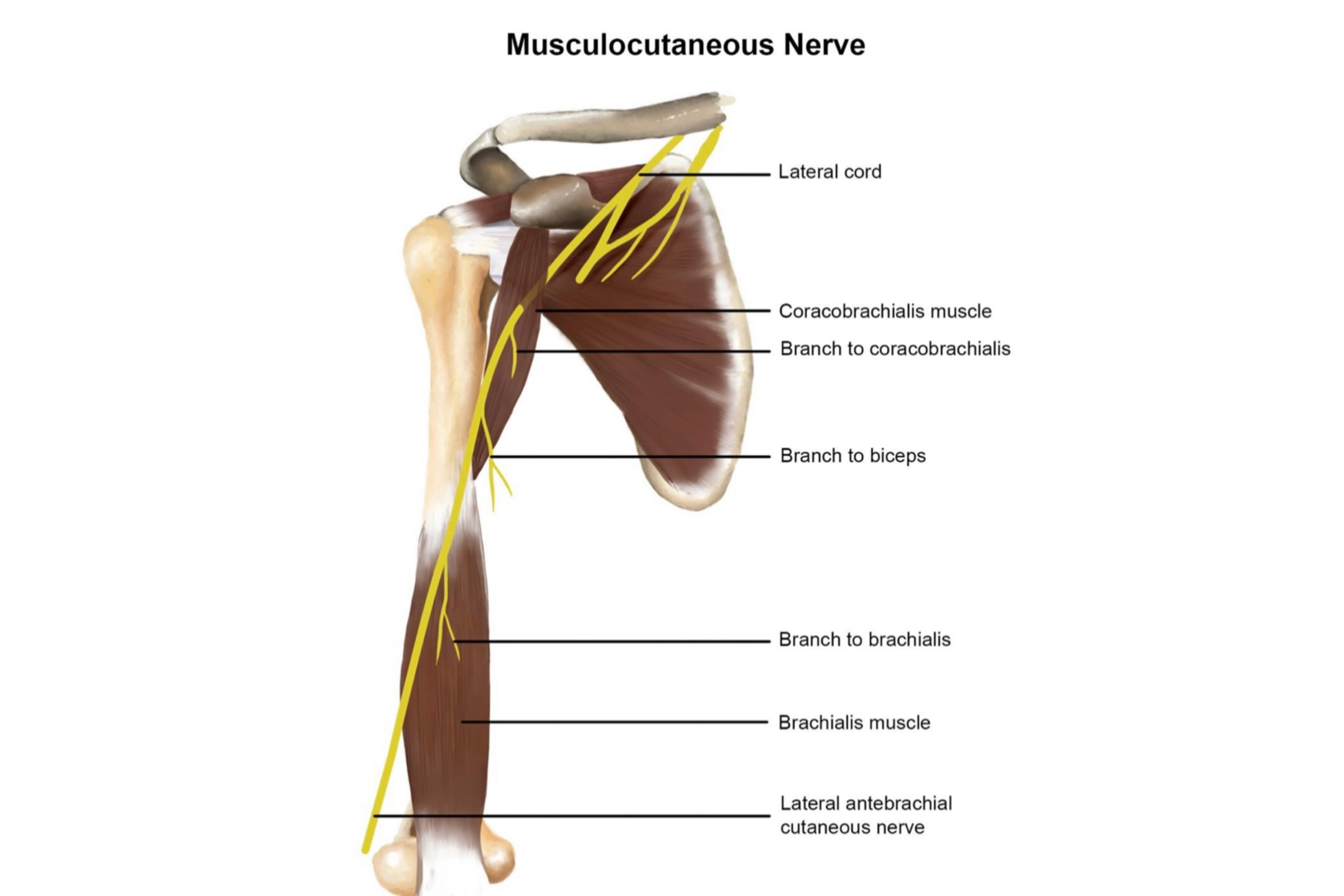
Musculocutaneous Nerve
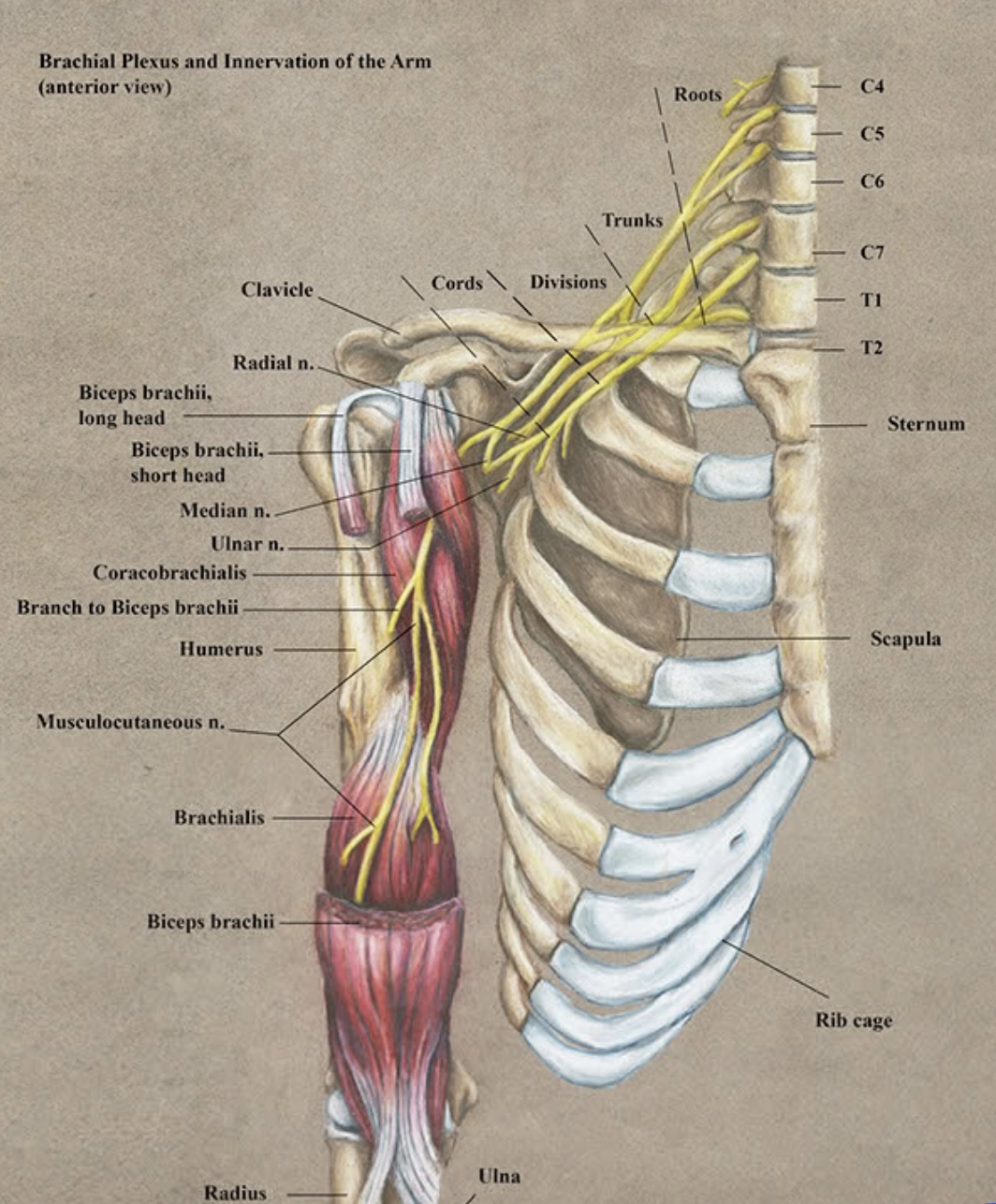
By : Malak AlsammanOrigin , End , Course and Relation
Origin :
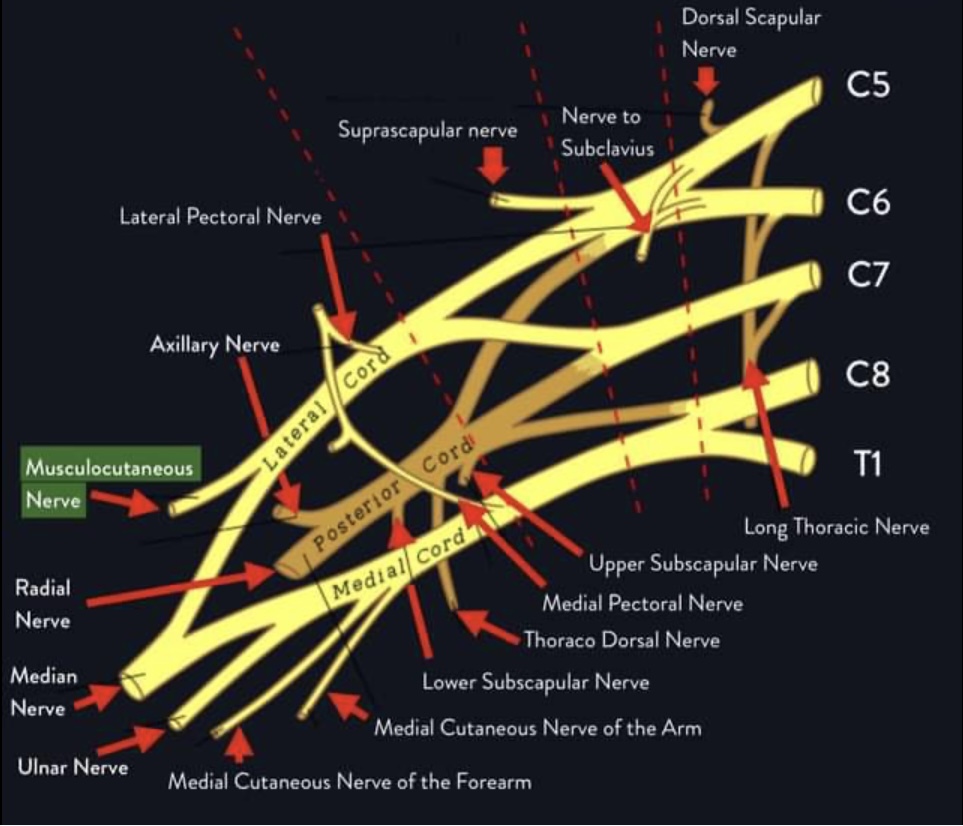
From the lateral cord of the brachial plexus (C5,6,7)
End :
It ends as lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm .
Course and Relation
• It arises from the lateral cord of brachial plexus ...
• It emerges at the inferior border of pectoralis minor muscle ...
• In axilla it runs lateral to the 3rd part of axillary a.
• Then it leaves the axilla and enters the arm by piercing coracobrachialis muscle (near its point of insertion on the humerus ...at middle of the arm ) it also gives branch to it
• Then it passes down in the arm between brachialis m.(superficial to it) and biceps brachii m.(Deep to it ) it innervates both these muscles and also it gives articular branches to humerus and elbow joint .
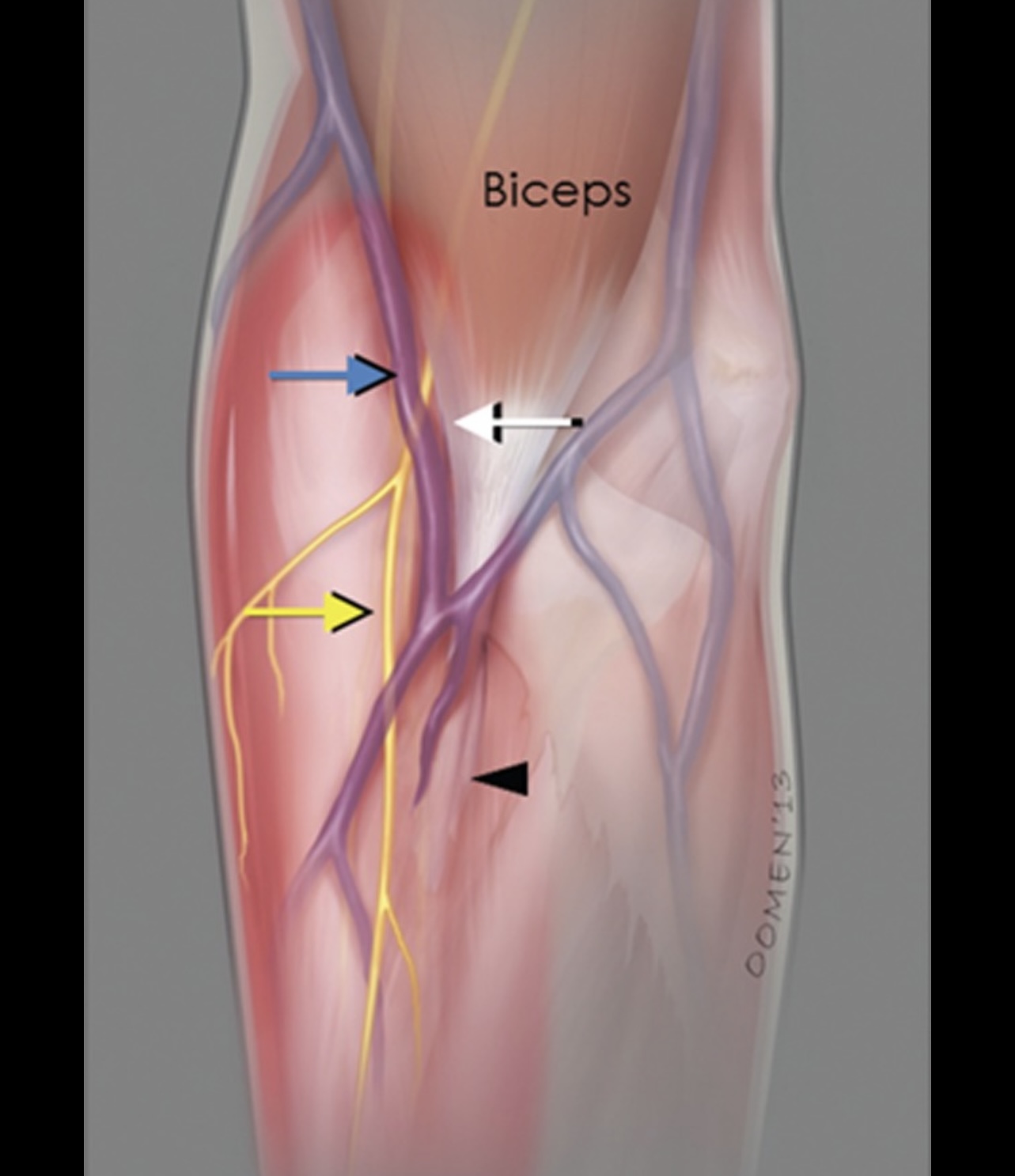
• After that it emerges lateral to the biceps tendon at the elbow and pierces deep facia to enter the forearm and to become subcutaneous and it continues as Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
From the lateral cord of the brachial plexus (C5,6,7)
End :
It ends as lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm .
Course and Relation
• It arises from the lateral cord of brachial plexus ...
• It emerges at the inferior border of pectoralis minor muscle ...
• In axilla it runs lateral to the 3rd part of axillary a.
• Then it leaves the axilla and enters the arm by piercing coracobrachialis muscle (near its point of insertion on the humerus ...at middle of the arm ) it also gives branch to it
• Then it passes down in the arm between brachialis m.(superficial to it) and biceps brachii m.(Deep to it ) it innervates both these muscles and also it gives articular branches to humerus and elbow joint .
• After that it emerges lateral to the biceps tendon at the elbow and pierces deep facia to enter the forearm and to become subcutaneous and it continues as Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.

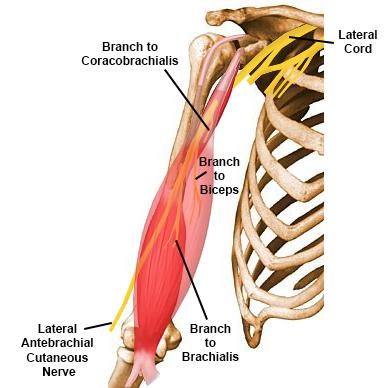

Branches of Musculocutaneous nerve
• Muscular : to BBC ( Biceps brachii , Brachialis , Coracobrachialis )
• Note : these muscles flex the upper arm at the shoulder joint and the elbow joint ..in addition the Biceps also perform forearm supination.
• Cutaneous : continues as lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm which gives sensation to the lateral side of the forearm.
• Articular : to the elbow joint and to the humerus.
• Note : these muscles flex the upper arm at the shoulder joint and the elbow joint ..in addition the Biceps also perform forearm supination.
• Cutaneous : continues as lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm which gives sensation to the lateral side of the forearm.
• Articular : to the elbow joint and to the humerus.

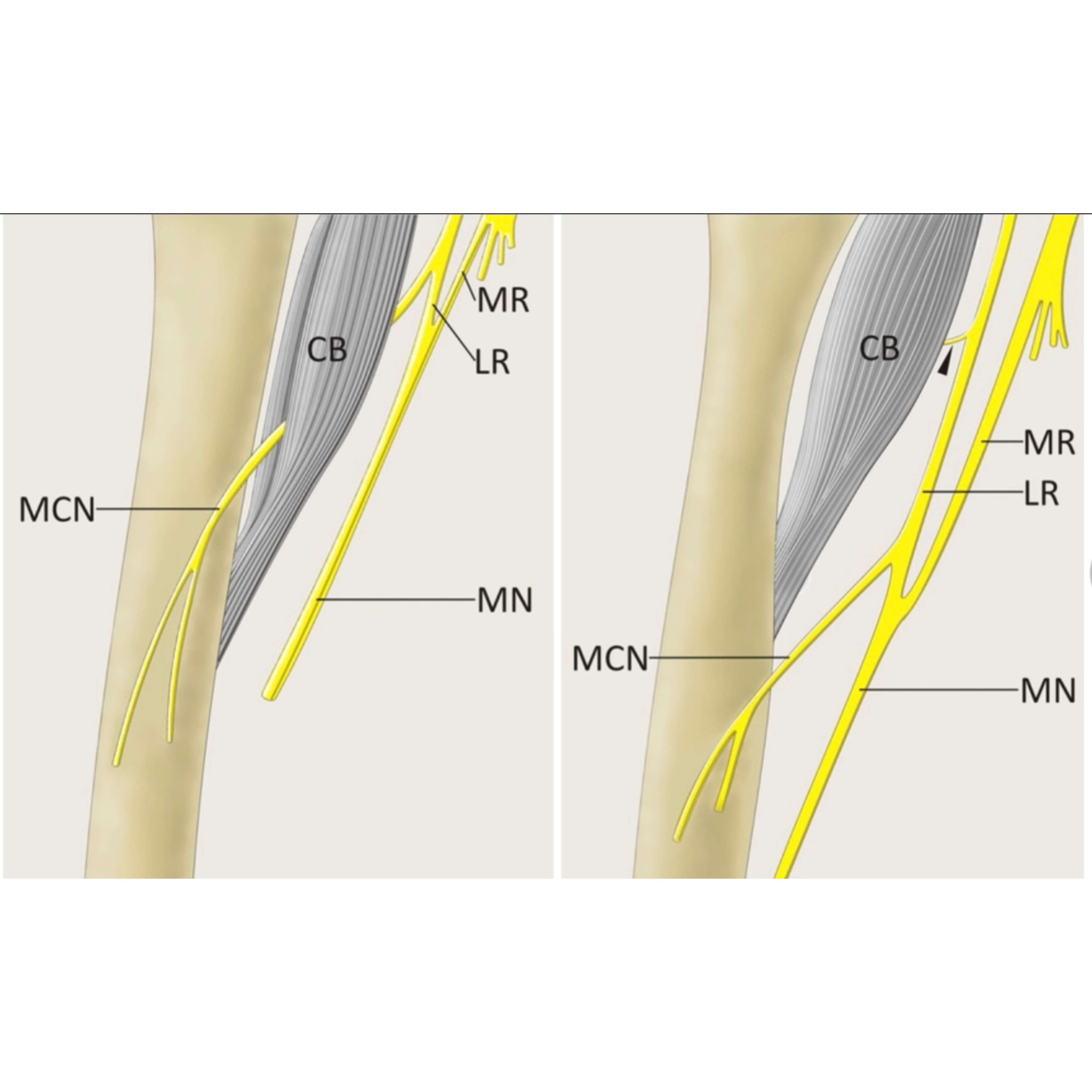
Musculocutaneous nerve variations
The musculocutaneous nerve is well recognised to have a varied anatomical course ..this may lead to clinical implications in surgery and diagnosis.
• It can interact with the median nerve, adhering to the nerve and exchanging fibres.
• it can pass under the coracobrachialis instead of through it
• It can pass through biceps brachii muscle
• In a very rare conditions we found that the Musculocutaneous nerve absent .
• In this case the median nerve act as principal surrogate .
• In this case :
• Coracobrachialis m. (is supplied by a nerve from the lateral cord of brachial plexus)
• Biceps brachii m.(is supplied by the lateral root of median nerve )
• Brachialis m. (is supplied by a branch of median nerve )
• It can interact with the median nerve, adhering to the nerve and exchanging fibres.
• it can pass under the coracobrachialis instead of through it
• It can pass through biceps brachii muscle
• In a very rare conditions we found that the Musculocutaneous nerve absent .
• In this case the median nerve act as principal surrogate .
• In this case :
• Coracobrachialis m. (is supplied by a nerve from the lateral cord of brachial plexus)
• Biceps brachii m.(is supplied by the lateral root of median nerve )
• Brachialis m. (is supplied by a branch of median nerve )

Clinical Points
• Musculocutaneous nerve is rarely injured because of its protected position deep to biceps brachii m.
• But it may become injured by :
• Brachial Plexus damage
• Compression injury like weight lifting or sports involving lots of forearm flexing and supination.
• Shoulder injury
• Dislocation of the shoulder joint.
The injury to Musculocutaneous nerve causes :
• Loss of sensation of the lateral aspect of the forearm
• Paralysis in the muscles supplied by it (Coracobrachialis , Biceps
brachii and the greater part of Brachialis ) and this cause :
• Flexion at elbow and shoulder are weakened but still can be
performed by the Pectoralis major and Brachioradialis
• Supination of the forearm is weak but still can be performed by Brachioradialis
• Note: Brachialis muscle is also supplied by the radial nerve (the radial nerve supplies the lateral part of the brachialis m.)
Treatment
• Always the treatment depends upon the level of damage
• So some cases can be treated by non-surgical methods such ...rest , ice , anti-
inflammatory medications or physical therapy.
• If non-surgical methods failed .... surgical decompression may become necessary.
• In some cases, nerve grafting or nerve transfer may be necessary for restoring function
• Note:A nerve graft is a piece of nerve tissue that serves as a bridge to fill a gap between the two ends of a damaged nerve.
• But it may become injured by :
• Brachial Plexus damage
• Compression injury like weight lifting or sports involving lots of forearm flexing and supination.
• Shoulder injury
• Dislocation of the shoulder joint.
The injury to Musculocutaneous nerve causes :
• Loss of sensation of the lateral aspect of the forearm
• Paralysis in the muscles supplied by it (Coracobrachialis , Biceps
brachii and the greater part of Brachialis ) and this cause :
• Flexion at elbow and shoulder are weakened but still can be
performed by the Pectoralis major and Brachioradialis
• Supination of the forearm is weak but still can be performed by Brachioradialis
• Note: Brachialis muscle is also supplied by the radial nerve (the radial nerve supplies the lateral part of the brachialis m.)
Treatment
• Always the treatment depends upon the level of damage
• So some cases can be treated by non-surgical methods such ...rest , ice , anti-
inflammatory medications or physical therapy.
• If non-surgical methods failed .... surgical decompression may become necessary.
• In some cases, nerve grafting or nerve transfer may be necessary for restoring function
• Note:A nerve graft is a piece of nerve tissue that serves as a bridge to fill a gap between the two ends of a damaged nerve.
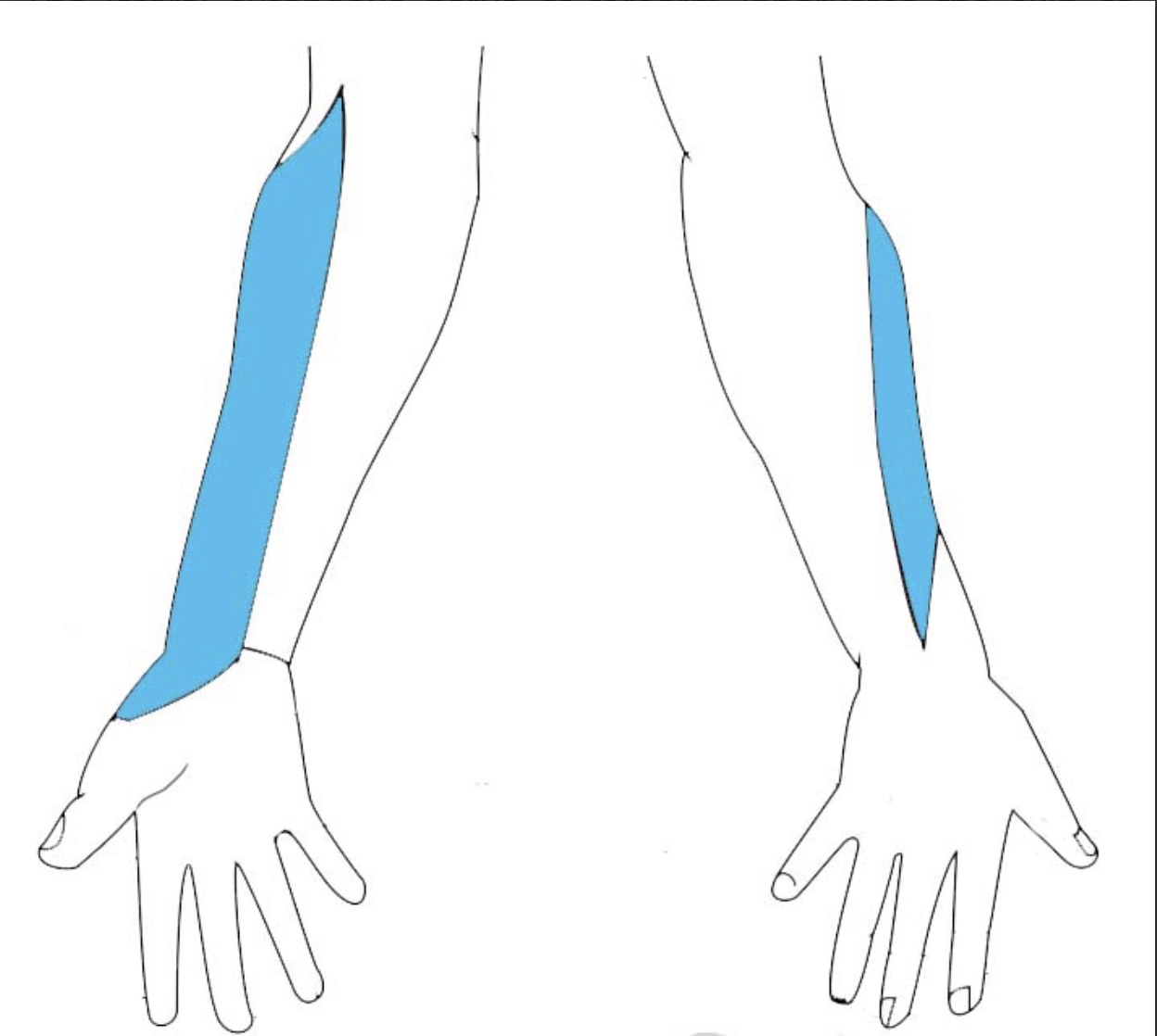
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
• It is the continuation of the musculocutaneous nerve which is also known as Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
• It provides the sensory innervation of the lateral aspect of the forearm
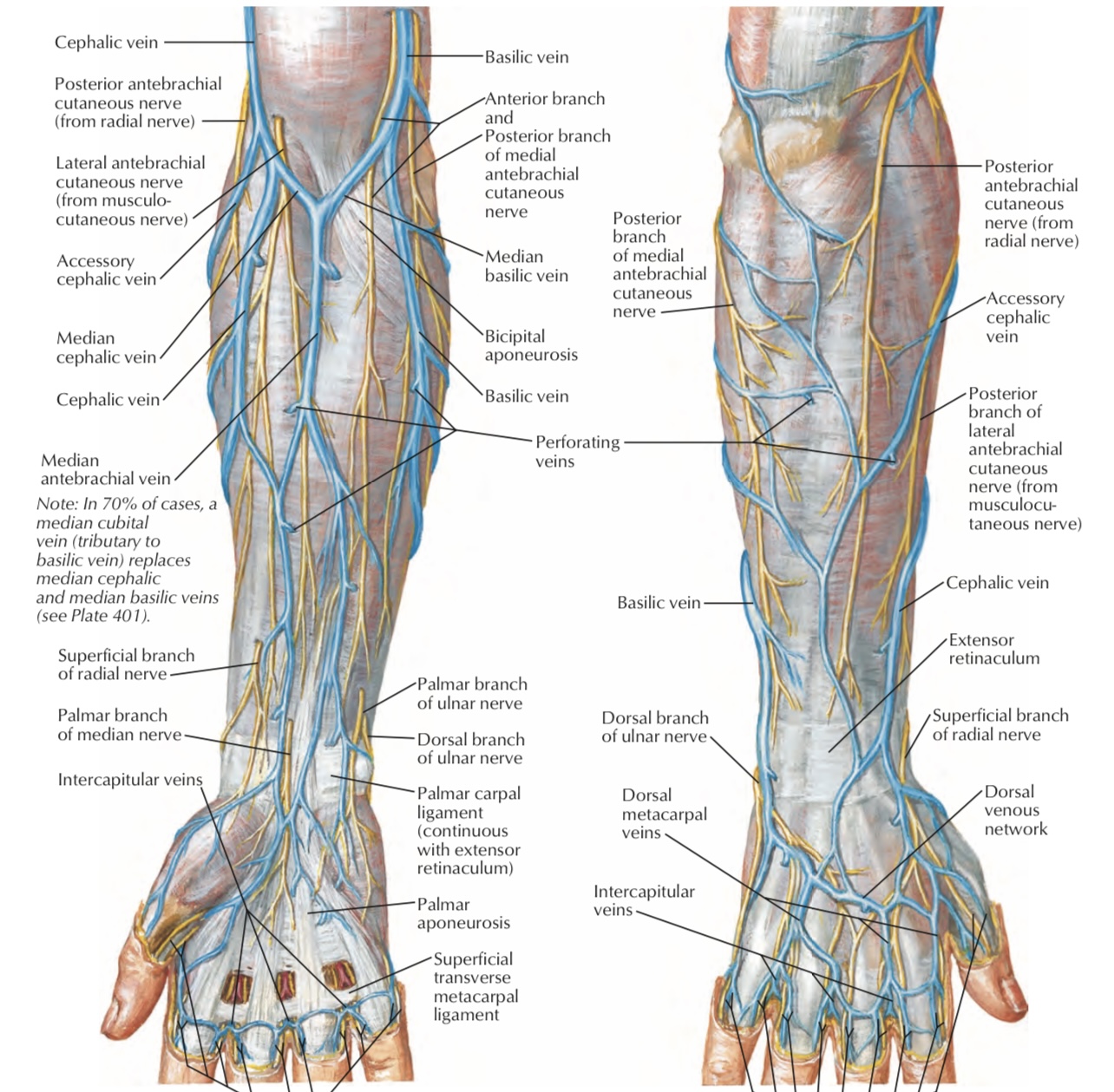
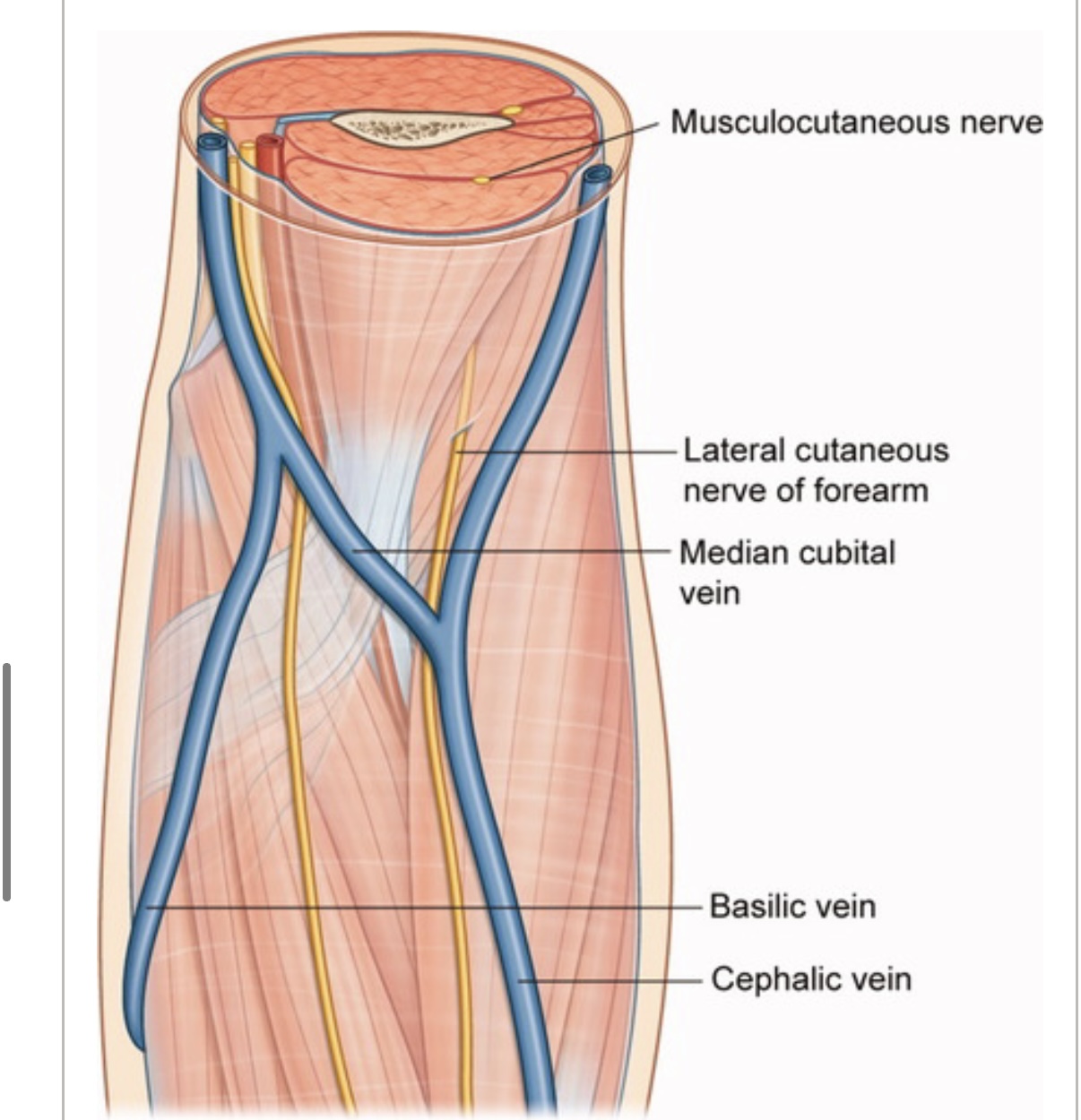
• Its course starts at the lateral border of biceps tendon
• It runs below cephalic vein
• It divides into Anterior and Posterior branches
• The Anterior branch :
It descends distally at the anterolateral aspect of the forearm ..it ends above wrist by communicating with
the superficial branch of radial nerve and palmar cutaneous branch of medial nerve
• The posterior branch :
• It descends distally at the posterolateral aspect of the forearm ..it ends by communicating with the superficial branch of radial nerve and the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm (branch of radial nerve ).
• It provides the sensory innervation of the lateral aspect of the forearm
• Its course starts at the lateral border of biceps tendon
• It runs below cephalic vein
• It divides into Anterior and Posterior branches
• The Anterior branch :
It descends distally at the anterolateral aspect of the forearm ..it ends above wrist by communicating with
the superficial branch of radial nerve and palmar cutaneous branch of medial nerve
• The posterior branch :
• It descends distally at the posterolateral aspect of the forearm ..it ends by communicating with the superficial branch of radial nerve and the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm (branch of radial nerve ).
Injury to Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
• Cuts and wounds of the forearm can sever the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm resulting in loss of sensation along the lateral aspect of the forearm.
• It is uncommon but this nerve can be compressed by biceps tendon at the position where its course begin
• This can occur by strenuous upper limb activities
• The symptoms are :
Pain in the area of injury , loss of sensation and numbness in the lateral aspect of the forearm
• The treatment :
Anti inflammatory drugs could help ..beside rest ....if this didn’t help A surgical methods are needed to fix the problem
Another rare condition of Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm injury is an injury could happen during cannulation or blood collection (venipuncture)
Because of its location in the cubital fossa near median cubital vein (most common vein to collect blood).
• It is uncommon but this nerve can be compressed by biceps tendon at the position where its course begin
• This can occur by strenuous upper limb activities
• The symptoms are :
Pain in the area of injury , loss of sensation and numbness in the lateral aspect of the forearm
• The treatment :
Anti inflammatory drugs could help ..beside rest ....if this didn’t help A surgical methods are needed to fix the problem
Another rare condition of Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm injury is an injury could happen during cannulation or blood collection (venipuncture)
Because of its location in the cubital fossa near median cubital vein (most common vein to collect blood).
References
Cutaneous distribution of the musculocutaneous nerve. TeachMeAnatomy https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/nerves/musculocutaneous-nerve/
Netter - plate 402
Musculocutaneous Nerve -Medbullets Step 1https://step1.medbullets.com/msk/107064/musculocutaneous-nerve
Musculocutaneous Nerve -Anatomy-Orthobullets https://www.orthobullets.com/anatomy/10102/musculocutaneous-nerve
Musculocutaneous Nerve Variations -ResearchGate https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Two-different-anatomical-variations-of-the-musculocutaneous-and-median-nerves-a-Typical_fig3_330451014
Musculocutaneous Nerve Variations -pulsus Group https://www.pulsus.com/scholarly-articles/variations-in-branching-pattern-of-musculocutaneous-nerve-with-respect-to-communicating-branch-between-musculocutaneous-and-median-4655.html
The brachial plexus- Nysora https://www.nysora.com/
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm-Wiley Online Library https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.7863/ultra.33.8.1475
Musculocutaneous Nerve - Physiopedia
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Musculocutaneous_Nerve
The Musculocutaneous Nerve - TeachMeAnatomy https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/nerves/musculocutaneous-nerve/
Kenhub - Musculocutaneous nerve https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-musculocutaneous-nerve
Keith L.Moore _Arthur F.Dalley _Anne M.R. Agur ,Moore ,Seventh edition , S723,737-738 ,743
Richard L. Drake _A.wayne vogl _ Adam W. M. Mitchell , Gray Anatomy , Fourth edition , S 731,749
Lawrence E. Winest Snell , 10th edition ,S 344 ,356
Some parts of This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 936 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
Netter - plate 402
Musculocutaneous Nerve -Medbullets Step 1https://step1.medbullets.com/msk/107064/musculocutaneous-nerve
Musculocutaneous Nerve -Anatomy-Orthobullets https://www.orthobullets.com/anatomy/10102/musculocutaneous-nerve
Musculocutaneous Nerve Variations -ResearchGate https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Two-different-anatomical-variations-of-the-musculocutaneous-and-median-nerves-a-Typical_fig3_330451014
Musculocutaneous Nerve Variations -pulsus Group https://www.pulsus.com/scholarly-articles/variations-in-branching-pattern-of-musculocutaneous-nerve-with-respect-to-communicating-branch-between-musculocutaneous-and-median-4655.html
The brachial plexus- Nysora https://www.nysora.com/
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm-Wiley Online Library https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.7863/ultra.33.8.1475
Musculocutaneous Nerve - Physiopedia
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Musculocutaneous_Nerve
The Musculocutaneous Nerve - TeachMeAnatomy https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/nerves/musculocutaneous-nerve/
Kenhub - Musculocutaneous nerve https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-musculocutaneous-nerve
Keith L.Moore _Arthur F.Dalley _Anne M.R. Agur ,Moore ,Seventh edition , S723,737-738 ,743
Richard L. Drake _A.wayne vogl _ Adam W. M. Mitchell , Gray Anatomy , Fourth edition , S 731,749
Lawrence E. Winest Snell , 10th edition ,S 344 ,356
Some parts of This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 936 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
