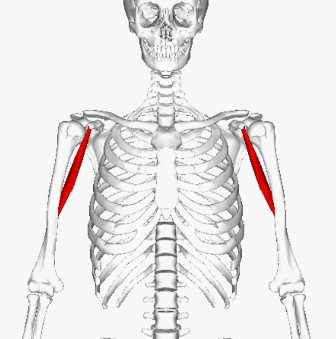
Coracobrachialis
By : Fahad Al-BakThe Naming:-
/KOR-a-ko-BRA-key-AL-is/
coraco: as in the coracoid process of the scapula.
brachialis: meaning the arm (brachium [the arm]).
coraco: as in the coracoid process of the scapula.
brachialis: meaning the arm (brachium [the arm]).
General:-
-A Muscle of the anterior compartment; located in the superomedial part of the arm. It is an elongated muscle, unlike the Biceps Brachii and the Brachialis, this muscle belongs to the Muscles of the Glenohumeral Joint.
Surface: -
- It is possible to view the muscle from the anterior side of it.
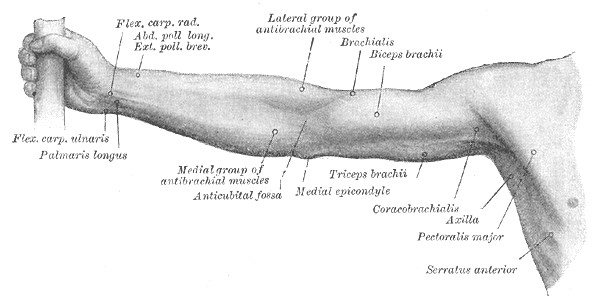
Supply: -
It gets the blood supply from the muscular branches of the Brachial Artery (the continuation of the Axillary Artery) and the Anterior Circumflex Humeral Artery (a branch of the Axillary Artery).
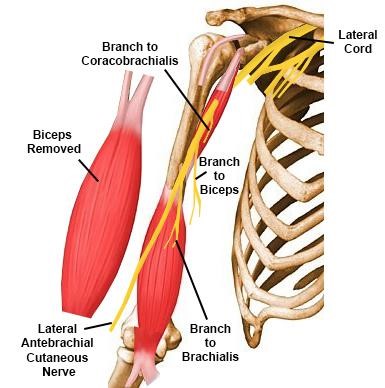
The nerve supply for the Coracobrachialis is the Musculocutaneous n.
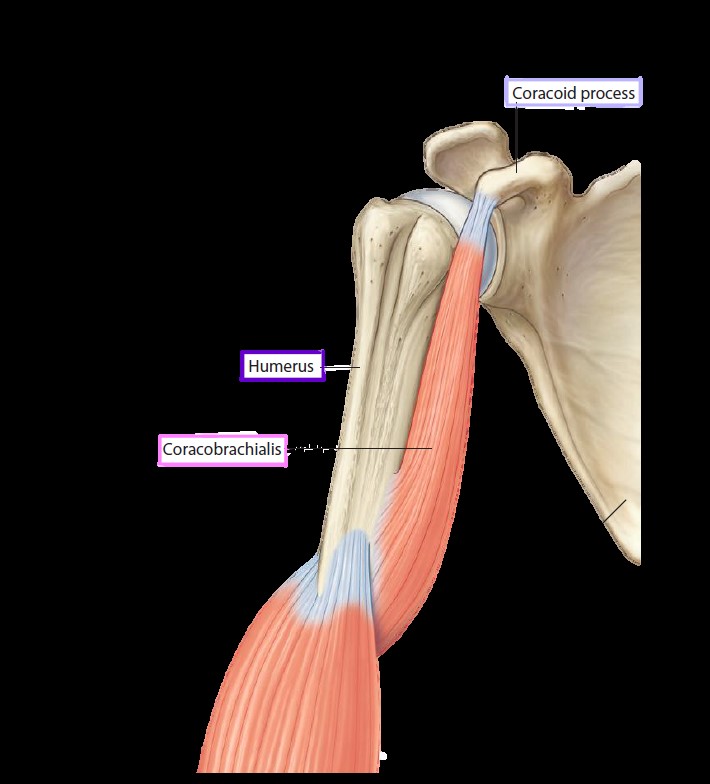
Origin & Insertion
Origin: Tip of coracoid process of scapula (the apex).
Insertion: Middle third of medial surface of humerus.
Motion & Action
-The coracobrachialis helps flex and adduct the arm and stabilize the glenohumeral joint (the Shoulder joint).
-When the arm is abducted and extended, the coracobrachialis muscle acts as a strong antagonist to the deltoid muscle.
-With the deltoid and long head of the triceps, it serves as a shunt muscle, resisting downward dislocation of the head of the humerus, as when carrying a heavy suitcase.
-When the arm is abducted and extended, the coracobrachialis muscle acts as a strong antagonist to the deltoid muscle.
-With the deltoid and long head of the triceps, it serves as a shunt muscle, resisting downward dislocation of the head of the humerus, as when carrying a heavy suitcase.
On Your Feet Notes/ In The Field Notes: -
- Coracobrachialis is a useful landmark for other structures in the arm.
For example: the musculocutaneous nerve pierces it, and the distal part of its attachment indicates the location of the nutrient foramen of the humerus.
For example: the musculocutaneous nerve pierces it, and the distal part of its attachment indicates the location of the nutrient foramen of the humerus.
Clinical Notes: -
-The overuse of the coracobrachialis can lead to a hardening of the muscle. Common causes include, among others, bench pressing with extremely heavy weights and carrying heavy loads with hanging arms. A typical symptom is pain in the arm and shoulder, radiating down to the back of the hand.
In more severe cases the musculocutaneous nerve, which goes through the coracobrachialis, can become trapped (entrapment). Clinically, the affected patients show skin sensation disturbances on the radial part of the forearm and a weakened flexion in the elbow, as the nerve also supplies the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. In contrast, an actual rupture of the coracobrachialis is extremely rare and almost only occurs in serious accidents.
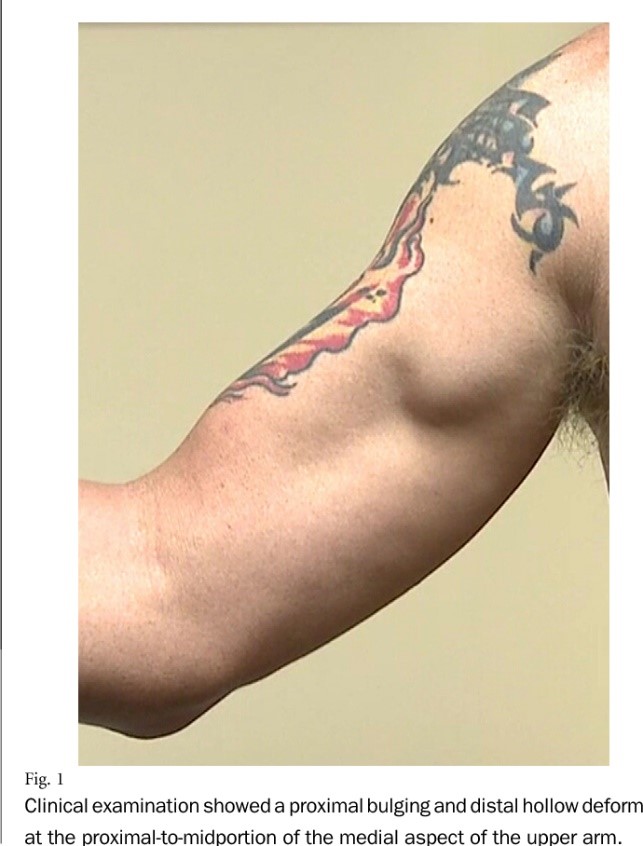
-Coracobrachialis Tendon Tear: Due to sudden movement of over use the tendon of the muscle may get weaken and rupture.
In more severe cases the musculocutaneous nerve, which goes through the coracobrachialis, can become trapped (entrapment). Clinically, the affected patients show skin sensation disturbances on the radial part of the forearm and a weakened flexion in the elbow, as the nerve also supplies the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. In contrast, an actual rupture of the coracobrachialis is extremely rare and almost only occurs in serious accidents.
-Coracobrachialis Tendon Tear: Due to sudden movement of over use the tendon of the muscle may get weaken and rupture.
Relations:-
-From an anterior perspective, the coracobrachialis lies deep to the deltoid and the pectoralis major.
-Proximally, the coracobrachialis lies medial to the short head of the biceps brachii. More distally, the coracobrachialis is deep to the short head of the biceps brachii.
-The coracobrachialis attaches onto the shaft of the humerus on the medial side between the attachments of the brachialis and the triceps brachii (medial head).
-The proximal attachment of the coracobrachialis is the coracoid process of the scapula. The short head of the biceps brachii and the pectoralis minor also attach to the coracoid process.
-The coracobrachialis is located within the deep front arm line myofascial meridian.
-Proximally, the coracobrachialis lies medial to the short head of the biceps brachii. More distally, the coracobrachialis is deep to the short head of the biceps brachii.
-The coracobrachialis attaches onto the shaft of the humerus on the medial side between the attachments of the brachialis and the triceps brachii (medial head).
-The proximal attachment of the coracobrachialis is the coracoid process of the scapula. The short head of the biceps brachii and the pectoralis minor also attach to the coracoid process.
-The coracobrachialis is located within the deep front arm line myofascial meridian.
Notes:-
1. The proximal attachment of the coracobrachialis blends with the proximal attachment of the short
head of the biceps brachii.
2. The musculocutaneous nerve pierces through the coracobrachialis.
head of the biceps brachii.
2. The musculocutaneous nerve pierces through the coracobrachialis.
Sources: -
- Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition.
- The Muscular System Manual: The Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body
Book by Joseph E Muscolino.
- Gray's Atlas of Anatomy 2nd Edition-2015.
-Traumatic Rupture of the Coracobrachialis Muscle: A Case Report
-Coracobrachialis Muscle -ken Hub
- The Muscular System Manual: The Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body
Book by Joseph E Muscolino.
- Gray's Atlas of Anatomy 2nd Edition-2015.
-Traumatic Rupture of the Coracobrachialis Muscle: A Case Report
-Coracobrachialis Muscle -ken Hub
