Saphenous nerve
By : Safa QusayIntroduction
The saphenous nerve is the largest and the biggest branch of the femoral nerve and is responsible for the medial portion of the lower leg and foot innervation. The femoral artery travels with the saphenous nerve through adductor canal (it also called “ Hunter's canal ” ), and at the medial condyle of the distal femur, this nerve supplies the knee(the medial portion) and the lower leg .
The function of the saphenous nerve:
The saphenous nerve is a cutaneous branch from the femoral nerve ,so it has sensory function and hasn't any motor function.
The course of the saphenous nerve:
In the thigh
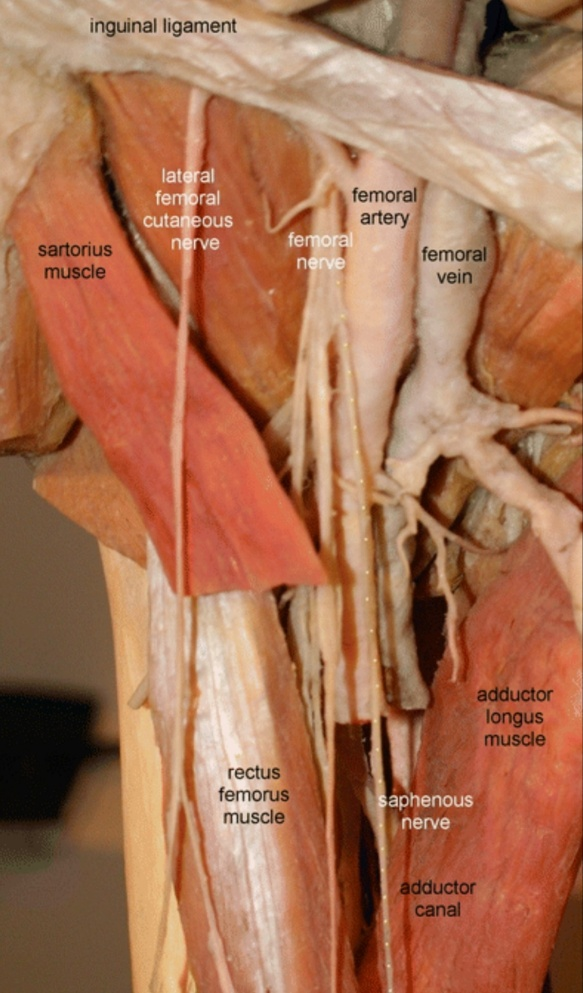
It starts as a branch from the femoral nerve from lumbar plexus( L3-L4 )in the femoral triangle when it is running laterally to the femoral artery (in femoral triangle)
It starts as a branch from the femoral nerve from lumbar plexus( L3-L4 )in the femoral triangle when it is running laterally to the femoral artery (in femoral triangle)
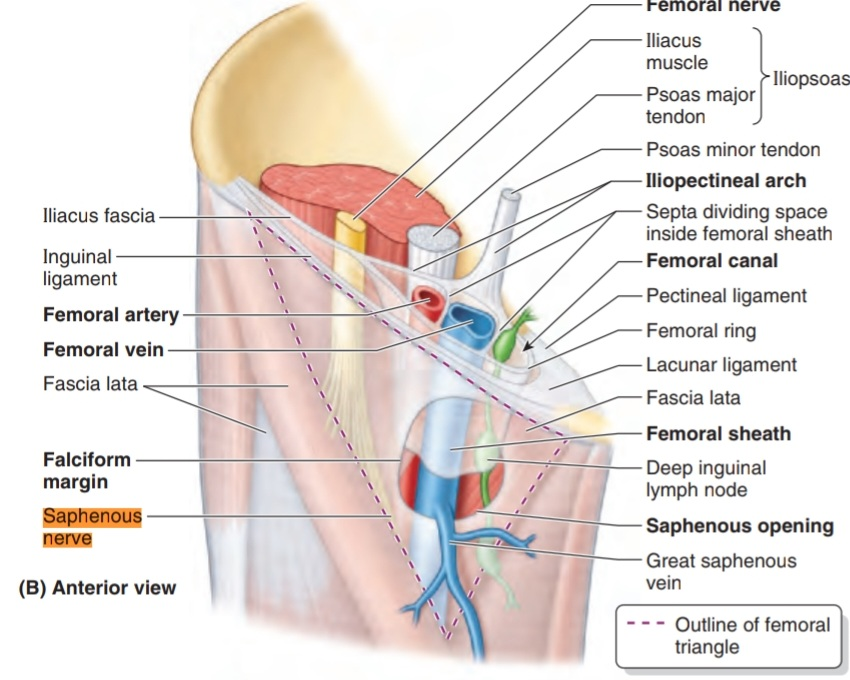
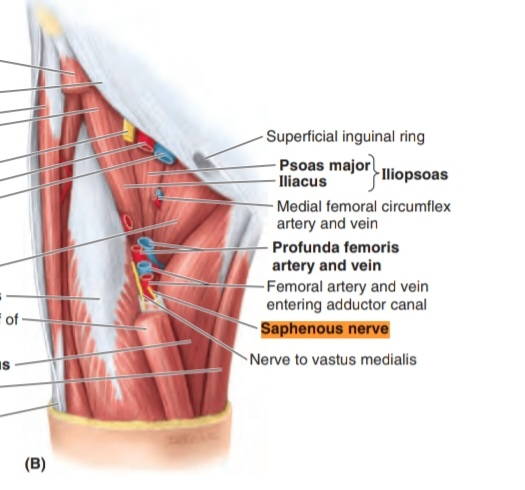
and then passes between the structures of the thigh through the adductor canal
Note
The adductor canal is an intermuscular passageway deep to the sartorius muscle, by which the major neurovascular bundle o the thigh travels the middle third of the thigh.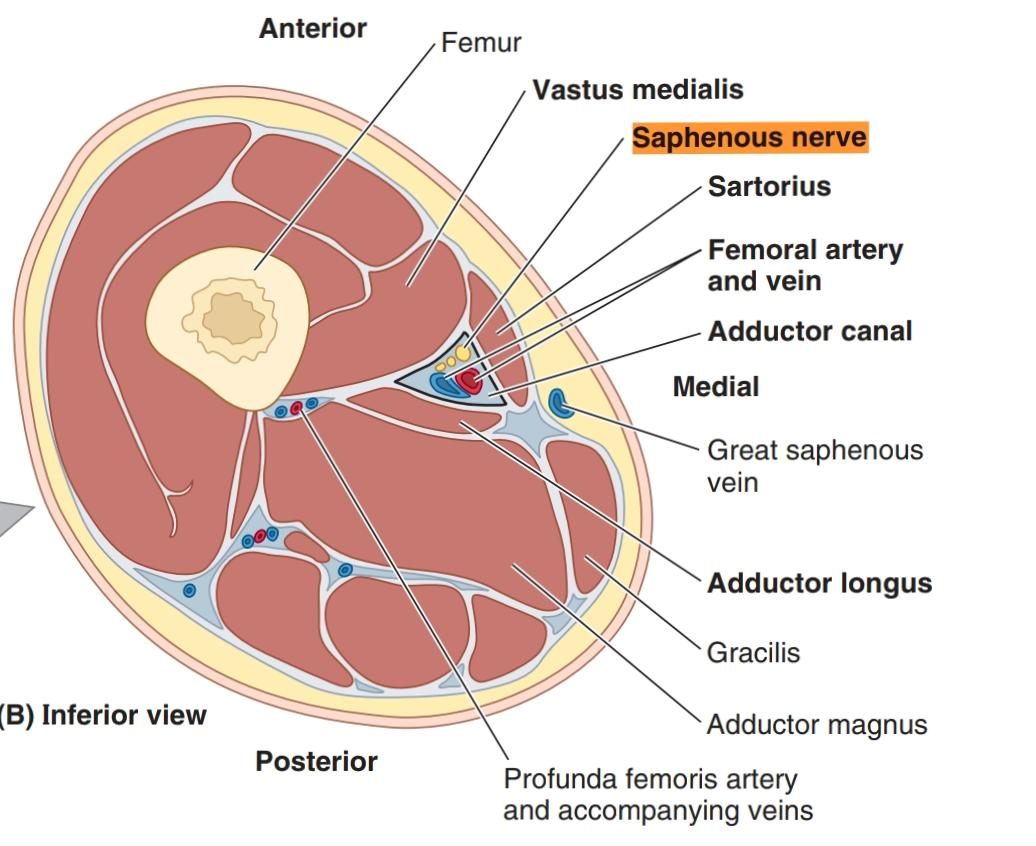
Enter the adductor canal
When it crosses the femoral artery anterior and run medial to the artery ( in the adductor canal)
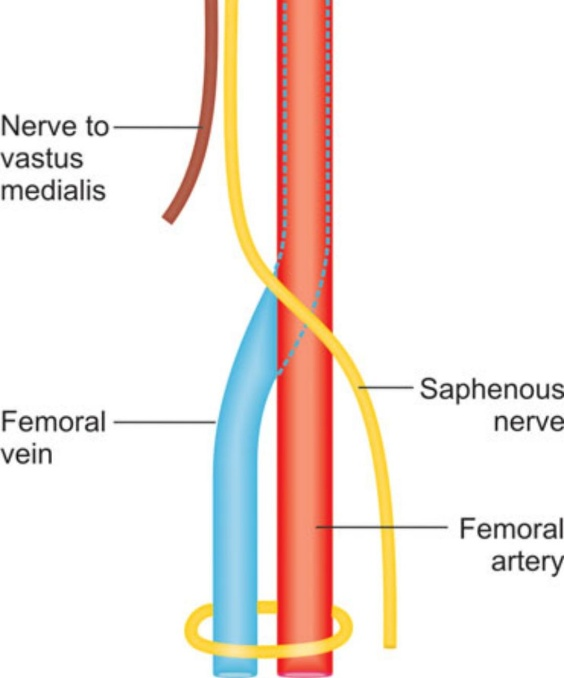
then leaves the adductor canal and descends behind the sartorius muscle and gracilis muscle ( pierces the fascia between the two muscles and the tendon of Sartorius m.)to be subcutaneous (in the medial edge of knee joint )and supplies the skin of the anterior surface of patella .
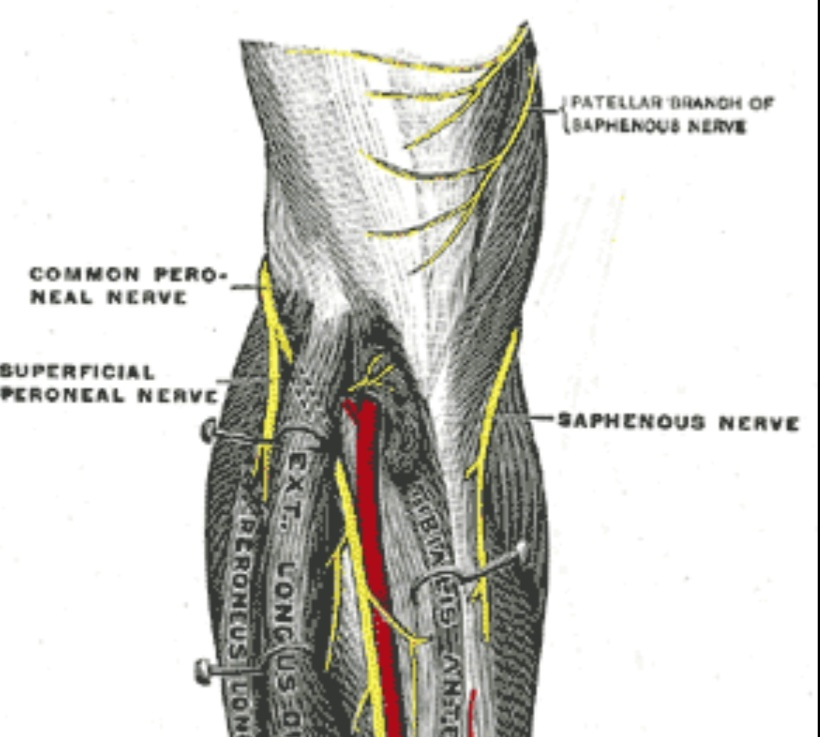
Note :it doesn’t pass through the adductor hiatus
Note
it is an opening in the distal attachment of the adductor magnus muscle.( the saphenous nerve doesn’t pass through it)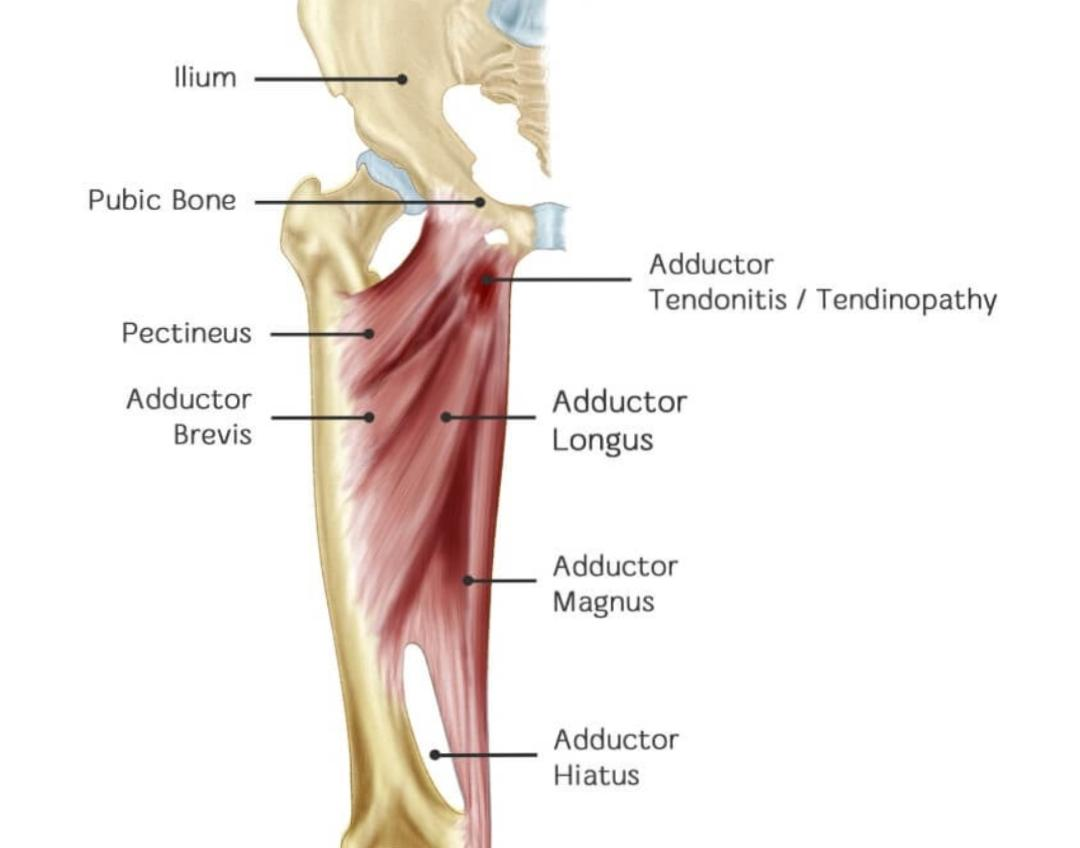
Adductor hiatus:
In the middle of the thigh ,it gives a branch to the subsartorial plexus
Note
It is a plexus formed by 1. Medial cutaneous branch from femoral nerve 2. Saphenous nerve 3. Cutaneous branch from the anterior division of the obturator nerve. 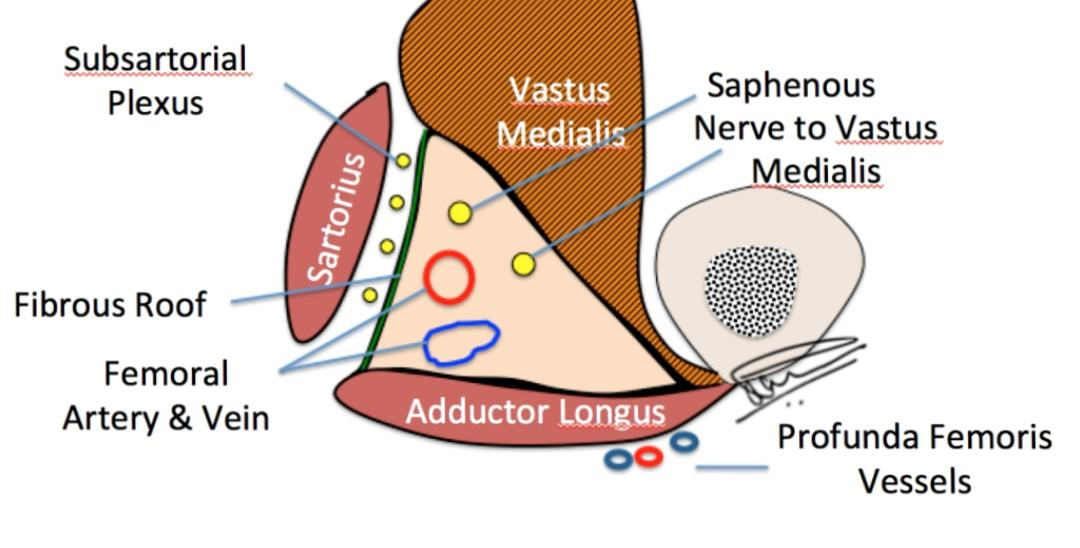
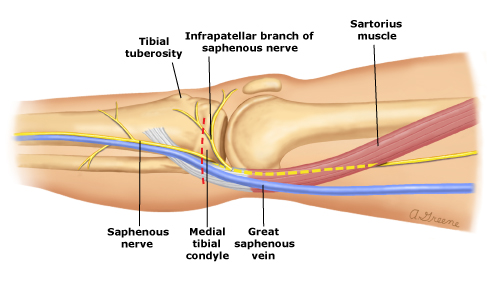
And then it leaves the adductor canal and runs medial to arrive to the medial condyle of femur and it gives the largest branch .
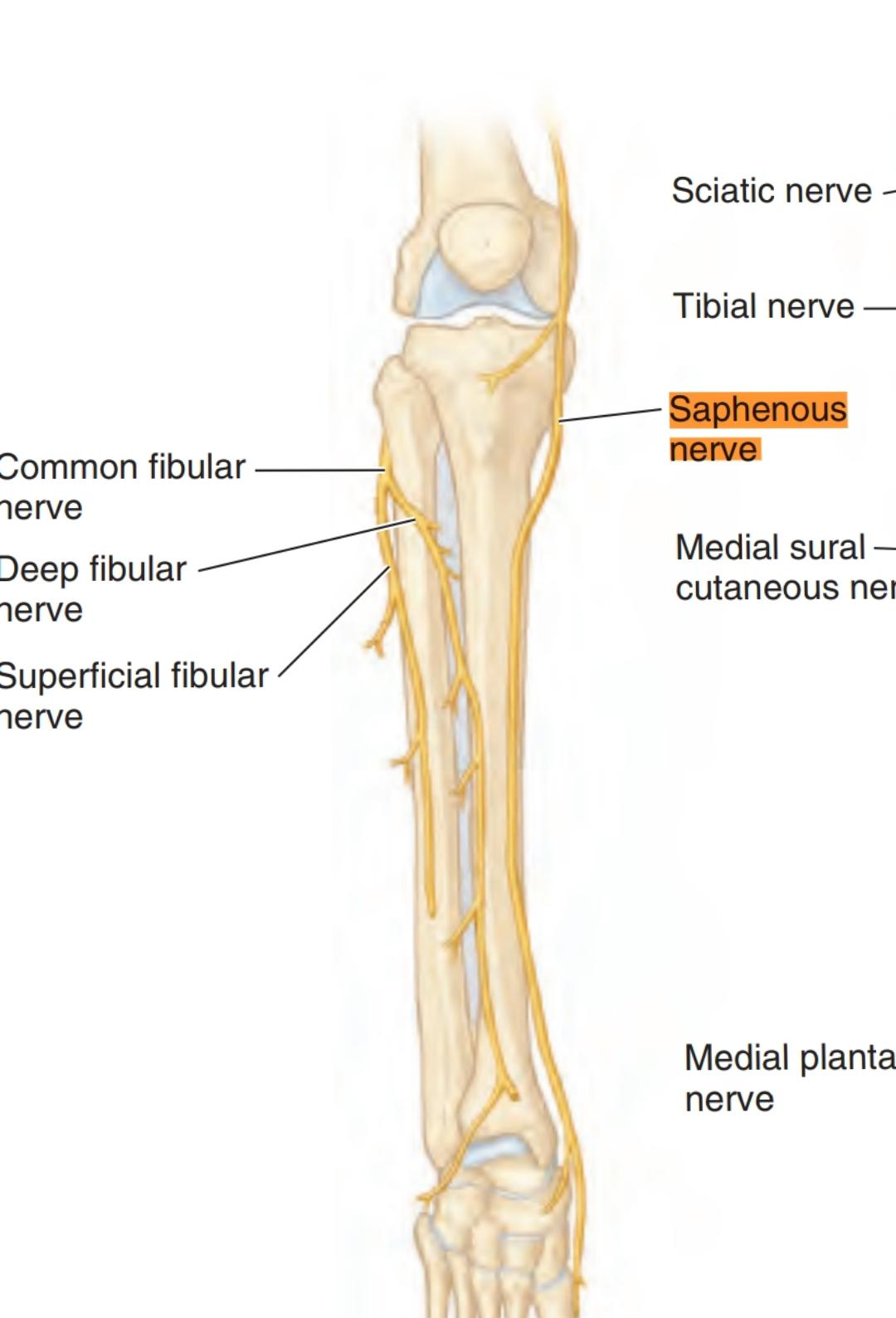
This branch is called infrapatellar nerve . This nerve shares to form the peripatellar plexus (it is a plexus found in front of the patella bone and the ligament of patella and the tip of tibia) and supplies the anteroinferior and medial aspects of the knee .
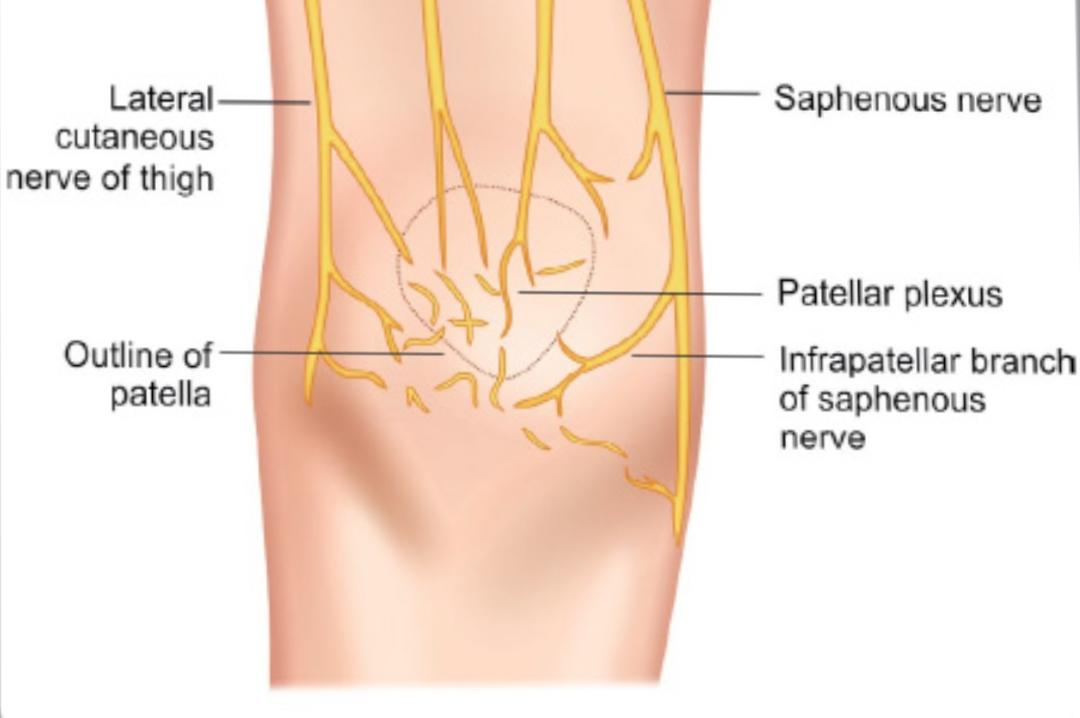
Patellar plexus
In the leg
The saphenous nerve continues to run down behind the medial edge of the tibia ( medial aspect of the leg)
The saphenous nerve continues to run down behind the medial edge of the tibia ( medial aspect of the leg)
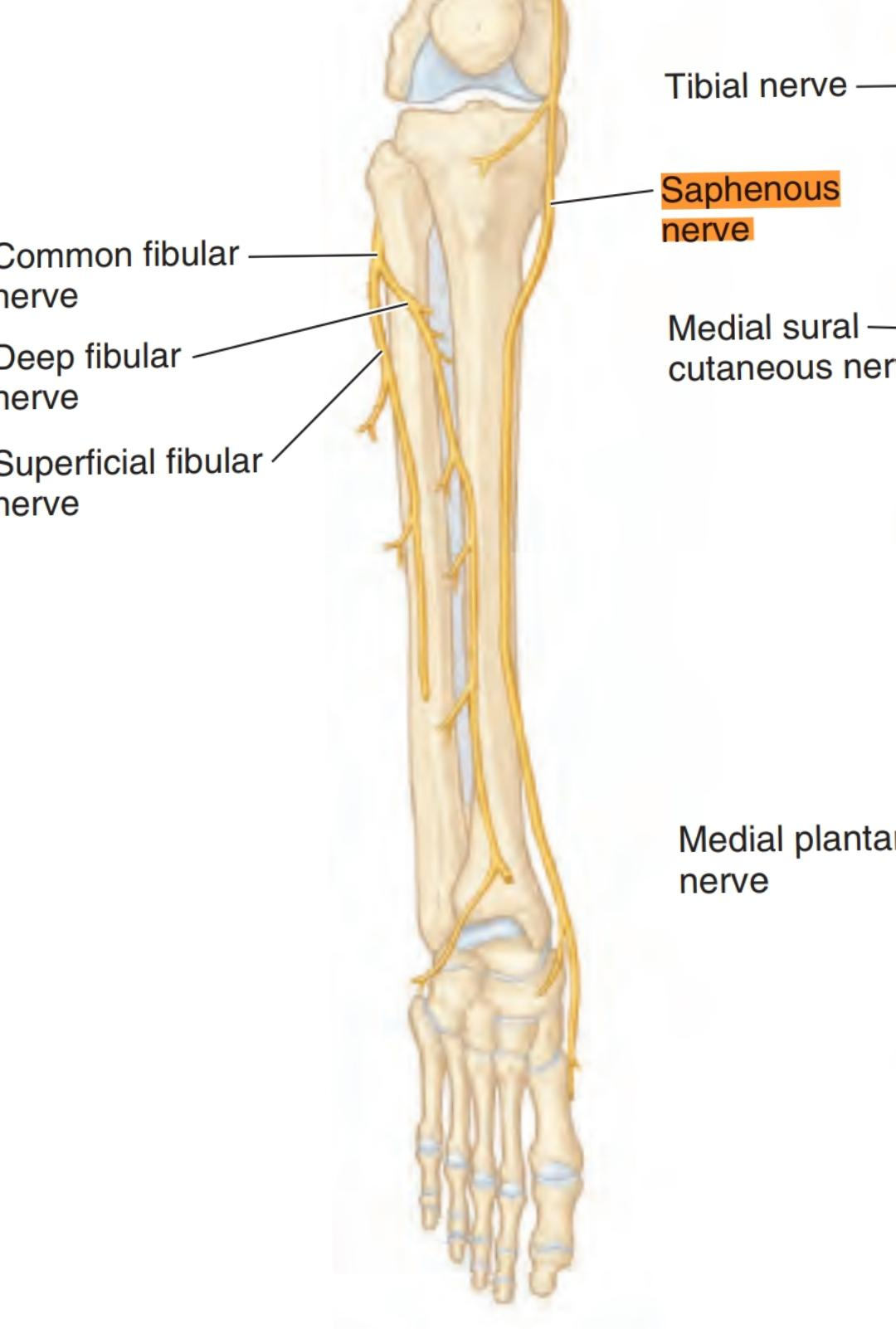
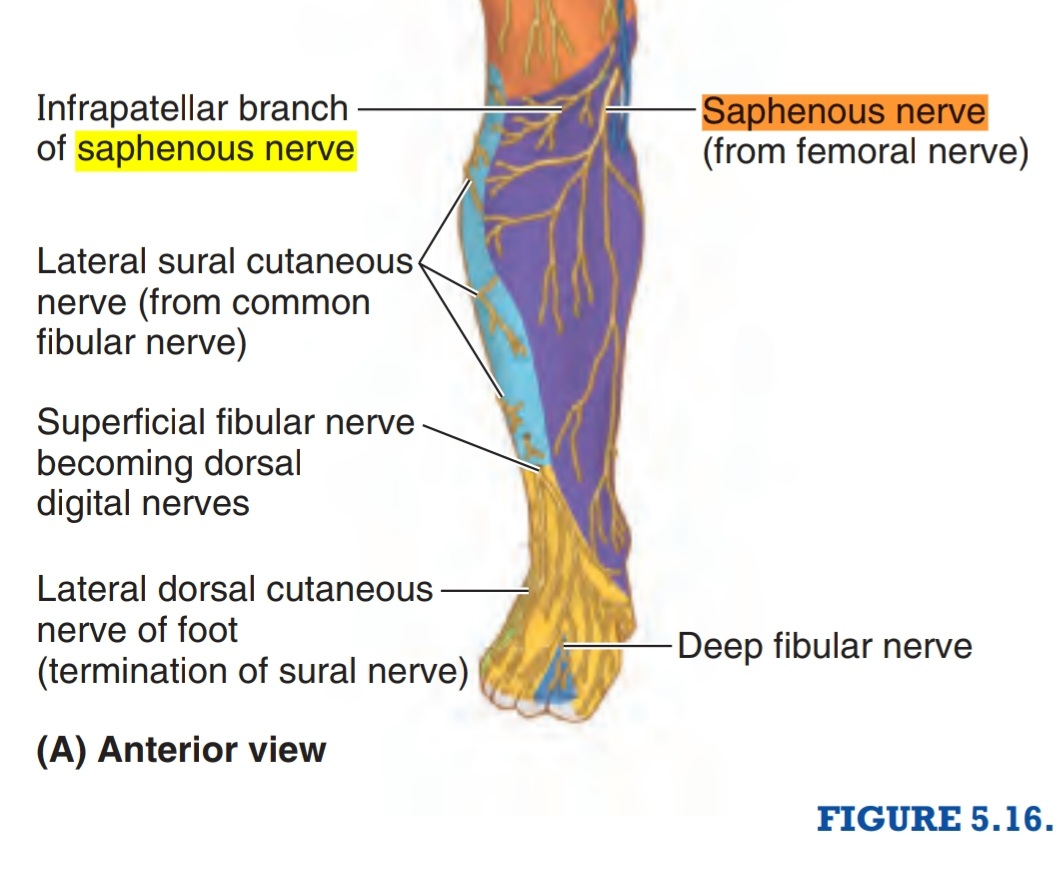
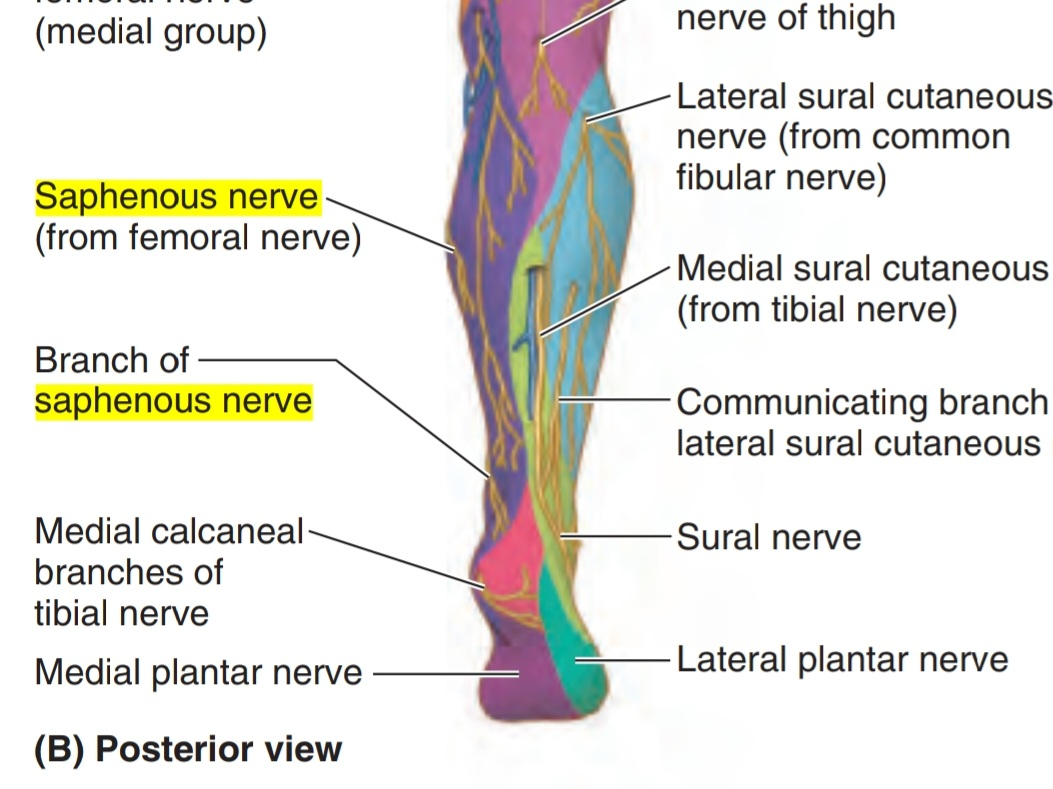
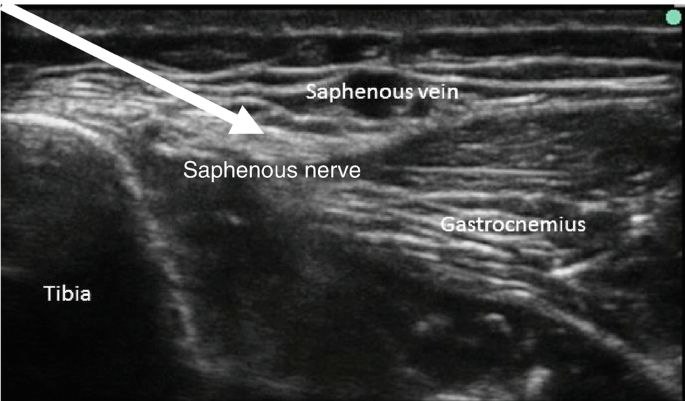
It runs with the greater saphenous vein ( posterior to it ) then continues medial to arrive to the medial malleolus tip ( proximal 3cm ) where it divides into two branches( anterior and posterior) but the saphenous vein doesn’t divide and continues in the foot. These branches terminate in the integument near to the tip of the medial malleolus. While arriving to the lower third of the leg before arriving to the medial malleolus, it gives the medial crural cutaneous branches to supply the sensation of the anterior and medial surfaces of the leg
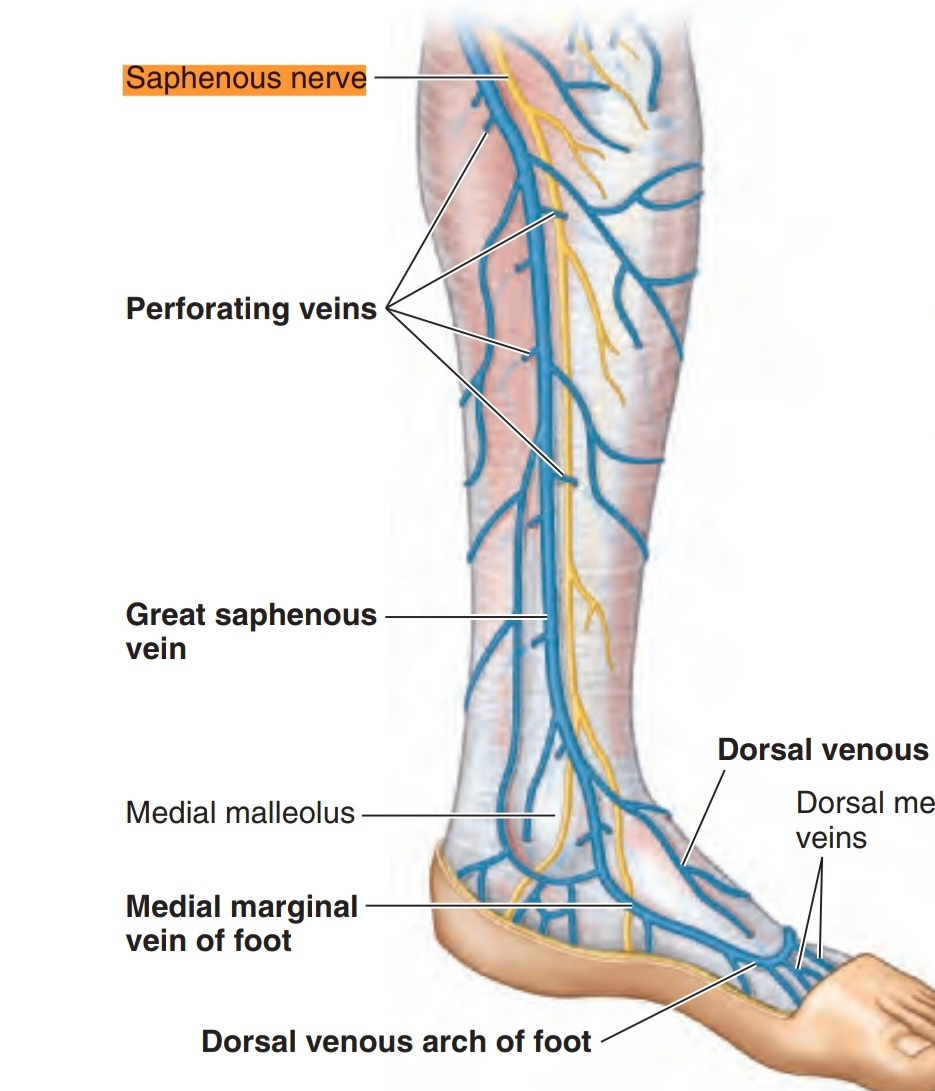
branches of the saphenous nerve:
1. Branch to subsartorial plexus
2. The largest branch of its branches is called infrapatellar nerve. This nerve shares to form the peripatellar plexus and supplies the anteroinferior and medial aspects of the knee
3. The medial crural cutaneous branches to supply the sensation of the anterior and medial surfaces of the leg.
2. The largest branch of its branches is called infrapatellar nerve. This nerve shares to form the peripatellar plexus and supplies the anteroinferior and medial aspects of the knee
3. The medial crural cutaneous branches to supply the sensation of the anterior and medial surfaces of the leg.
Cutaneous spaces of the saphenous nerve:
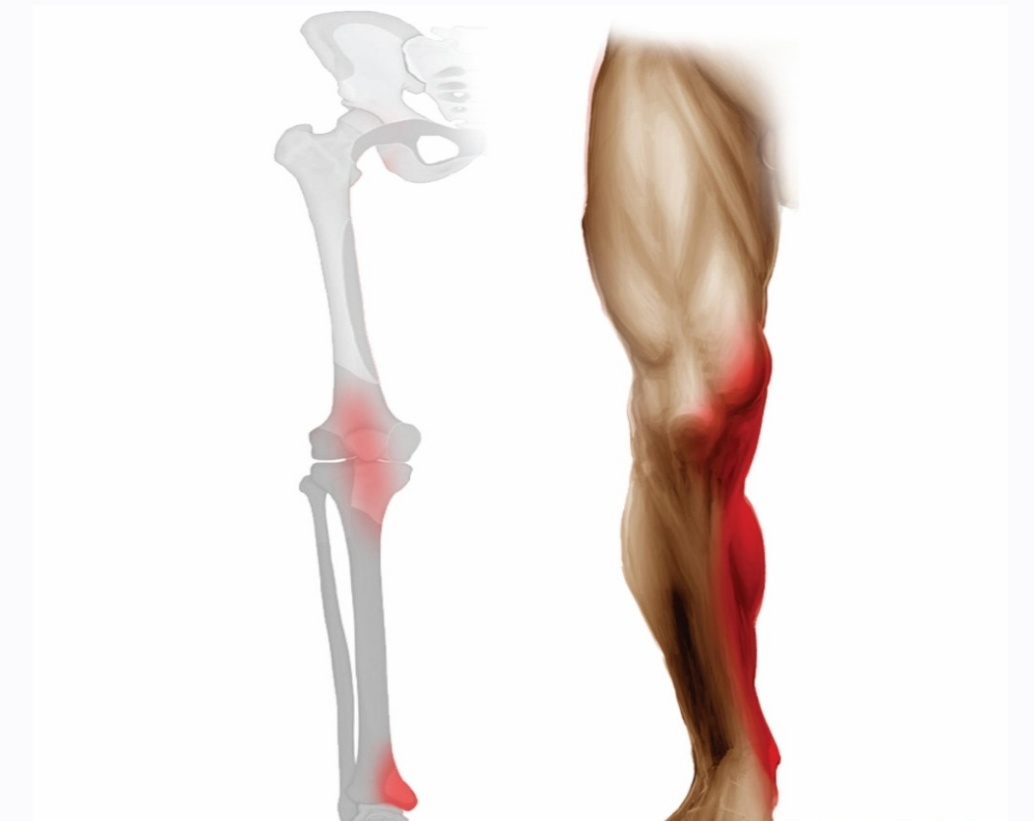
Clinical notes of the saphenous nerve :
It does not usually get damaged or injured because of its location deep in the structures of the thigh, but some injuries may occur, such as
Entrapment, known as Gonalgia Paresthetica
It can be occurred by
• Irritation
• Compression at the adductor canal or anywhere along the course of the nerve .
• Also it could be caused by the effect of the surgery .
At the outlet of the adductor canal is one of the most common areas to occur there.
Entrapment, known as Gonalgia Paresthetica
It can be occurred by
• Irritation
• Compression at the adductor canal or anywhere along the course of the nerve .
• Also it could be caused by the effect of the surgery .
At the outlet of the adductor canal is one of the most common areas to occur there.
Symptoms
1. Mild pain in the thigh or leg
2. Pain may be accompanied by burning
3. Pain increases when the person is carrying something heavy
Treatment
It does not require a surgical intervention, it could be treated by
1.Anti-inflammatory drugs
2.Exercise
1. Mild pain in the thigh or leg
2. Pain may be accompanied by burning
3. Pain increases when the person is carrying something heavy
Treatment
It does not require a surgical intervention, it could be treated by
1.Anti-inflammatory drugs
2.Exercise
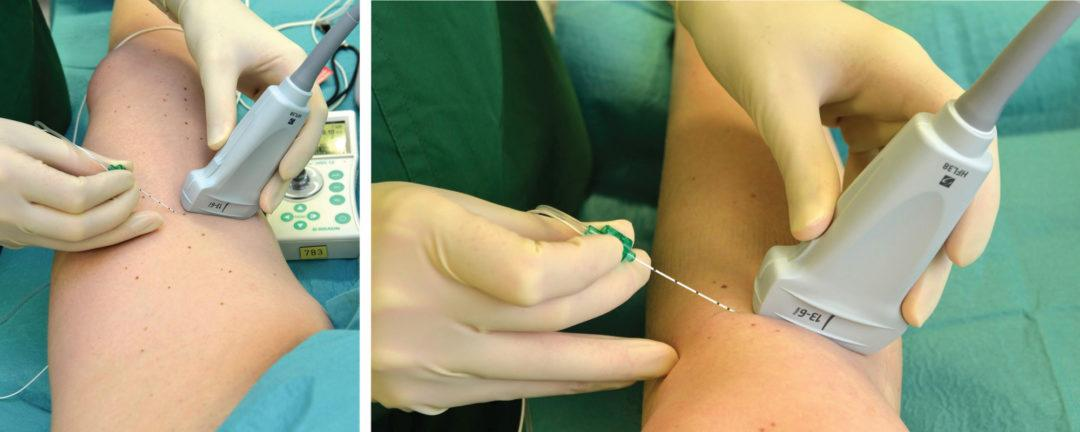
saphenous nerve block
The saphenous nerve block is common used in both
1.Emergency and perioperative settings procedural
2.Anesthesia and post procedural pain management .
The useful use of regional anaesthesia procedure is often used to block pain in the medial ankle and leg
It can be used under the ultrasound guidance to do this technique
1.Emergency and perioperative settings procedural
2.Anesthesia and post procedural pain management .
The useful use of regional anaesthesia procedure is often used to block pain in the medial ankle and leg
It can be used under the ultrasound guidance to do this technique
References:
1.MOORE Clinically Oriented ANATOMY Keith L. Moore Arthur F. Dalley Anne M.R. Agur617_618
2.Saphenous nerve Author : Roberto Grujičić MD . kenhub.https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/saphenous-nerve
3.Saphenous Nerve B.T. Carey , in Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences ( Second Edition ) 2014 ، science direct
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/veterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine/saphenous-nerve
4.Saphenous nerve Entrapment or Gonalgia Parenthetical, SPECTRUM HEALTHCARE
https://www.spectrumhealthcare.com.au/blog/?post=saphenous-nerve-entrapment-or-gonalgia-paresthetica
5.Saphenous Nerve Block Arnold C , Alvarado AC , Brady MF .book
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536967/
The figures
• from springer
• From uptodata
• From omega online publishers
• From anesthesia,pain,intensive care
• From jaypeedigital/ebook reader
• From research gate
• Moore Clinically Oriented ANATOMY FIGURE 5.26,5.25.,5.74,5.30.
1.MOORE Clinically Oriented ANATOMY Keith L. Moore Arthur F. Dalley Anne M.R. Agur617_618
2.Saphenous nerve Author : Roberto Grujičić MD . kenhub.https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/saphenous-nerve
3.Saphenous Nerve B.T. Carey , in Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences ( Second Edition ) 2014 ، science direct
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/veterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine/saphenous-nerve
4.Saphenous nerve Entrapment or Gonalgia Parenthetical, SPECTRUM HEALTHCARE
https://www.spectrumhealthcare.com.au/blog/?post=saphenous-nerve-entrapment-or-gonalgia-paresthetica
5.Saphenous Nerve Block Arnold C , Alvarado AC , Brady MF .book
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536967/
The figures
• from springer
• From uptodata
• From omega online publishers
• From anesthesia,pain,intensive care
• From jaypeedigital/ebook reader
• From research gate
• Moore Clinically Oriented ANATOMY FIGURE 5.26,5.25.,5.74,5.30.
