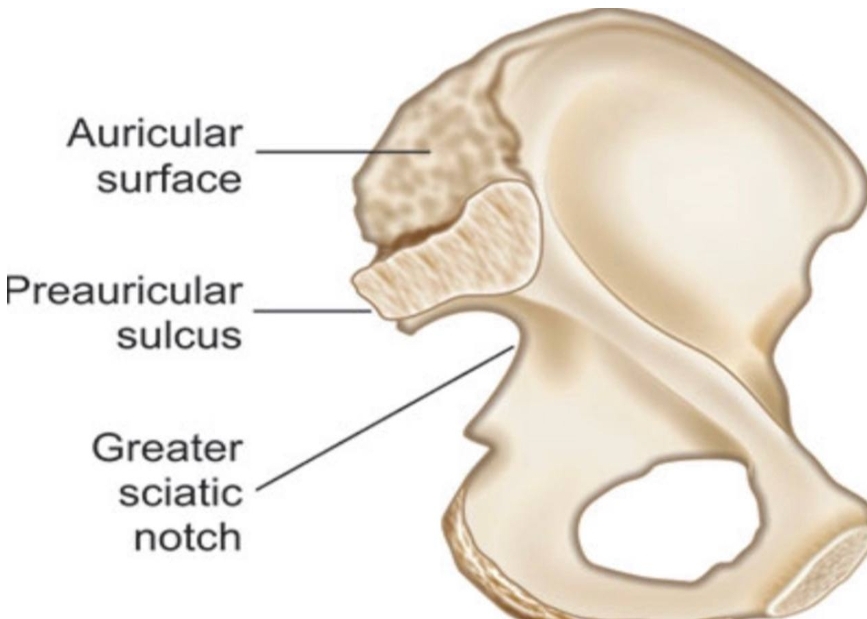
The contents :
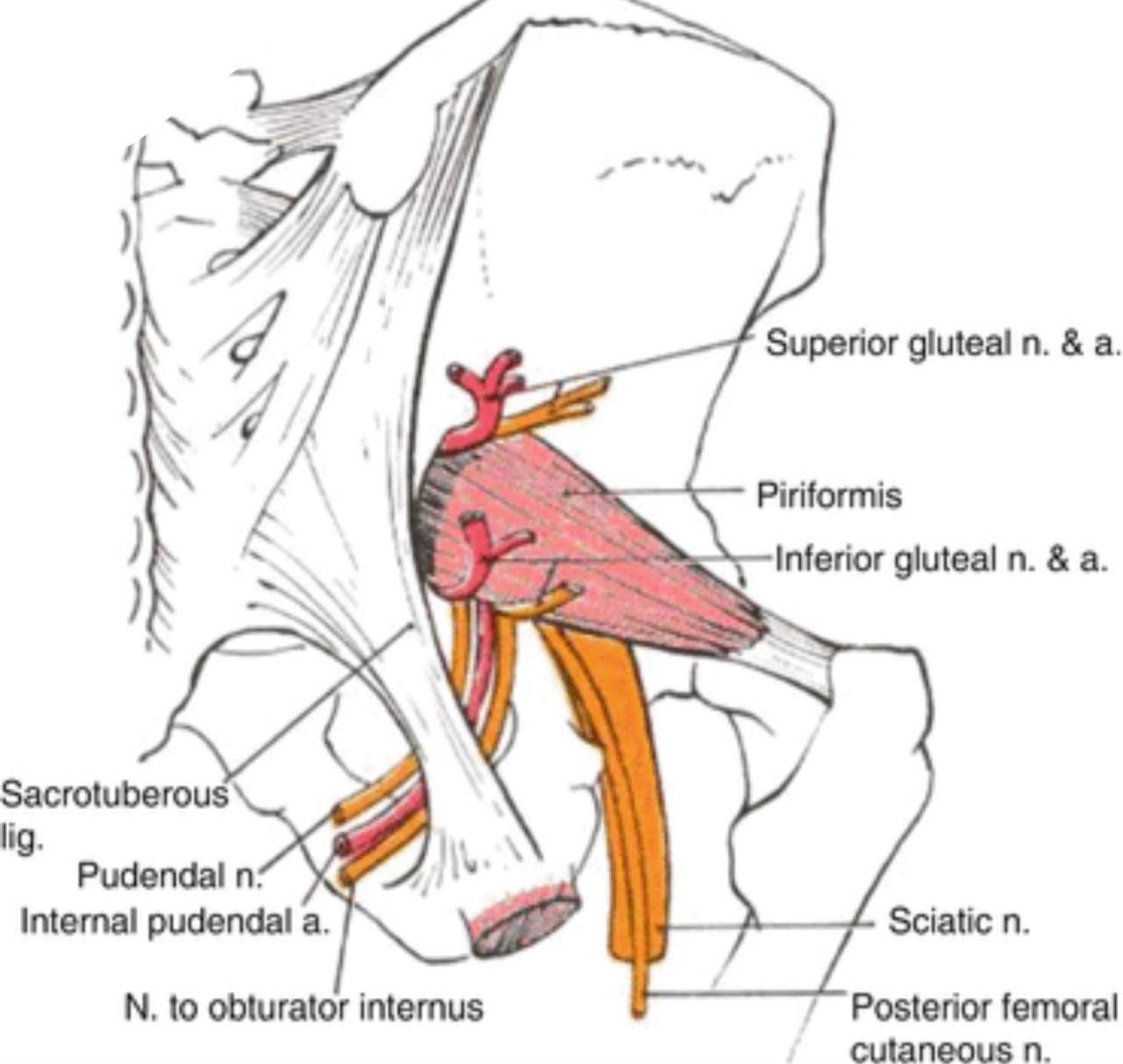
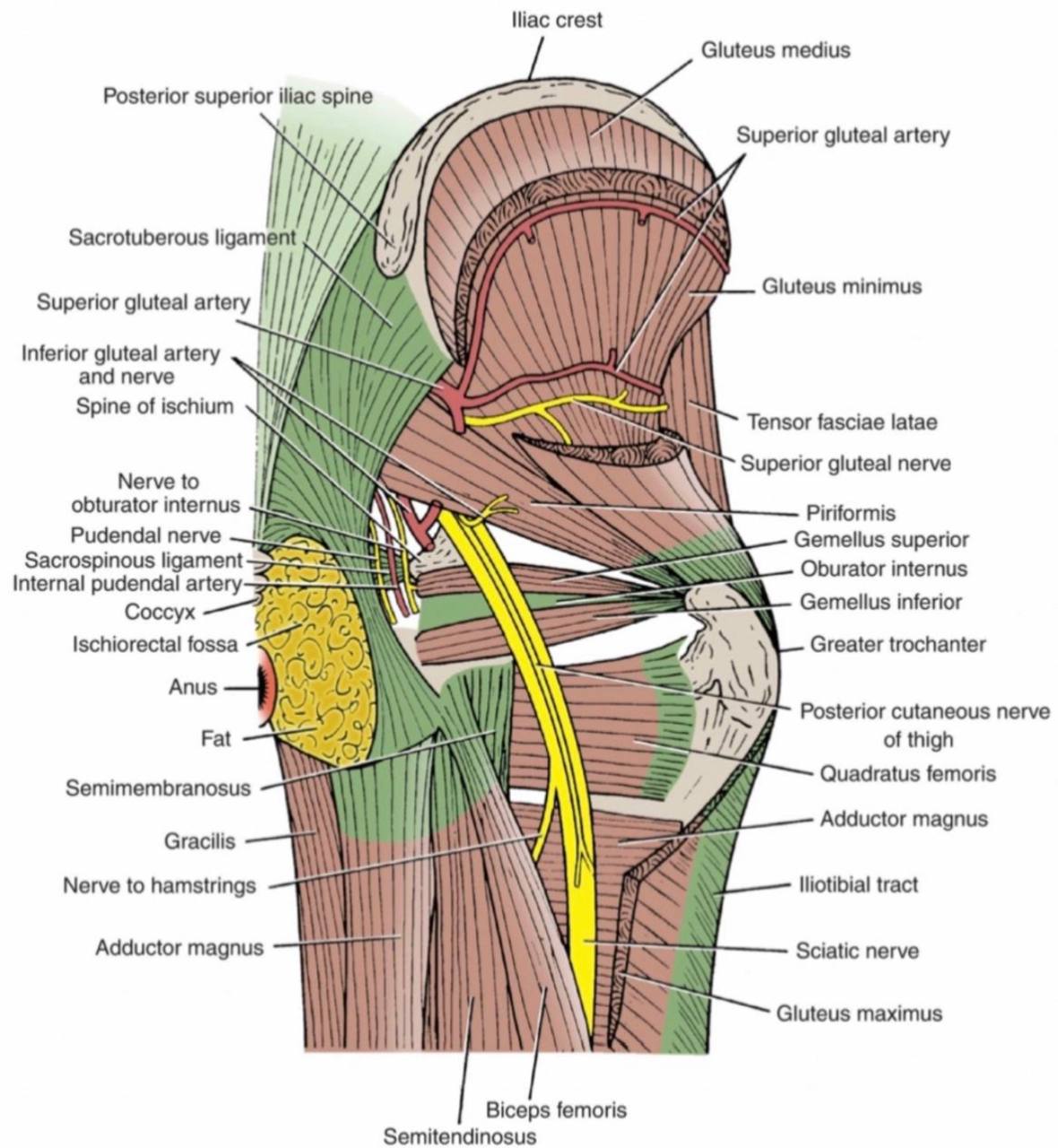
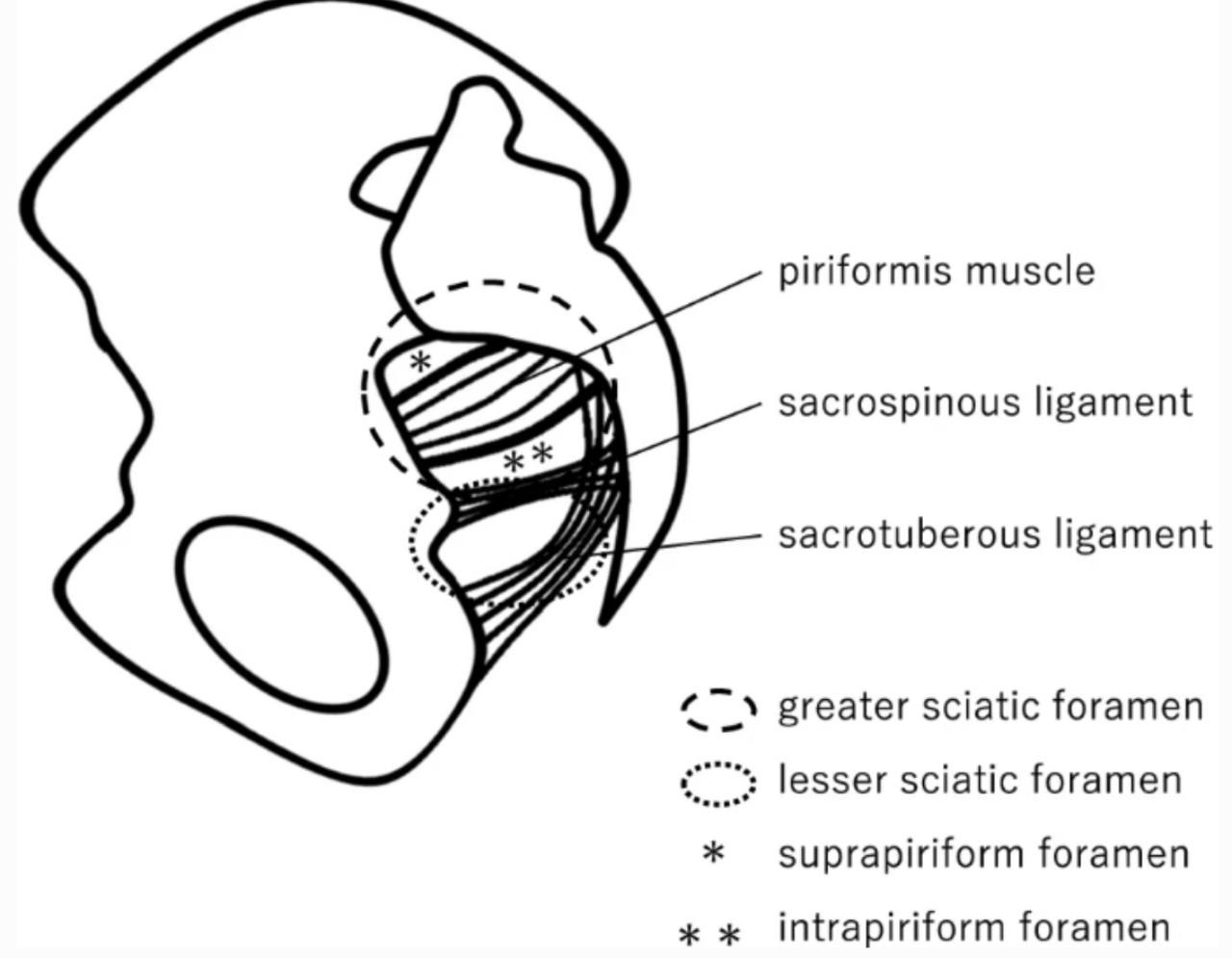
. The structure that pass through the greater sciatic foramen:
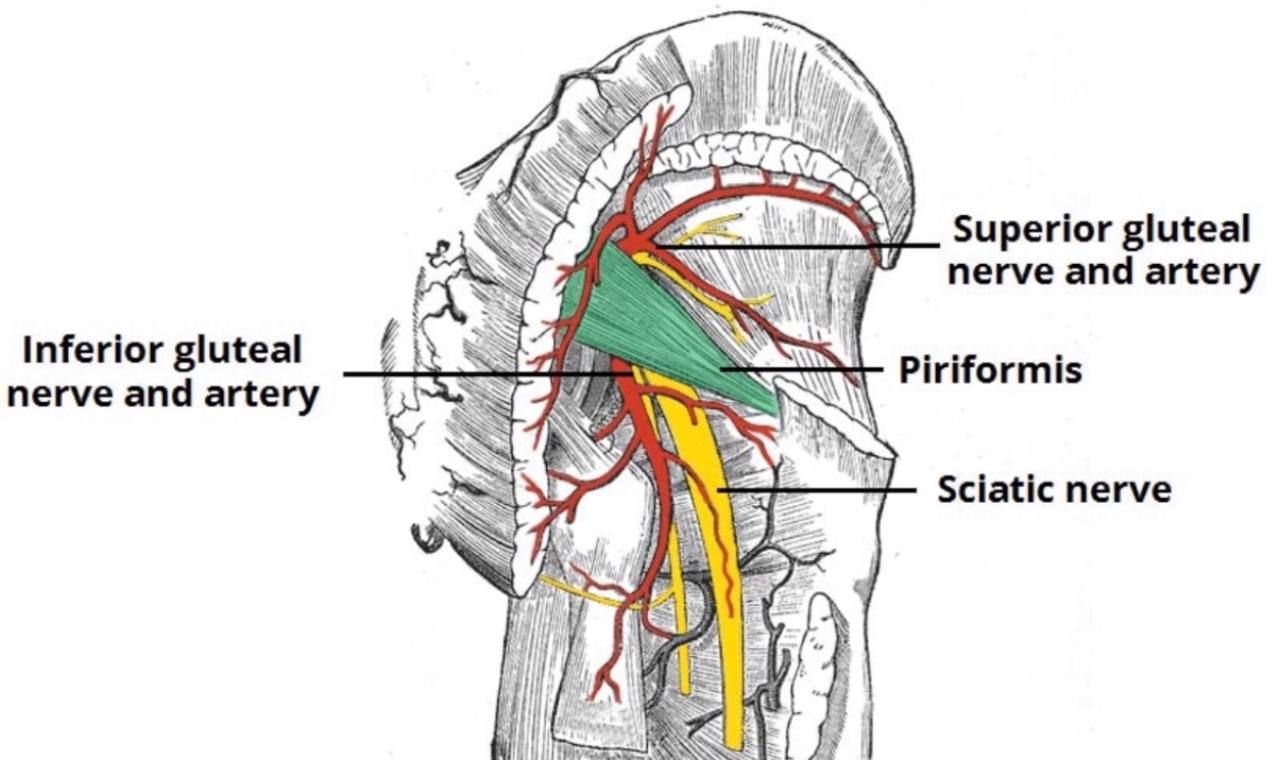
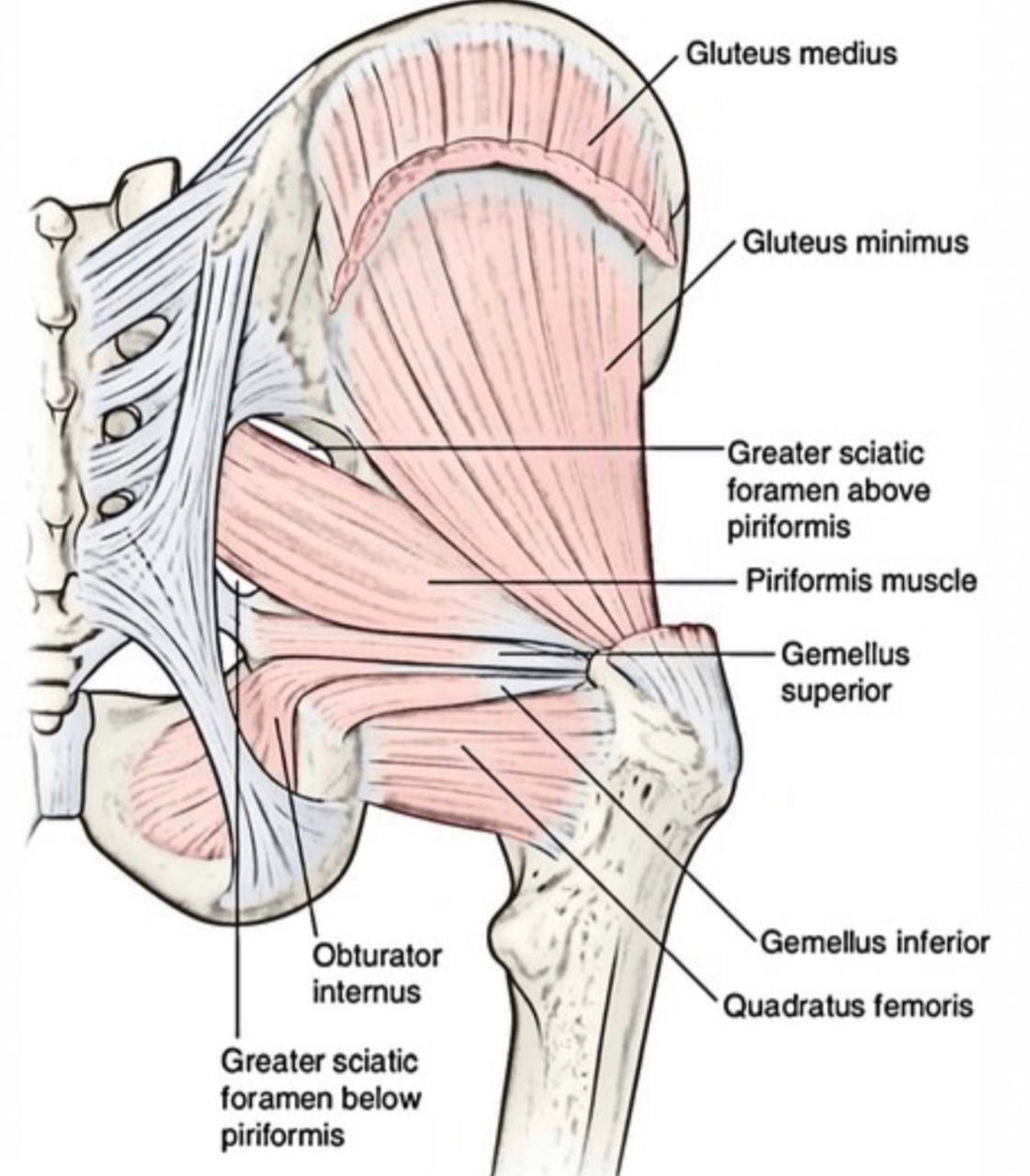
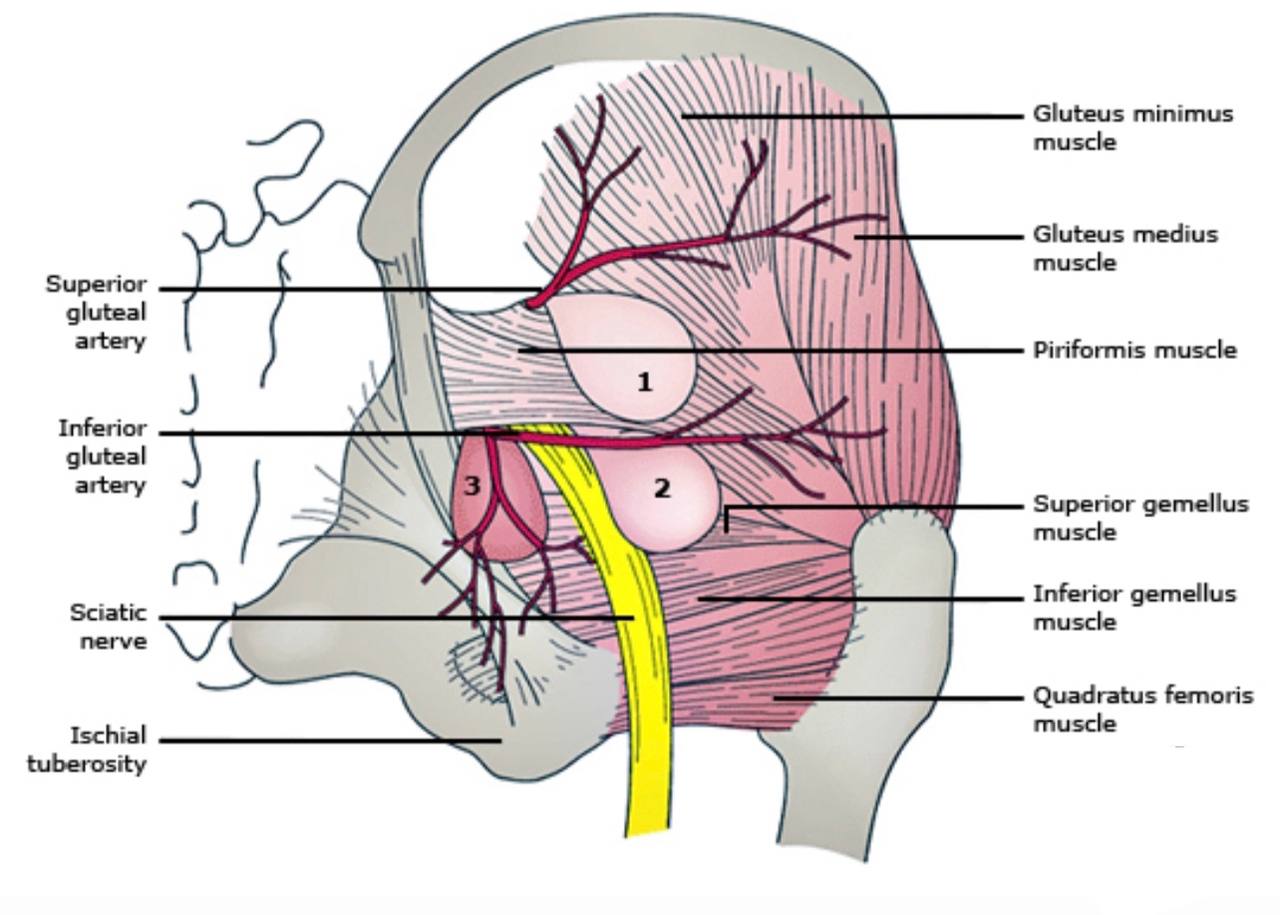
. Piriformis muscle: it is a small muscle which is considered the land
mark for the greater sciatic foramen. It divides the greater sciatic foramen
into two parts (foramina):
1.Above (supra-piriformis)
2.Below (infra-piriformis)
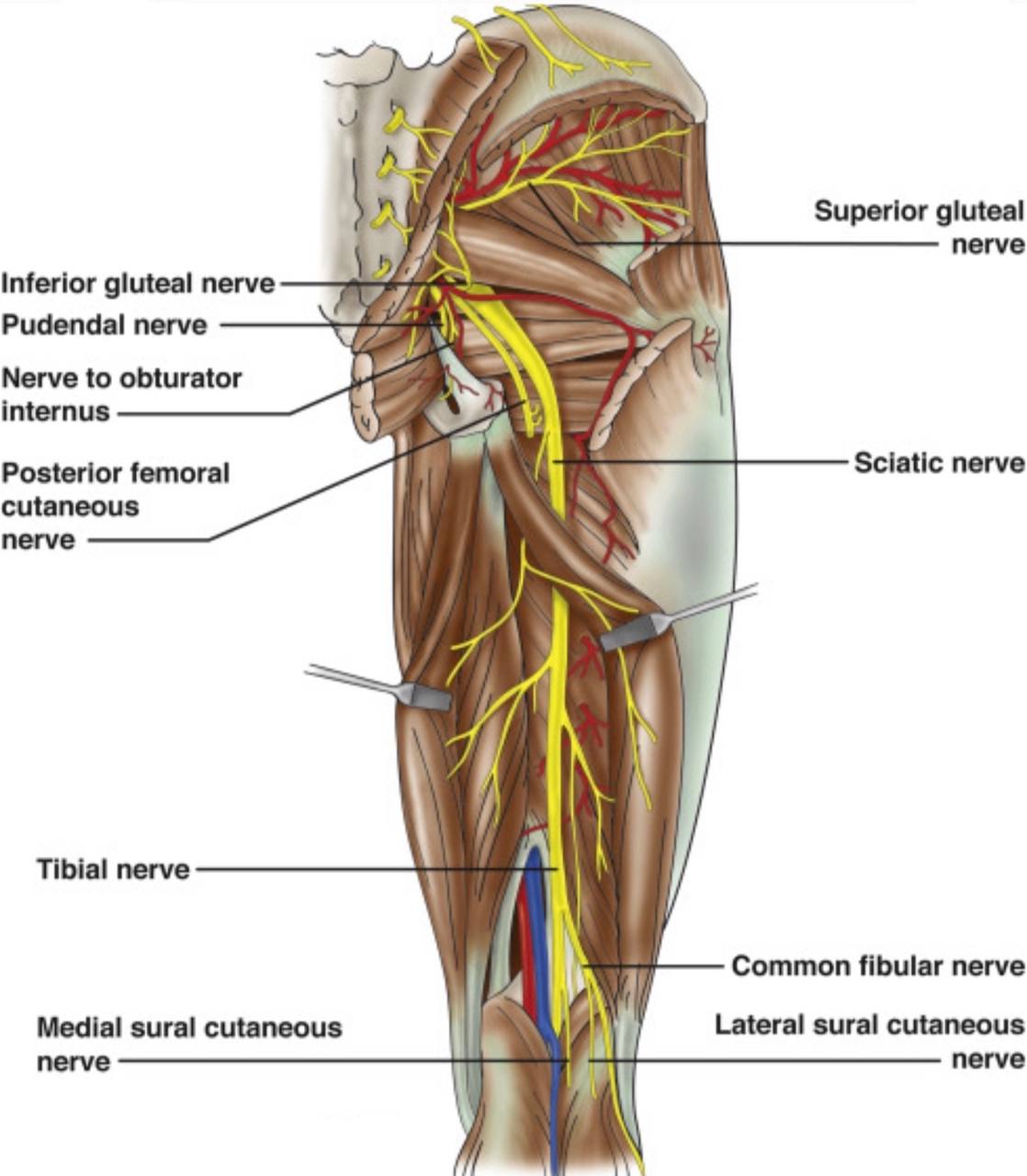
The structures that pass above the supra-piriformis foramen :
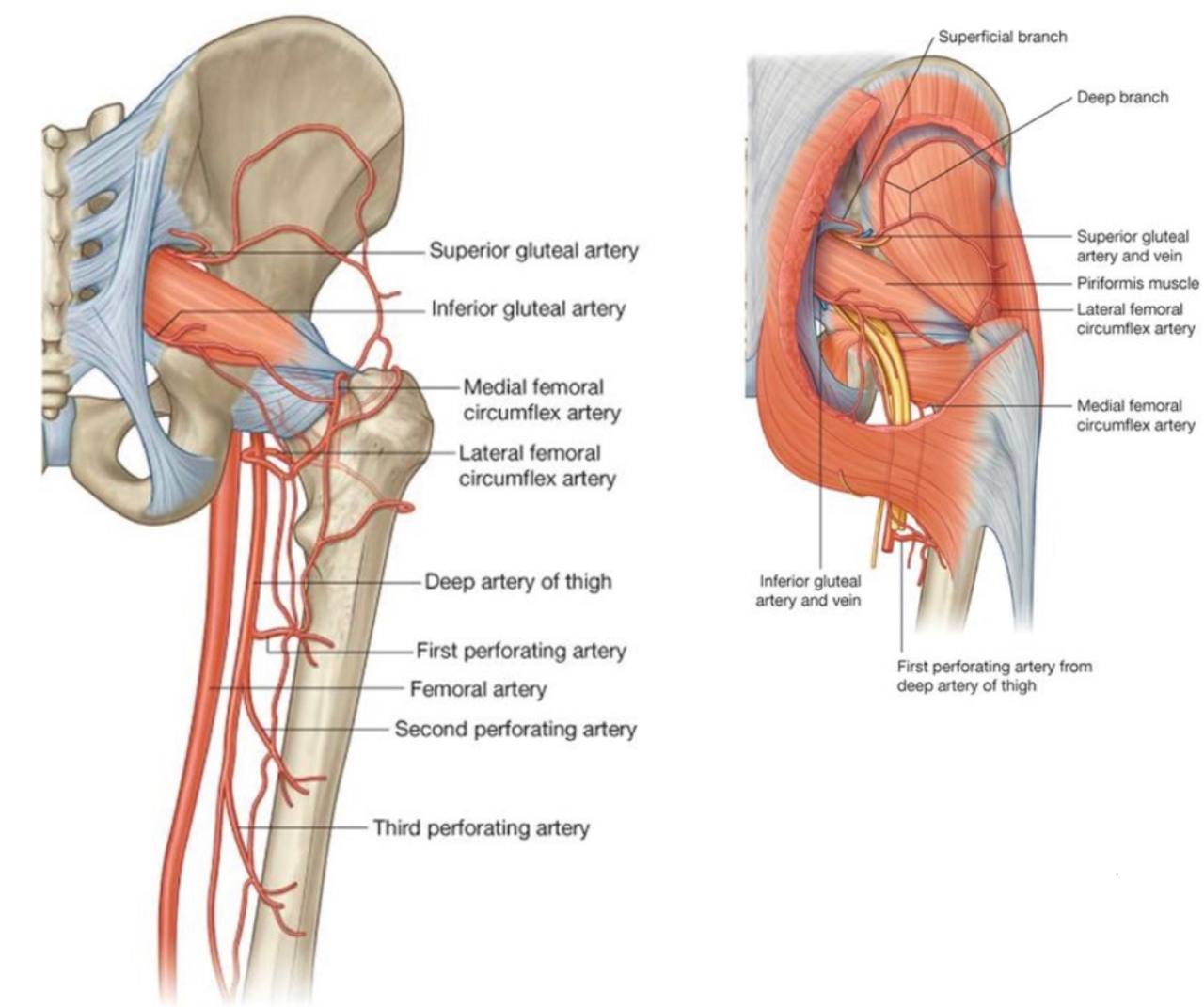
. 1)Superior gluteal nerve (L4-L5-S1).
. 2)Superior gluteal vessels (vein and artery).
The structures that pass below the infra-piriformis foramen:
A)Three structures pass laterally :
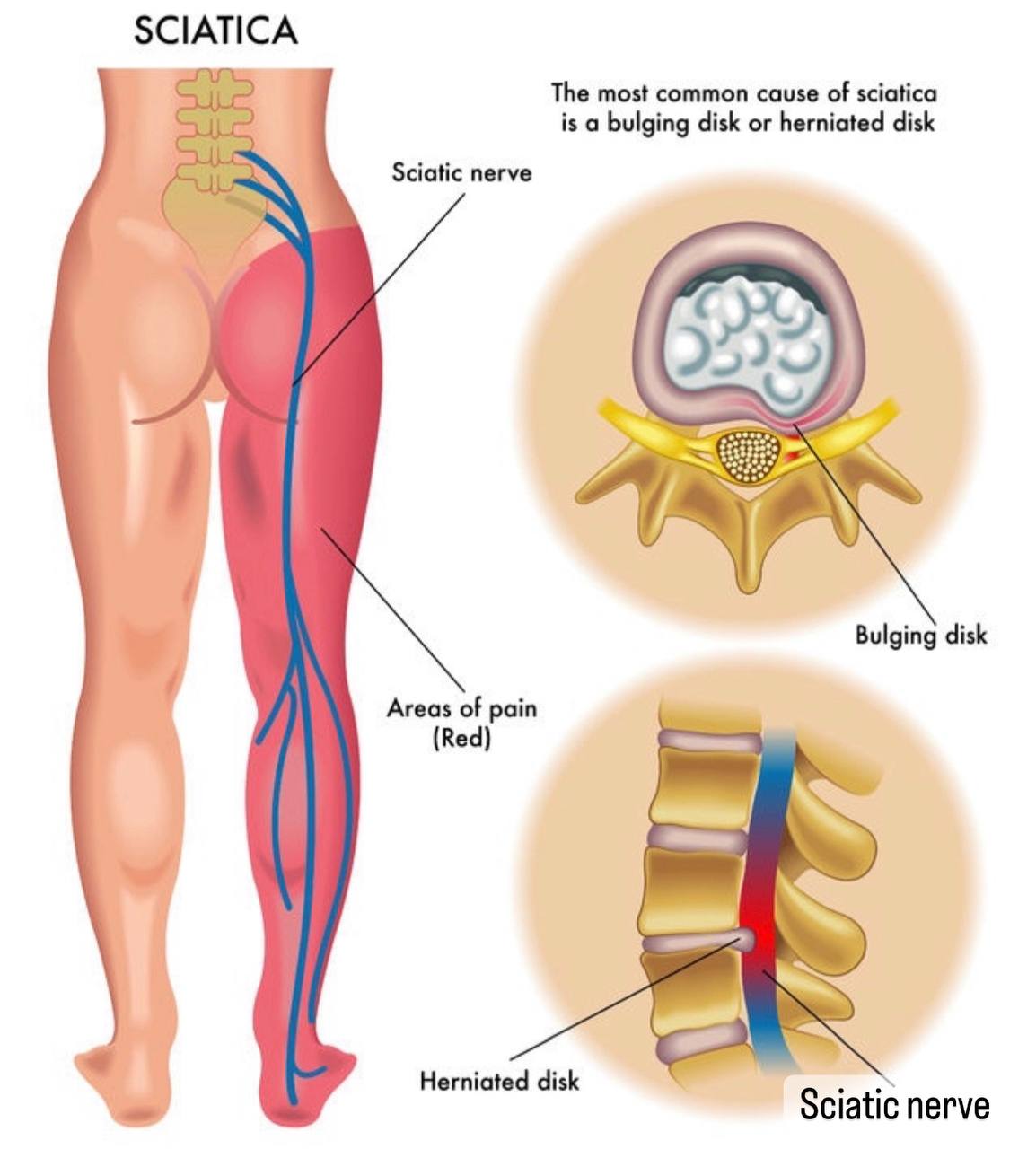
. 1) Sciatic nerve(L4-L5-S1-S2-S3) (it is the largest nerve in the body).
. 2) Posterior (femoral)cutaneous nerve of the thigh(S1-S2-S3).
. 3) Nerve to the quadratus femoris and gemellus inferior.
B)Two structures pass in the middle :
. 1) Inferior gluteal nerve(L5-S1-S2).
. 2) Inferior gluteal vessels (vein and artery).
C)Three structures pass medially :
. 1) Nerve to the obturator internus and gemellus superior
. 2) Pudendal nerve(S2-S3-S4).
. 3) Internal pudendal vessels (vein and artery).
NOTE :in the 11-17%of the people, the sciatic nerve or one of its
parts pierce the piriformis muscle instead of passing below it.
. Piriformis muscle: it is a small muscle which is considered the land
mark for the greater sciatic foramen. It divides the greater sciatic foramen
into two parts (foramina):
1.Above (supra-piriformis)
2.Below (infra-piriformis)
The structures that pass above the supra-piriformis foramen :
. 1)Superior gluteal nerve (L4-L5-S1).
. 2)Superior gluteal vessels (vein and artery).
The structures that pass below the infra-piriformis foramen:
A)Three structures pass laterally :
. 1) Sciatic nerve(L4-L5-S1-S2-S3) (it is the largest nerve in the body).
. 2) Posterior (femoral)cutaneous nerve of the thigh(S1-S2-S3).
. 3) Nerve to the quadratus femoris and gemellus inferior.
B)Two structures pass in the middle :
. 1) Inferior gluteal nerve(L5-S1-S2).
. 2) Inferior gluteal vessels (vein and artery).
C)Three structures pass medially :
. 1) Nerve to the obturator internus and gemellus superior
. 2) Pudendal nerve(S2-S3-S4).
. 3) Internal pudendal vessels (vein and artery).
NOTE :in the 11-17%of the people, the sciatic nerve or one of its
parts pierce the piriformis muscle instead of passing below it.
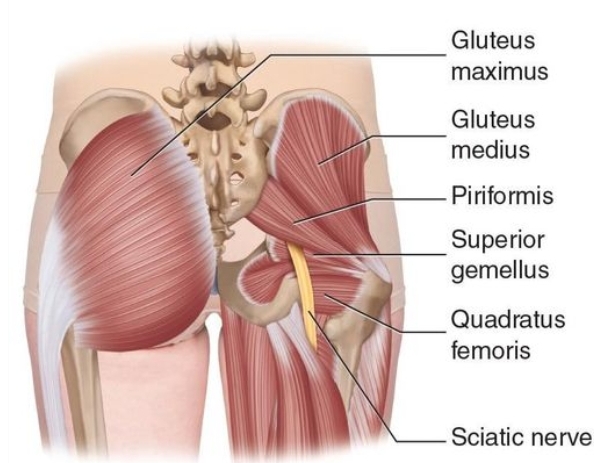
Lesser sciatic foramen :
. lesser sciatic foramen : it is a small opening in the ischium bone (part
of the hip bone )in the pelvis below the greater sciatic foramen. It
allows the passage of the structures between the gluteal region and
perineum.
of the hip bone )in the pelvis below the greater sciatic foramen. It
allows the passage of the structures between the gluteal region and
perineum.
The Borders :
. Anteriorly : ischial spine, tuberosity of the ischium and
lesser sciatic notch.
. Posteriorly : sacrotuberous ligament.
. Superiorly : sacrospinous ligament and ischial spine.
lesser sciatic notch.
. Posteriorly : sacrotuberous ligament.
. Superiorly : sacrospinous ligament and ischial spine.
The contents :
1)Tendon of the obturator internus muscle.
. The Structure pass medially :
2)Pudendal nerve(S2-S3-S4).
. The Structures pass in the middle:
3)Internal pudenal vessels (vein and artery).
. The Structure pass laterally :
4)Nerve to the obturator internus.
NOTE :the pudendal nerve , the internal pudendal vessels and the
nerve to the obturator internus leave the pelvis through the greater
sciatic foramen (to become in the gluteal region)and they re-enter the
pelvis by passing below the piriformis muscle to the lesser sciatic
foramen (to become in the perineum region in the pelvis ).
. The Structure pass medially :
2)Pudendal nerve(S2-S3-S4).
. The Structures pass in the middle:
3)Internal pudenal vessels (vein and artery).
. The Structure pass laterally :
4)Nerve to the obturator internus.
NOTE :the pudendal nerve , the internal pudendal vessels and the
nerve to the obturator internus leave the pelvis through the greater
sciatic foramen (to become in the gluteal region)and they re-enter the
pelvis by passing below the piriformis muscle to the lesser sciatic
foramen (to become in the perineum region in the pelvis ).
The clinical notes :
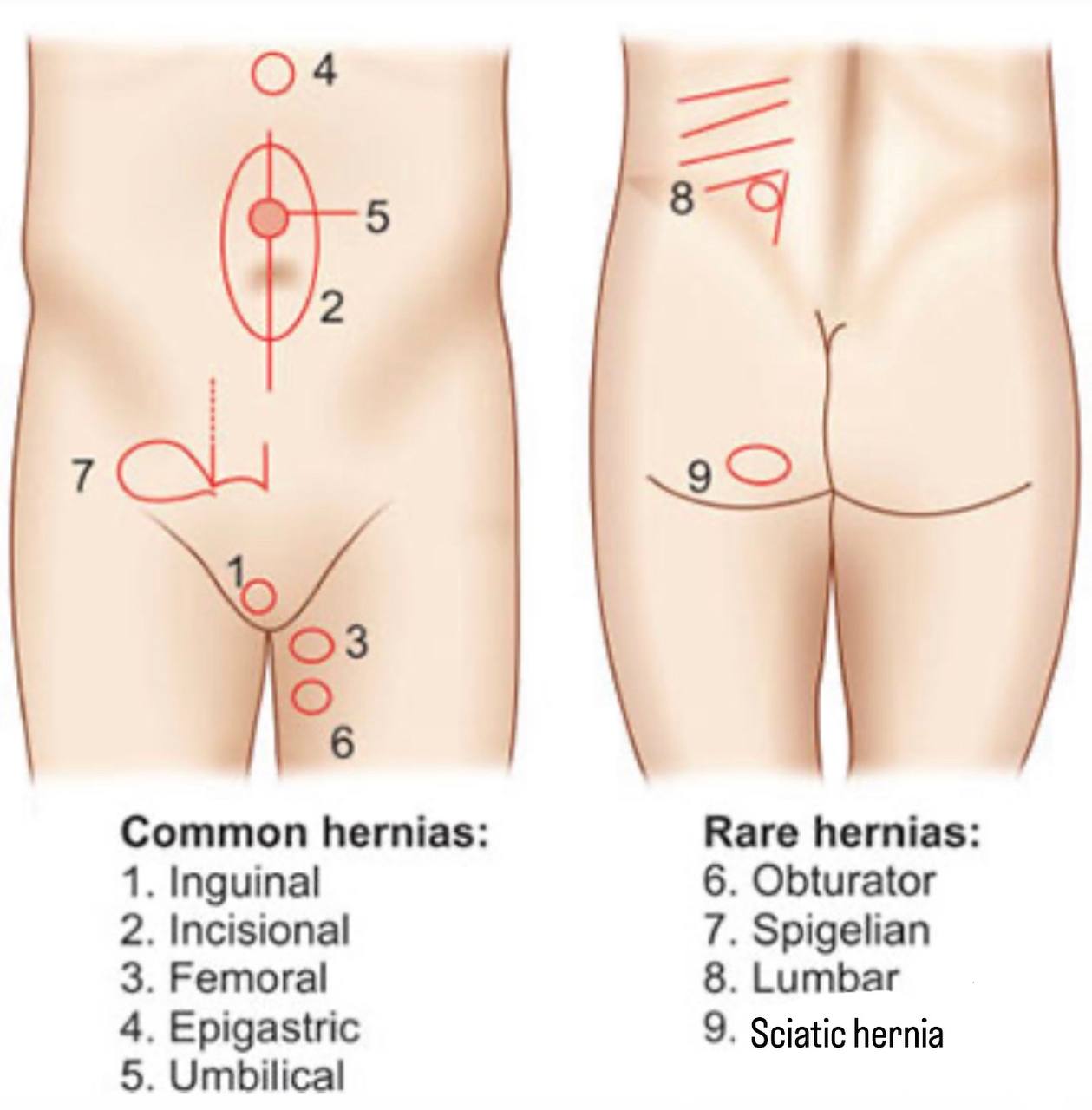
. Sciatic hernia : it is a herniation occurs in the pelvic floor through the
greater or the lesser sciatic foramen…It is a very rare case (it is
considered one of the rarest types of hernia).
. Also Known :
. sacrosciatic hernia.
. ischiatic hernia.
. ischiocele hernia.
. gluteal hernia.
. This disease occurs in adults and children.. In adults...it is more common in the women,
especially older women, due to the expansion of the pelvis.
. In this disease ,the hernia sac contains the peritoneal sac and its contents such
as:
. 1) small intestine.
. or 2) ureter.
. or 3) omentum.
. or 4) ovary.
. or 5) fallopian tubes.
. or 6) colon.
. or 7) bladder.
. or 8) Meckel's diverticulum.
greater or the lesser sciatic foramen…It is a very rare case (it is
considered one of the rarest types of hernia).
. Also Known :
. sacrosciatic hernia.
. ischiatic hernia.
. ischiocele hernia.
. gluteal hernia.
. This disease occurs in adults and children.. In adults...it is more common in the women,
especially older women, due to the expansion of the pelvis.
. In this disease ,the hernia sac contains the peritoneal sac and its contents such
as:
. 1) small intestine.
. or 2) ureter.
. or 3) omentum.
. or 4) ovary.
. or 5) fallopian tubes.
. or 6) colon.
. or 7) bladder.
. or 8) Meckel's diverticulum.
Types of sciatic hernia:
1)Supra Piriformis hernia( Most common) : More commonly, at this site,
the hernia protrudes above the piriformis muscle and travels along the
superior gluteal artery and nerve.
2)Infra Piriformis hernia : at this site ,The infra piriformis hernia travels with
the sciatic nerve, the inferior gluteal vessels, and the internal pudendal
vessels.
3)Below the sacrospinous ligament(Subspinous hernia)through lesser
sciatic foramen: at this site , The hernia leaves the pelvis through the lesser
sciatic foramen, medially to the sciatic nerve and the internal pudendal
vessels.
the hernia protrudes above the piriformis muscle and travels along the
superior gluteal artery and nerve.
2)Infra Piriformis hernia : at this site ,The infra piriformis hernia travels with
the sciatic nerve, the inferior gluteal vessels, and the internal pudendal
vessels.
3)Below the sacrospinous ligament(Subspinous hernia)through lesser
sciatic foramen: at this site , The hernia leaves the pelvis through the lesser
sciatic foramen, medially to the sciatic nerve and the internal pudendal
vessels.
The cause :
It could be occurred due to :
1) The emaciation of the body.
2) Pelvic floor muscle atrophy as a result of nerve entrapment due to hernia .
3) Pre-peritoneal fat loss.
4) Multiple pregnancy can cause looseness in the abdominal and pelvic muscles
and leads to this disease.
5) Also, chronic diseases such as pressure inside the abdomen can lead to this
disease.
6) This disease may be caused due to congenital defects in the development of the
piriformis muscle or the pelvic bones.
1) The emaciation of the body.
2) Pelvic floor muscle atrophy as a result of nerve entrapment due to hernia .
3) Pre-peritoneal fat loss.
4) Multiple pregnancy can cause looseness in the abdominal and pelvic muscles
and leads to this disease.
5) Also, chronic diseases such as pressure inside the abdomen can lead to this
disease.
6) This disease may be caused due to congenital defects in the development of the
piriformis muscle or the pelvic bones.
the symptoms :
. Symptoms depend on the organs inside the hernia:
1) It can lead to bowel obstruction..pelvic pain..back pain..obstruction of the
ureter..sciatica…urinary retention.. Urinary tract disorder.. nerve entrapment.
2) The patient may suffer from a nausea and vomiting along with abdominal pain.
3) A sciatic hernia can lead to the formation of an abscess in the gluteal region,
especially after the strangulated bowel perforation.
4) When the ureter is in the hernia sac, the patient may suffer from renal
colic due to obstruction of the ureter... Also, the sciatic-ureter hernia may
cause pyelonephritis and acute sepsis.
. Note /Sciatica is caused by the compression of the sciatic nerve by a hernia.
. Note/Ureteral hernia occurs if the ureter is in the herniated tissue.
1) It can lead to bowel obstruction..pelvic pain..back pain..obstruction of the
ureter..sciatica…urinary retention.. Urinary tract disorder.. nerve entrapment.
2) The patient may suffer from a nausea and vomiting along with abdominal pain.
3) A sciatic hernia can lead to the formation of an abscess in the gluteal region,
especially after the strangulated bowel perforation.
4) When the ureter is in the hernia sac, the patient may suffer from renal
colic due to obstruction of the ureter... Also, the sciatic-ureter hernia may
cause pyelonephritis and acute sepsis.
. Note /Sciatica is caused by the compression of the sciatic nerve by a hernia.
. Note/Ureteral hernia occurs if the ureter is in the herniated tissue.
The diagnosis :
. This disease is difficult to diagnose due to its deep location under
the gluteus maximus muscle, therefore, in most cases, a physical
examination for this condition is insufficient, so the doctor resorts to
diagnosis by:
1) Ultrasound imaging.
2) Computed tomography.
3) Magnetic resonance imaging to check whether the nerves in that
area are trapped or not.
4) X-rays, CT scans, or color Dopplers.
Note /Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are the best diagnostic
methods.
the gluteus maximus muscle, therefore, in most cases, a physical
examination for this condition is insufficient, so the doctor resorts to
diagnosis by:
1) Ultrasound imaging.
2) Computed tomography.
3) Magnetic resonance imaging to check whether the nerves in that
area are trapped or not.
4) X-rays, CT scans, or color Dopplers.
Note /Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are the best diagnostic
methods.
The treatment :
1) sciatic herniae are repaired either through an open or laparoscopic approaches.
The open approach is more commonly used in emergency situations.
2) The treatment is by surgery or laparoscopy, and it requires artificial
reinforcement to get the best result ( using mesh plug and patch).
3) It can be repaired by high ligation of the hernia sac using laparoscopy..In this
method, it is possible to have a recurrence rate of the sciatic hernia.
Note/During surgery, attention should be paid to: gluteal arteries, pudendal
arteries, sciatic nerves, pudendal nerves, and ureters.
The open approach is more commonly used in emergency situations.
2) The treatment is by surgery or laparoscopy, and it requires artificial
reinforcement to get the best result ( using mesh plug and patch).
3) It can be repaired by high ligation of the hernia sac using laparoscopy..In this
method, it is possible to have a recurrence rate of the sciatic hernia.
Note/During surgery, attention should be paid to: gluteal arteries, pudendal
arteries, sciatic nerves, pudendal nerves, and ureters.
References:
1)LAWRENCE E. WINESKI / SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Tenth EDITION/Plate(1280).
2)LAWRENCE E. WINESKI / SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Tenth EDITION/Plate(1021).
3)Moore K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2014)- Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition (546 plates).
4)Greater sciatic foramen and lesser sciatic foramen /teachmeanatomy/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiDnYnh1qX7AhXxSPEDHZHDBq8QFnoECBQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fteachmeanatomy.info%2Fpelvis%2Fareas%2Fsciatic-foramen%2F&usg=AOvVaw32nKcfJMDEVxhGC6nL84EC
5)Greater sciatic foramen /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjq__7p2KX7AhV1VvEDHYBICvgQFnoECBEQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Fgreater-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw2j46dyQVMJuJ3DFp6bc249
6)lesser sciatic foramen /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiQqseb2aX7AhXKXvEDHZmVCqIQFnoECBAQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Flesser-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw1xqYDWe0824wB8qQrZ9im0
7)Greater sciatic foramen/Sciencedirect/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiH5MLI2aX7AhV3SvEDHcCNDOwQFnoECBkQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Ftopics%2Fveterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine%2Fgreater-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw3076y3tue42s1G4B_vCyup
8)lesser sciatic foramen /Sciencedirect/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiH5MLI2aX7AhV3SvEDHcCNDOwQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Ftopics%2Fveterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine%2Flesser-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw07zdj_veCjmMSCFVwgnNZj
9)sciatic foramen /Epomedicine/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj37ZKe26X7AhWSRPEDHb0RATMQFnoECA0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fepomedicine.com%2Fmedical-students%2Fstructures-passing-through-sciatic-foramen-and-pudendal-canal-mnemonic%2F&usg=AOvVaw3RQCqx-FKqHzA7DEiGuO1S
10)sciatic nerve /physiopedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiZ2cTf3aX7AhW3RPEDHWAWCw4QtwJ6BAgPEAE&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FSciatic_Nerve&usg=AOvVaw3Bn_lu1nzsGYkzXu8mruYv
11)Sciatic hernia/Sciencedirect /https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjH7e6Yyr_6AhUzhv0HHRWbBnYQFnoECC8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Fscience%2Farticle%2Fpii%2FS0002961009002219&usg=AOvVaw04UtQfCgE9GKILIFkEyoC-
12)Sciatic hernia /hindawi/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwighNqp5q37AhXKQvEDHRjgAbsQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.hindawi.com%2Fjournals%2Fcriu%2F2014%2F787528%2F&usg=AOvVaw2T0F7SW1CjPUFgduglkF8B
13)Sciatic hernia/sciencedirect/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjR7P3A5a37AhUFSPEDHUJxC8MQFnoECBIQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Fscience%2Farticle%2Fpii%2FS1682606X15000262&usg=AOvVaw1Op3uwD7qGD6_xeaML3O05
14)Sciatic hernia /link.springer/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjcpuyE5a37AhVDXvEDHQj8BjwQFnoECAsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Flink.springer.com%2Farticle%2F10.1007%2Fs10029-009-0509-y&usg=AOvVaw3ytz1Bium5bZgUHWFUxnNx
15)Sciatic hernia /academic.oup/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiPqIjD5K37AhWmSPEDHbObCHMQFnoECDgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Facademic.oup.com%2Fjscr%2Farticle%2F2013%2F12%2Frjt102%2F2282494&usg=AOvVaw0MzkTbYHPcwXc2C-U5Wv1r
16)Sciatic hernia /surgicalcasereports.springeropen/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj-0J3w5q37AhU4SPEDHQ4nAJYQFnoECAgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fsurgicalcasereports.springeropen.com%2Farticles%2F10.1186%2Fs40792-022-01362-4&usg=AOvVaw2xvE4J13UWnp02TQaOkEPw
17)Sciatic hernia /facs/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiWh8zr4K37AhXdSvEDHT09CbUQFnoECA0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.facs.org%2Ffor-medical-professionals%2Fnews-publications%2Fjournals%2Fcase-reviews%2Fissues%2Fv2n3%2Fchiang-rare%2F&usg=AOvVaw1MiI-AuI0QYlehejN3iqs9
18)Sciatic hernia /ncbi.nlm.nih/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwicju6z6a37AhXFRPEDHTH4AawQFnoECAsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fpmc%2Farticles%2FPMC8752626%2F&usg=AOvVaw33439SuXOo6OJnpe2IYcPk
19)Anterior sacroiliac ligament /physiopedia /https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj59pmH3q37AhUCX_EDHReNDVUQgaEJegQICRAA&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FAnterior_Sacroiliac_Ligament&usg=AOvVaw0QCmPqf-THO2Fp2e0cqpRY
20)Sciatic nerve /scielo/https://www.scielo.br/j/anp/a/zysyM3xrZYw7bMj6pWwbXKM/?lang=en
20)Sciatic nerve /ama ba /https://www.ama.ba/index.php/ama/article/download/488/pdf
22)Piriformia muscle /sciencedirect/https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/piriformis-syndrome
23)Lesser scaitic notch/radiopaedia/ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/lesser-sciatic-notch
24)Greater sciatic notch /radiopedia/ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/greater-sciatic-notch
25)Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (January 1, 2011), Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (eds.), "Chapter 11 - The pelvis", Clinical Application of Neuromuscular Techniques, Volume 2 (Second Edition), Oxford: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 299–389, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06815-7.00011-5, ISBN 978-0-443-06815-7, retrieved February 6, 2021
26)This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 309 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
2)LAWRENCE E. WINESKI / SNELLŚ CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS/Tenth EDITION/Plate(1021).
3)Moore K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2014)- Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition (546 plates).
4)Greater sciatic foramen and lesser sciatic foramen /teachmeanatomy/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiDnYnh1qX7AhXxSPEDHZHDBq8QFnoECBQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fteachmeanatomy.info%2Fpelvis%2Fareas%2Fsciatic-foramen%2F&usg=AOvVaw32nKcfJMDEVxhGC6nL84EC
5)Greater sciatic foramen /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjq__7p2KX7AhV1VvEDHYBICvgQFnoECBEQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Fgreater-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw2j46dyQVMJuJ3DFp6bc249
6)lesser sciatic foramen /Radiopaedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiQqseb2aX7AhXKXvEDHZmVCqIQFnoECBAQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fradiopaedia.org%2Farticles%2Flesser-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw1xqYDWe0824wB8qQrZ9im0
7)Greater sciatic foramen/Sciencedirect/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiH5MLI2aX7AhV3SvEDHcCNDOwQFnoECBkQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Ftopics%2Fveterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine%2Fgreater-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw3076y3tue42s1G4B_vCyup
8)lesser sciatic foramen /Sciencedirect/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiH5MLI2aX7AhV3SvEDHcCNDOwQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Ftopics%2Fveterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine%2Flesser-sciatic-foramen&usg=AOvVaw07zdj_veCjmMSCFVwgnNZj
9)sciatic foramen /Epomedicine/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj37ZKe26X7AhWSRPEDHb0RATMQFnoECA0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fepomedicine.com%2Fmedical-students%2Fstructures-passing-through-sciatic-foramen-and-pudendal-canal-mnemonic%2F&usg=AOvVaw3RQCqx-FKqHzA7DEiGuO1S
10)sciatic nerve /physiopedia/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiZ2cTf3aX7AhW3RPEDHWAWCw4QtwJ6BAgPEAE&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FSciatic_Nerve&usg=AOvVaw3Bn_lu1nzsGYkzXu8mruYv
11)Sciatic hernia/Sciencedirect /https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjH7e6Yyr_6AhUzhv0HHRWbBnYQFnoECC8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Fscience%2Farticle%2Fpii%2FS0002961009002219&usg=AOvVaw04UtQfCgE9GKILIFkEyoC-
12)Sciatic hernia /hindawi/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwighNqp5q37AhXKQvEDHRjgAbsQFnoECAoQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.hindawi.com%2Fjournals%2Fcriu%2F2014%2F787528%2F&usg=AOvVaw2T0F7SW1CjPUFgduglkF8B
13)Sciatic hernia/sciencedirect/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjR7P3A5a37AhUFSPEDHUJxC8MQFnoECBIQBQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Fscience%2Farticle%2Fpii%2FS1682606X15000262&usg=AOvVaw1Op3uwD7qGD6_xeaML3O05
14)Sciatic hernia /link.springer/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjcpuyE5a37AhVDXvEDHQj8BjwQFnoECAsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Flink.springer.com%2Farticle%2F10.1007%2Fs10029-009-0509-y&usg=AOvVaw3ytz1Bium5bZgUHWFUxnNx
15)Sciatic hernia /academic.oup/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiPqIjD5K37AhWmSPEDHbObCHMQFnoECDgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Facademic.oup.com%2Fjscr%2Farticle%2F2013%2F12%2Frjt102%2F2282494&usg=AOvVaw0MzkTbYHPcwXc2C-U5Wv1r
16)Sciatic hernia /surgicalcasereports.springeropen/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj-0J3w5q37AhU4SPEDHQ4nAJYQFnoECAgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fsurgicalcasereports.springeropen.com%2Farticles%2F10.1186%2Fs40792-022-01362-4&usg=AOvVaw2xvE4J13UWnp02TQaOkEPw
17)Sciatic hernia /facs/https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiWh8zr4K37AhXdSvEDHT09CbUQFnoECA0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.facs.org%2Ffor-medical-professionals%2Fnews-publications%2Fjournals%2Fcase-reviews%2Fissues%2Fv2n3%2Fchiang-rare%2F&usg=AOvVaw1MiI-AuI0QYlehejN3iqs9
18)Sciatic hernia /ncbi.nlm.nih/ https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwicju6z6a37AhXFRPEDHTH4AawQFnoECAsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fpmc%2Farticles%2FPMC8752626%2F&usg=AOvVaw33439SuXOo6OJnpe2IYcPk
19)Anterior sacroiliac ligament /physiopedia /https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj59pmH3q37AhUCX_EDHReNDVUQgaEJegQICRAA&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.physio-pedia.com%2FAnterior_Sacroiliac_Ligament&usg=AOvVaw0QCmPqf-THO2Fp2e0cqpRY
20)Sciatic nerve /scielo/https://www.scielo.br/j/anp/a/zysyM3xrZYw7bMj6pWwbXKM/?lang=en
20)Sciatic nerve /ama ba /https://www.ama.ba/index.php/ama/article/download/488/pdf
22)Piriformia muscle /sciencedirect/https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/piriformis-syndrome
23)Lesser scaitic notch/radiopaedia/ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/lesser-sciatic-notch
24)Greater sciatic notch /radiopedia/ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/greater-sciatic-notch
25)Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (January 1, 2011), Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (eds.), "Chapter 11 - The pelvis", Clinical Application of Neuromuscular Techniques, Volume 2 (Second Edition), Oxford: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 299–389, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06815-7.00011-5, ISBN 978-0-443-06815-7, retrieved February 6, 2021
26)This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 309 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
References of images :
Cover image/sciatic foramina /lecturio/https://www.lecturio.com/concepts/gluteal-region/
Fig. 1/sciatic foramina/teachmeanatomy/https://teachmeanatomy.info/pelvis/areas/sciatic-foramen/
Fig. 2/Greater sciatic foramen /oerpub. Github/The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis
Fig. 3/borders of Greater sciatic foramen /musculoskeletalkey/https://musculoskeletalkey.com/the-sacroiliac-joint-2/
Fig.4/hip bone/theskeletalsystem/https://www.theskeletalsystem.net/pelvis/hip-bone.html
Fig. 5/hip bone /lumen learning/https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap1/chapter/the-pelvic-girdle-and-pelvis/
Fig. 6/auricular surface in the hip bone /jaypeeDigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9789350251089/ch8
Fig. 7/piriformis muscle/Neurokinetic Therapy/https://ar-ar.facebook.com/NeuroKineticTherapy/posts/10158184030330180/
Fig. 8/structures that pass above and below the piriformis muscle /teachmeanatomy/https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/muscles/gluteal-region/
Fig. 9/structures that pass above and below the piriformis muscle/jaypeeDigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9788180618307/ch20
Fig. 10/structures that pass above and below the piriformis/ScienceDirect/https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323776028000118
Fig. 11/lesser sciatic foramen /Quizlet/https://quizlet.com/231907709/sciatic-foramenae-greater-lesser-flash-cards/
Fig. 12/The Borders of the lesser sciatic foramen /musculoskeletalkey/https://musculoskeletalkey.com/the-sacroiliac-joint-2/
Fig. 13/hip bone /lumen learning/https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap1/chapter/the-pelvic-girdle-and-pelvis/
Fig. 14/The contents of the lesser sciatic foramen /RANZCRPart1 wiki_fandom/https://ranzcrpart1.fandom.com/wiki/Radiological_spaces_and_foramina:Pelvis:Greater_and_lesser_sciatic_foramen
Fig.15/Gluteal region/Earth's lab/https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/gluteal-region/
Fig. 16/Snell’s Clinical Anatomy by Regions _Figure 11.17
Fig. 17/artery in gluteal region /SlidePlayer/ https://slideplayer.com/amp/8886433/
Fig. 18/hernia in the body /jaypeedigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9789350259443/ch18
Fig.19/Types of sciatic hernia/Ykhoa. Org/https://ykhoa.org/d/image.htm?imageKey=SURG/53186
Fig. 20/supra piriformis and infra piriformis foramen /https://surgicalcasereports.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40792-022-01362-4
Fig.21/sciatica/spineUniverse/https://www.spineuniverse.com/conditions/sciatica/sciatica-causes
Fig. 22/Ureteral hernia /International journal of emergency medicine /Urosepsis secondary to ureterosciatic hernia corrected with ...
Fig. 1/sciatic foramina/teachmeanatomy/https://teachmeanatomy.info/pelvis/areas/sciatic-foramen/
Fig. 2/Greater sciatic foramen /oerpub. Github/The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis
Fig. 3/borders of Greater sciatic foramen /musculoskeletalkey/https://musculoskeletalkey.com/the-sacroiliac-joint-2/
Fig.4/hip bone/theskeletalsystem/https://www.theskeletalsystem.net/pelvis/hip-bone.html
Fig. 5/hip bone /lumen learning/https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap1/chapter/the-pelvic-girdle-and-pelvis/
Fig. 6/auricular surface in the hip bone /jaypeeDigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9789350251089/ch8
Fig. 7/piriformis muscle/Neurokinetic Therapy/https://ar-ar.facebook.com/NeuroKineticTherapy/posts/10158184030330180/
Fig. 8/structures that pass above and below the piriformis muscle /teachmeanatomy/https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/muscles/gluteal-region/
Fig. 9/structures that pass above and below the piriformis muscle/jaypeeDigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9788180618307/ch20
Fig. 10/structures that pass above and below the piriformis/ScienceDirect/https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323776028000118
Fig. 11/lesser sciatic foramen /Quizlet/https://quizlet.com/231907709/sciatic-foramenae-greater-lesser-flash-cards/
Fig. 12/The Borders of the lesser sciatic foramen /musculoskeletalkey/https://musculoskeletalkey.com/the-sacroiliac-joint-2/
Fig. 13/hip bone /lumen learning/https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap1/chapter/the-pelvic-girdle-and-pelvis/
Fig. 14/The contents of the lesser sciatic foramen /RANZCRPart1 wiki_fandom/https://ranzcrpart1.fandom.com/wiki/Radiological_spaces_and_foramina:Pelvis:Greater_and_lesser_sciatic_foramen
Fig.15/Gluteal region/Earth's lab/https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/gluteal-region/
Fig. 16/Snell’s Clinical Anatomy by Regions _Figure 11.17
Fig. 17/artery in gluteal region /SlidePlayer/ https://slideplayer.com/amp/8886433/
Fig. 18/hernia in the body /jaypeedigital/https://www.jaypeedigital.com/eReader/chapter/9789350259443/ch18
Fig.19/Types of sciatic hernia/Ykhoa. Org/https://ykhoa.org/d/image.htm?imageKey=SURG/53186
Fig. 20/supra piriformis and infra piriformis foramen /https://surgicalcasereports.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40792-022-01362-4
Fig.21/sciatica/spineUniverse/https://www.spineuniverse.com/conditions/sciatica/sciatica-causes
Fig. 22/Ureteral hernia /International journal of emergency medicine /Urosepsis secondary to ureterosciatic hernia corrected with ...
Reference of the video:
1)lap sciatic hernia repair(L) /sumesh kaistha/https://youtu.be/hWeiR8wYsuU
