Brachial Plexus
By : Rashad Omar
Firstly , what is the brachial plexus ?
It’s a collection of ventral rami of (C5 to T8 ) spinal nerves
Position :- partly in neck ( in the posterior triangle) and partly in axilla
* the clavicle overlies the plexus dividing it into two parts ( supraclavicular above & infraclavicular below )
It’s a collection of ventral rami of (C5 to T8 ) spinal nerves
Position :- partly in neck ( in the posterior triangle) and partly in axilla
* the clavicle overlies the plexus dividing it into two parts ( supraclavicular above & infraclavicular below )
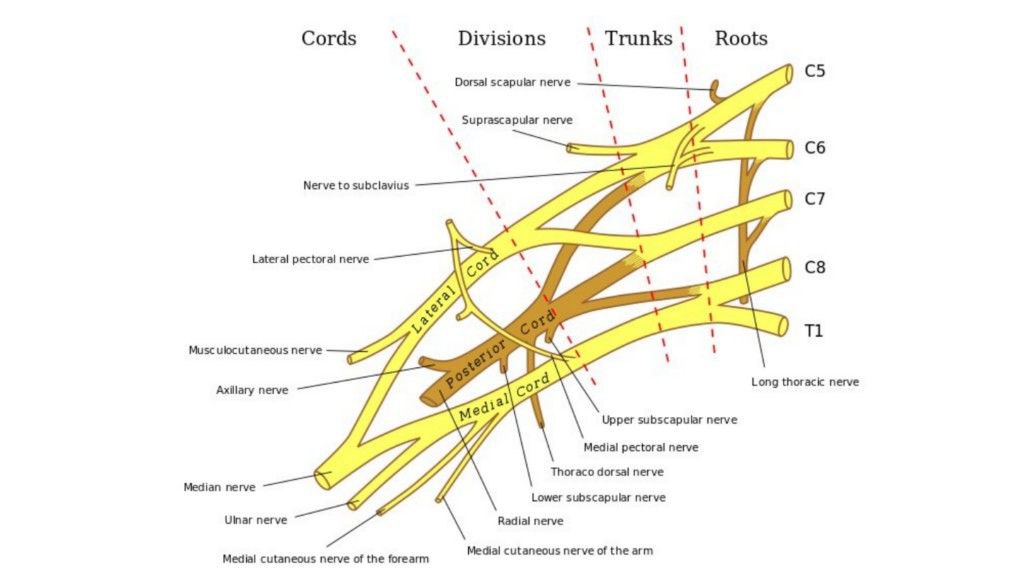
Overview
The 5 roots unite forming 3 trunks ( in the neck ) each root divides into anterior & posterior division as the plexus pass through the cervico-axillary canal ( behind the clavicle ) then the divisions unite forming 3 cords (in axilla)
* the axillary a. , axillary v. & the cords of brachial plexus are enclosed by sheath of deep fascia called the axillary sheath
* the axillary a. , axillary v. & the cords of brachial plexus are enclosed by sheath of deep fascia called the axillary sheath
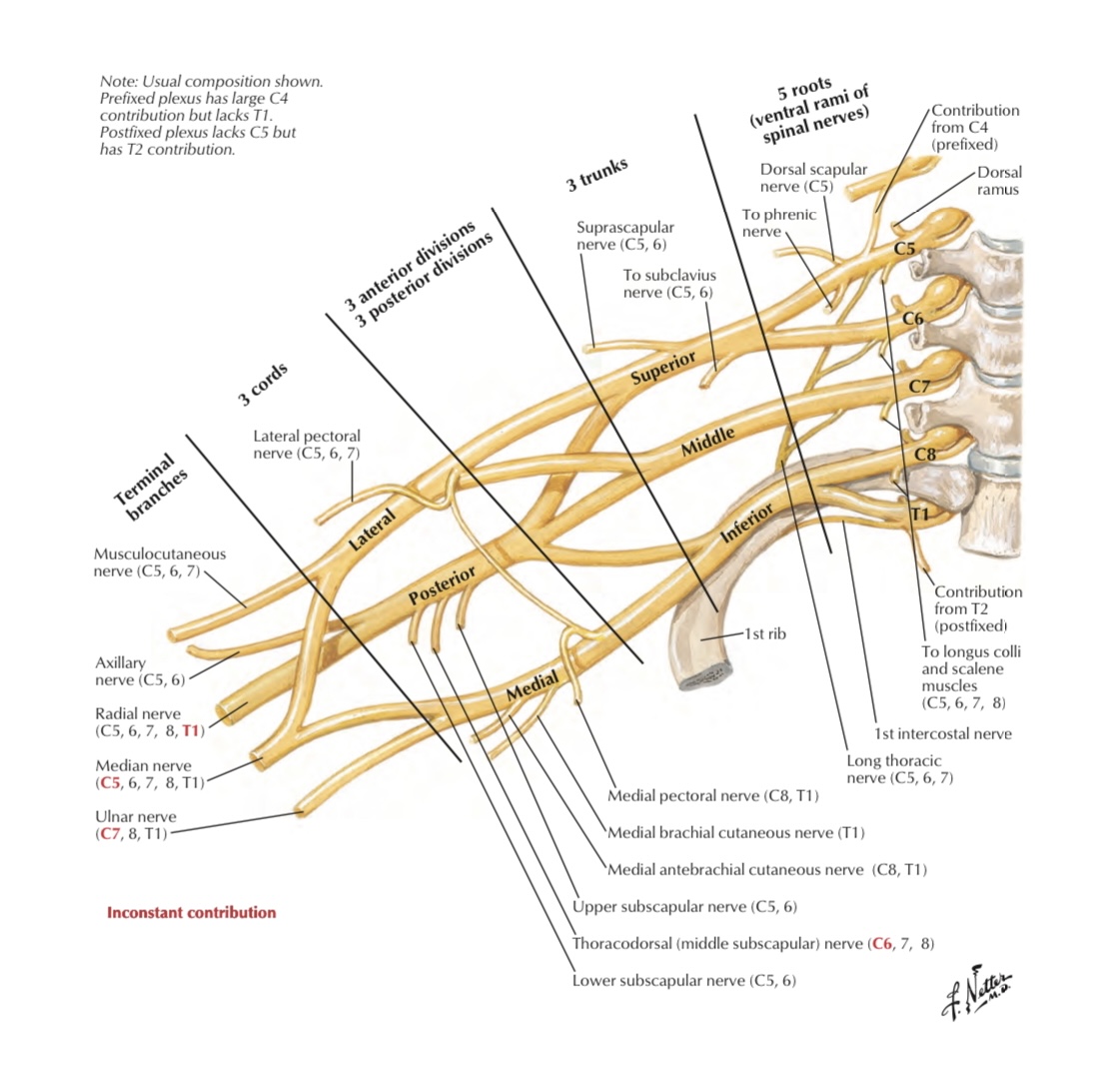
Details
Roots : ( five roots )
are the ventral ( anterior ) rami of (C5 _ T1) spinal nerves
are the ventral ( anterior ) rami of (C5 _ T1) spinal nerves
Trunks :- (three trunks)
1 _ upper trunk :- union of C5 , C6 roots
2 _ middle trunk :- continuation of C7 root
3 _ lower trunk :- union of C8 , T1 roots
1 _ upper trunk :- union of C5 , C6 roots
2 _ middle trunk :- continuation of C7 root
3 _ lower trunk :- union of C8 , T1 roots
Divisions :- (6 divisions)
each trunk divides into anterior & posterior divisions
each trunk divides into anterior & posterior divisions
Cords :- (three cords)
1 _ lateral cord : union of anterior divisions of upper & middle trunks
2 _ medial cord : continuation of anterior division of the lower trunk
3 _ posterior cord : union of posterior divisions of the 3 trunks
* the cords are named according to their position with the 2nd part of axillary artery.
1 _ lateral cord : union of anterior divisions of upper & middle trunks
2 _ medial cord : continuation of anterior division of the lower trunk
3 _ posterior cord : union of posterior divisions of the 3 trunks
* the cords are named according to their position with the 2nd part of axillary artery.
Branches :-
generally , the main terminal branches of the plexus are ( the axillary , musculocutaneous , radial , ulnar & median nerves)
*the axillary n. supplies the shoulder region and the others distribute through the arm and the forearm
generally , the main terminal branches of the plexus are ( the axillary , musculocutaneous , radial , ulnar & median nerves)
*the axillary n. supplies the shoulder region and the others distribute through the arm and the forearm
from roots : ( 4 branches )
1 _ long thoracic n. ( C5 , C6 & C7 ) to serratus anterior m.
2 _ dorsal scapular n. ( C5 )to levator scapulae & two rhomboids
3 _ twigs ( small branches ) to scalenus and longus coli m.
4 _ branch to phrenic n. (C5)
*The last two are small & not important branches
1 _ long thoracic n. ( C5 , C6 & C7 ) to serratus anterior m.
2 _ dorsal scapular n. ( C5 )to levator scapulae & two rhomboids
3 _ twigs ( small branches ) to scalenus and longus coli m.
4 _ branch to phrenic n. (C5)
*The last two are small & not important branches
from the upper trunk ( C5 &C6 ): (2 branches )
1 _ suprascapular n. to supraspinatus& infraspinatus m.
2 _ branch to subclavius m.
1 _ suprascapular n. to supraspinatus& infraspinatus m.
2 _ branch to subclavius m.
from lateral cord ( 3 branches )
1 _ lateral pectoral n. ( C5 , C6 ) to pectoralis major m.
2 _ lateral root of median n. ( C5 , C6 )
3 _ musculocutaneous n. ( C5 , C6 , C7 )to anterior compartment of the arm
1 _ lateral pectoral n. ( C5 , C6 ) to pectoralis major m.
2 _ lateral root of median n. ( C5 , C6 )
3 _ musculocutaneous n. ( C5 , C6 , C7 )to anterior compartment of the arm
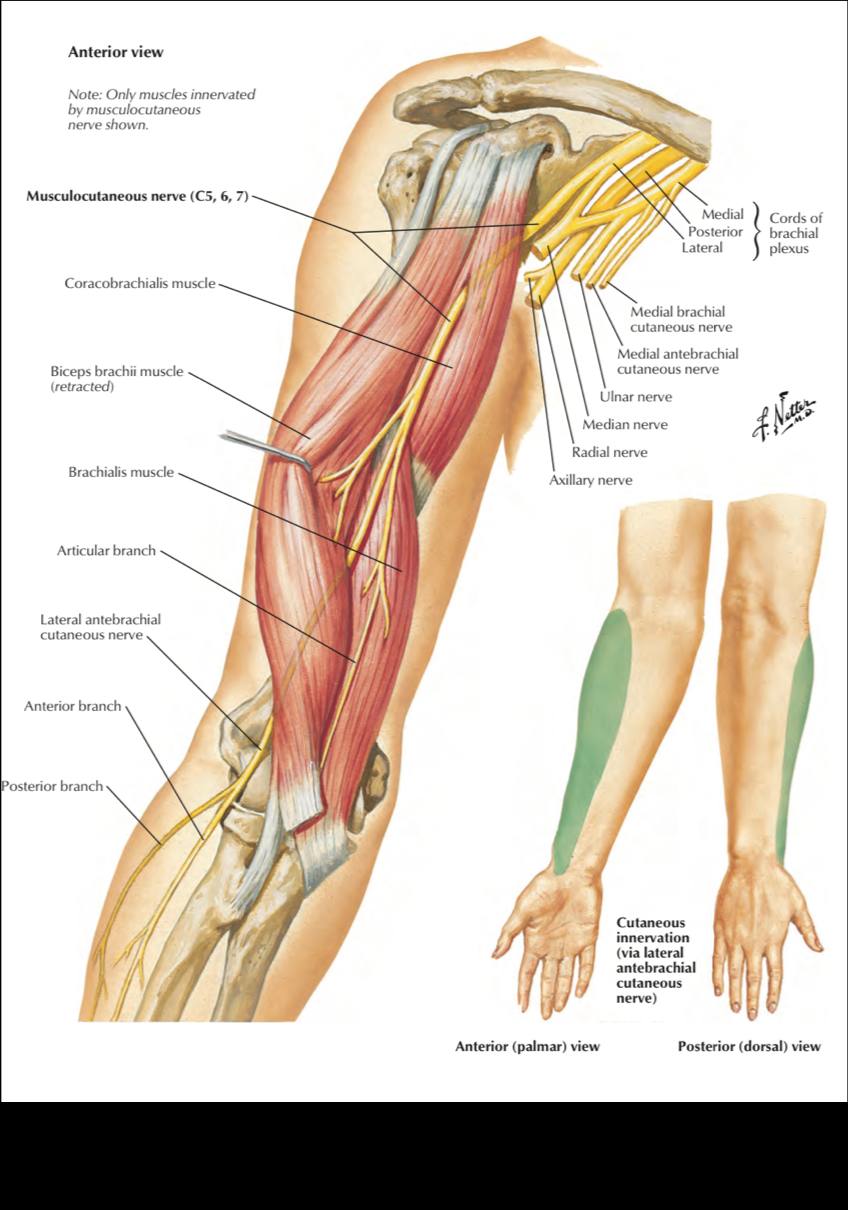
from medial cord ( 5 branches )
1 _ medial pectoral n. (C8 , T1 ) to pectoralis major & minor
2 _ medial root of median n. ( C8 ,T1 )
3 _ medial cutaneous n. of arm (C8 ,T1 ) also called Medial brachial cutaneous n.
4 _ medial cutaneous n. of forearm (C8 ,T1) also called Medial antebrachial cutaneous n.
5 _ ulnar n. (C7 , C8 , T1 ) mainly supplies the muscles of hand
1 _ medial pectoral n. (C8 , T1 ) to pectoralis major & minor
2 _ medial root of median n. ( C8 ,T1 )
3 _ medial cutaneous n. of arm (C8 ,T1 ) also called Medial brachial cutaneous n.
4 _ medial cutaneous n. of forearm (C8 ,T1) also called Medial antebrachial cutaneous n.
5 _ ulnar n. (C7 , C8 , T1 ) mainly supplies the muscles of hand
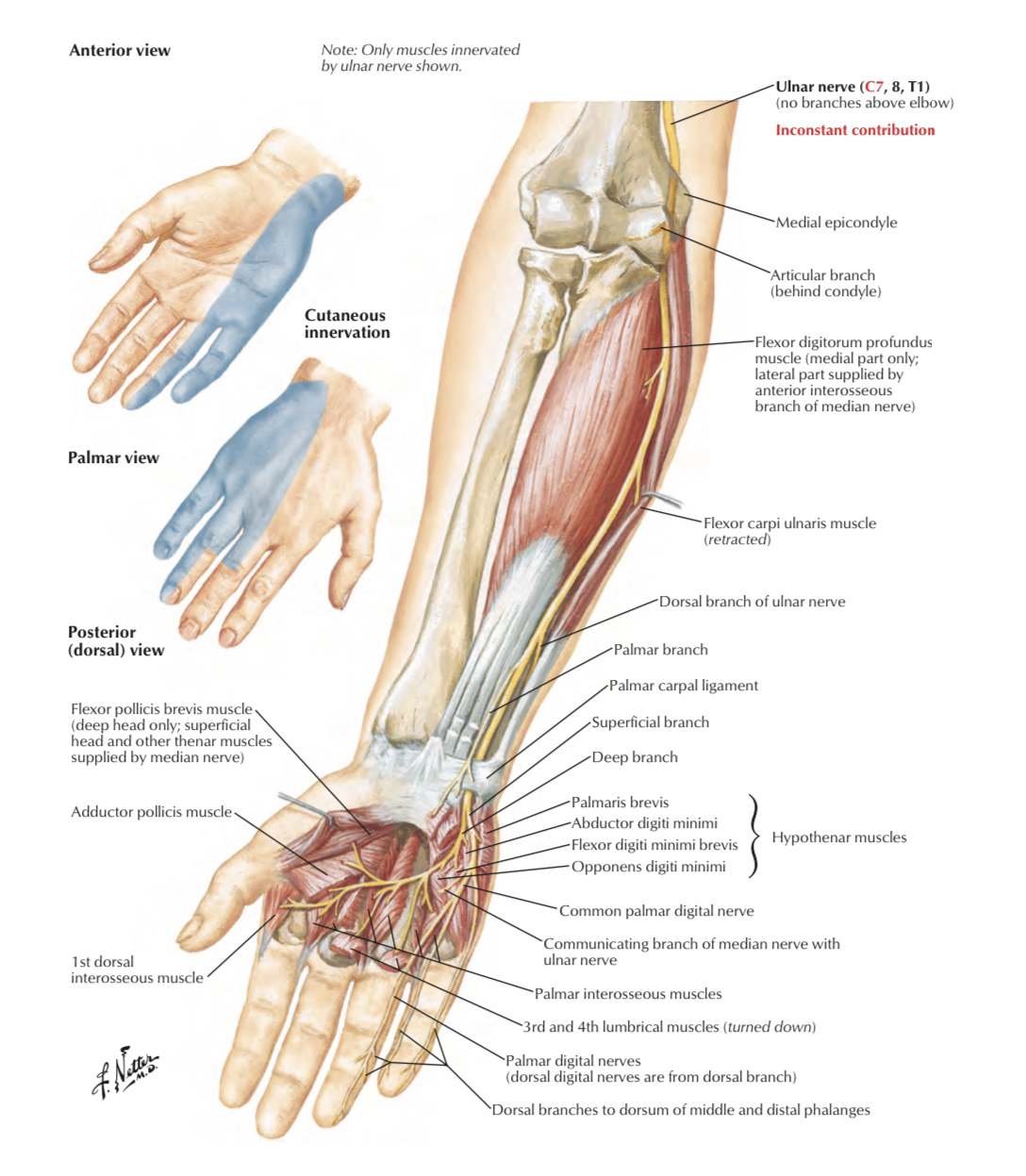
From posterior cord ( 5 branches )
1 _ upper subscapular n. (C5, C6 ) to subscapularis m.
2 _ lower subscapular n. (C5 , C6 ) to subscapularis & terese major m.
3 _ thoracodorsal n. ( C5 , C6 , C7 ) to latissimus dorsi m.
4 _ axillary n. (C5 , C6 ) to deltoid & terese minor m.
5 _ radial n. ( C5 , C6 , C7 , C8 , T1 ) the largest branch
to posterior compartment of arm & forearm
1 _ upper subscapular n. (C5, C6 ) to subscapularis m.
2 _ lower subscapular n. (C5 , C6 ) to subscapularis & terese major m.
3 _ thoracodorsal n. ( C5 , C6 , C7 ) to latissimus dorsi m.
4 _ axillary n. (C5 , C6 ) to deltoid & terese minor m.
5 _ radial n. ( C5 , C6 , C7 , C8 , T1 ) the largest branch
to posterior compartment of arm & forearm
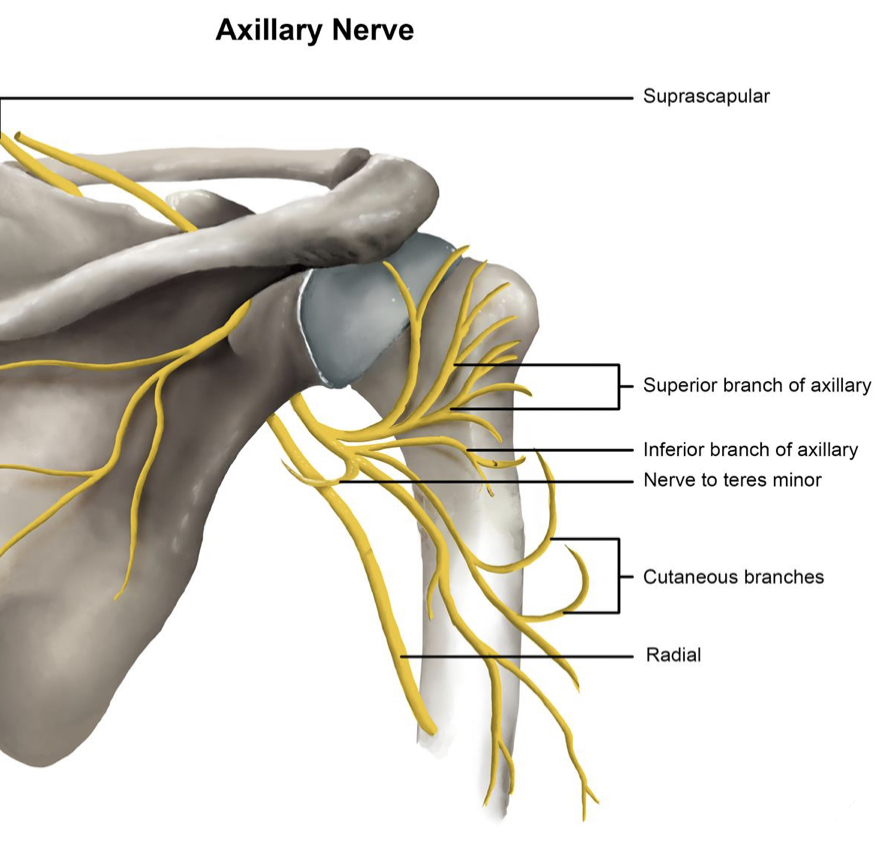
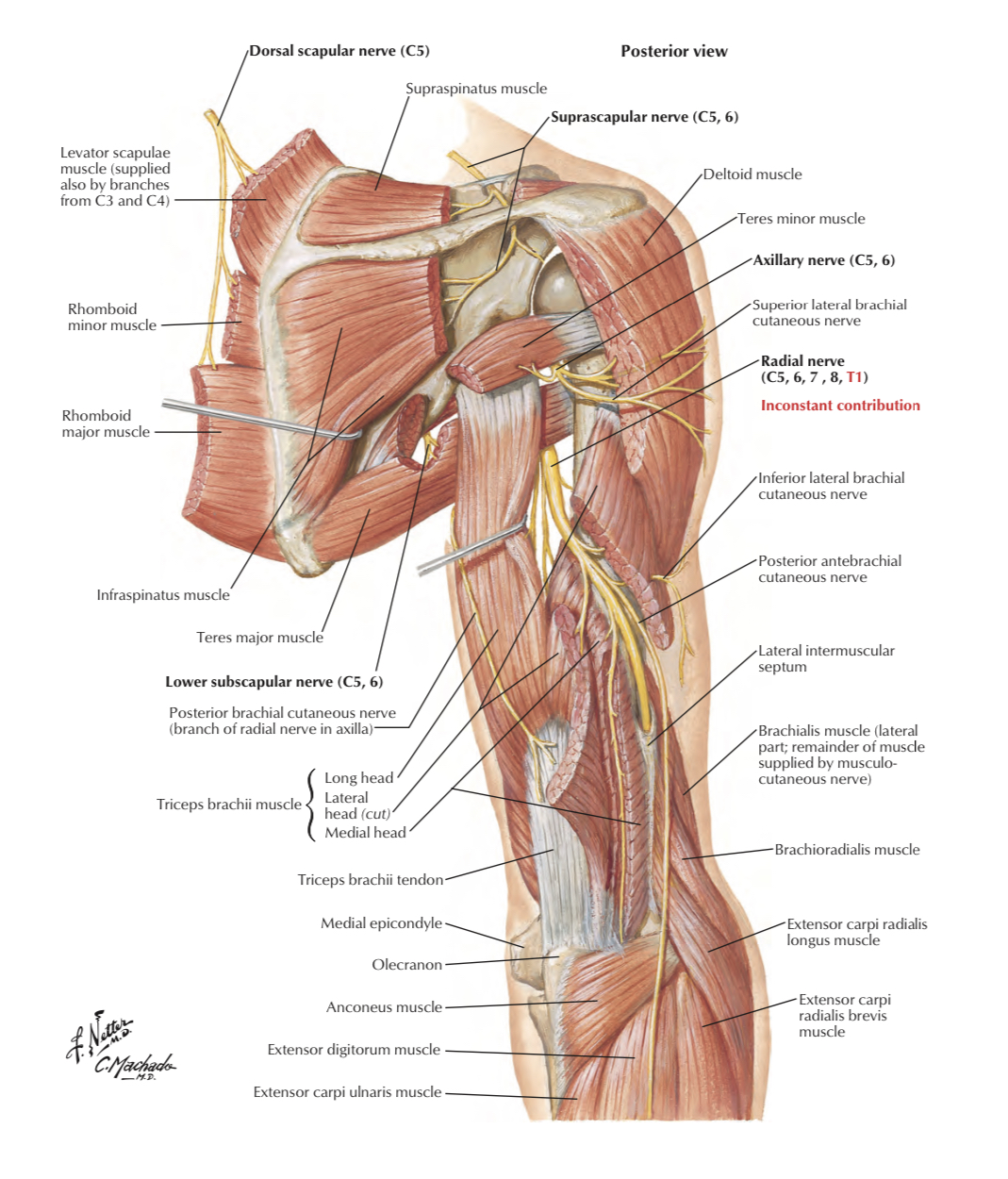
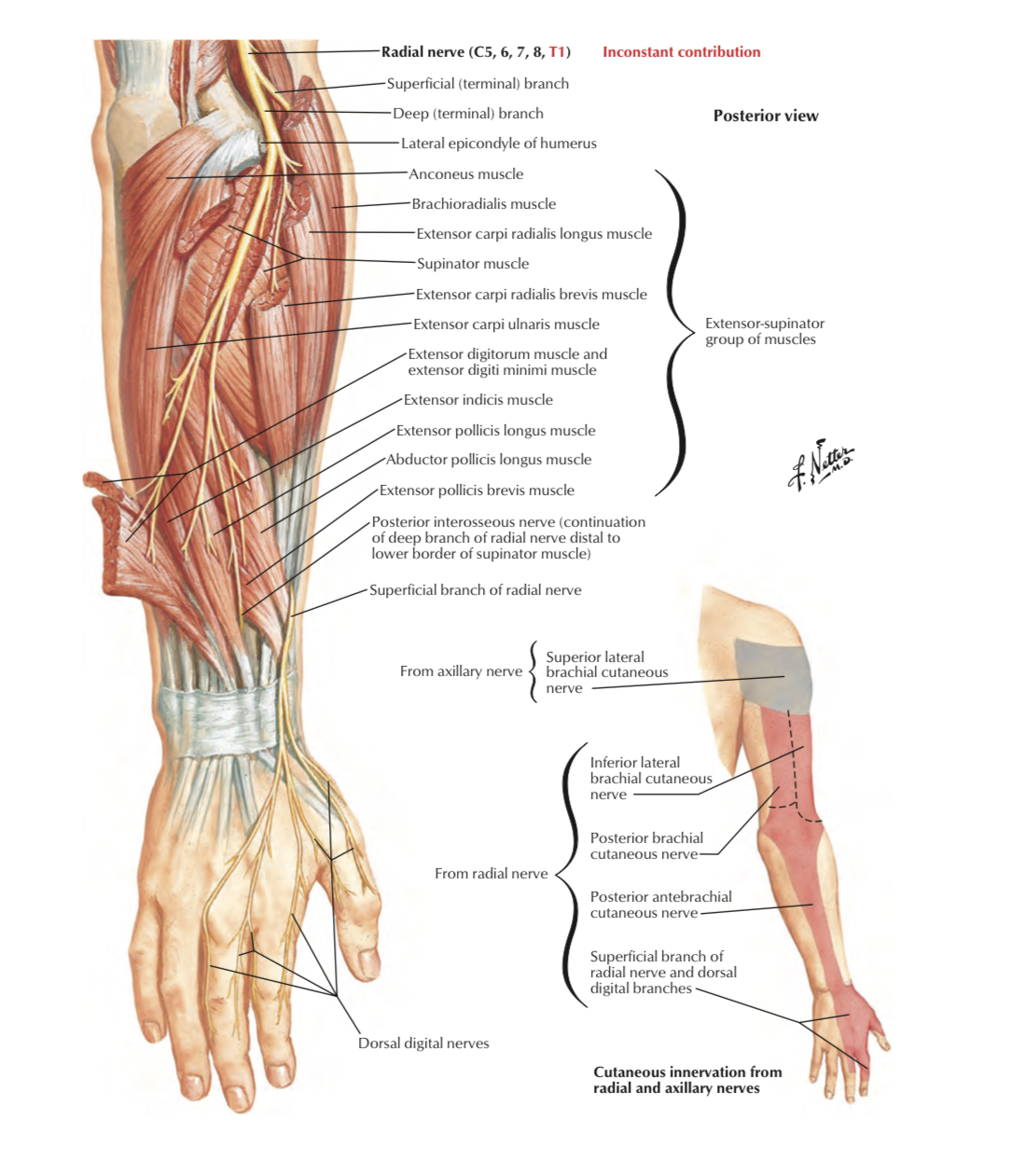
Axillary nerve
Cutaneous innervation
Most the sensory innervation of the upper limbs is derived from the brachial plexus except nerves to shoulder are derived from the cervical plexus ( collection of anterior rami of first 4 cervical spinal nerves ).
*There are lateral , medial & posterior ( but no anterior ) cutaneous nerves of arm and forearm this pattern corresponds to the cords of the brachial plexus.
*There are lateral , medial & posterior ( but no anterior ) cutaneous nerves of arm and forearm this pattern corresponds to the cords of the brachial plexus.
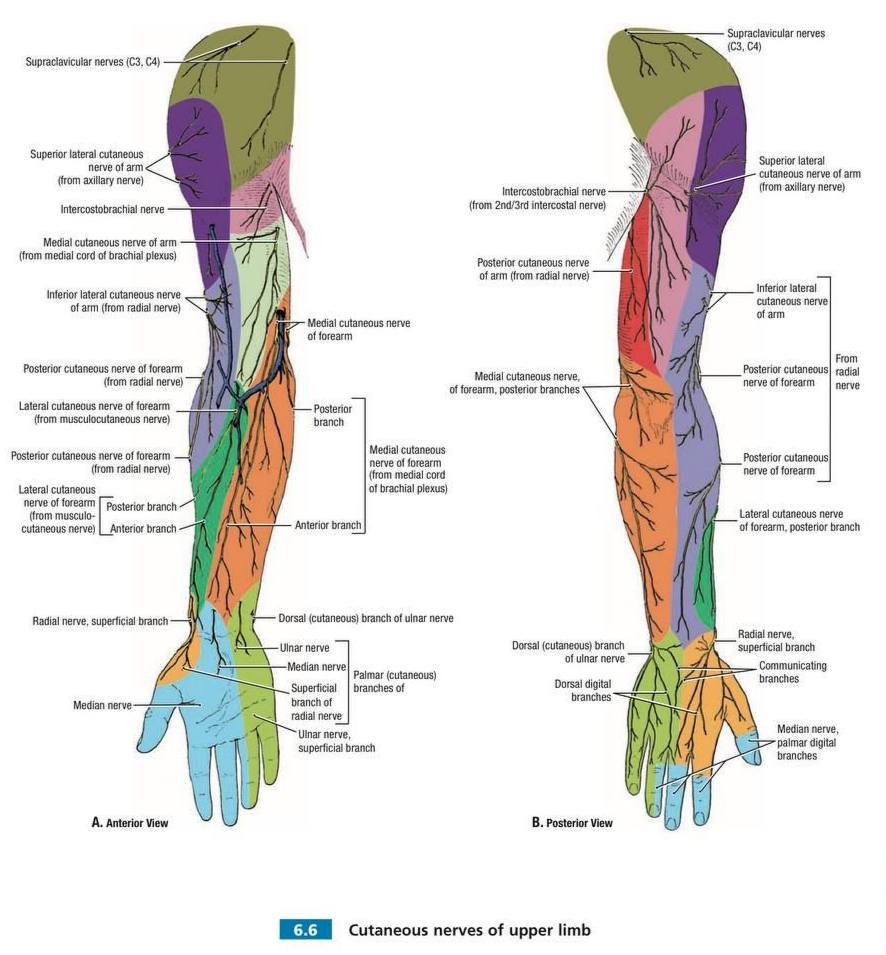
Cutaneous innervation of arm & shoulder
1. Supraclavicular n. (C3,4): branch of cervical plexus. It supplies skin over the
upper half of deltoid (shoulder region)
2. Upper lateral cutaneous n. of arm (Superior lateral brachial
cutaneous n.) (C5,6): branch of axillary n. It supplies skin
over the lower half of deltoid (shoulder region)
3. Lower lateral cutaneous n. of arm ( Inferior lateral brachial cutaneous n. )(C5,6): branch of radial n. It supplies skin of lateral side of arm (below deltoid)
4. Intercostobrachial n. (T2): it is the lateral branch of second intercostal n. It supplies skin of upper part of medial side of arm (close to axilla)
5. Medial cutaneous n. of arm ( Medial brachial cutaneous n. )(C8,T1): branch of medial cord of brachial plexus. It supplies skin of medial side of arm (below axilla)
6. Posterior cutaneous n. of arm ( Posterior brachial cutaneous n )(C5,6,7,8,T1): branch of radial n. It supplies skin of back of arm (from deltoid tuberosity to elbow).
1. Supraclavicular n. (C3,4): branch of cervical plexus. It supplies skin over the
upper half of deltoid (shoulder region)
2. Upper lateral cutaneous n. of arm (Superior lateral brachial
cutaneous n.) (C5,6): branch of axillary n. It supplies skin
over the lower half of deltoid (shoulder region)
3. Lower lateral cutaneous n. of arm ( Inferior lateral brachial cutaneous n. )(C5,6): branch of radial n. It supplies skin of lateral side of arm (below deltoid)
4. Intercostobrachial n. (T2): it is the lateral branch of second intercostal n. It supplies skin of upper part of medial side of arm (close to axilla)
5. Medial cutaneous n. of arm ( Medial brachial cutaneous n. )(C8,T1): branch of medial cord of brachial plexus. It supplies skin of medial side of arm (below axilla)
6. Posterior cutaneous n. of arm ( Posterior brachial cutaneous n )(C5,6,7,8,T1): branch of radial n. It supplies skin of back of arm (from deltoid tuberosity to elbow).
Cutaneous innervation of forearm
1 _Posterior cutaneous n. of forearm ( Posterior antebrachial cutaneous n. )(C5,6,7,8): branch of radial n. It supplies skin of back of forearm (from elbow to wrist).
2 _ Medial cutaneous n. of forearm (Medial antebrachial cutaneous n.)
(C8,T1): branch of medial cord of brachial plexus. It supplies skin of medial side of forearm. It divides into anterior & posterior branches
3 _ Lateral cutaneous n. of forearm (Lateral antebrachial cutaneous n. )(C5,6): continuation of musculocutaneous n. It supplies skin of lateral side of forearm & skin over base of thenar eminence. It divides into anterior & posterior branches.
cutaneous innervation of hand
1 _ Palmar cutaneous branch of median n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin of lateral two-thirds of the palm
2 _ Palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin of medial third of the palm.
3 _ Dorsal cutaneous branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin of medial third of back of hand.
4 _ Superficial branch of radial n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin of lateral two-thirds of back of hand.
5 _ Palmar digital branch of median n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin over palmar side of lateral three & a half fingers, also the skin over back of distal phalanx of lateral three & a half fingers.
6 _ Palmar digital branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin of palmar side of medial one & a half fingers, also the skin over back of distal phalanx of medial one & a half fingers.
7 _Dorsal digital branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin over back of proximal & middle phalanges of medial one & a half fingers .
8 _ Dorsal digital branch of radial n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin over back of proximal & middle phalanges of lateral three & a half fingers
1 _ Palmar cutaneous branch of median n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin of lateral two-thirds of the palm
2 _ Palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin of medial third of the palm.
3 _ Dorsal cutaneous branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin of medial third of back of hand.
4 _ Superficial branch of radial n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin of lateral two-thirds of back of hand.
5 _ Palmar digital branch of median n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin over palmar side of lateral three & a half fingers, also the skin over back of distal phalanx of lateral three & a half fingers.
6 _ Palmar digital branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin of palmar side of medial one & a half fingers, also the skin over back of distal phalanx of medial one & a half fingers.
7 _Dorsal digital branch of ulnar n. (C8,T1): supplies skin over back of proximal & middle phalanges of medial one & a half fingers .
8 _ Dorsal digital branch of radial n. (C6,7,8): supplies skin over back of proximal & middle phalanges of lateral three & a half fingers
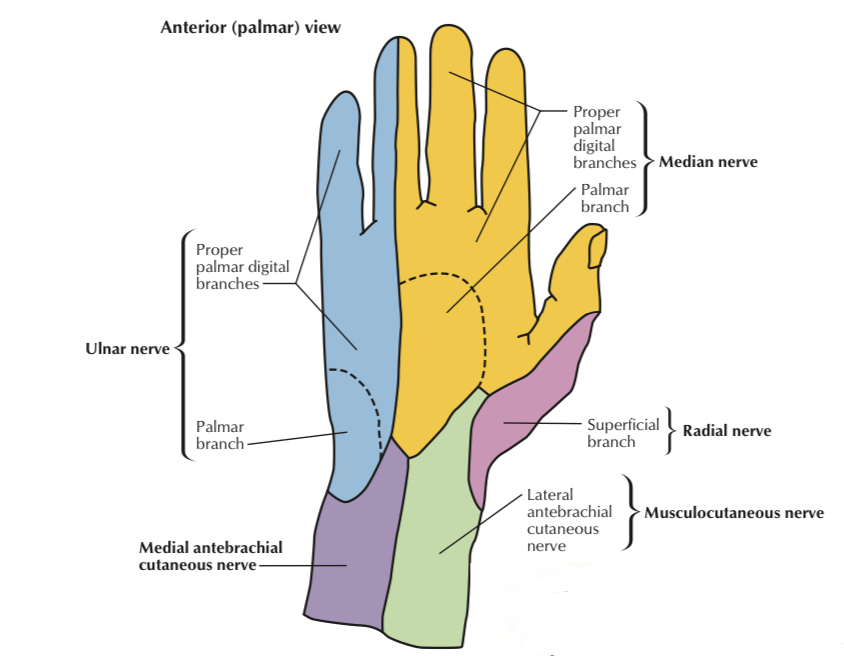
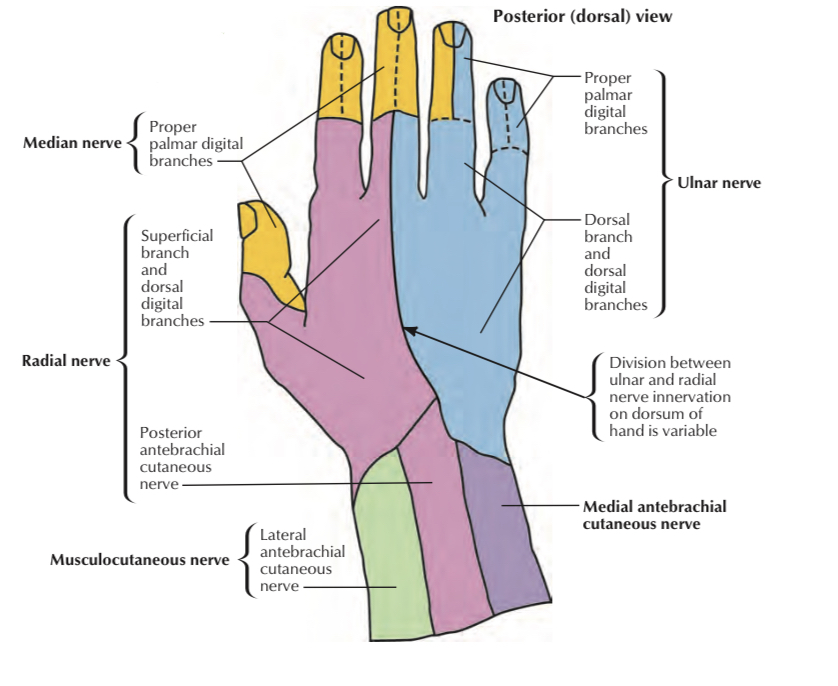
Palmar side
Clinical notes
Brachial plexus injuries :-
The injuries of brachial plexus have a wide range of ways such as stress , stretch & pressure.
The injuries of brachial plexus have a wide range of ways such as stress , stretch & pressure.
Causes of brachial plexus injuries
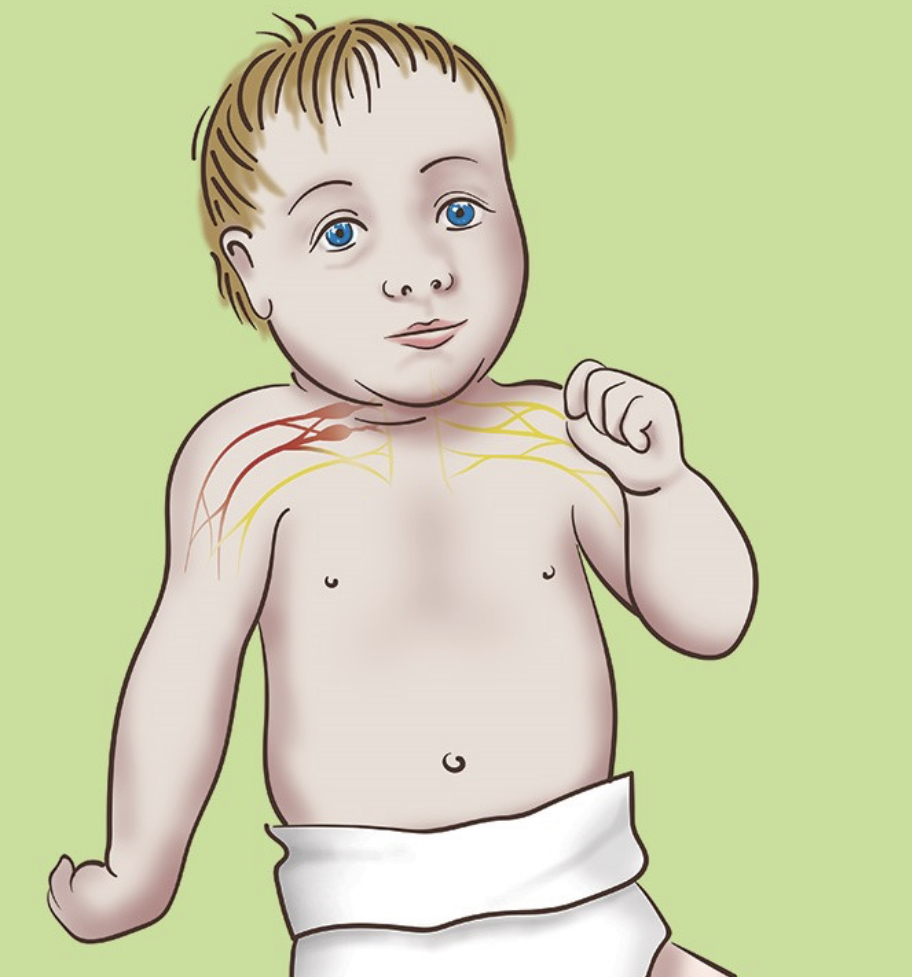
-in infants:
Injury of brachial plexus is common during delivery especially in large babies , Babies in breech position (bottom end comes out first).
In adults :
In adults, there are many causes of brachial plexus injuries, including:
1 _ Blunt trauma: such as falls , motor & car accidents.
2 _ Medical trauma: a nerve can be injured during a surgical operations, or damaged by an injection or due to the posture of the body during surgery
3 _ Gunshot wounds: a bullet tears through or near the nerves.
4 _ Cancer: causing brachial plexus syndrome also called ( Parsonage Turner syndrome ) that is due to the compression of the tumor or direct invasion of the plexus by the tumor.
-in infants:
Injury of brachial plexus is common during delivery especially in large babies , Babies in breech position (bottom end comes out first).
In adults :
In adults, there are many causes of brachial plexus injuries, including:
1 _ Blunt trauma: such as falls , motor & car accidents.
2 _ Medical trauma: a nerve can be injured during a surgical operations, or damaged by an injection or due to the posture of the body during surgery
3 _ Gunshot wounds: a bullet tears through or near the nerves.
4 _ Cancer: causing brachial plexus syndrome also called ( Parsonage Turner syndrome ) that is due to the compression of the tumor or direct invasion of the plexus by the tumor.
the symptoms may include :
1 _ sensory loss
2 _ muscular weakness or paralysis
3 _ pain
1 _ sensory loss
2 _ muscular weakness or paralysis
3 _ pain
Brachial plexus injuries may take place in one of two forms :
Erb’s palsy:
Also called ( waiter's tip ) , the injury of upper trunk of brachial plexus (C5 , C6 ) causes this syndrome .
It results from excessive displacement of head to the opposite side or depression of shoulder on the same side , it also occurs in babies during difficult delivery.
the axillary , suprascapular ,nerve to subclavius & musculocutaneous nerves are all affected and become functionless , therefore there will be :-
1 _ loss of abduction & lateral rotation of shoulder
2 _ loss of flexion of elbow
3 _ loss of supination of forearm
as aresult limbs will hang by the side , adducted arm & pronated forearm .
also there will be loss of sensation over the lower half of deltoid down to the lateral side of forearm
Also called ( waiter's tip ) , the injury of upper trunk of brachial plexus (C5 , C6 ) causes this syndrome .
It results from excessive displacement of head to the opposite side or depression of shoulder on the same side , it also occurs in babies during difficult delivery.
the axillary , suprascapular ,nerve to subclavius & musculocutaneous nerves are all affected and become functionless , therefore there will be :-
1 _ loss of abduction & lateral rotation of shoulder
2 _ loss of flexion of elbow
3 _ loss of supination of forearm
as aresult limbs will hang by the side , adducted arm & pronated forearm .
also there will be loss of sensation over the lower half of deltoid down to the lateral side of forearm
Klumpke’s palsy ( claw hand ) :
the injury of lower trunk of brachial plexus (C8 , T1 ) causes this syndrome .
It is usually caused by excessive abduction of the arm or in the case of a person falling from aheight clutching at an object to save himself.
The Ulnar nerve mainly affected , therefore there will be :
1 _ extension at metacarpophalangeal joints
2 _ flexion at interphalangeal joints
due to paralysis of the intrinsic muscles of hand ( lumbricals , all interossei & hypothenar muscles ) this condition also called claw hand
3 _ loss of sensation along the medial side of arm &forearm
the injury of lower trunk of brachial plexus (C8 , T1 ) causes this syndrome .
It is usually caused by excessive abduction of the arm or in the case of a person falling from aheight clutching at an object to save himself.
The Ulnar nerve mainly affected , therefore there will be :
1 _ extension at metacarpophalangeal joints
2 _ flexion at interphalangeal joints
due to paralysis of the intrinsic muscles of hand ( lumbricals , all interossei & hypothenar muscles ) this condition also called claw hand
3 _ loss of sensation along the medial side of arm &forearm

Brachial plexus injury treatment
The brachial plexus injuries can be treated either surgically or nonsurgically and the treatment depends on the Severity, type and time of injury (since when did it happen ) , in addition some conditions don’t need any treatment ( such as nerves that have just stretched).
The nonsurgical treatment mainly include the physical therapy and drugs to control the pain.
For the surgical treatment of the injury the time frame is important factor for recovery , the muscles that are unconnected to nerves for 18 month may have weakened to the point where it is no longer possible.
The brachial plexus injuries can be treated either surgically or nonsurgically and the treatment depends on the Severity, type and time of injury (since when did it happen ) , in addition some conditions don’t need any treatment ( such as nerves that have just stretched).
The nonsurgical treatment mainly include the physical therapy and drugs to control the pain.
For the surgical treatment of the injury the time frame is important factor for recovery , the muscles that are unconnected to nerves for 18 month may have weakened to the point where it is no longer possible.
Reference
1- LAWRENCE E. WINESKI Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions /10th edition (2018 ) / pp.137_ 141 p.148
2- Brachial plexus injury / Johns Hopkins medicine / Link : https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/brachial-plexus-injuries?amp=true
2- Brachial plexus injury / Johns Hopkins medicine / Link : https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/brachial-plexus-injuries?amp=true
Reference of images
1 _ figure 1 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 416
2 _ figure 2 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 462
3 _ figure 3 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 464
4 _ figure 4 : Axillary nerve , Medbullets ، https://images.app.goo.gl/UDkSqJaQdwAavahR9
5 _ figure 5 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 465
6 _ figure 6 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 466
7 _ figure 7 : Grant’s Atlas of Anatomy / plate 484
8 _ figure 8 & figure 9 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 459
9 _ figure 10 : Erb’s palsy / GIRONES LAWYERES / https://images.app.goo.gl/1wrsddGH3Gn9UQ9i9
10 _ figure 11 : Klumpe’s palsy / Birth Injury Guide /https://images.app.goo.gl/2yU1ifPqy8B64q6eA
11 _ cover image : brachial plexus ، Johns Hopkins medicine , https://images.app.goo.gl/8QzpymAgCCrcdZPa9
2 _ figure 2 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 462
3 _ figure 3 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 464
4 _ figure 4 : Axillary nerve , Medbullets ، https://images.app.goo.gl/UDkSqJaQdwAavahR9
5 _ figure 5 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 465
6 _ figure 6 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 466
7 _ figure 7 : Grant’s Atlas of Anatomy / plate 484
8 _ figure 8 & figure 9 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 459
9 _ figure 10 : Erb’s palsy / GIRONES LAWYERES / https://images.app.goo.gl/1wrsddGH3Gn9UQ9i9
10 _ figure 11 : Klumpe’s palsy / Birth Injury Guide /https://images.app.goo.gl/2yU1ifPqy8B64q6eA
11 _ cover image : brachial plexus ، Johns Hopkins medicine , https://images.app.goo.gl/8QzpymAgCCrcdZPa9
