
Cutaneous Innervation Of The Lower Limb
By : Rashad OmarOverview
Most the sensory innervation of the lower extremities is done mainly by the nerve fibres of the (L1 to S3) segments of the spinal cord
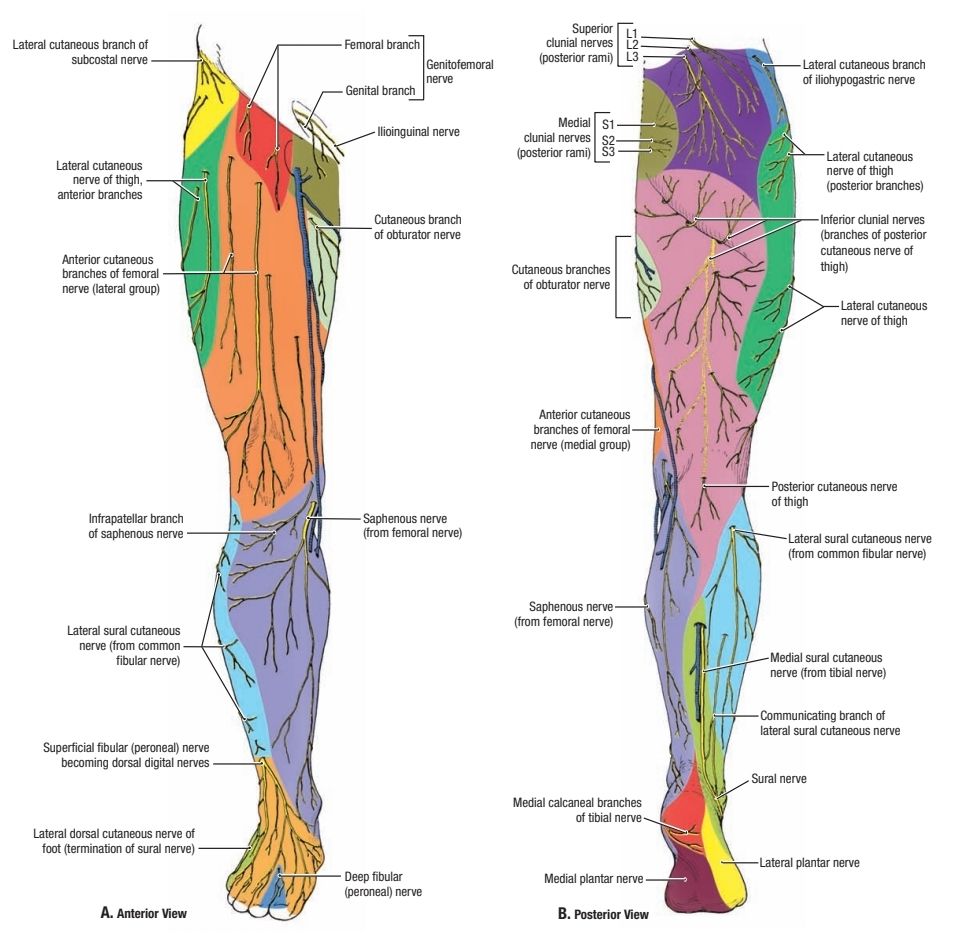
Cutaneous nerves of the thigh
1. Lateral cutaneous n. of the thigh: also called lateral femoral cutaneous n. , it originates from the posterior divisions of the lumbar plexus (L2 and 3), Passes deep to inguinal ligament, 2–3 cm medial to anterior superior iliac spine ,it divides into anterior & posterior branches to supply the lateral surface of the thigh & the lower lateral quadrant of the buttock.
2. genitofemoral n.: is a branch of the lumbar plexus (L1 and 2), enters the thigh behind the middle of the inguinal ligament it ends by dividing into two terminal branches :
Femoral branch : also called lumboinguinal branch supplies skin over lateral part of femoral triangle in both sexes
Genital branch : supplies skin of anterior scrotum )in male ) or labia majora ( in female )
3. Ilioinguinal n.: is a branch of the lumbar plexus (L1), enters the thigh by passing in the superficial inguinal ring , it supplies small area of skin inferior to the medial part of the inguinal ligament, (also supplies parts of skin of penis in male and clitoris in female)
4. Medial cutaneous n. of the thigh: is a branch of the femoral n., provides sensation to the medial side of the thigh and shares in the formation of the patellar plexus
5. Intermediate cutaneous n. of the thigh: is a branch of the femoral n., divides into two branches that supply the anterior aspect of the thigh and joins the patellar plexus.
6. the anterior division of obturator n.: gives many cutaneous branches ( L2_ L4 )that supply many parts of skin on the medial surface of the thigh.
7. Posterior cutaneous n. of the thigh: is a branch of the sacral plexus (S1–S3) , leaves the gluteal region by passing under the lower border of the gluteus maximus m. it descends on the posterior aspect of the thigh & popliteal fossa it provides sensation to the back of the thigh & the upper part of the leg by number of branches.
8. Patellar plexus: it’s located anterior to the knee and formed from the terminal branches of the medial , lateral & the intermediate cutaneous n. of the thigh and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous n.
2. genitofemoral n.: is a branch of the lumbar plexus (L1 and 2), enters the thigh behind the middle of the inguinal ligament it ends by dividing into two terminal branches :
Femoral branch : also called lumboinguinal branch supplies skin over lateral part of femoral triangle in both sexes
Genital branch : supplies skin of anterior scrotum )in male ) or labia majora ( in female )
3. Ilioinguinal n.: is a branch of the lumbar plexus (L1), enters the thigh by passing in the superficial inguinal ring , it supplies small area of skin inferior to the medial part of the inguinal ligament, (also supplies parts of skin of penis in male and clitoris in female)
4. Medial cutaneous n. of the thigh: is a branch of the femoral n., provides sensation to the medial side of the thigh and shares in the formation of the patellar plexus
5. Intermediate cutaneous n. of the thigh: is a branch of the femoral n., divides into two branches that supply the anterior aspect of the thigh and joins the patellar plexus.
6. the anterior division of obturator n.: gives many cutaneous branches ( L2_ L4 )that supply many parts of skin on the medial surface of the thigh.
7. Posterior cutaneous n. of the thigh: is a branch of the sacral plexus (S1–S3) , leaves the gluteal region by passing under the lower border of the gluteus maximus m. it descends on the posterior aspect of the thigh & popliteal fossa it provides sensation to the back of the thigh & the upper part of the leg by number of branches.
8. Patellar plexus: it’s located anterior to the knee and formed from the terminal branches of the medial , lateral & the intermediate cutaneous n. of the thigh and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous n.
Cutaneous innervation of the leg
1. Saphenous n. ( L3 , L4 ) : is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral n. pass through the adductor canal but doesn’t leave the adductor hiatus ( the adductor hiatus is an opening between the two sites of insertion of adductor magnus ) it provides sensation to the skin of medial aspect of the leg & extends to the medial side of the foot .
2. Posterior cutaneous n. of the thigh (S1–S3 ) : provides sensation to the skin over the popliteal fossa and the upper part of the posterior surface of the leg
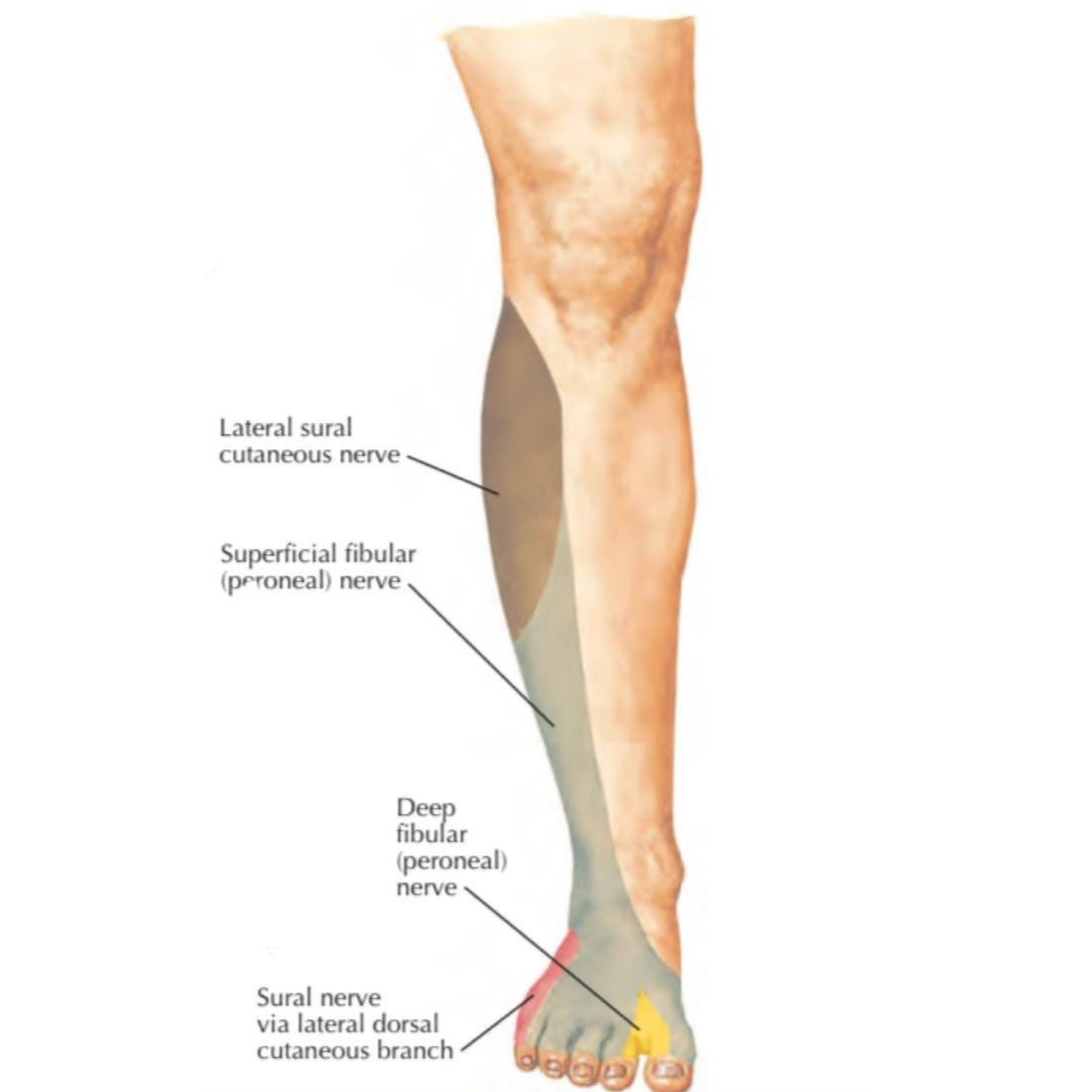
3. Sural n. ( S1 , S2 ) : formed by the joining of the medial sural n. ( from tibial n. ) & lateral sural n. ( from common peroneal ( fibular ) n. supplies the skin of the posterolateral aspect of the leg & lateral border of foot.
4. Superficial fibular (peroneal ) n. ( L4–S1 ) : branch of the common peroneal ( fibular ) n. , it provides sensation to the skin of the over the lower part of the anterolateral surface of leg & extend to the dorsum of foot except the adjacent side between th 1st & 2nd toes
2. Posterior cutaneous n. of the thigh (S1–S3 ) : provides sensation to the skin over the popliteal fossa and the upper part of the posterior surface of the leg
3. Sural n. ( S1 , S2 ) : formed by the joining of the medial sural n. ( from tibial n. ) & lateral sural n. ( from common peroneal ( fibular ) n. supplies the skin of the posterolateral aspect of the leg & lateral border of foot.
4. Superficial fibular (peroneal ) n. ( L4–S1 ) : branch of the common peroneal ( fibular ) n. , it provides sensation to the skin of the over the lower part of the anterolateral surface of leg & extend to the dorsum of foot except the adjacent side between th 1st & 2nd toes
cutaneous innervation of dorsum of foot
1. Superficial peroneal n. : supplies most of the skin of dorsal surface of foot except the adjacent side of 1st & 2nd toes and the lateral side of foot and the little toe.
2. Deep peroneal n. : supplies skin over the adjacent side of 1st & 2nd toes
Sural n. : branch of tibial n. supplies skin over the lateral side of the foot and the dorsal aspect of little toe
2. Deep peroneal n. : supplies skin over the adjacent side of 1st & 2nd toes
Sural n. : branch of tibial n. supplies skin over the lateral side of the foot and the dorsal aspect of little toe
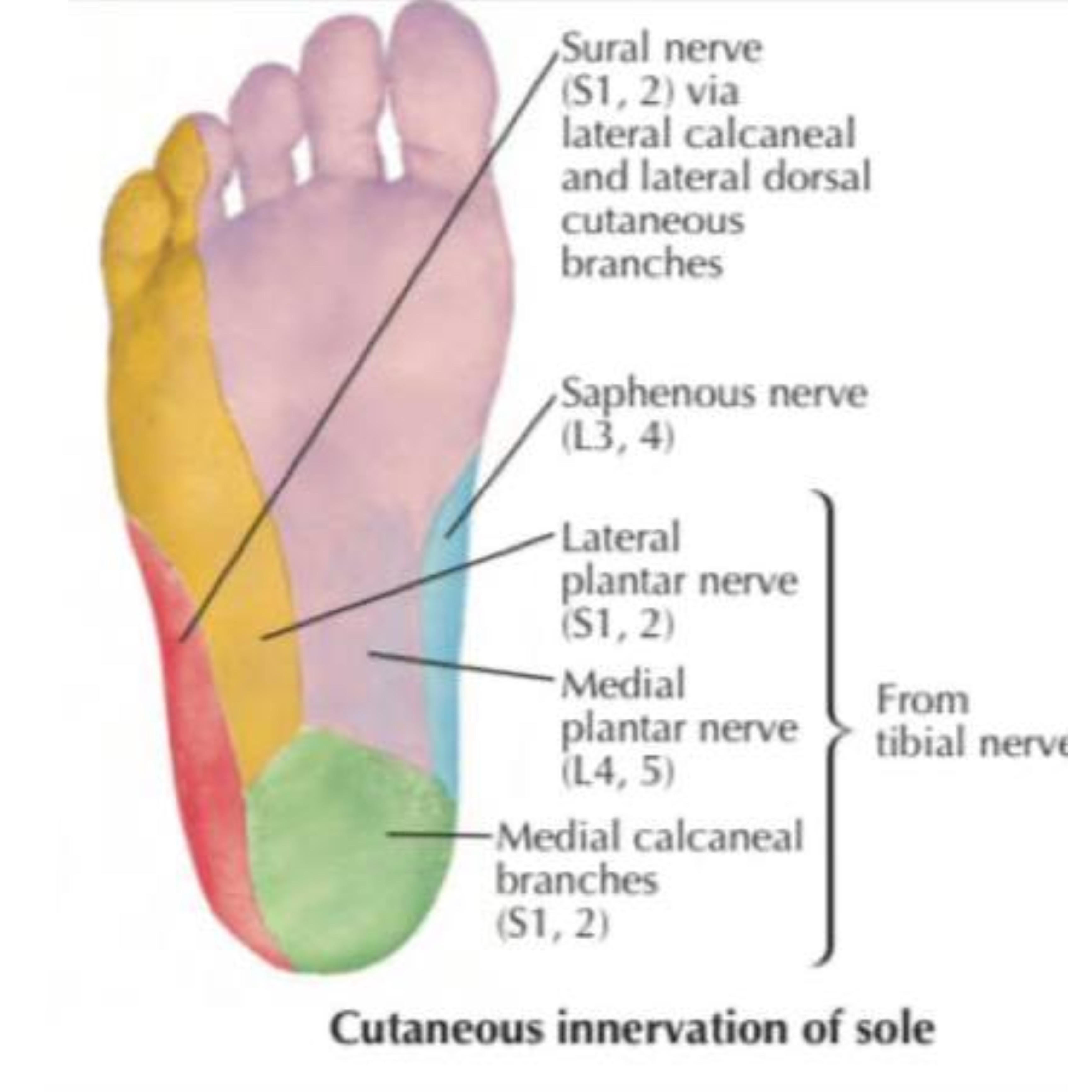
Cutaneous innervation of sole of foot
1. Medial calcaneal n. : branch of tibial n. supplies the skin over the medial side of the heel.
2. Cutaneous branches : from medial plantar n. supplies skin over the medial 2 thirds of the sole of foot.
3. Cutaneous branches : from lateral plantar n. supplies skin over the lateral third of sole of foot.
2. Cutaneous branches : from medial plantar n. supplies skin over the medial 2 thirds of the sole of foot.
3. Cutaneous branches : from lateral plantar n. supplies skin over the lateral third of sole of foot.
Cutaneous innervation of the lower limb
Clinical notes
Diabetic Neuropathy
Is a condition that may affect people who have diabetes ( high blood sugar level ) and it causes type of nerve damage and its defect may extend to the internal organs like heart and bladder , commonly it affects nerves in legs and feet .
There four main type of neuropathy :
1. Peripheral neuropathy (affects nerves in the limbs firstly in feet
2. Autonomic neuropathy ( affects the autonomic nervous system )
3. Proximal neuropathy ( this type can affect nerves in chest & abdomen areas and also affect leg, thigh & the buttock
3. Focal neuropathy ( mononeuropathy ) this type affects only single nerve
The most common type of neuropathy is the peripheral neuropathy that firstly damages nerves in the lower limbs especially in legs.
Causes of diabetic neuropathy :
1. High glucose ( blood sugar ) level
2. Large amounts of fats in the blood
The symptoms of the peripheral include within them :
1. numbness or little loss in sensation
2. reduce the ability to feel temperature or pain
3. Serious foot problems like infection , ulcers , bone or joint damage
Other symptoms such as muscle weakness
*the symptoms depend on the type you have and on the affected nerve .
We can reduce or keep the problem from developing by control the blood sugar level & healthy lifestyle.
*One of the most important complication of this disease include loss of feet and legs so even small cuts may turn into ulcer before you notice , in severe cases the infection may reach the bone and cause necrosis or tissue death and sometimes we have to amputate the affected part .( there are other complications but not related to the lower limb )
Is a condition that may affect people who have diabetes ( high blood sugar level ) and it causes type of nerve damage and its defect may extend to the internal organs like heart and bladder , commonly it affects nerves in legs and feet .
There four main type of neuropathy :
1. Peripheral neuropathy (affects nerves in the limbs firstly in feet
2. Autonomic neuropathy ( affects the autonomic nervous system )
3. Proximal neuropathy ( this type can affect nerves in chest & abdomen areas and also affect leg, thigh & the buttock
3. Focal neuropathy ( mononeuropathy ) this type affects only single nerve
The most common type of neuropathy is the peripheral neuropathy that firstly damages nerves in the lower limbs especially in legs.
Causes of diabetic neuropathy :
1. High glucose ( blood sugar ) level
2. Large amounts of fats in the blood
The symptoms of the peripheral include within them :
1. numbness or little loss in sensation
2. reduce the ability to feel temperature or pain
3. Serious foot problems like infection , ulcers , bone or joint damage
Other symptoms such as muscle weakness
*the symptoms depend on the type you have and on the affected nerve .
We can reduce or keep the problem from developing by control the blood sugar level & healthy lifestyle.
*One of the most important complication of this disease include loss of feet and legs so even small cuts may turn into ulcer before you notice , in severe cases the infection may reach the bone and cause necrosis or tissue death and sometimes we have to amputate the affected part .( there are other complications but not related to the lower limb )
Saphenous vein stripping:
Because the saphenous nerve follow the great saphenous vein in its course so it may be injured or damaged in the surgery of stripping of the saphenous vein ( vein stripping is a surgery to remove the varicose vein ) this damage of the saphenous nerve may cause pain , paraesthesia or complete loss of sensation in the medial aspect of leg.
Because the saphenous nerve follow the great saphenous vein in its course so it may be injured or damaged in the surgery of stripping of the saphenous vein ( vein stripping is a surgery to remove the varicose vein ) this damage of the saphenous nerve may cause pain , paraesthesia or complete loss of sensation in the medial aspect of leg.

Saphenous nerve
Reference
1. LAWRENCE E. WINESKI Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions /10th edition (2018 ) /p. ( 533 , 554 , 563 )
2. -Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition / p. ( 537 , 538 )
3. The femoral nerve , Author : Dr Krupa Samani , TeachMe Anatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/nerves/femoral-nerve/
4. Diabetic neuropathy , Author : mayo clinic staff , Mayo clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20371580
2. -Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition / p. ( 537 , 538 )
3. The femoral nerve , Author : Dr Krupa Samani , TeachMe Anatomy , https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/nerves/femoral-nerve/
4. Diabetic neuropathy , Author : mayo clinic staff , Mayo clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20371580
Reference of images
1. Cover image : cutaneous innervation if lower extremity , UpToDate , https://images.app.goo.gl/yj7dPLiX5TRbafmQ7
2. figure 1 : Grant’s atlas of anatomy plate 359
3. figure 2 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 529
4. figure 3 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 528
5. figure 4 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 525
2. figure 1 : Grant’s atlas of anatomy plate 359
3. figure 2 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 529
4. figure 3 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 528
5. figure 4 : Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy / plate 525
