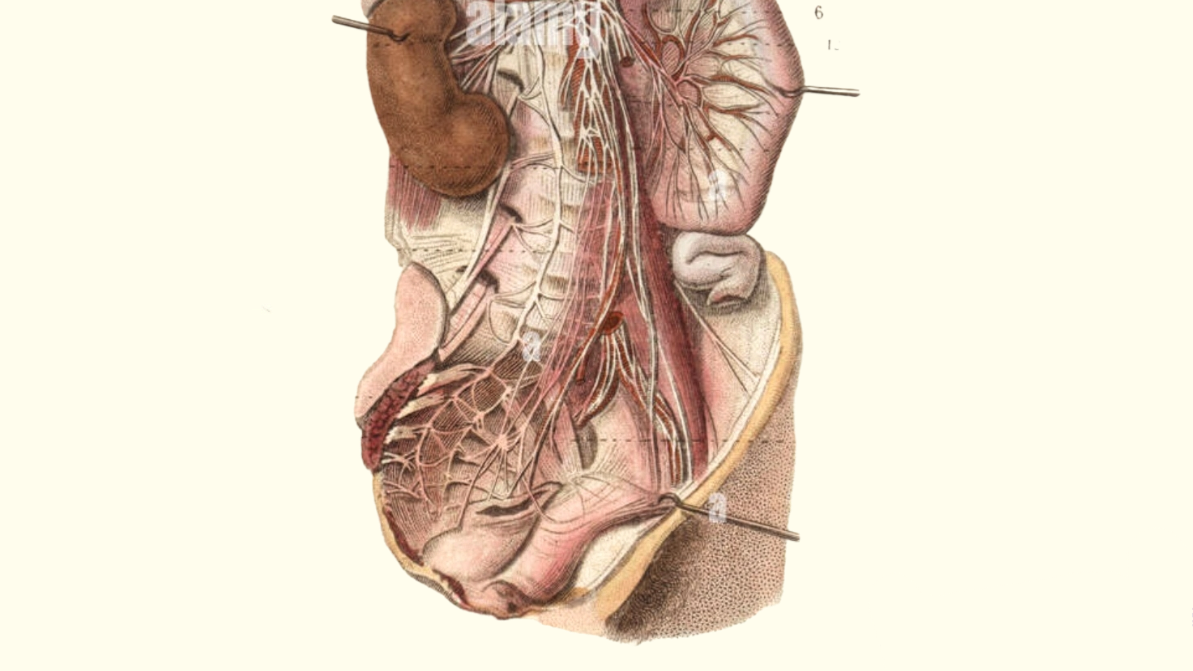
Lumbar Plexus
By : Omar M. Subhi Altaie● Overview
• Name & location
The word " Lumbar " referred to the place between the umbilicaus (bellybutton) and the sacrum in the hip bone of the human body from the posterior aspect; the last five vertebrae of the spinal column.
And the word " plexus " is simply means a network of nerves that formed at lumbar place.
And the word " plexus " is simply means a network of nerves that formed at lumbar place.
• Origin
As we know the spinal nerve that comes from spinal cord of the Central nervous system has its anterior and posterior divisions, the anterior divisions of the spinal nerve after passing through the intervertebral foramina from both sides of the vertebrae at the lower level of vertebral column, just above the sacrum.
The roots of the lumbar nerves from the first to fourth lumbar are anastomosing with each other to form the lumbar plexus, some fibers from the last (12th) thoracic spinal nerve also joined the network.
The roots of the lumbar nerves from the first to fourth lumbar are anastomosing with each other to form the lumbar plexus, some fibers from the last (12th) thoracic spinal nerve also joined the network.

The roots of the plexus are joined, near their origins, by gray rami communicantes from the lumbar ganglia of the sympathetic trunk, and they are not very organized; some roots receive rami communicantes from two ganglia and others share one ganglion to receive rami communicantes. The first two nerves and sometimes the third and fourth are connected to the lumbar part of the sympathetic trunk by white rami communicantes.(as seen in the figure2)
Small fibers of the forth lumbar nerve( named nervus furcalis) is communicating with the fifth one and creating the lumbosacral trunk which involves in the formation of the sacral plexus, eventhough, some text books consider them as one plexus in the name of lumbosacral plexus .
Small fibers of the forth lumbar nerve( named nervus furcalis) is communicating with the fifth one and creating the lumbosacral trunk which involves in the formation of the sacral plexus, eventhough, some text books consider them as one plexus in the name of lumbosacral plexus .
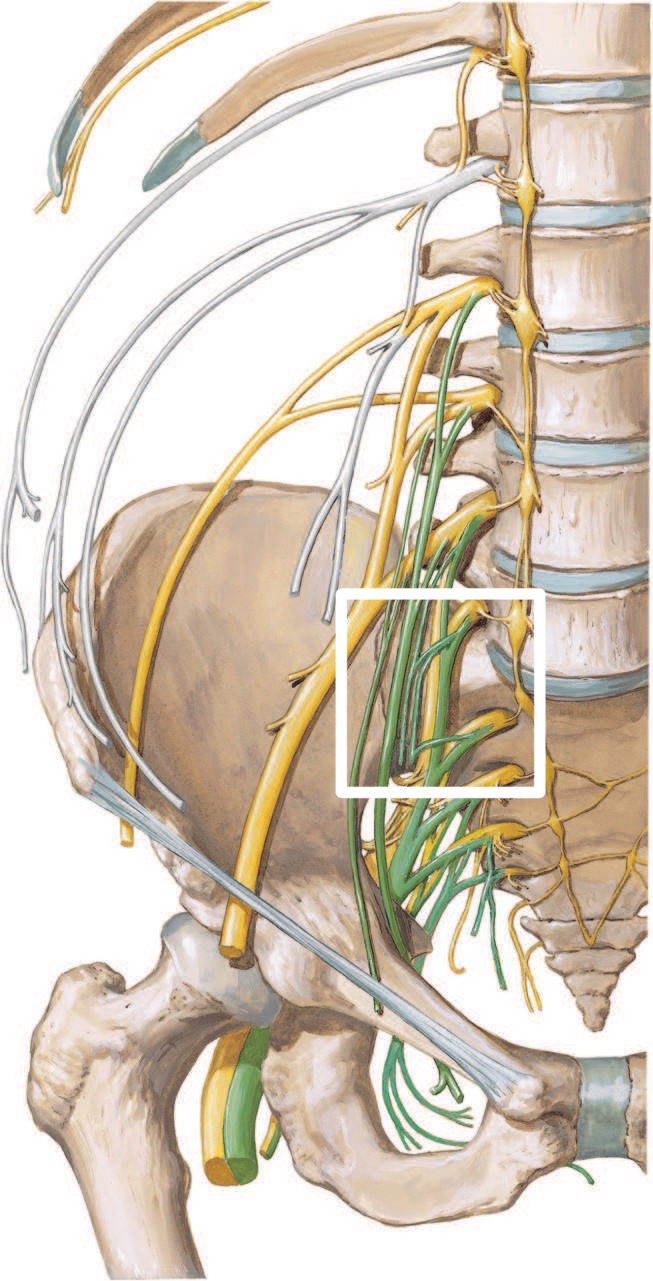
(in the square, the lumbosacral trunk)
• Significance
The plexus in turn divided into branches continues as independent nerves whiches innervate the lower limbs and places of the pelvis and lower abdomen.
Nerves originate from lumbar plexus are major nerves in motor and sensation of the lower limbs; the main two nerves originate from the plexus innervate the medial and anterior of thigh muscles that allow flexion, extention and adduction of the thigh at knee and hip joints.
Nerves originate from lumbar plexus are major nerves in motor and sensation of the lower limbs; the main two nerves originate from the plexus innervate the medial and anterior of thigh muscles that allow flexion, extention and adduction of the thigh at knee and hip joints.
● Nerves & Relations
The lumbar plexus lies at the posterior aspect of the Psoas major muscle that lies anterior to the transverse processes of the vertebrae inferiorto the kidneys, the main branches of the plexus also setting near to the muscle:-
1. iliohypogastric nerve
passing lateral to the Psoas major after originating from the first lumbar spinal nerve at the level between the L1 and L2 vertebrae, it has motor innervation to the internal oblique and abdominal transverse muscles. It then divided into two branches anterior and lateral cutaneous branches whiches distributed in the sensory innervation to the lateral side of the skin in the gluteus and the skin of hypogastric region respectively.
Note
(the region just below the umbilicaus)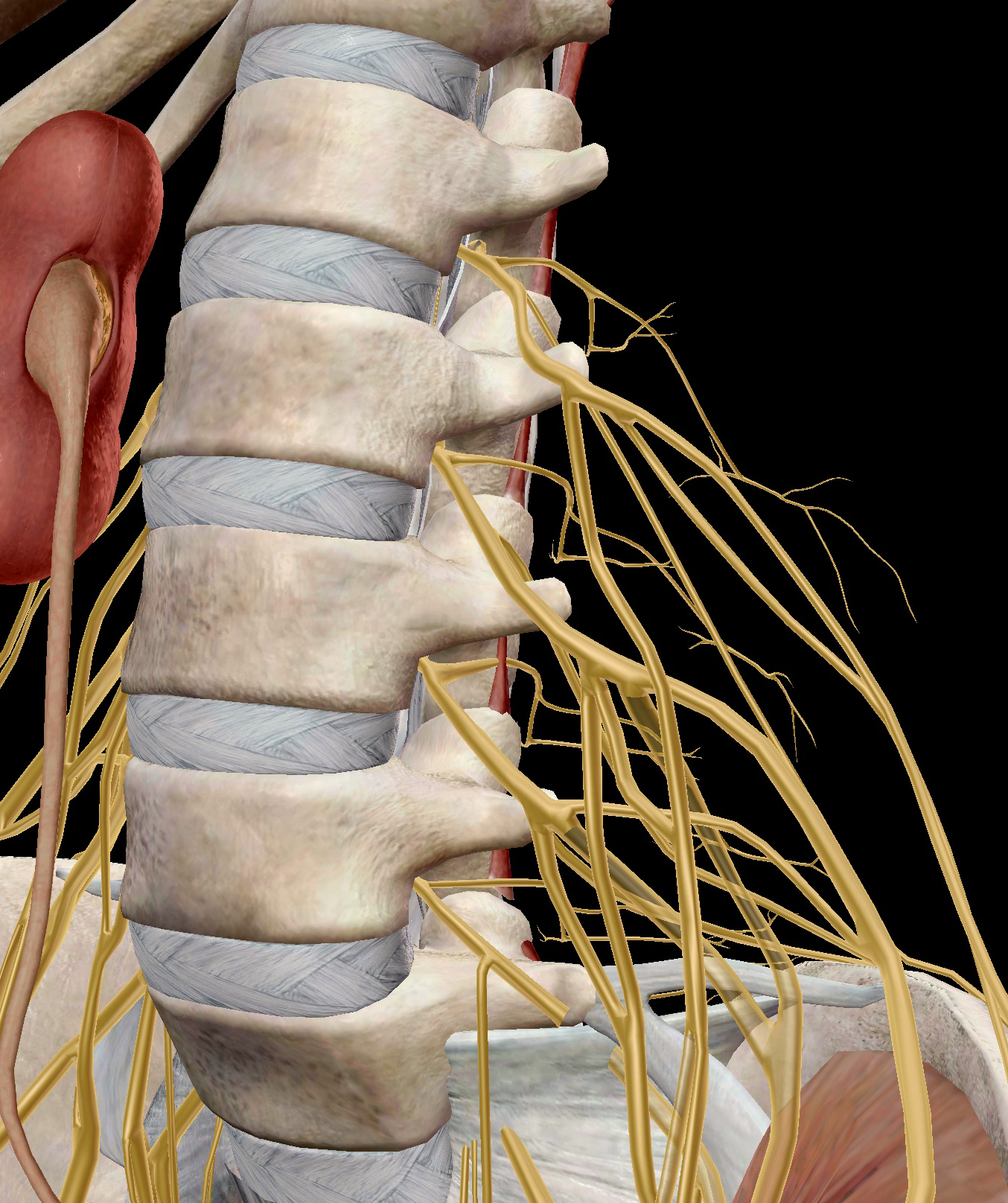
2. ilioinguinal nerve
The other branch of the first lumbar spinal nerve that pass near to the first branch lateralto the Psoas major muscle , it also has motor innervation to the internal obliques and abdominal transverse muscles. The sensory innervation by this nerve is variable between males and females; in males it becomes the anterior scrotal nerve and innervate the base of the penis and the upper part of the scrotum, but in the females it divided at its distal portion to become anterior labial nerves that innervate the labia majora and mons pubis of female genitals , both males and females received sensory innervation to parts of thigh by this nerve.
The size of the nerve is variable, depending on how large is the iliohypogastric nerve, occasionally, the ilioinguinal nerve is very small that ends by joining the iliohypogastric nerve which in turn take its distribution.
The size of the nerve is variable, depending on how large is the iliohypogastric nerve, occasionally, the ilioinguinal nerve is very small that ends by joining the iliohypogastric nerve which in turn take its distribution.
3. genitofemoral nerves
originate from the first lumbar spinal nerve and receive fibers from the second, it continues as one nerve and passing downward after perforating the Psoas major muscle and continues anteriorly under cover of the peritoneum, it then divided into two separated nerves:
• femoral or lumboinguinal nerve give sensory to the skin of parts of the thigh in both men and women, small fibers of this nerve may be found in the femoral artery that runs near to it.
• genital or external spermatic :- supplies sensory to skin of mons pubis in women and then accompanies the round ligaments of the uterus and end there, it gives some sensory fibers to the scrotum in men, and also give motor innervation to the cremaster muscle this muscle is responsible for contraction of the testicles when a man get in a cold environment or in, this muscle pulls the testicles toward the body to raise their temperature.
• femoral or lumboinguinal nerve give sensory to the skin of parts of the thigh in both men and women, small fibers of this nerve may be found in the femoral artery that runs near to it.
• genital or external spermatic :- supplies sensory to skin of mons pubis in women and then accompanies the round ligaments of the uterus and end there, it gives some sensory fibers to the scrotum in men, and also give motor innervation to the cremaster muscle this muscle is responsible for contraction of the testicles when a man get in a cold environment or in, this muscle pulls the testicles toward the body to raise their temperature.
4. Lateral femoral nerve :-
it passes lateral to the Psoas major muscle after originating from the second and third posterior divisions of lumbar spinal nerves. It passes the Iliacus muscle obliquely towards the ASIS (anterior superior illiac spine). This nerve has only sensory innervation to the skin that covers the lateral side of thigh.
5. Femoral nerve :-
lateral to the Psoas major muscle after originating from the posterior divisions of the roots of second , third and fourth lumbar spinal nerves , it then continues to innervate most of muscles of the anterior part of thigh whiches work at the hip and knee joints.
Read more about it here .
Read more about it here .
6. Obturator nerve:-
it passes medial to the Psoas major muscle after originating from the anterior divisions of the roots of the second, third and fourth lumbar spinal nerves, continues to innervate muscles of the medial side of the thigh.
Read more about it here .
Read more about it here .
* Accessory Obturator Nerve:-
this nerve is absent in more cases (present in 29% of cases) , arising from anterior divisions of thrid and fourth lumbar spinal nerves. It passes medially to the Psoas major muscle under to Pectineus where it divides into many branches one of them innervate the muscle and other distributed to the hip joint.
When the nerve is absent , the joint receives two branches from the obturator nerve instead.
When the nerve is absent , the joint receives two branches from the obturator nerve instead.
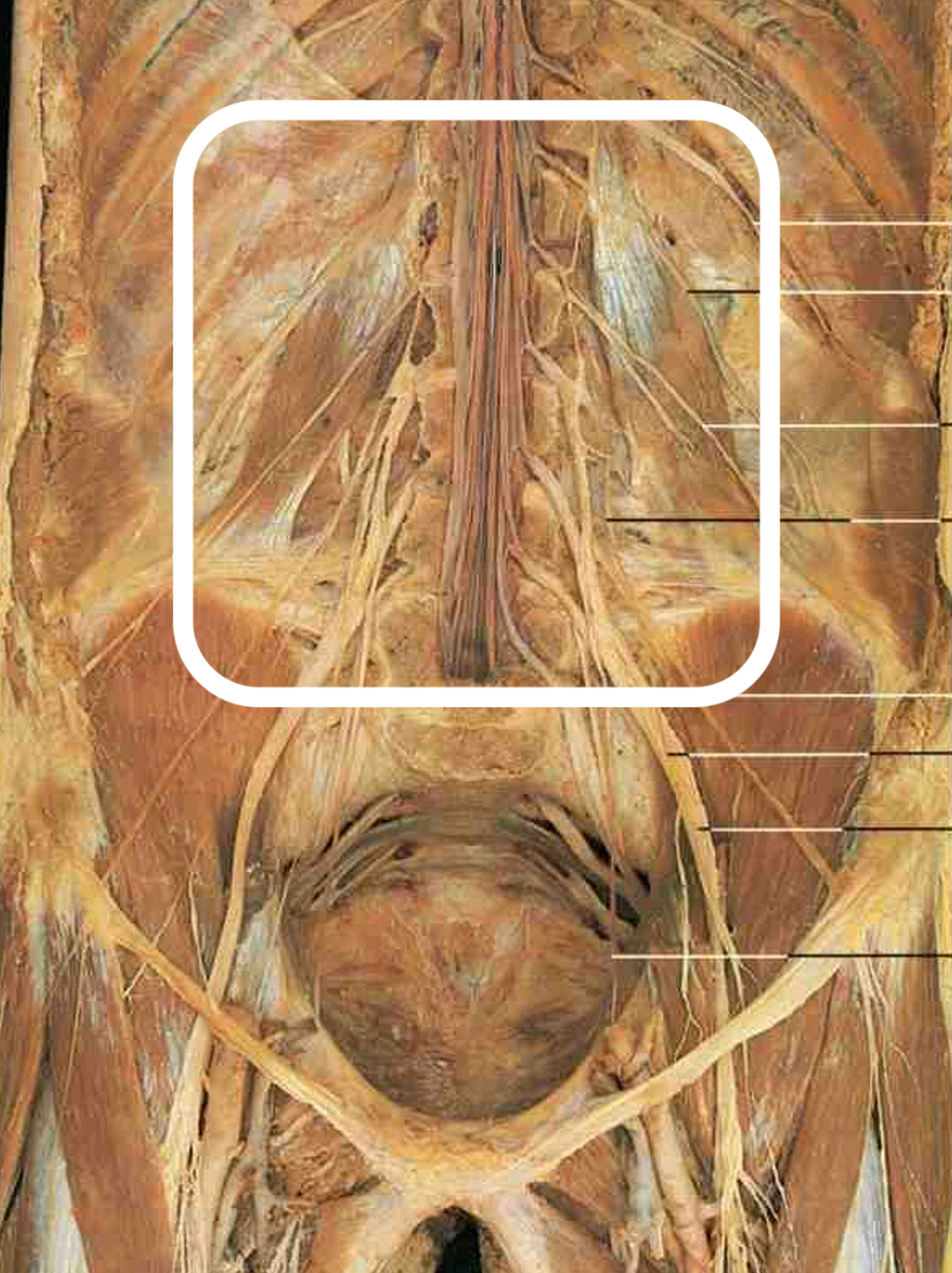

● Notes
• Blood supply
As mentioned, the major part of the plexus is related behind the Psoas major muscle which has such big blood supply ; so it can share the blood supply with that large muscle.
As mentioned, the major part of the plexus is related behind the Psoas major muscle which has such big blood supply ; so it can share the blood supply with that large muscle.
• Mnemonic
Here is a great mnemonic to remember the main branches of lumbar plexus :
I L ive F ar
A way I n O ldenburg, G ermany
I = iliohypogastric
L = lateral femoral
F = femoral
A = accessory obturator
I = ilioinguinal
O = obturator
G = genitofemoral
Here is a great mnemonic to remember the main branches of lumbar plexus :
I L ive F ar
A way I n O ldenburg, G ermany
I = iliohypogastric
L = lateral femoral
F = femoral
A = accessory obturator
I = ilioinguinal
O = obturator
G = genitofemoral
Clinical Relevance
• lumbosacral plexopathy
A damage that might occurs to the nerves bundle in a rare syndrome that called lumbosacral plexo-pathy affecting one or both lumbar and sacral plexuses, patients cannot feel their weak muscles, they also feel burning and numbness, or even be so sensitive to a small touch.
The more obvious cause of the nerve damage that occurs by the high level of blood sugar in what called diabetic amyotrophy causing a severe pain in the hip and buttocks. Idiopathic plexopathy is also a cause of that disorder.
Tumours can cause this plexopathy due to the compression that is disturbing of the plexus and causes that pain, the treatment of this condition in mainly removing of that tumor if possible, high-dose corticosteroids is used as treatment for the Idiopathic plexopathy and diabetic amyotrophy .
A damage that might occurs to the nerves bundle in a rare syndrome that called lumbosacral plexo-pathy affecting one or both lumbar and sacral plexuses, patients cannot feel their weak muscles, they also feel burning and numbness, or even be so sensitive to a small touch.
The more obvious cause of the nerve damage that occurs by the high level of blood sugar in what called diabetic amyotrophy causing a severe pain in the hip and buttocks. Idiopathic plexopathy is also a cause of that disorder.
Tumours can cause this plexopathy due to the compression that is disturbing of the plexus and causes that pain, the treatment of this condition in mainly removing of that tumor if possible, high-dose corticosteroids is used as treatment for the Idiopathic plexopathy and diabetic amyotrophy .
• hernia of Lumbar disc
Occlusion or blockage of the foramen could be occurred by this hernia that the nerves are passing through them; thus that might put compression on lumbar spinal nerves on their way to form the lumbar plexus. This syndrome can cause paresth-esia or burning and weakening in the nerves of the lumbar plexus; might then making the person not able to contract his muscles that the lumbar plexus innervate.
Occlusion or blockage of the foramen could be occurred by this hernia that the nerves are passing through them; thus that might put compression on lumbar spinal nerves on their way to form the lumbar plexus. This syndrome can cause paresth-esia or burning and weakening in the nerves of the lumbar plexus; might then making the person not able to contract his muscles that the lumbar plexus innervate.
• Lumbar plexus injury
Accidents occurring on the road can lead sometimes to lumbar plexus injuries, it is mostly because of bone fractions or lesions near to the plexus.
Injury happened after car crash that affect bones and lead to compression of the nerves by these fractured bones, the more the bone is damaged, the more the condition is severe and needed more time to be recovered.
Accidents occurring on the road can lead sometimes to lumbar plexus injuries, it is mostly because of bone fractions or lesions near to the plexus.
Injury happened after car crash that affect bones and lead to compression of the nerves by these fractured bones, the more the bone is damaged, the more the condition is severe and needed more time to be recovered.
REFERENCES
• Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, Anne M. R Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) page 313
• Anatomy, Back, Lumbar Plexus, National library of medicine, by Singh O, Al Khalili Y. 2022, jan, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545137/#:~:text=Nerves%20that%20arise%20directly%20from,after%20exiting%20the%20lumbar%20plexus.
• Lumbar Plexus, physiopedia https://www.physio-pedia.com/Lumbar_Plexus
• Cremaster muscle , By The Healthline Editorial Team on January 23, 2018 Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/cremaster-muscle
• The Lumbosacral Plexus (Plexus Lumbosacralis) Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. https://www.bartleby.com/107/212.html
• Lumber plexus, Teach me anatomy website, https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/nerves/lumbar-plexus/
• In lumbosacral plexus injuries can we identify indicators that predict spontaneous recovery or the need for surgical treatment? Results from a clinical study on 72 patients, national library of medicine website: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3896705/#__sec10title
• Anatomy, Back, Lumbar Plexus, National library of medicine, by Singh O, Al Khalili Y. 2022, jan, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545137/#:~:text=Nerves%20that%20arise%20directly%20from,after%20exiting%20the%20lumbar%20plexus.
• Lumbar Plexus, physiopedia https://www.physio-pedia.com/Lumbar_Plexus
• Cremaster muscle , By The Healthline Editorial Team on January 23, 2018 Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/cremaster-muscle
• The Lumbosacral Plexus (Plexus Lumbosacralis) Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. https://www.bartleby.com/107/212.html
• Lumber plexus, Teach me anatomy website, https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/nerves/lumbar-plexus/
• In lumbosacral plexus injuries can we identify indicators that predict spontaneous recovery or the need for surgical treatment? Results from a clinical study on 72 patients, national library of medicine website: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3896705/#__sec10title
IMAGES REFERENCES
• cover image by alamy website: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-sympathetic-nervous-system-in-the-thoracic-lumbar-and-sacral-plexus-38256322.html
• Fig1 & fig2 Frank H. Netter, Atlas of Human Anatomy (7th edition) plate : 484-485
• Fig4 & fig5 Chihiro Yokochi, E. Lutejen-Drecoll, and Johannes W. Rohen Color Atlas of Anatomy 7th Edition pages: 471,475
• Fig3 :human Anatomy atlas app 2021 (nervous system)
• Fig1 & fig2 Frank H. Netter, Atlas of Human Anatomy (7th edition) plate : 484-485
• Fig4 & fig5 Chihiro Yokochi, E. Lutejen-Drecoll, and Johannes W. Rohen Color Atlas of Anatomy 7th Edition pages: 471,475
• Fig3 :human Anatomy atlas app 2021 (nervous system)
