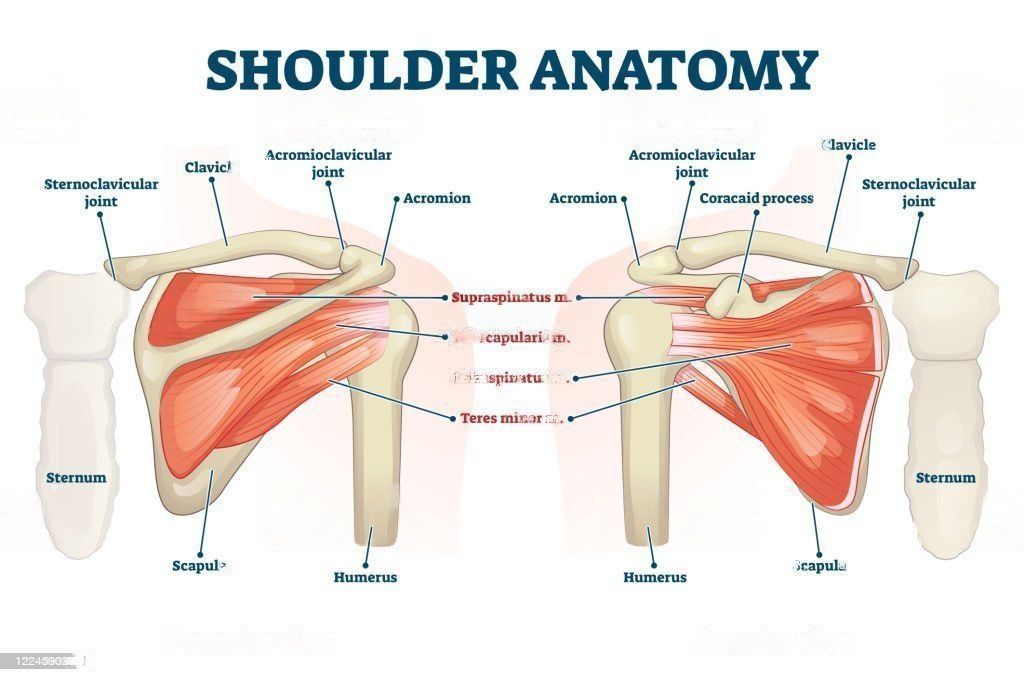
Common Shoulder Injuries
By : Yaser MohammedIntroduction
Shoulder injuries are widespread and frequently occur as this joint is the most mobile, least stable body part.
One of the causes of these injuries is that the ball of the upper arm is larger than the socket of the shoulder, which decreases its stability making it vulnerable to injuries , especially in athletic activities that involve excessive, repetitive, overhead motion (such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting). Even, Injuries can occur during everyday activities.
Most shoulder injuries involve the muscles, tendons, and ligaments rather than the bones , as we said, athletes suffer highly from these injuries because if they feel pain and play ignoring it this can cause a dislocation in the shoulder.
Shoulder injuries can be classified into three degrees of injuries:
One of the causes of these injuries is that the ball of the upper arm is larger than the socket of the shoulder, which decreases its stability making it vulnerable to injuries , especially in athletic activities that involve excessive, repetitive, overhead motion (such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting). Even, Injuries can occur during everyday activities.
Most shoulder injuries involve the muscles, tendons, and ligaments rather than the bones , as we said, athletes suffer highly from these injuries because if they feel pain and play ignoring it this can cause a dislocation in the shoulder.
Shoulder injuries can be classified into three degrees of injuries:
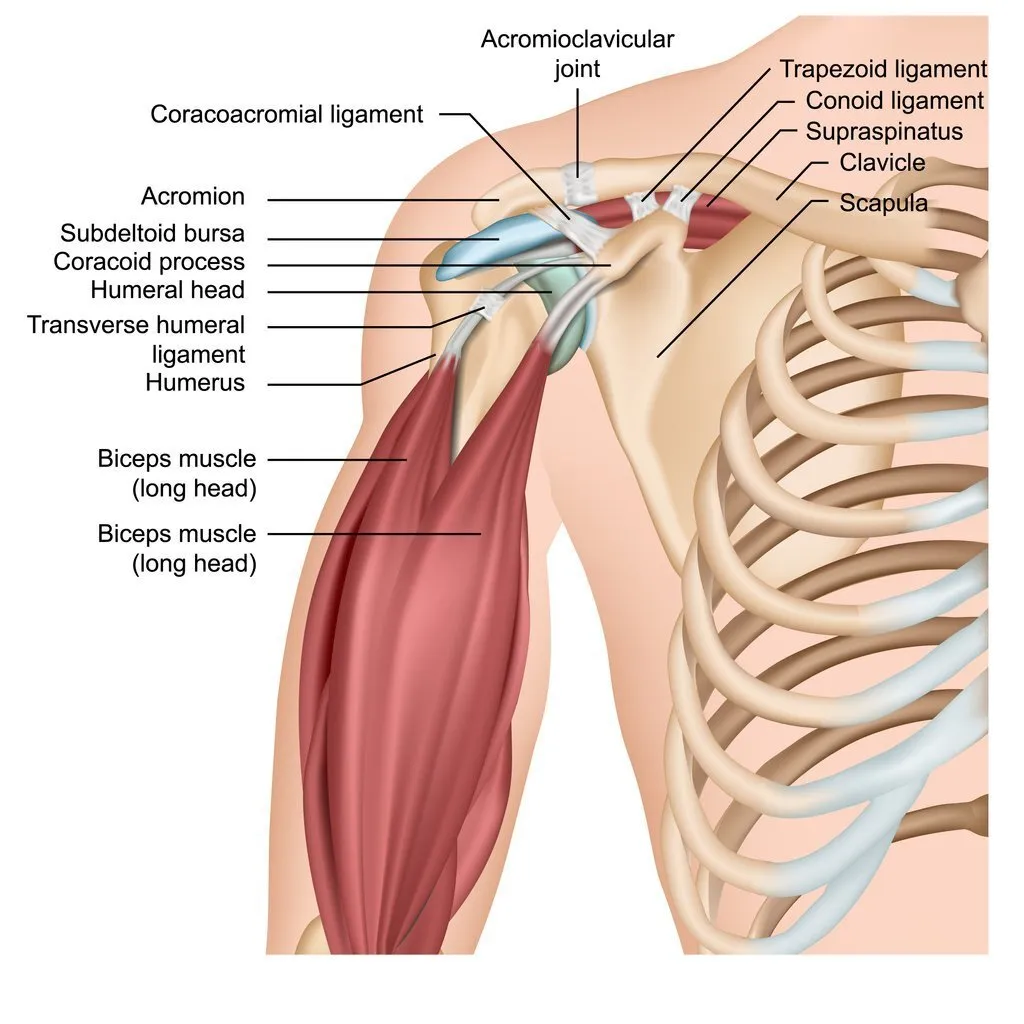
Shoulder Ligament Anatomy
1- Shoulder instability:
Shoulder instability happens most often in young people and athletes. When one of the shoulder joints moves or is forced out of its normal position. causing muscles and ligaments that hold the joint are stretched beyond their normal limits, The shoulder becomes unstable.
For younger people , this health problem may be a normal part of growth and development. Shoulders often stiffen or tighten with age. While in athletes , shoulder instability is caused by certain motions that put great force on the shoulder, stretching the shoulder ligaments over time. It can cause pain that comes on either quickly or gradually. Treatment includes rest, physical therapy, or surgery.
For younger people , this health problem may be a normal part of growth and development. Shoulders often stiffen or tighten with age. While in athletes , shoulder instability is caused by certain motions that put great force on the shoulder, stretching the shoulder ligaments over time. It can cause pain that comes on either quickly or gradually. Treatment includes rest, physical therapy, or surgery.
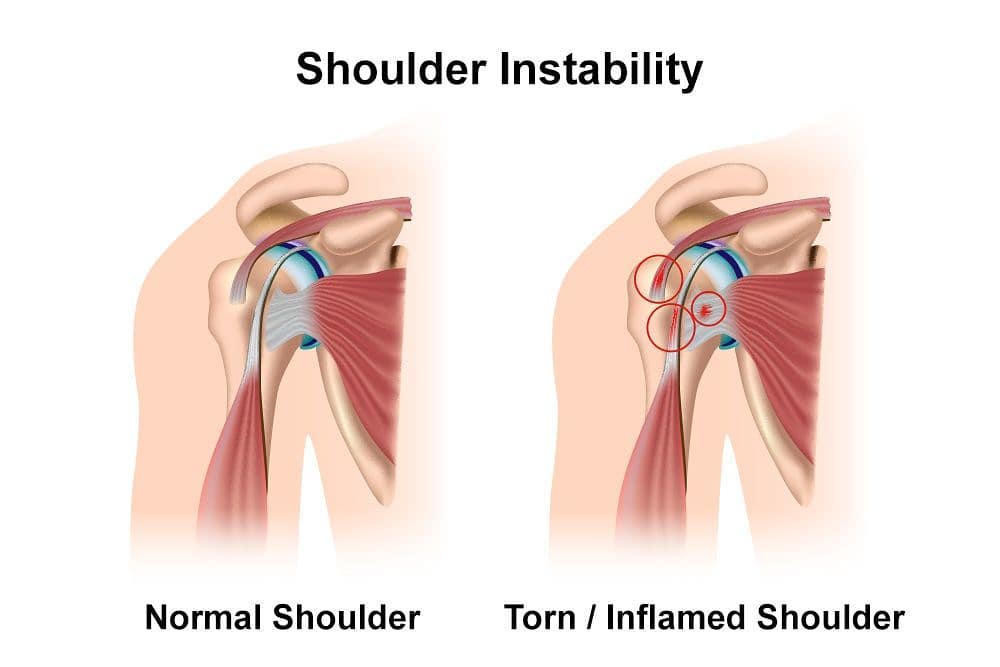
Instable shoulder comparing it with normal shoulder
2- Shoulder separation, or Sprain
Typically a shoulder spra in can occur when force is placed on the arm and stretches the shoulder ligaments. This motion causes tearing to the ligaments of the shoulder. While a shoulder separation happens when the ligaments that hold the clavicle to the acromion tear. causing the clavicle to be pushed out of place and may form a bump at the top of the shoulder.
Sprains often happen during falls (when your hand or arm is outstretched to stop the fall, or when you fall on a hard surface), car accidents, or sports injuries where the shoulder is directly impacted.
When the sprain happens, it causes high pain, a misshapen shoulder, and a decrease in shoulder movement.
Treatment depends on the severity of the sprain, but in most cases, it can be with nonsurgical treatments such as:
• Rest
• Sling
• Ice ( To help ease pain and swelling, apply ice right after the injury)
• Anti-inflammatory medication
• Physical therapy and rehabilitation
• Electrotherapy treatments
Sprains often happen during falls (when your hand or arm is outstretched to stop the fall, or when you fall on a hard surface), car accidents, or sports injuries where the shoulder is directly impacted.
When the sprain happens, it causes high pain, a misshapen shoulder, and a decrease in shoulder movement.
Treatment depends on the severity of the sprain, but in most cases, it can be with nonsurgical treatments such as:
• Rest
• Sling
• Ice ( To help ease pain and swelling, apply ice right after the injury)
• Anti-inflammatory medication
• Physical therapy and rehabilitation
• Electrotherapy treatments
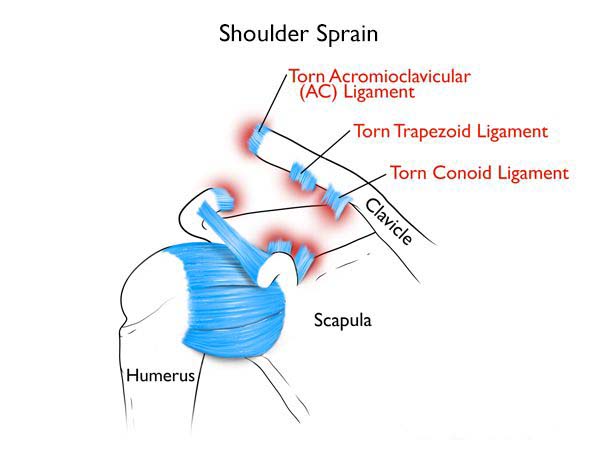
Shoulder sprain
3- Shoulder dislocation and subluxation
Shoulder subluxation occurs when the humeral head partially slides in and out of place. While shoulder dislocations occur when the humerus comes all the way out of the glenoid. These injuries occur when the ligaments that hold the shoulder bones tear and can't hold the joint together.
Falling onto an outstretched hand, arm or the shoulder itself can cause shoulder dislocation, causing pain on the shoulder that increases with movement.
Because the presence of the coracoacromial arch and support of the rotator cuff are effective in preventing upward dislocation, most dislocations of the humeral head occur in the downward (inferior) direction.
Anterior dislocation of the glenohumeral joint: occurs most often in young adults, particularly athletes. It occurs due to excessive extension and lateral rotation of the humerus. Causing the head of the humerus to be driven infero-anteriorly, and the fibrous layer of the joint capsule and glenoid labrum may be stripped from the anterior aspect of the glenoid cavity in the action.
Inferior dislocation of the glenohumeral joint: This dislocation often occurs after an avulsion fracture of the greater tubercle of the humerus, because of the absence of the upward and medial pull produced by muscles attaching to the tubercle.
Falling onto an outstretched hand, arm or the shoulder itself can cause shoulder dislocation, causing pain on the shoulder that increases with movement.
Because the presence of the coracoacromial arch and support of the rotator cuff are effective in preventing upward dislocation, most dislocations of the humeral head occur in the downward (inferior) direction.
Anterior dislocation of the glenohumeral joint:
Note
Anterior dislocation refers to the humeral head descends anterior to the infraglenoid tubercle and long head of the triceps.Inferior dislocation of the glenohumeral joint
Note
Posterior dislocation refers to the humeral head descends posterior to the infraglenoid tubercle and long head of the triceps.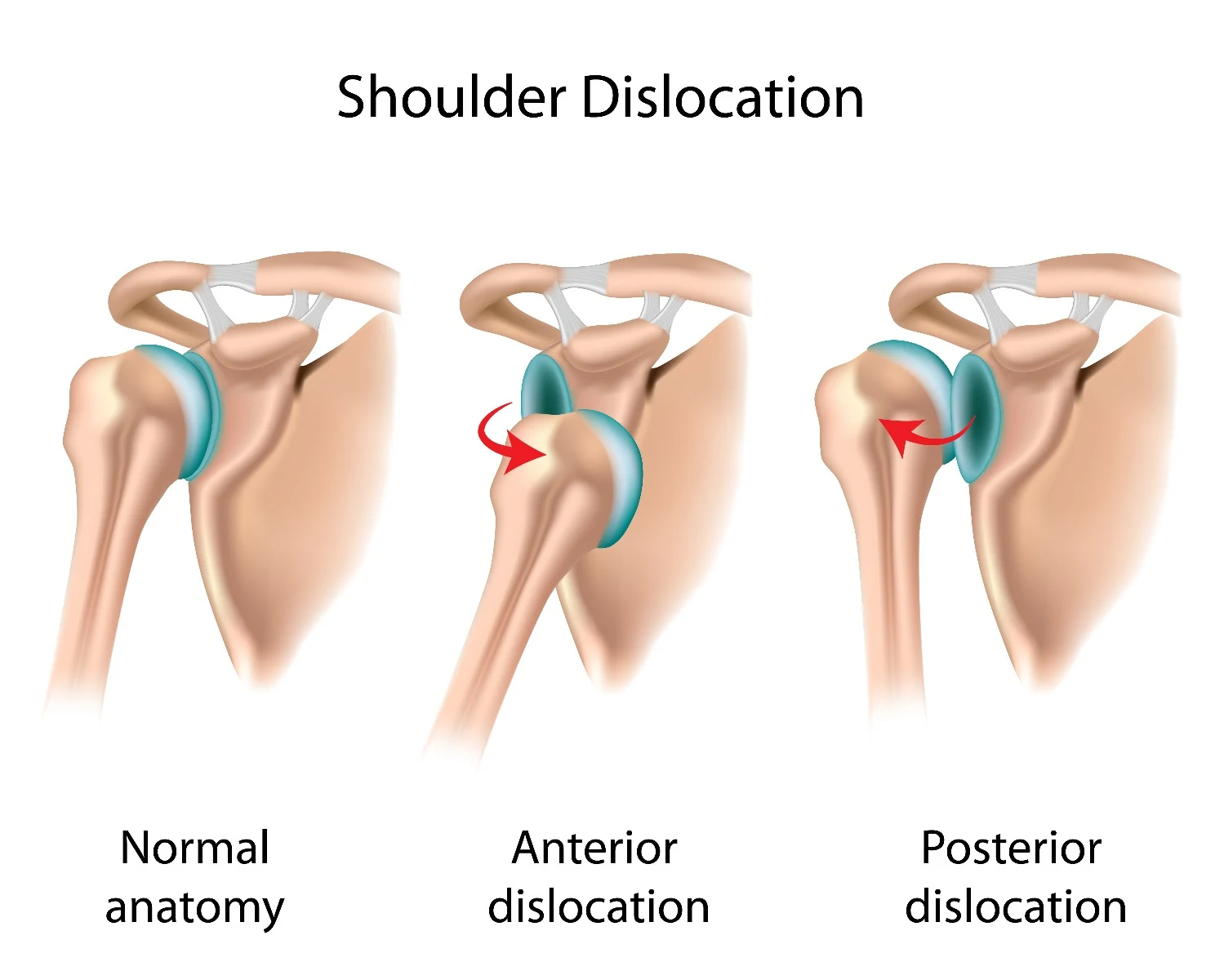
Anterior and posterior shoulder dislocations
Axillary Nerve Injury
The axillary nerve may be injured when the glenohumeral joint dislocates because of its close relation to the inferior part of the joint capsule. Axillary nerve injury causes paralysis of the deltoid which means the inability to abduct the arm to or above the
horizontal level ( ROM 15 to 180 degrees ) and loss of sensation in a small area of skin covering the central part of the deltoid. These symptoms can help us in indication.
horizontal level ( ROM 15 to 180 degrees ) and loss of sensation in a small area of skin covering the central part of the deltoid. These symptoms can help us in indication.
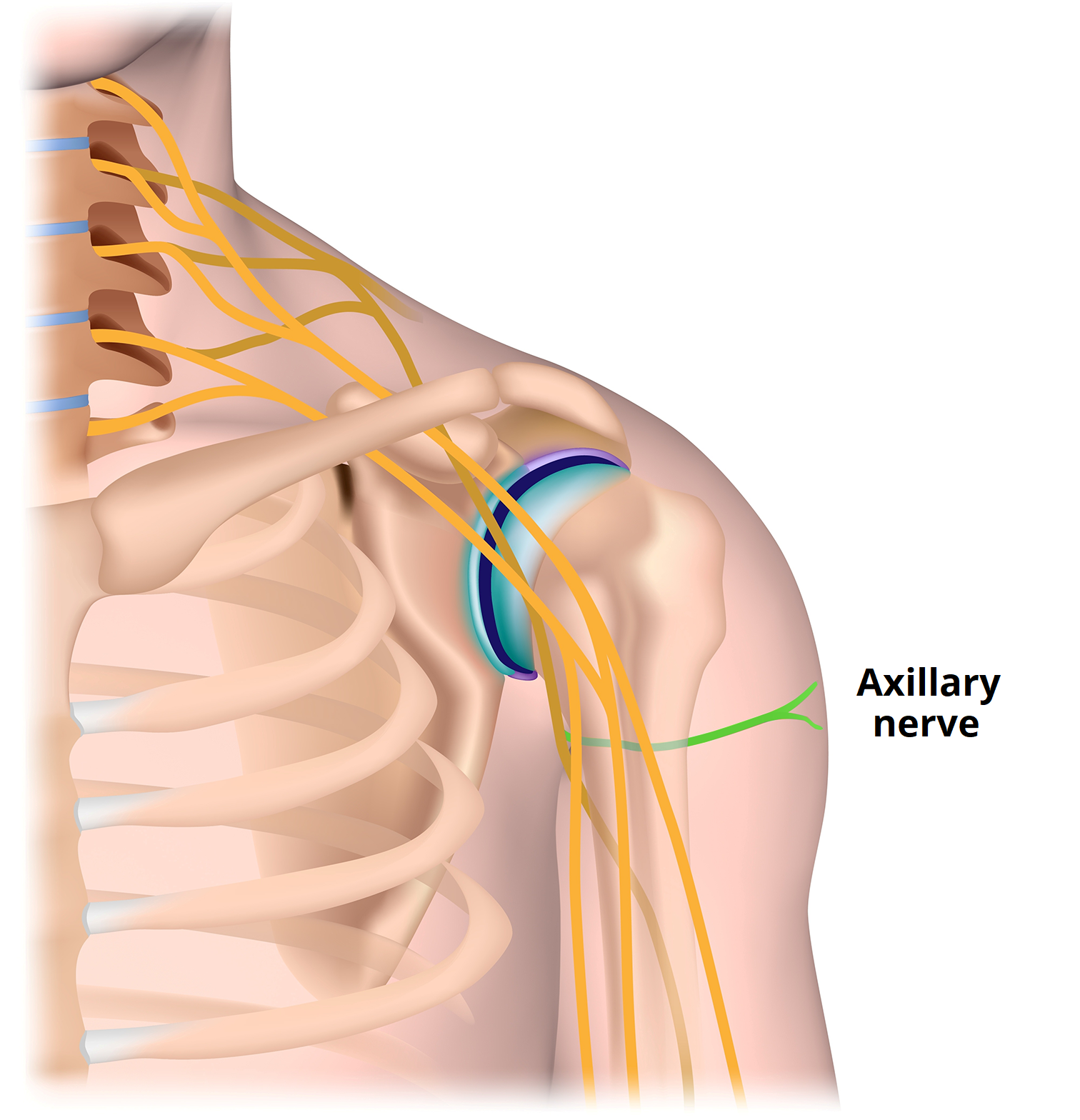
Overview of the course of the axillary nerve.
Glenoid Labrum Tears
The labrum is a tough ring of cartilage found in the GH joint, it connects the ball and socket joint bones and holds them together allowing them to move smoothly with as little pain as possible (as in the shoulder and the hip joints ) here it connects the humeral head to the scapula.
Therefore, when the labral tear occurs, the ball and socket may dislodge or disconnect from each other, causing instability and loss of lubrication, causing sharp pain.
Tearing of the fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum commonly occurs in athletes and in those who already have shoulder instability and subluxation (partial dislocation) of the glenohumeral joint.
This tear often results from the sudden contraction of the biceps or forceful subluxation of the humeral head over the glenoid labrum. Usually, a tear occurs in the anterosuperior part of the labrum.
Physical activities that help to treat Shoulder Injuries:
• Shoulder Exercises.
• Basic shoulder strengthening.
• Wall push-ups.
• Shoulder press-ups.
Therefore, when the labral tear occurs, the ball and socket may dislodge or disconnect from each other, causing instability and loss of lubrication, causing sharp pain.
Tearing of the fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum commonly occurs in athletes and in those who already have shoulder instability and subluxation (partial dislocation) of the glenohumeral joint.
This tear often results from the sudden contraction of the biceps or forceful subluxation of the humeral head over the glenoid labrum. Usually, a tear occurs in the anterosuperior part of the labrum.
Physical activities that help to treat Shoulder Injuries:
• Shoulder Exercises.
• Basic shoulder strengthening.
• Wall push-ups.
• Shoulder press-ups.
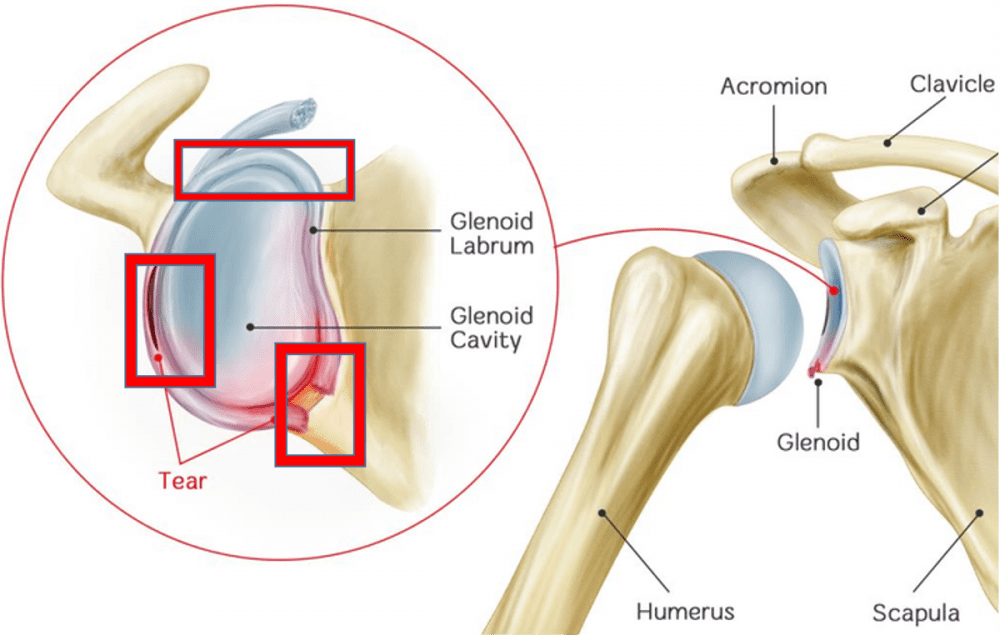
Glenoid Labrum Tears
Glenohumeral Joint Injection
Glenohumeral joint-injection: In some cases, in severe pain, the GH joint can be injected with a local anesthetic and corticosteroid to reduce shoulder pain from the joint. Through this procedure one of the conservative treatment options that are finite before surgery is indicated, other joints also can undergo this action as acromioclavicular joint, sternoclavicular joint, and others.
This non-surgical treatment is relatively safe with minimal risks, but also it may have side effects as example infections, the pain increased, and weakness¬¬¬.
This non-surgical treatment is relatively safe with minimal risks, but also it may have side effects as example infections, the pain increased, and weakness¬¬¬.
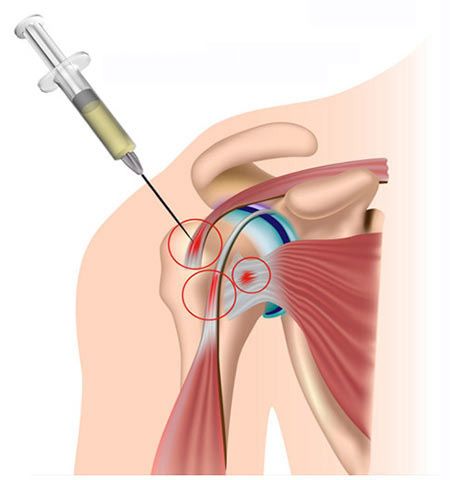
Glenohumeral Joint Injection
References
1) Moore K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2014)- Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition (814-815 plates).
2) Common Injuries of the Shoulder. University Rochester Medical Center , Health Encyclopedia.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=1&contentid=832
3) Common Shoulder Injuries, OrthoInfo
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/common-shoulder-injuries/
4) Glenohumeral Joint Injury, Genesis orthopedics & sports medicine.
https://genesisortho.com/patient-education/shoulder-overview/glenohumeral-joint-injury/
5) Anterior Glenohumeral Joint Dislocation , National library of medicine.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557862/
2) Common Injuries of the Shoulder. University Rochester Medical Center , Health Encyclopedia.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=1&contentid=832
3) Common Shoulder Injuries, OrthoInfo
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/common-shoulder-injuries/
4) Glenohumeral Joint Injury, Genesis orthopedics & sports medicine.
https://genesisortho.com/patient-education/shoulder-overview/glenohumeral-joint-injury/
5) Anterior Glenohumeral Joint Dislocation , National library of medicine.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557862/
References of images
Cover image: Shoulder Anatomy Vector Illustration Labeled Skeleton And Muscle Scheme Stock Illustration. https://media.istockphoto.com/vectors/shoulder-anatomy-vector-illustration-labeled-skeleton-and-muscle-vector-id1224590255
fig 1: Shoulder Ligament Anatomy, www.joionline.net.
https://marvel-b1-cdn.bc0a.com/f00000000041628/ix-cdn.b2e5.com/images/41628/41628_0b4a5dc4918545e48e0ff95b19d8b8c7_1653408038.jpeg
fig 3: Shoulder sprain, Los Angeles Football Club medical team.
https://cdn.vox-cdn.com/thumbor/47NeHbMCiQTh-HS6GP_jBG-uT3c=/0x0:600x450/920x0/filters:focal(0x0:600x450):format(webp):no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/18464389/Shoulder_sprain.jpg
fog 4: Anterior and posterior shoulder dislocations, performance health.
https://www.performancehealth.com/media/wysiwyg/blog/articles/shoulder-dislocation.jpg
fig 5: Overview of the course of the axillary nerve. Teachme anatomy.
https://teachmeanatomy.info/wp-content/uploads/Axillary-Nerve-Overview.png
fig 6: The Shoulder Labrum: Three Zones of Injury: Elan J Golan, MD: Orthopedic Surgeon.
https://sa1s3optim.patientpop.com/assets/images/provider/photos/2408259.png.
fig 7: NYC Shoulder Joint Injection. Sports Injury & Pain Management Clinic of NYC
https://www.sportspainmanagementnyc.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/shoulder-injection-nyc.jpg
fig 1: Shoulder Ligament Anatomy, www.joionline.net.
https://marvel-b1-cdn.bc0a.com/f00000000041628/ix-cdn.b2e5.com/images/41628/41628_0b4a5dc4918545e48e0ff95b19d8b8c7_1653408038.jpeg
fig 3: Shoulder sprain, Los Angeles Football Club medical team.
https://cdn.vox-cdn.com/thumbor/47NeHbMCiQTh-HS6GP_jBG-uT3c=/0x0:600x450/920x0/filters:focal(0x0:600x450):format(webp):no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/18464389/Shoulder_sprain.jpg
fog 4: Anterior and posterior shoulder dislocations, performance health.
https://www.performancehealth.com/media/wysiwyg/blog/articles/shoulder-dislocation.jpg
fig 5: Overview of the course of the axillary nerve. Teachme anatomy.
https://teachmeanatomy.info/wp-content/uploads/Axillary-Nerve-Overview.png
fig 6: The Shoulder Labrum: Three Zones of Injury: Elan J Golan, MD: Orthopedic Surgeon.
https://sa1s3optim.patientpop.com/assets/images/provider/photos/2408259.png.
fig 7: NYC Shoulder Joint Injection. Sports Injury & Pain Management Clinic of NYC
https://www.sportspainmanagementnyc.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/shoulder-injection-nyc.jpg
