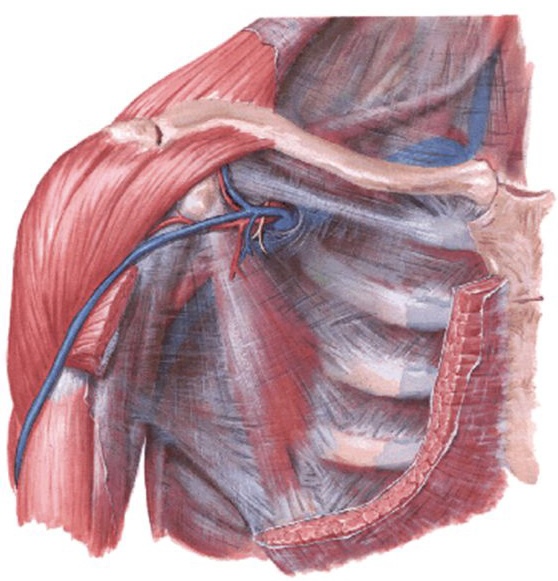
Clavipectoral fascia
By : Sarah NabeelDefinition of fascia
A fascia is a fibrous connective tissue found throughout the body.
The function of fascia is to wrap around the neurovascular structures,organs and muscles in order to reduce friction between adjacent structures as well as to protect them from abrasions.
The fascia of the body can be divided into three groups:
Superficial fascia: as the fascia of the anterior abdominal wall:
1-Camper's fascia(the fatty outer layer)
2-Scarpa's fascia(the deep membranous layer)
Deep fascia: as the fascia of the pectoral region (clavipectoral fascia).
Visceral or parietal fascia: as the pleural membrane of the lungs
The function of fascia is to wrap around the neurovascular structures,organs and muscles in order to reduce friction between adjacent structures as well as to protect them from abrasions.
The fascia of the body can be divided into three groups:
Superficial fascia: as the fascia of the anterior abdominal wall:
1-Camper's fascia(the fatty outer layer)
2-Scarpa's fascia(the deep membranous layer)
Deep fascia: as the fascia of the pectoral region (clavipectoral fascia).
Visceral or parietal fascia: as the pleural membrane of the lungs
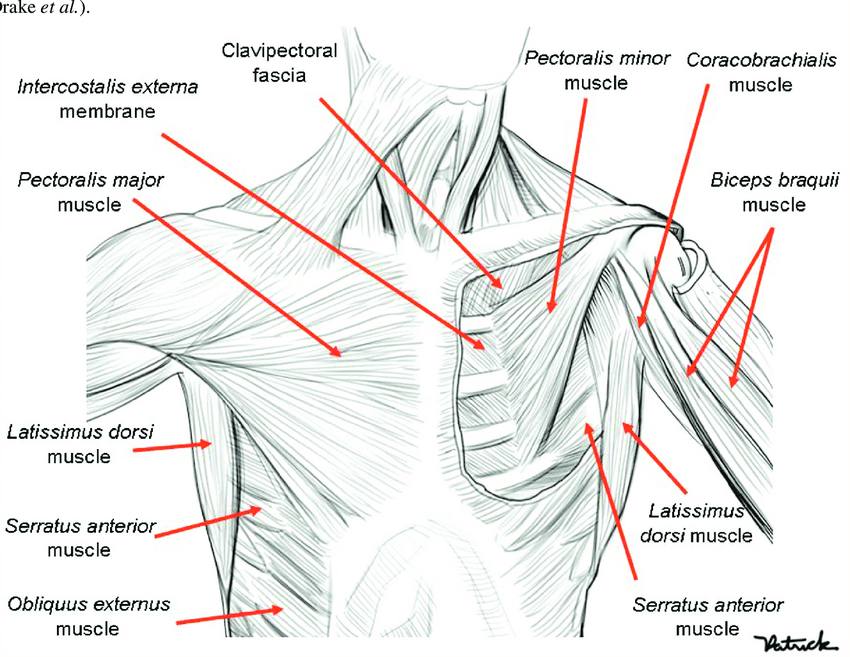
Clavipectoral fascia
A deep fascia in the pectoral region,suspends the floor of the axilla
The fascia runs as a loose connective tissue sheet between:
A)Medially
-First costal cartilage
-External intercostal membrane of first two intercostal spaces
B)Laterally
-coracoid process of scapula
-coracoclavicular ligament
C)Superiorly
-subclavian groove on the inferior surface of the clavicle
D)Inferiorly
-continuous with suspensory ligament of axilla
E)Deep
-continuous with axillaray sheath
F)Superficial
-deep fascia of pectoralis major muscle
The fascia runs as a loose connective tissue sheet between:
A)Medially
-First costal cartilage
-External intercostal membrane of first two intercostal spaces
B)Laterally
-coracoid process of scapula
-coracoclavicular ligament
C)Superiorly
-subclavian groove on the inferior surface of the clavicle
D)Inferiorly
-continuous with suspensory ligament of axilla
E)Deep
-continuous with axillaray sheath
F)Superficial
-deep fascia of pectoralis major muscle
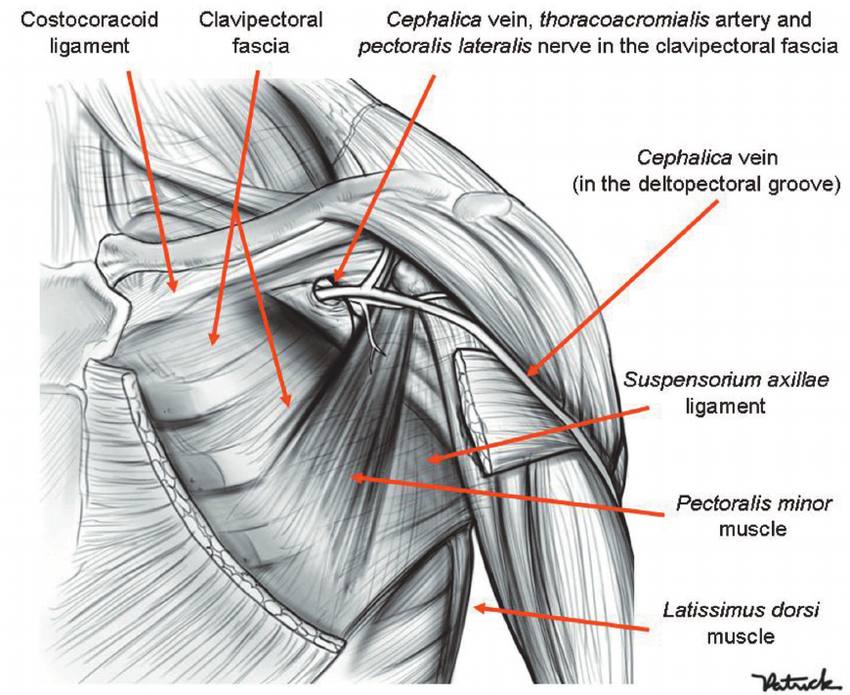
The structures that pierced clavipectoral fascia
1-Cephalic vein
2-Thoracoacromial artery and vein
3-Lymphatics
4-Lateral pectoral nerve
2-Thoracoacromial artery and vein
3-Lymphatics
4-Lateral pectoral nerve
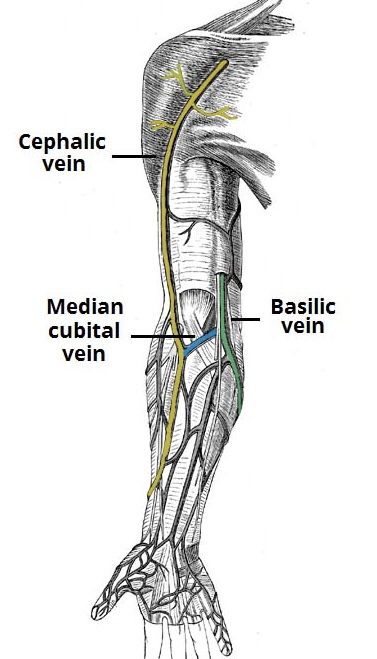
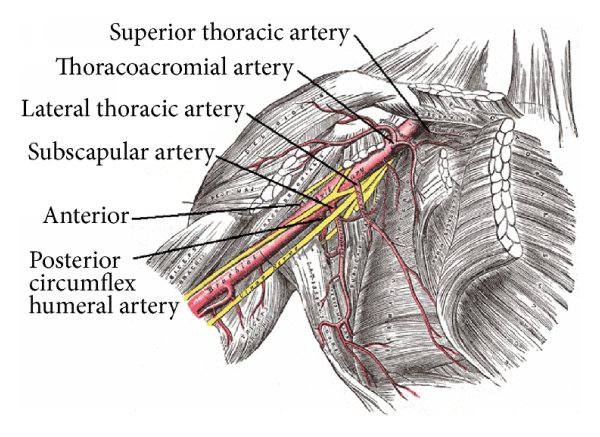
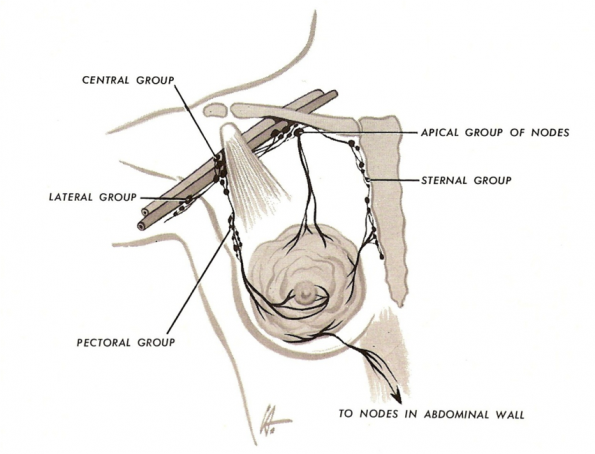
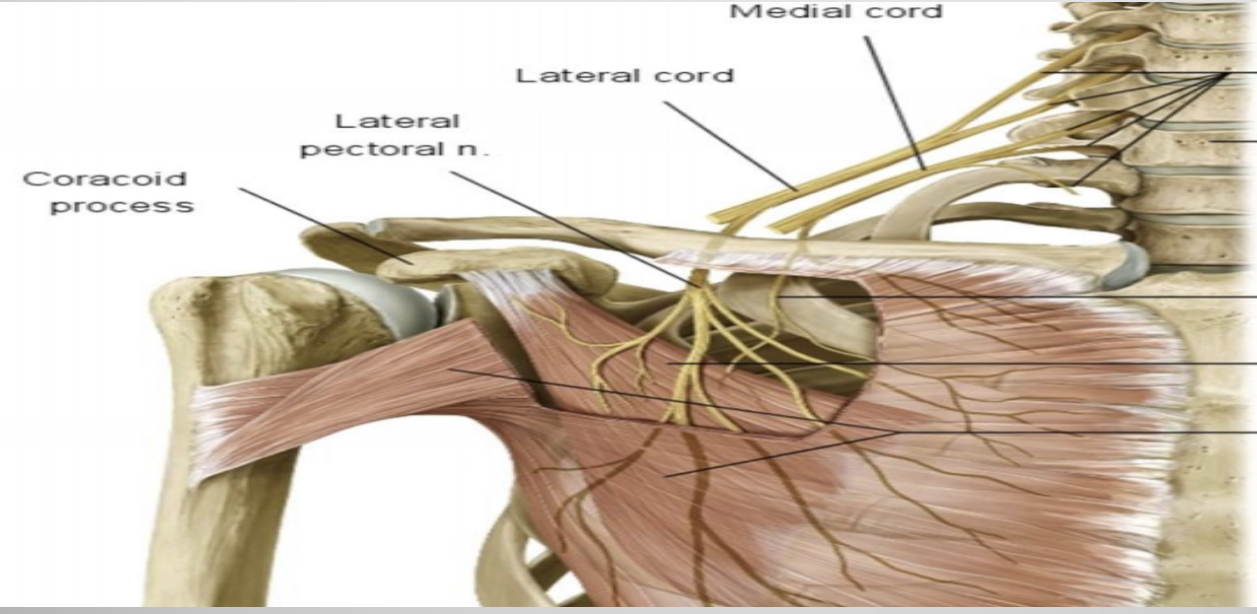
Cephalic vein
Function of clavipectoral fascia
Generally,the main role of fascia is to allow smooth movement of adjacent structure over each other
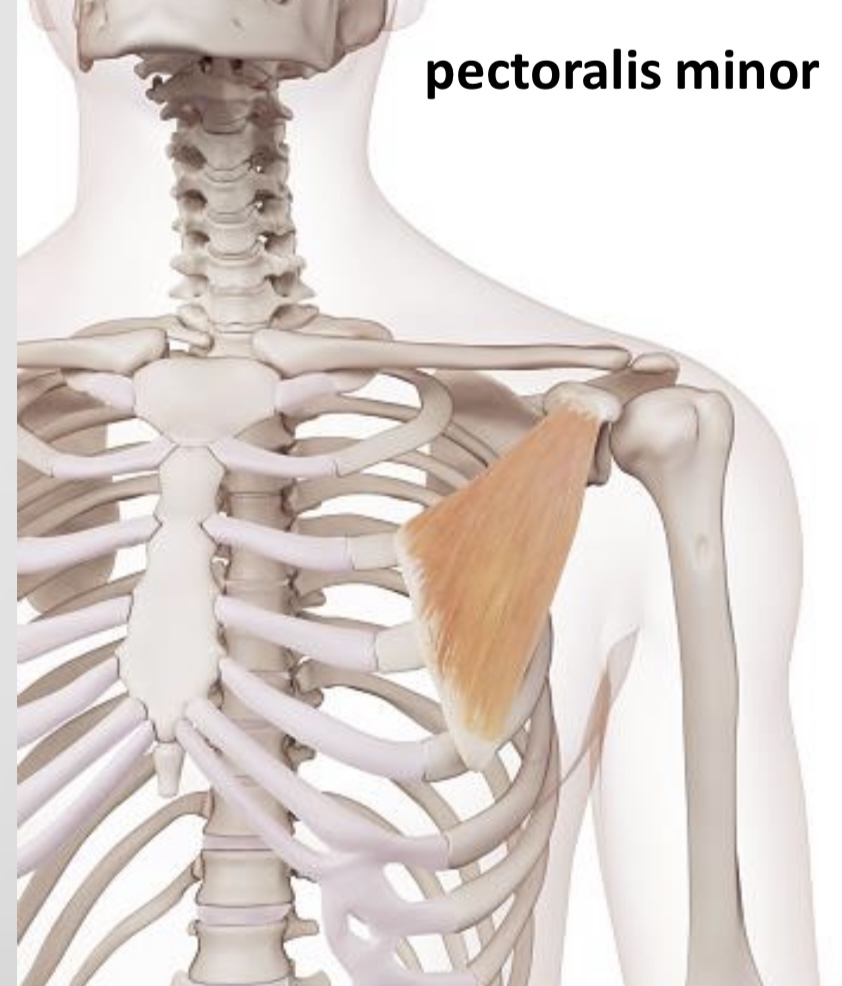
The clavipectoral fascia has no difference,it permits the gliding of pectoralis major muscle over pectoralis minor muscle
The clavipectoral fascia has no difference,it permits the gliding of pectoralis major muscle over pectoralis minor muscle
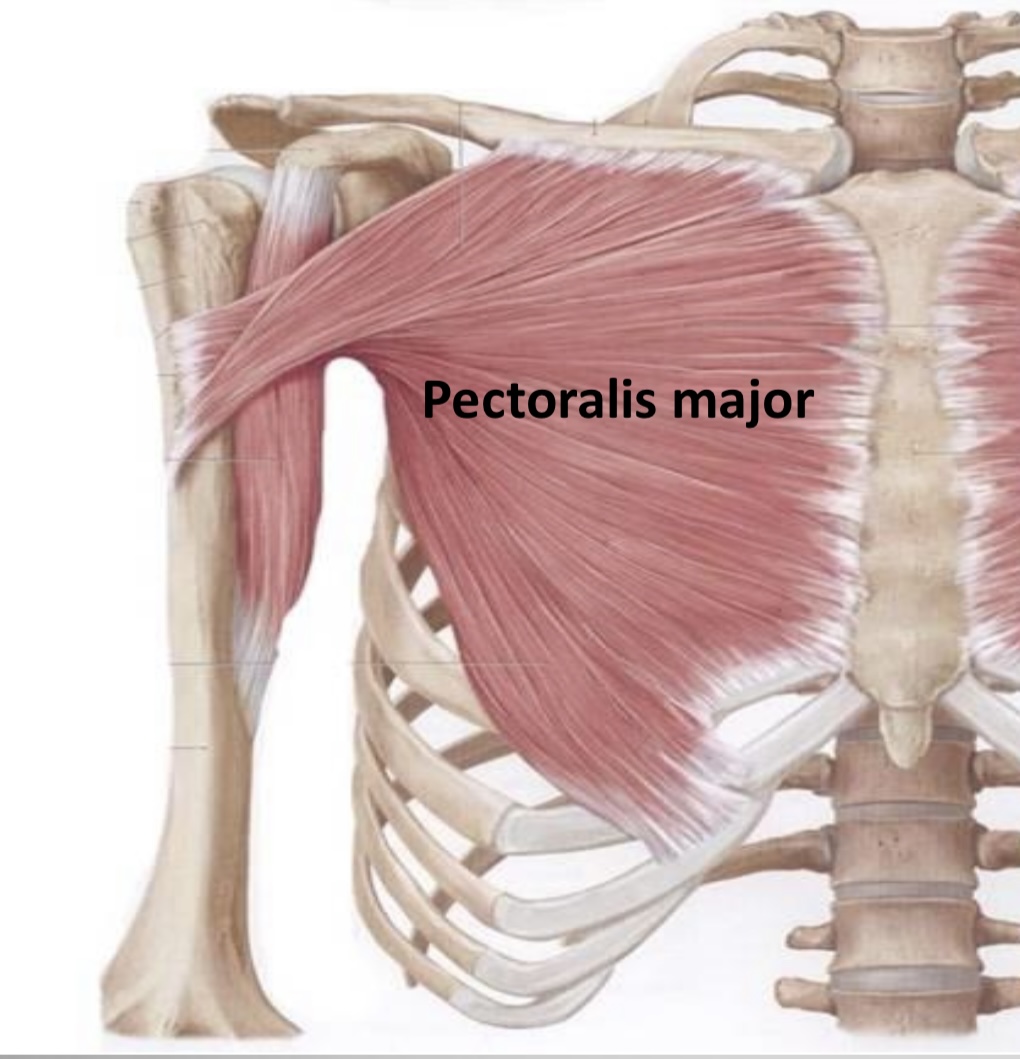
Surgical note
The clavipectoral fascia is frequently excised during shoulder arthroplasty( the process of replacing the shoulder joint).
A common complication of this procedure is joint immobility.
One referred factor is that the true clavipectoral fascia has been replaced by fibrotic tissue.
It’s removal and other scar tissue removal is important to manage this complication and it’s intergrity.
A common complication of this procedure is joint immobility.
One referred factor is that the true clavipectoral fascia has been replaced by fibrotic tissue.
It’s removal and other scar tissue removal is important to manage this complication and it’s intergrity.
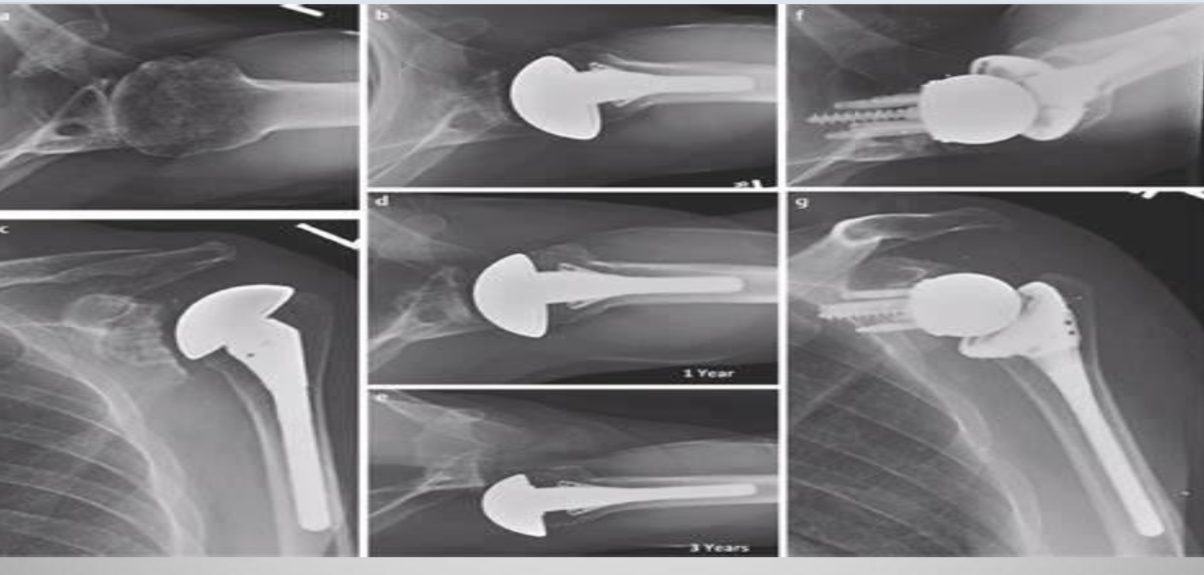
This radiographs show the shoulder joint after shoulder arthroplasty
References:
1-Sinnatamby,Chummy S, and R.J Last. Last’s Anatomy. 12th ed.
Edinburgh:Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier,2011.print.
2-Cofield,Robert H,and John W Sperling.Revision and Complex Shoulder Arthroplasty.1sr ed.Philadelphia:Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott William &Wilkins,2010.print
Reference for figures:
1-Color atlas of anatomy 7th:plate402
2-Hansen,John,and Frank H Netter .Better’s Atlas of Human Anatomy.
6th Ed.Philadelphia,penn
Sanders Elsevier,2014.Print
Edinburgh:Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier,2011.print.
2-Cofield,Robert H,and John W Sperling.Revision and Complex Shoulder Arthroplasty.1sr ed.Philadelphia:Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott William &Wilkins,2010.print
Reference for figures:
1-Color atlas of anatomy 7th:plate402
2-Hansen,John,and Frank H Netter .Better’s Atlas of Human Anatomy.
6th Ed.Philadelphia,penn
Sanders Elsevier,2014.Print
