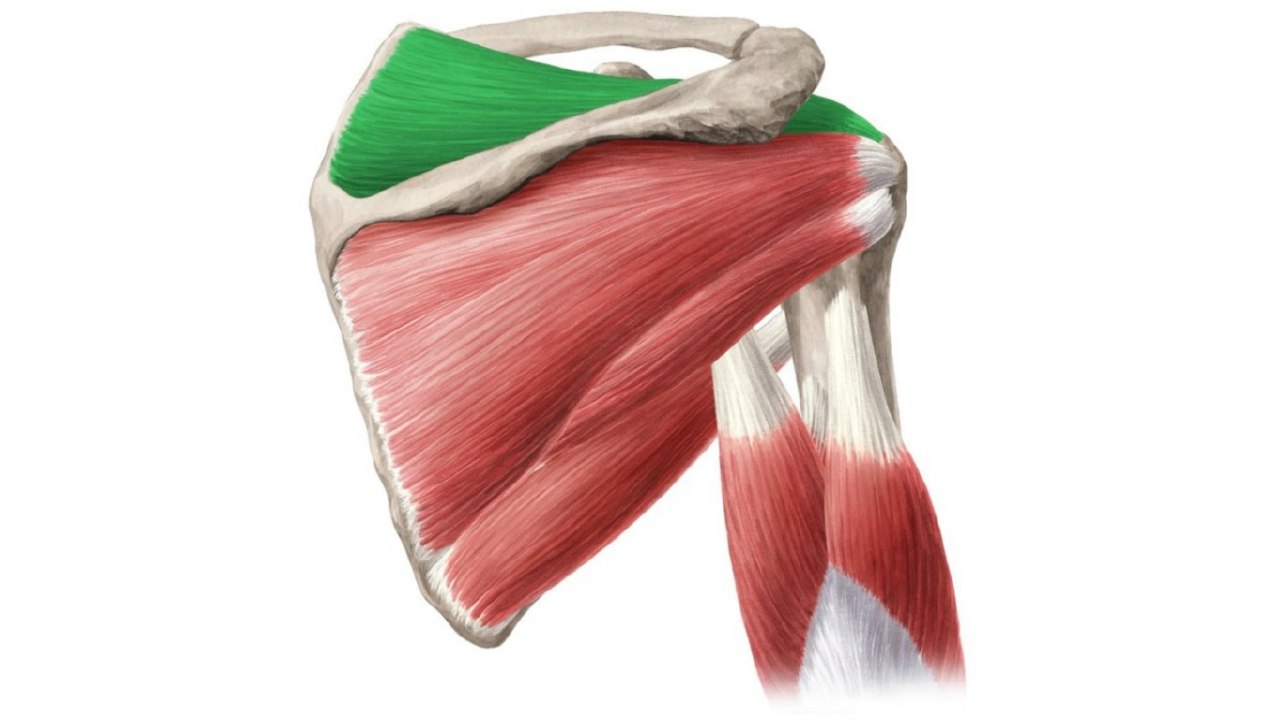
Supraspinatus
By : Karam AlanazIntroduction
* The supraspinatus is one of the four rotator cuff muscles. The rotator cuff muscles are the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. Sometimes the rotator cuff muscles are called the SITS muscles; each of the four letters stands for the first letter of the four rotator cuff muscles. Supraspinatus is the first S of SITS .
* the name of it tells us that one of this muscle’s attachments is the supraspinous fossa of the scapula ( above the spine ) .
* the name of it tells us that one of this muscle’s attachments is the supraspinous fossa of the scapula ( above the spine ) .
General
* ATTACHMENT : Supraspinous Fossa of the Scapula and Greater Tubercle of the
Humerus .
* The smallest among the rotator cuff muscles .
* works on the shoulder joint .
* The supraspinatus muscle fibre architecture is pennate.
Humerus .
* The smallest among the rotator cuff muscles .
* works on the shoulder joint .
* The supraspinatus muscle fibre architecture is pennate.

Supply
INNERVATION : The Suprascapular Nerve (C5,C6) , from upper ( superior ) trunk of brachial plexus .
ARTERIAL : The Suprascapular Artery (a branch of the Thyrocervical Artery) .
ARTERIAL : The Suprascapular Artery (a branch of the Thyrocervical Artery) .
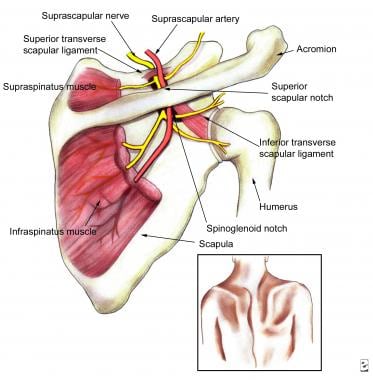
Origin
Supraspinous Fossa of the Scapula (the medial 2⁄3) .
NOTE : The supraspinatus is one of three muscles that attach onto the greater tubercle of the humerus. The two other muscles that attach here are the infraspinatus and the teres minor.
NOTE : The supraspinatus is one of three muscles that attach onto the greater tubercle of the humerus. The two other muscles that attach here are the infraspinatus and the teres minor.
Insersion
Greater Tubercle of the Humeru (the superior facet) .
NOTE : The distal tendon of the supraspinatus adheres to the capsule of the glenohumeral joint, which is deep to the supraspinatus.
NOTE : The distal tendon of the supraspinatus adheres to the capsule of the glenohumeral joint, which is deep to the supraspinatus.
Movement(Action)
( initiation abduction at the shoulder joint ( 0-15 degree) and acts with the other rotates cuff muscles ) .
A-Standard Mover Action :
1- The supraspinatus crosses the GH joint over the top of the joint , therefore it abducts the arm at the GH joint ( Note : the similarity of the direction of fibers of the supraspinatus to the direction of fibres of the middle deltoid. For quite some time it was believed that the supraspinatus could only initiate abduction of the arm at the GH joint and that the deltoid would have to complete this motion.
2- The supraspinatus pulls the arm up into the plane of the scapula. Given that the scapula is approximately 30–35 degrees off the frontal plane toward the sagittal plane, the arm is not pulled purely into abduction in the frontal plane, but somewhat into flexion in the sagittal plane. It is worth noting that if a person has rounded shoulders, the scapulae lie even farther from the frontal plane and closer to the sagittal plane, increasing the component of flexion action by the supraspinatus (and commensurately decreasing the amount of pure abduction in the frontal plane). Some texts refer to the action of the supraspinatus not as abduction, but as scaption to describe the fact that the arm is moved in the plane of the scapula, which is a combination of abduction and flexion.
B-Reverse Mover Action :
*If the supraspinatus contracts and the humerus is fixed, it pulls on the scapula, causing the glenoid fossa to orient downward. Therefore it downwardly rotates the
scapula relative to the humerus at the GH joint. When the scapula moves relative to the arm at the GH joint, it also moves relative to the rib cage at the scapulocostal joint .
NOTES :
1- The supraspinatus Stabilizes the shoulder (GH) joint Stabilizes the scapula .
2- Some sources state that the supraspinatus can also contribute to horizontal extension (horizontal abduction) of the arm at the GH joint.
3- When in anatomic position, the supraspinatus cannot create transverse plane rotation of the arm at the GH joint. However, many sources state that when the humerus is first rotated, the supraspinatus can contribute to rotation. Most likely, this rotation function will be to “de-rotate” the humerus back to anatomic position. Therefore the supraspinatus could be considered to be a de- rotator muscle.
4- The supraspinatus is the only one of the four rotator cuff muscles that does not contribute to a transverse plane rotation action of the arm at the GH joint .
A-Standard Mover Action :
1- The supraspinatus crosses the GH joint over the top of the joint , therefore it abducts the arm at the GH joint ( Note : the similarity of the direction of fibers of the supraspinatus to the direction of fibres of the middle deltoid. For quite some time it was believed that the supraspinatus could only initiate abduction of the arm at the GH joint and that the deltoid would have to complete this motion.
2- The supraspinatus pulls the arm up into the plane of the scapula. Given that the scapula is approximately 30–35 degrees off the frontal plane toward the sagittal plane, the arm is not pulled purely into abduction in the frontal plane, but somewhat into flexion in the sagittal plane. It is worth noting that if a person has rounded shoulders, the scapulae lie even farther from the frontal plane and closer to the sagittal plane, increasing the component of flexion action by the supraspinatus (and commensurately decreasing the amount of pure abduction in the frontal plane). Some texts refer to the action of the supraspinatus not as abduction, but as scaption to describe the fact that the arm is moved in the plane of the scapula, which is a combination of abduction and flexion.
B-Reverse Mover Action :
*If the supraspinatus contracts and the humerus is fixed, it pulls on the scapula, causing the glenoid fossa to orient downward. Therefore it downwardly rotates the
scapula relative to the humerus at the GH joint. When the scapula moves relative to the arm at the GH joint, it also moves relative to the rib cage at the scapulocostal joint .
NOTES :
1- The supraspinatus Stabilizes the shoulder (GH) joint Stabilizes the scapula .
2- Some sources state that the supraspinatus can also contribute to horizontal extension (horizontal abduction) of the arm at the GH joint.
3- When in anatomic position, the supraspinatus cannot create transverse plane rotation of the arm at the GH joint. However, many sources state that when the humerus is first rotated, the supraspinatus can contribute to rotation. Most likely, this rotation function will be to “de-rotate” the humerus back to anatomic position. Therefore the supraspinatus could be considered to be a de- rotator muscle.
4- The supraspinatus is the only one of the four rotator cuff muscles that does not contribute to a transverse plane rotation action of the arm at the GH joint .
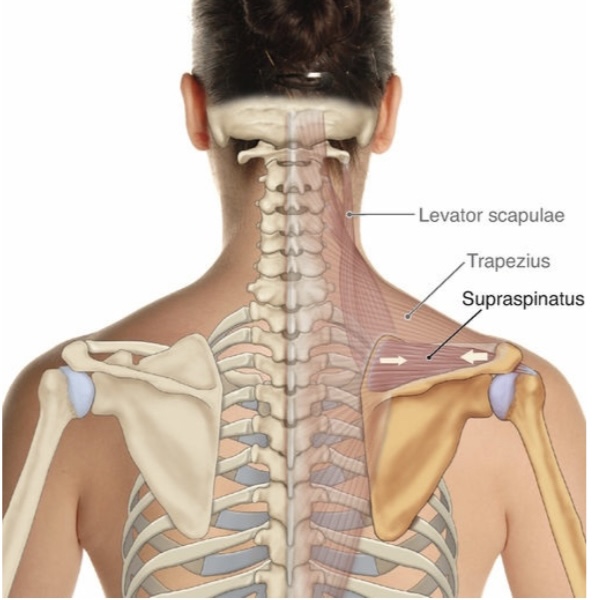
Relation
1-The supraspinatus is superior to the spine of the scapula.
2-The proximal attachment of the supraspinatus is deep to the trapezius.
3-The distal tendon of the supraspinatus courses deep to the acromion process of the scapula to then attach distally onto the greater tubercle of the humerus, deep to the deltoid.
4-The supraspinatus is located within the deep back arm line and may be involved with the deep front arm line myofascial meridians.
NOTE : The acromion process and the deltoid are superior to the supraspinatus. There is a bursa called the subacromial and/or subdeltoid bursa that is located between the supraspinatus and these two other structures.
2-The proximal attachment of the supraspinatus is deep to the trapezius.
3-The distal tendon of the supraspinatus courses deep to the acromion process of the scapula to then attach distally onto the greater tubercle of the humerus, deep to the deltoid.
4-The supraspinatus is located within the deep back arm line and may be involved with the deep front arm line myofascial meridians.
NOTE : The acromion process and the deltoid are superior to the supraspinatus. There is a bursa called the subacromial and/or subdeltoid bursa that is located between the supraspinatus and these two other structures.

Examine(Palpation)
* HOW DO YOU EXAMINE THE SUPRASPINATUS MUSCLE ( PALPATION ) ?
BY JOBE’S TEST :
The supraspinatous muscle is the most commonly injuries muscle, The main function of the deltoid and supraspinatous muscle is abduction of the shoulder . weakness of the shoulder abduction can be attributed to the supraspinatus muscle or the deltoid muscle injury or pathology.
in fact the deltoid muscle can abduct the shoulder despite supraspinatous weakness or dysfunction
The jobe’s test or the empty can test is the best test to study the supraspinatous muscle .
*The jobe’s test achieves isolation of the supraspinatous muscle and test its integrity strength and function independently of the deltoid muscle .
*STEPS :
1-The examiner abduct the arm to 90° then the examiner brings the arm 30° forward to bring the arm into the scapular plane .
2-the arm should then be integrally are rotated with the thumb pointed to the floor. 3- the examiner will then apply a downward directed force and the patient will try to resist this force .
4- pain or weakness indicators supraspinatous tendon pathology
BY JOBE’S TEST :
The supraspinatous muscle is the most commonly injuries muscle, The main function of the deltoid and supraspinatous muscle is abduction of the shoulder . weakness of the shoulder abduction can be attributed to the supraspinatus muscle or the deltoid muscle injury or pathology.
in fact the deltoid muscle can abduct the shoulder despite supraspinatous weakness or dysfunction
The jobe’s test or the empty can test is the best test to study the supraspinatous muscle .
*The jobe’s test achieves isolation of the supraspinatous muscle and test its integrity strength and function independently of the deltoid muscle .
*STEPS :
1-The examiner abduct the arm to 90° then the examiner brings the arm 30° forward to bring the arm into the scapular plane .
2-the arm should then be integrally are rotated with the thumb pointed to the floor. 3- the examiner will then apply a downward directed force and the patient will try to resist this force .
4- pain or weakness indicators supraspinatous tendon pathology
