
Lower Triangular Space
By : Amna MohammedDefinition
It is an intermuscular space, is also known as Lateral triangle space , Triangle interval & Triceps hiatus .
Location
Located below the shoulder (glenohumeral) joint.
The borders
has 3 borders
Superiorly: Teres major m.
Medially: The long head of the triceps m.
Laterally: The shaft of the humerus bone
Superiorly: Teres major m.
Medially: The long head of the triceps m.
Laterally: The shaft of the humerus bone
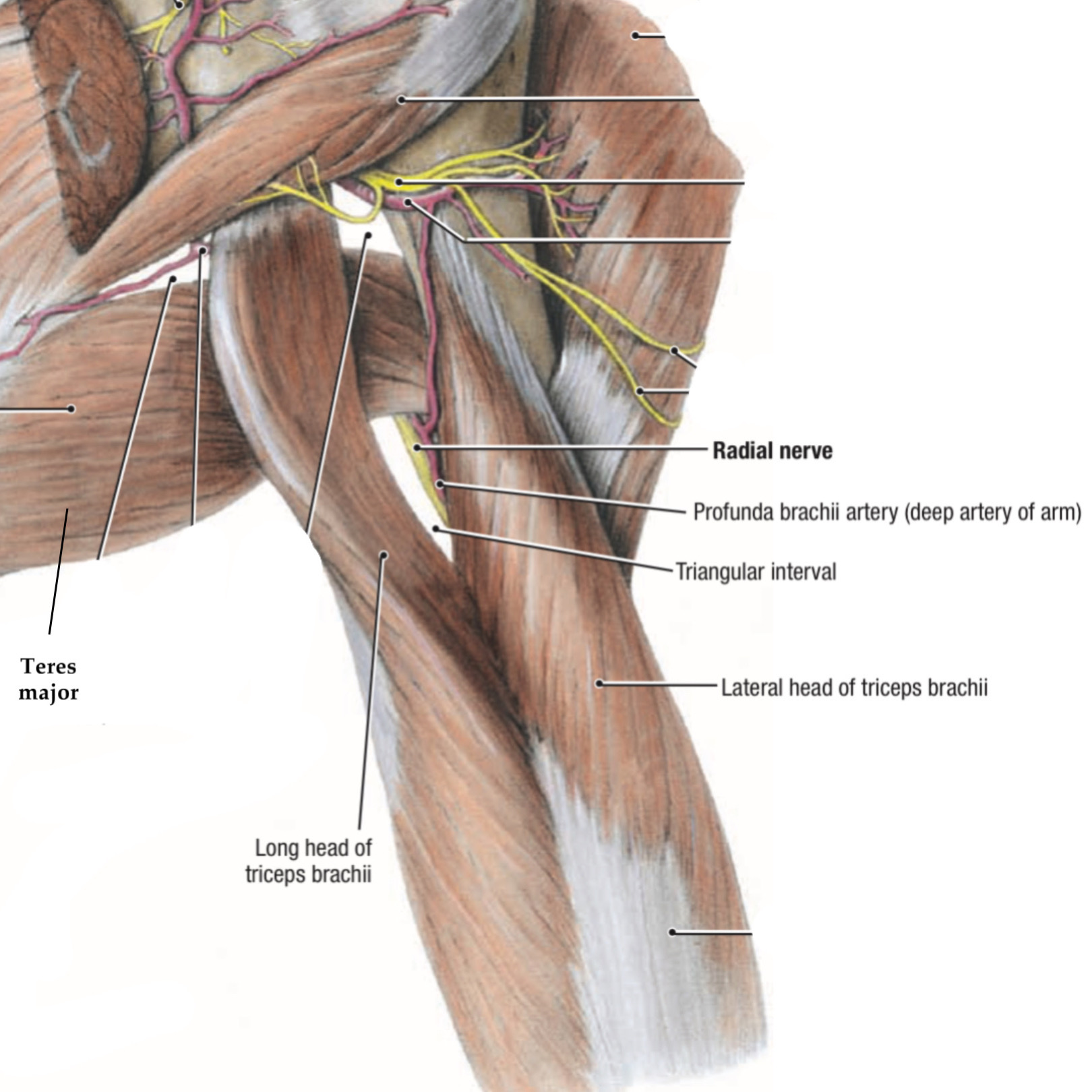
Posterior view, right upper limb.
Note\ For some sources, there is a diversity in the structure that is considered as the lateral border, some of them consider the medial head of the triceps as the lateral border, the others consider the shaft of the humerus bone as the lateral border, In both cases, the difference is slight and does not affect.
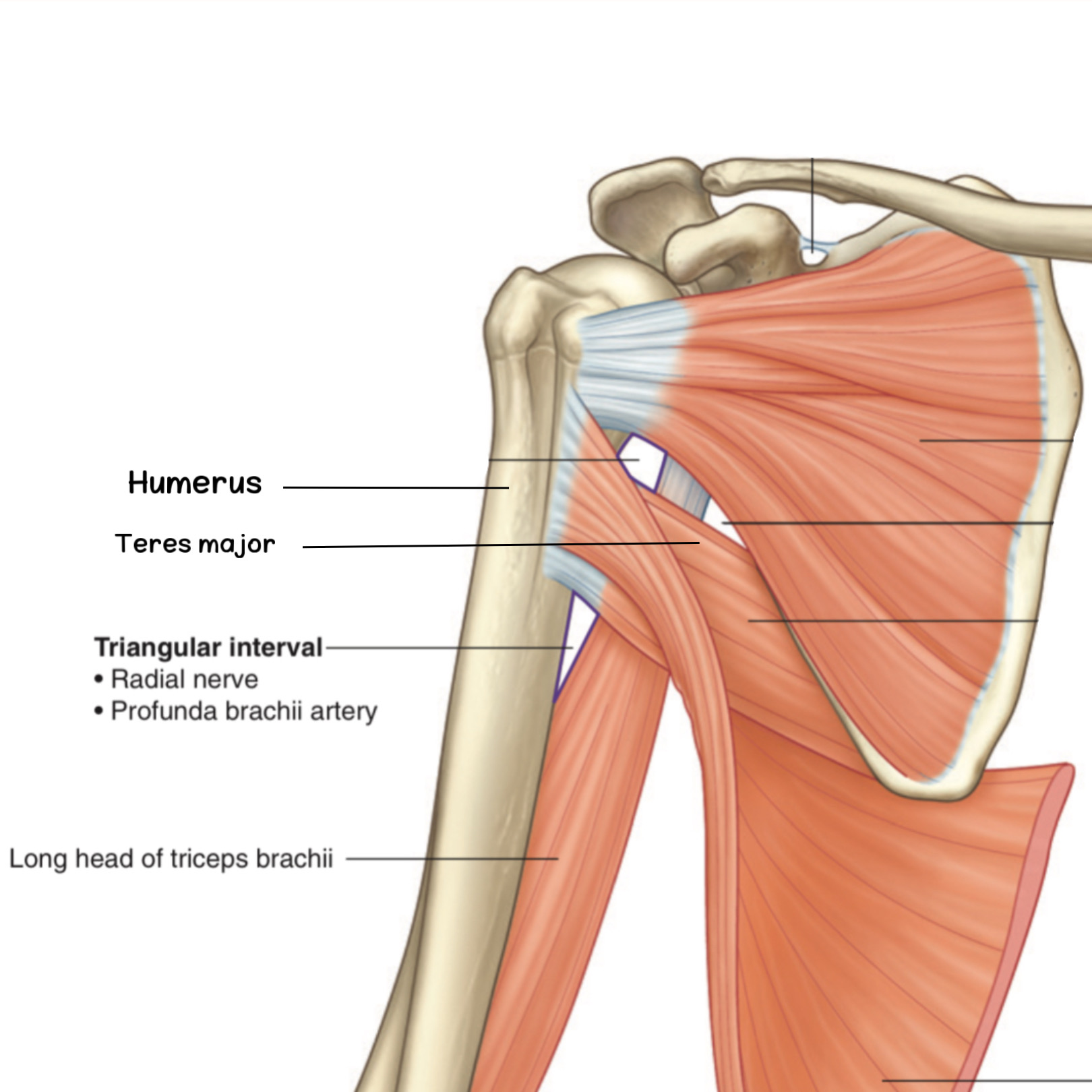
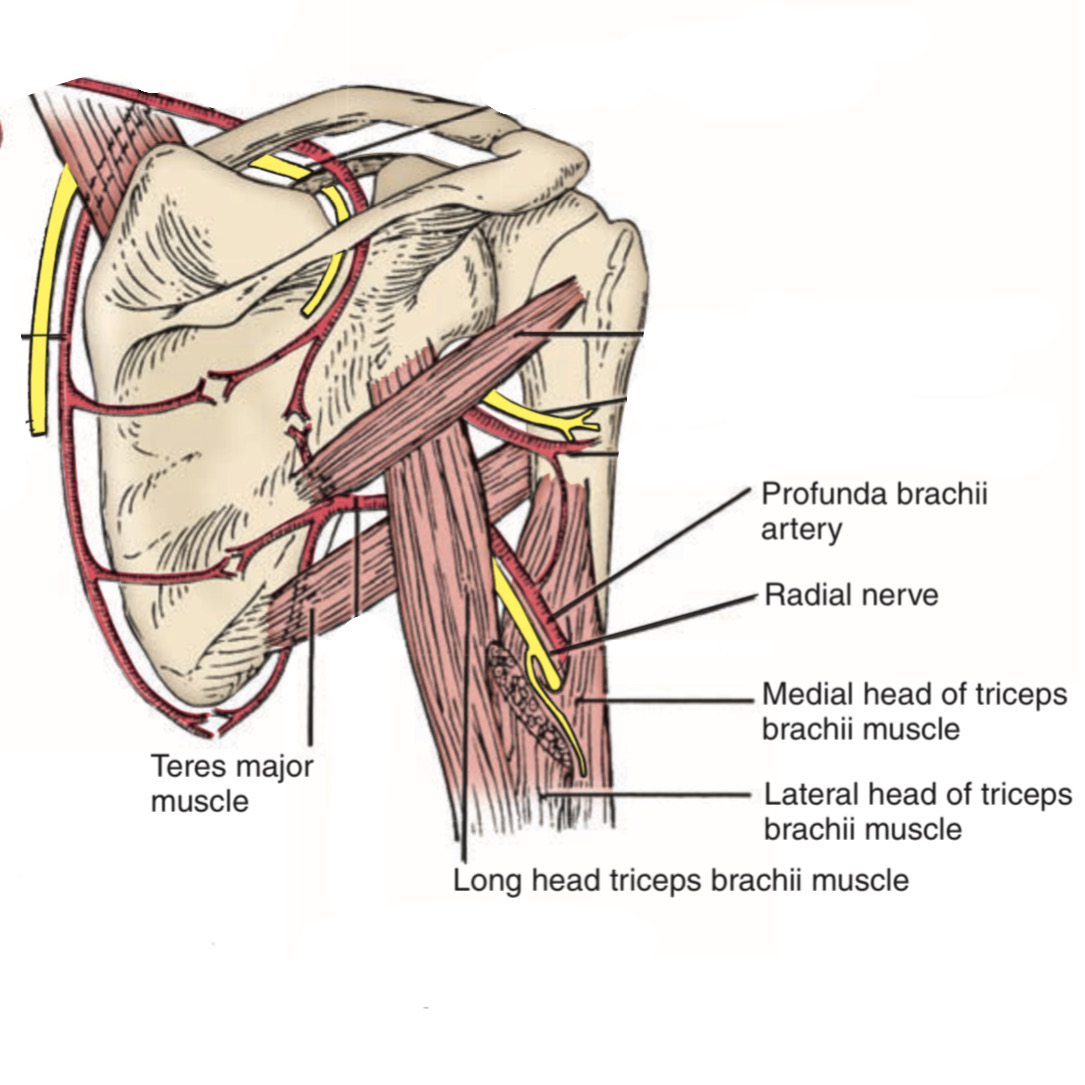
Anterior view, right upper limb.
The contents
there are two major structures that pass through this space ( 1 artery, & 1 nerve) :
1. The profunda brachii artery
Is the largest branch of the brachial artery, & passes to the posterior of the arm through the triangle interval accompanying the radial nerve during its path in the spiral groove of the humerus.
2. The radial nerve
Is the terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus passes through this space with the produnda brachii artery which innervates most muscles of the posterior side of the upper limb.
1. The profunda brachii artery
Is the largest branch of the brachial artery, & passes to the posterior of the arm through the triangle interval accompanying the radial nerve during its path in the spiral groove of the humerus.
2. The radial nerve
Is the terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus passes through this space with the produnda brachii artery which innervates most muscles of the posterior side of the upper limb.

Posterior view, right upper limb.
Clinical importance
The lower triangle space is considered as a passageway from the anterior region of the axilla to the posterior region of the arm.
Triangular Interval Syndrome(TIS)
It is a condition when the radial nerve is confined in the triangular interval for some reason & causes pain along the upper limb.
The possible causes of TIS
For these reasons the radial nerve is weak & vulnerable to being entrapped in this space:
1. Fibrous bands: structures that are located between the teres major m. & long head of the triceps m.
2. hypertrophy the teres major m.
3. performing sports and weight training which demand repetitive strong stretching and punching.
1. Fibrous bands: structures that are located between the teres major m. & long head of the triceps m.
2. hypertrophy
Note
hugeness3. performing sports and weight training which demand repetitive strong stretching and punching.
The Symptoms
1.Pain along the upper limb & shoulder.
2.Palsy the radial nerve.
2.Palsy the radial nerve.
The treatment
The treatment is non-surgical & includes:
1. Physical therapy.
2. Nerve activation.
3. Remedial exercises.
1. Physical therapy.
2. Nerve activation.
3. Remedial exercises.
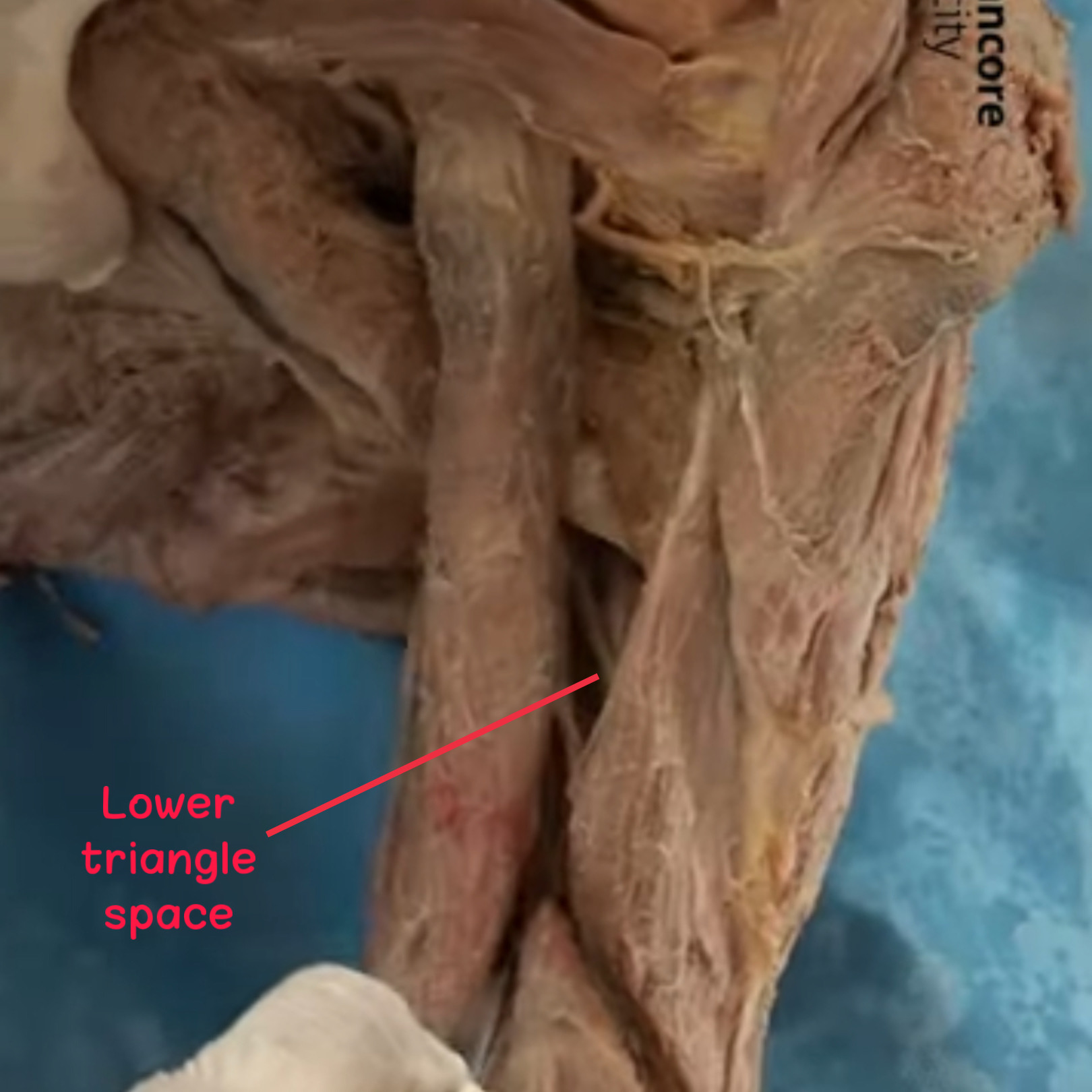
Posterior view, right upper limb.

A simple way to memorize the borders of the anatomical spaces in the upper limb.
References
Snell’s Clinical Anatomy By Regions (10th Edition)378
Gross Anatomy (7th Edition) 37(2-12)-38
Gray’s Anatomy for Students (4th Edition)720
BD_Chaurasia’s_Human_Anatomy, Volume 1 - Upper Limb Thorax (6th Edition) 71
Moore-Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) 723
Triangular interval syndrome: A differential diagnosis for upper extremity radicular pain- Pub Med- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20067361/
Triangular Interval & Quadrilateral Space Syndrome Quadrilateral Space Syndrome- OSTEOPATHY- https://osteopathy.colganosteo.com/triangular-interval-syndrome/
Gross Anatomy (7th Edition) Fig 3-37(2-12)
Fig 1-Grant’s Atlas Of Anatomy (13th Edition )6.42.
Gray’s Anatomy for Students (4th Edition)
Fig cover 705(7.37)
Fig2-718(7.45)
Gross Anatomy (7th Edition) Fig 3-37(2-12)
Fig 4-Gray’s Atlas Of Anatomy (2nd Edition)414
Fig 5-https://youtu.be/YetQwcWCuFQ
Fig 6-The way to memorize- Pinterest- https://pin.it/10zLzjN
Gross Anatomy (7th Edition) 37(2-12)-38
Gray’s Anatomy for Students (4th Edition)720
BD_Chaurasia’s_Human_Anatomy, Volume 1 - Upper Limb Thorax (6th Edition) 71
Moore-Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) 723
Triangular interval syndrome: A differential diagnosis for upper extremity radicular pain- Pub Med- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20067361/
Triangular Interval & Quadrilateral Space Syndrome Quadrilateral Space Syndrome- OSTEOPATHY- https://osteopathy.colganosteo.com/triangular-interval-syndrome/
Gross Anatomy (7th Edition) Fig 3-37(2-12)
Fig 1-Grant’s Atlas Of Anatomy (13th Edition )6.42.
Gray’s Anatomy for Students (4th Edition)
Fig cover 705(7.37)
Fig2-718(7.45)
Gross Anatomy (7th Edition) Fig 3-37(2-12)
Fig 4-Gray’s Atlas Of Anatomy (2nd Edition)414
Fig 5-https://youtu.be/YetQwcWCuFQ
Fig 6-The way to memorize- Pinterest- https://pin.it/10zLzjN
