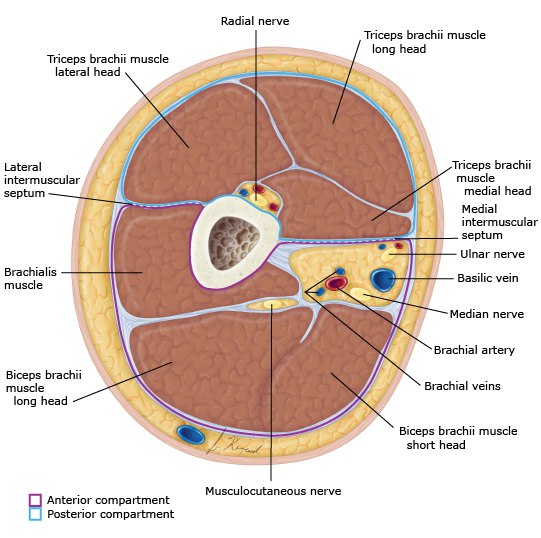
Deep fascia anterior and posterior compartment of arm
By : zahraa Al-ObaidiDefinition
Deep fascia (also known as the brachial fascia) is a thick connective tissue that surrounds, encases, and protects the organs, and creates septa on the bones to form the chambers، It also surrounds the nerves and blood vessels.
There are extended septa from this fascia. The septa extend between the muscles of the arm, the medial intermuscular septum and lateral intermuscular septum.
This septum forms the compartments of the arm:
1- anterior compartment.
2- posterior compartment.
figure no1
There are extended septa from this fascia. The septa extend between the muscles of the arm, the medial intermuscular septum and lateral intermuscular septum.
This septum forms the compartments of the arm:
1- anterior compartment.
2- posterior compartment.
figure no1
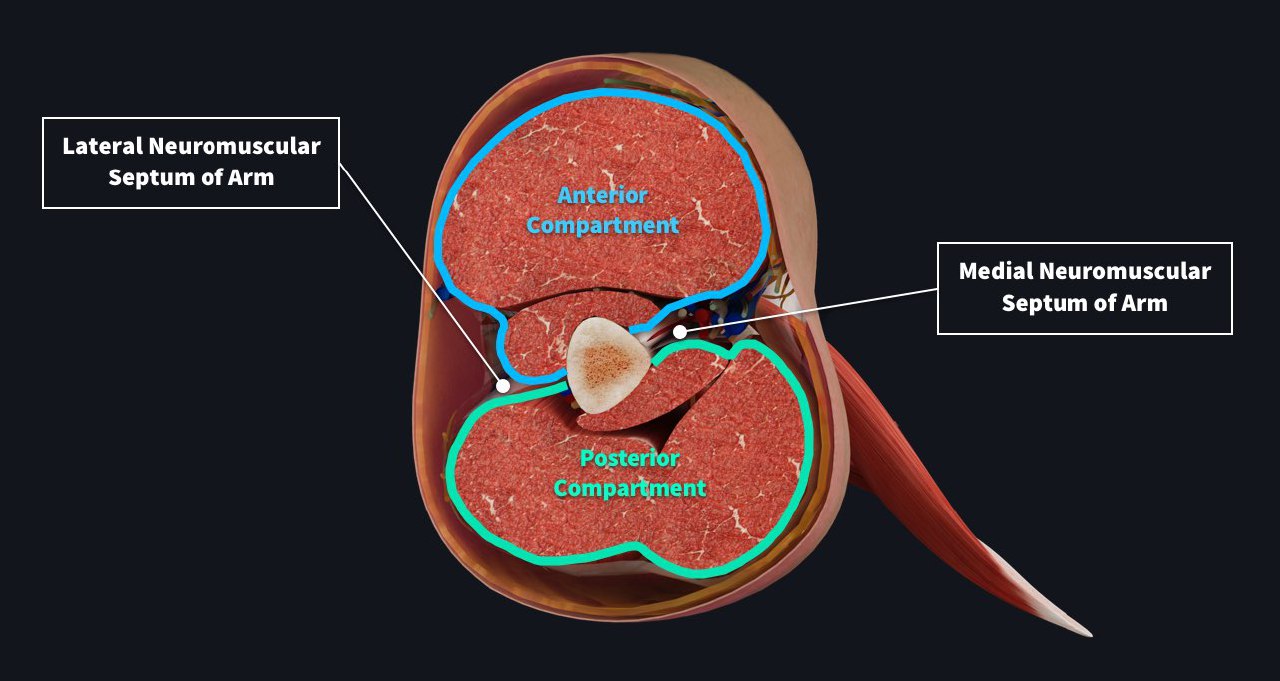
Medial intermuscular septum
It is the thickest septum in the arm extending from crest of lesser tubercle of humerus to the medial epicondyle of humerus.
It is mingled with Coracobrachialis tendon and also gives attachments to:
1-Infront:Brachialis muscle
2-Behind:Triceos brachii muscle the medial Intermuscular septum is pierced by many structures:
•Ulnar nerve
•Superior ulnar collateral artery and posterior branch of inferior ulnar collateral artery.
It is mingled with Coracobrachialis tendon and also gives attachments to:
1-Infront:Brachialis muscle
2-Behind:Triceos brachii muscle the medial Intermuscular septum is pierced by many structures:
•Ulnar nerve
•Superior ulnar collateral artery and posterior branch of inferior ulnar collateral artery.
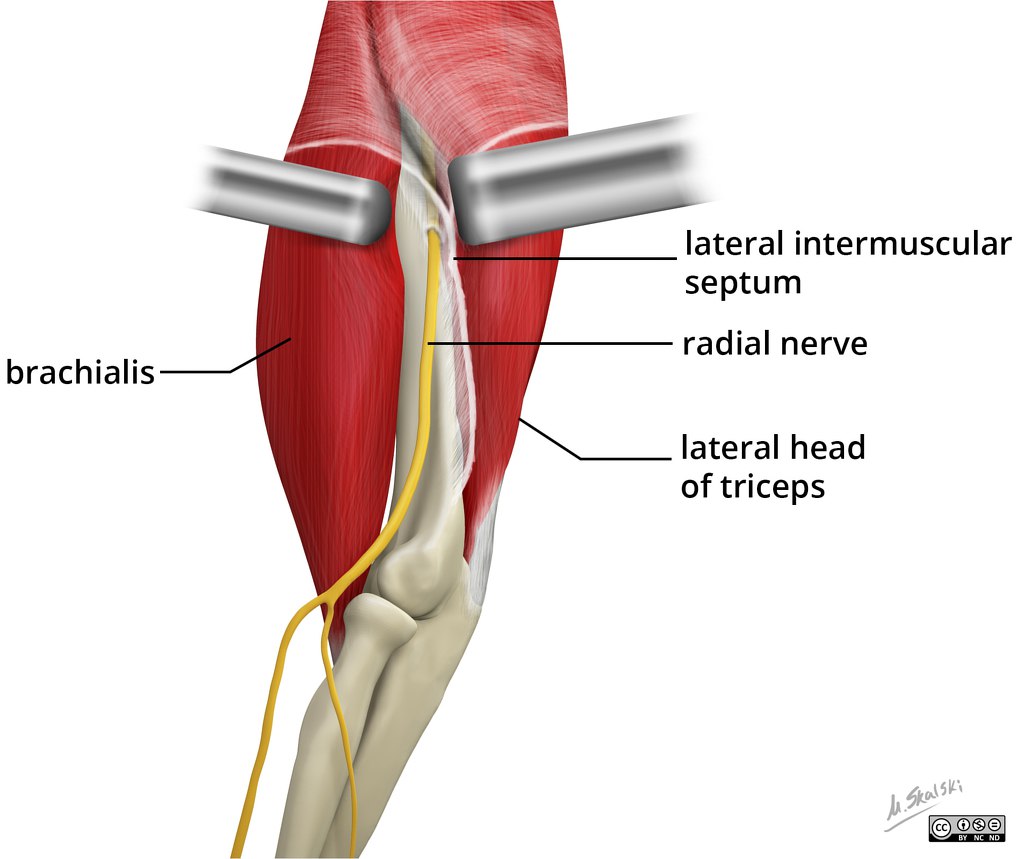
Lateral intermuscular septum
It is thinner than medial intermuscular septum, extending from the crest of greater tuberosity of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of humerus.
It is pierced by the radial nerve (the radial nerve pierces the lateral intermuscular septum before being divided to the deep and superficial branches). Lateral intermuscular septum damage may cause radial nerve compression. figure no2
These septum form the compartments of the arm (anterior compartment and posterior compartment)
It is pierced by the radial nerve (the radial nerve pierces the lateral intermuscular septum before being divided to the deep and superficial branches). Lateral intermuscular septum damage may cause radial nerve compression. figure no2
These septum form the compartments of the arm (anterior compartment and posterior compartment)
Anterior compartment of the arm
It is located in the front of the arm and is also called(the flexor compartment because all the muscles there do the flexion at elbow joint and adduction of the arm at the shoulder joint).
It contains three muscles:
1-Biceps brachii
2-brachialis
3-coracobrachialis
all these muscles do flexion of the arm.figure no3
Nerve Supply
The nerve supply of the anterior compartment is done by the musculocutaneous nerve(C5,6,7). the musculocutaneous pierces the coracobrachialis muscle.
Blood Supply the blood supply of the anterior compartment is done by the brachial artery.
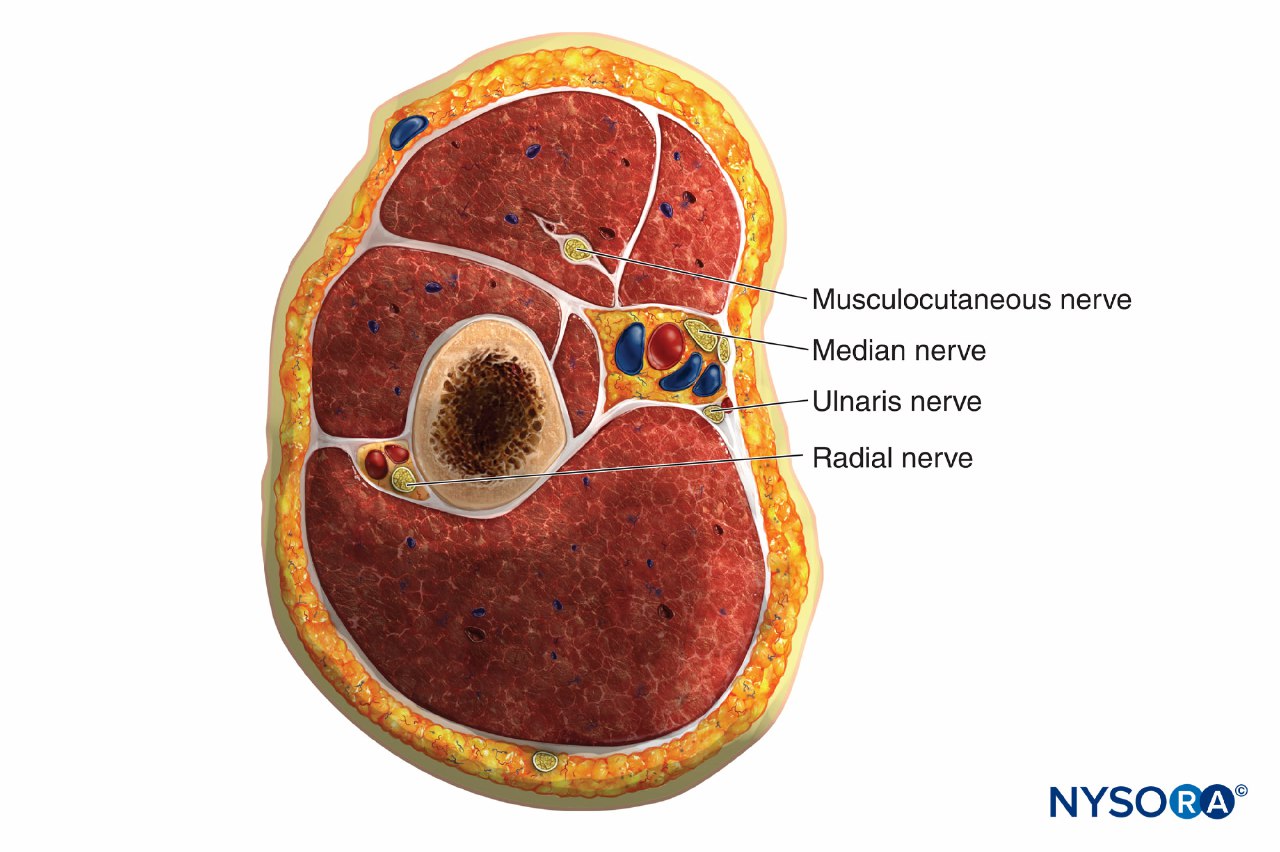
It contains many structures:
1-Brachial artery
2-Musculocutaneos nerve
3-Median nerve
4-Ulnar nerve

posterior compartment of the arm
Also called the extensor compartment , which is located behind the arm and contains triceps muscle and anconeus muscle.
These muscles do extension of the arm.figure no4
Nerve Supply
The nerve supply of the posterior compartment is done by the radial nerve(C5,6,7,8 and T1).
Blood Supply
•The blood supply of the posterior compartment is done by the profunda brachii artery.
Note :
•The radial nerve arises from (C5-C6-C7-C8-T1), from the posterior cord of brachial plexus. it runs together with deep branch of brachial artery(profunda brachial artery). it runs through the spiral groove ( radial groove) in the humerus bone.
•The radial nerve pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to convert from posterior compartment to the anterior compartment.
These muscles do extension of the arm.figure no4
Nerve Supply
The nerve supply of the posterior compartment is done by the radial nerve(C5,6,7,8 and T1).
Blood Supply
•The blood supply of the posterior compartment is done by the profunda brachii artery.
Note :
•The radial nerve arises from (C5-C6-C7-C8-T1), from the posterior cord of brachial plexus. it runs together with deep branch of brachial artery(profunda brachial artery). it runs through the spiral groove ( radial groove) in the humerus bone.
•The radial nerve pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to convert from posterior compartment to the anterior compartment.

Compartment Syndrome:
This condition occurs due to the increased pressure inside the compartment, which leads to reduce the blood flow and pressure on the nerve and damage the muscles in this area.
It occurs in many parts of the body, especially the leg and the arm.
The injury is discovered by measuring the pressure in that area, the doctor places a needle inside the part and measures the pressure in the area or a plastic catheter to monitor the pressure.
The fascia of the compartment is characterized by being strong and does not stretch easily.
When a Compartment Syndrome occurs, it leads to a fluid accumulation due to inflammation and injury, which increases pressure within the area and prevents blood flow to tissues and muscles, which leads to damage the organs and parts of the body and may lead to function loss and even death in serious cases.
In advanced cases, the disease is chronic.figure no5
It occurs in many parts of the body, especially the leg and the arm.
The injury is discovered by measuring the pressure in that area, the doctor places a needle inside the part and measures the pressure in the area or a plastic catheter to monitor the pressure.
The fascia of the compartment is characterized by being strong and does not stretch easily.
When a Compartment Syndrome occurs, it leads to a fluid accumulation due to inflammation and injury, which increases pressure within the area and prevents blood flow to tissues and muscles, which leads to damage the organs and parts of the body and may lead to function loss and even death in serious cases.
In advanced cases, the disease is chronic.figure no5
Causes
1- a broken bone.
2- a wound or an injury due to an operation in the blood vessels of the arm.
3- or due to wrong movements due to exercise or other injuries.
2- a wound or an injury due to an operation in the blood vessels of the arm.
3- or due to wrong movements due to exercise or other injuries.
Symptoms
1- severe pain in the area, the pain increases when pressure is applied.
2- swelling and puffiness (due to the fluids accumulation ).
3- Numbness.
4- there may be bruises.
5- As for chronic cases, there is stronger pain and muscle spasm.
2- swelling and puffiness (due to the fluids accumulation ).
3- Numbness.
4- there may be bruises.
5- As for chronic cases, there is stronger pain and muscle spasm.
Treatment
1-Treatment may relieve pain with rest and when pressure is removed (pressure may be due to strong and tight bandages), the bandages must be removed.
2-Analgesics are taken and strenuous movements that lead to increased pressure are avoided and the affected part or arm is placed below the level of the heart.
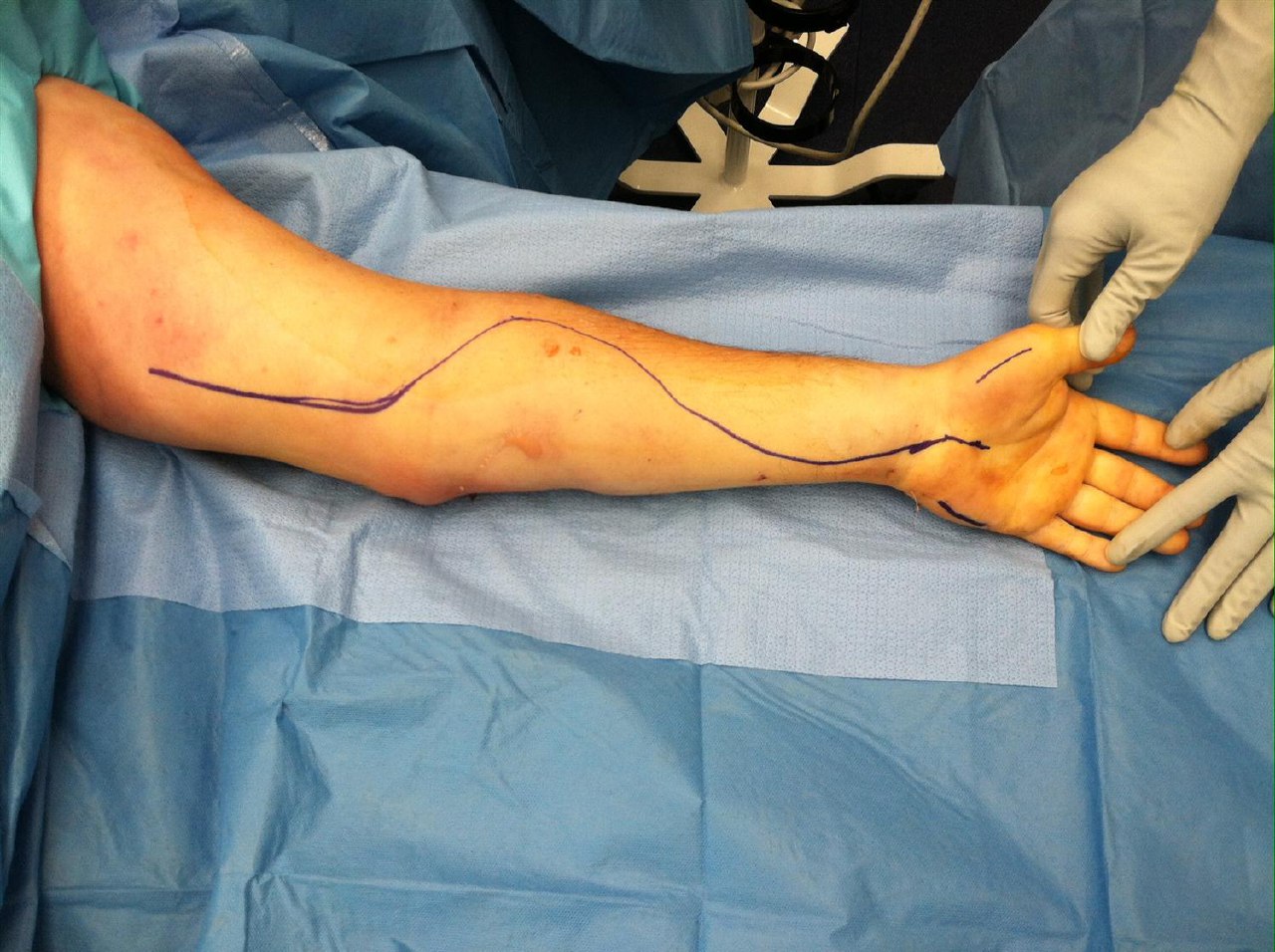
3-In severe cases, there may be a surgical treatment where the surgeon releases the pressure (makes a longitudinal incision in the skin), releases fluids and reduces pressure.
figure no6
References
1. compartment Syndrome; Matthew Hoffman, MD;Medically Reviewed by Carol DerSarkissian, MD ;October 19, 2020
2. Compartment Syndrome: Causes, Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatments;https://www.webmd.com/painmanagement/guide/c ompartment-syndrome-causes-treatments
3. Nerves of the Anterior & Posterior Compartments of the Arm; lesson4nervesofant&postarm; https://tinyurl.com/2vbdcew5
4. Anterior compartment of the arm ; Radiology Reference Article ; Radiopaedia.org;https://radiopaedia.org/articles/anteriorcompartment-of-the-arm
5. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012)
6. Moore KL, Dalley AF. Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (1999)
7. Identification and Surgical Management of Upper Arm and Forearm Compartment Syndrome; Adel Hanandeh, Vishnu R. Mani, Paul Bauer, Alexius Ramcharan, Brian Donaldson; National Library of Medicine; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31763085/
2. Compartment Syndrome: Causes, Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatments;https://www.webmd.com/painmanagement/guide/c ompartment-syndrome-causes-treatments
3. Nerves of the Anterior & Posterior Compartments of the Arm; lesson4nervesofant&postarm; https://tinyurl.com/2vbdcew5
4. Anterior compartment of the arm ; Radiology Reference Article ; Radiopaedia.org;https://radiopaedia.org/articles/anteriorcompartment-of-the-arm
5. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012)
6. Moore KL, Dalley AF. Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (1999)
7. Identification and Surgical Management of Upper Arm and Forearm Compartment Syndrome; Adel Hanandeh, Vishnu R. Mani, Paul Bauer, Alexius Ramcharan, Brian Donaldson; National Library of Medicine; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31763085/
References of figures
interface figure Compartments of the brachium - UpToDate
https://images.app.goo.gl/q1h7oJjodBdWiqew8
figure no1 Muscle compartments of the upper arm | Complete Anatomy
https://images.app.goo.gl/YFjgXfBaviyVACnQ9
figure no2
Radial nerve anatomy (illustrations) | Radiology Case ...
https://images.app.goo.gl/AsqvSTYvnk6R5Hyu9
figure no3 Arm - Anterior and Posterior Compartments , muscles of flexor and ...https://images.app.goo.gl/eYRwSeu6UPGJitKf6
figure no4
Arm: Anatomy [+video] - Lecturio Medical
https://images.app.goo.gl/PYsWXvydHsfMqupj9
figure no5
Acute Compartment Syndrome of the Limb: Implications for Regional ...
https://images.app.goo.gl/xmzA3mFCFxUhQdKr5
figure no6 Hand & Forearm Compartment Syndrome - Trauma - Orthobullets
https://images.app.goo.gl/g4PwNsnrNgmzbUrY7
https://images.app.goo.gl/q1h7oJjodBdWiqew8
figure no1 Muscle compartments of the upper arm | Complete Anatomy
https://images.app.goo.gl/YFjgXfBaviyVACnQ9
figure no2
Radial nerve anatomy (illustrations) | Radiology Case ...
https://images.app.goo.gl/AsqvSTYvnk6R5Hyu9
figure no3 Arm - Anterior and Posterior Compartments , muscles of flexor and ...https://images.app.goo.gl/eYRwSeu6UPGJitKf6
figure no4
Arm: Anatomy [+video] - Lecturio Medical
https://images.app.goo.gl/PYsWXvydHsfMqupj9
figure no5
Acute Compartment Syndrome of the Limb: Implications for Regional ...
https://images.app.goo.gl/xmzA3mFCFxUhQdKr5
figure no6 Hand & Forearm Compartment Syndrome - Trauma - Orthobullets
https://images.app.goo.gl/g4PwNsnrNgmzbUrY7
