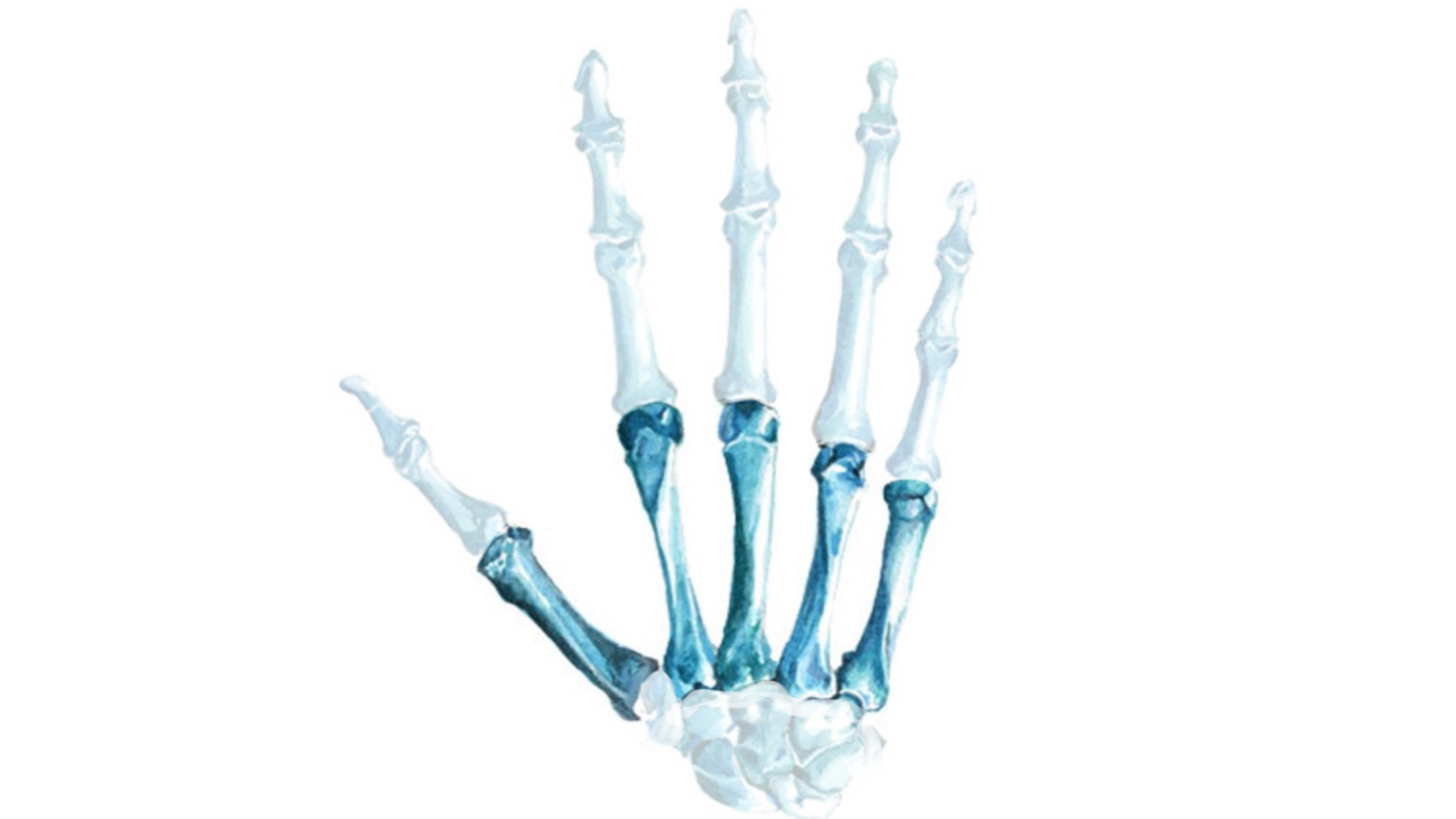
Metacarpal bones
By : Amna MohammedDefinition
A group of five bones belongs to the bones of the hand.
Location
They are located in the palm, between the carpal bones of the wrist & the phalanges of the fingers.
Shape
They are classified as diminutive long bones, so each of them has three parts:
1. The base: is the proximal end of the bone, extended in shape & articulates with the second line of the carpal bones.
2. The body (shaft): is the protracted part of the bone between the base& the head, concave at the palmar view, flat & convex at the dorsal view & has three surfaces ( medial, lateral & posterior) which appear as a triangle at the horizontal section.
3. The head: is the distal end of the bone, smooth & curved, articulates with the finger at its proximal phalanx, in the clenched fist position the head emerges.
1. The base: is the proximal end of the bone, extended in shape & articulates with the second line of the carpal bones.
2. The body (shaft): is the protracted part of the bone between the base& the head, concave at the palmar view, flat & convex at the dorsal view & has three surfaces ( medial, lateral & posterior) which appear as a triangle at the horizontal section.
3. The head: is the distal end of the bone, smooth & curved, articulates with the finger at its proximal phalanx, in the clenched fist position the head emerges.
Note: there is a part of the bone called the neck which is a region between the head & the shaft, its important because it has openings to allow the passage of the nutrition vessels to the bone.
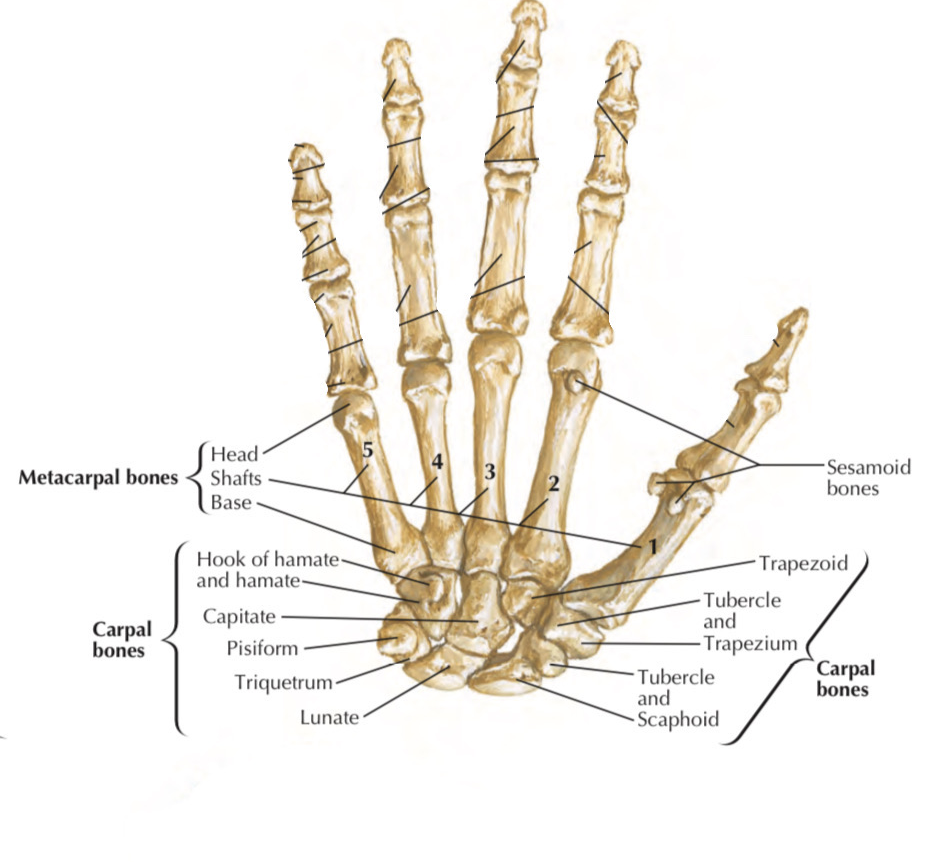
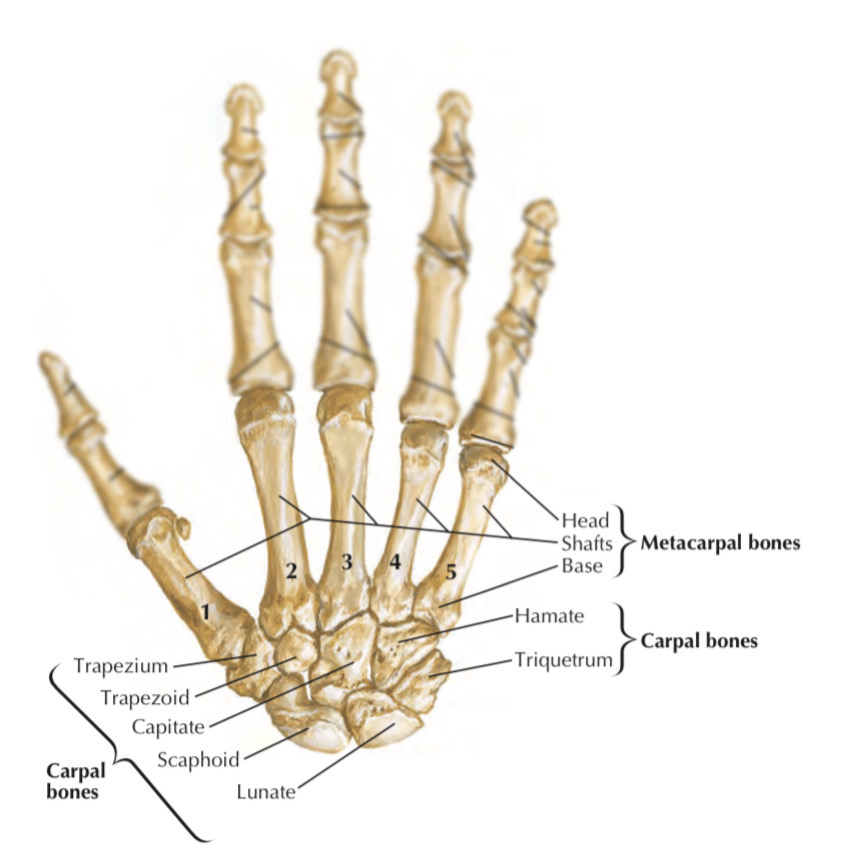
Right hand
Palmar view
Ossification of the metacarpal bones
1. During fetal life, the metacarpal bones are being ossified at their
heads & the base of the 1st metacarpal.
2. After the 11 age, all the metacarpal bones had been ossified.
heads & the base of the 1st metacarpal.
2. After the 11 age, all the metacarpal bones had been ossified.
Enumeration of the metacarpals (from lateral to medial)
1. Metacarpal of the thumb (1st):
It is the shortest & thickest one of the metacarpals.
It works independently and individually.
It has a special flexure on its base articular facet that forms a saddle joint with the trapezium bone of the carpal bones.
Its joint with the proximal phalanx is more perfect hinge movement because of its head articular facet roundness.
It is less than other metacarpals.
It has two sesamoid bones on the palmar surface below the head.
The main attachments are
1. The opponens opllicis m.
2. The abducter pollicis longus m.
3. The first palmar interosseous m.
It is the shortest & thickest one of the metacarpals.
It works independently and individually.
It has a special flexure on its base articular facet that forms a saddle joint with the trapezium bone of the carpal bones.
Its joint with the proximal phalanx is more perfect hinge movement because of its head articular facet roundness.
It is less than other metacarpals.
It has two sesamoid bones
Note
the sesamoid bone is a small bone embedded within a muscle or tendon near joint surfacesThe main attachments are
1. The opponens opllicis m.
2. The abducter pollicis longus m.
3. The first palmar interosseous m.
2. Metacarpal of the index (2nd)
It is the longest one of the metacarpals.
It has a Y shape.
On its base, it has 4 articular facets to form joints with:
1.Trapezium
2.Trapezoid
3.Capitate
4.The middle (3rd) metacarpal
Its head is spherical & forms a joint with the proximal phalanx of the index finger.
Unlike the 1st metacarpal, the 2nd metacarpal has just a one sesamoid bone on the palmar surface, just below the head.
The main attachmentss are:
1. The flexor carpi radialis m.
2. The extensor carpi radialis longus m.
3. The oblique head of the adductor pollicis m.
It is the longest one of the metacarpals.
It has a Y shape.
On its base, it has 4 articular facets to form joints with:
1.Trapezium
2.Trapezoid
3.Capitate
4.The middle (3rd) metacarpal
Its head is spherical & forms a joint with the proximal phalanx of the index finger.
Unlike the 1st metacarpal, the 2nd metacarpal has just a one sesamoid bone on the palmar surface, just below the head.
The main attachmentss are:
1. The flexor carpi radialis m.
2. The extensor carpi radialis longus m.
3. The oblique head of the adductor pollicis m.
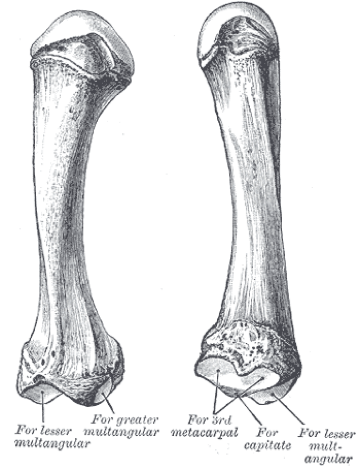
3. Metacarpal of the middle finger (3rd)
It is the second longest metacarpal bone after the index metacarpal.
Its base has 3 articular facets that form a joint with:
1.The 4th metacarpal on the medial side
2.Capitate
3.And has a small prominent elongated part to articulate with the 2nd metacarpal.
It has a rounded head to form the metacarpophalangeal joint with the proximal phalanx of the long finger.
The main attachmentss are:
1. the flexor carpi radialis m.
2. The extensor carpi radialis brevis m.
3. The oblique head of the adductor pollicis m.
4. The transverse head of the adductor pollicis m.
It is the second longest metacarpal bone after the index metacarpal.
Its base has 3 articular facets that form a joint with:
1.The 4th metacarpal on the medial side
2.Capitate
3.And has a small prominent elongated part to articulate with the 2nd metacarpal.
It has a rounded head to form the metacarpophalangeal joint with the proximal phalanx of the long finger.
The main attachmentss are:
1. the flexor carpi radialis m.
2. The extensor carpi radialis brevis m.
3. The oblique head of the adductor pollicis m.
4. The transverse head of the adductor pollicis m.
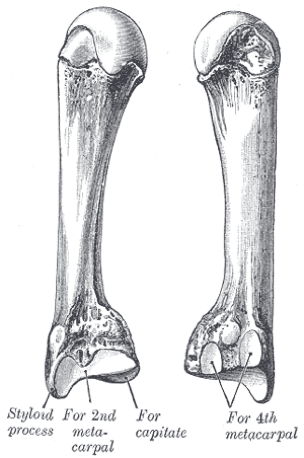
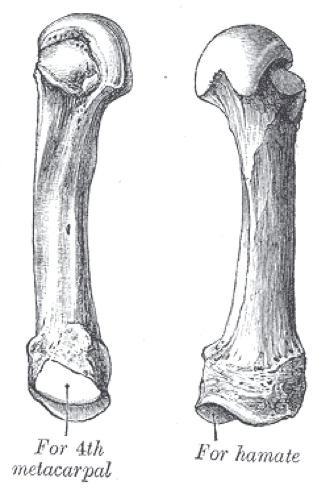
4. Metacarpal of the ring finger (4th)
It resembles the 2nd and the 3rd metacarpals in there features, except in:
1. It's a little smaller than them.
2. Its base has two essential articular facets( with the capitate & hamate bones) and a small articular region on its two sides to articulate with the 3rd and the 5th metacarpals.
Its spherical head forms a joint with the proximal phalanx of the ring finger.
The main attachment is:
1. The interossei m. only.
It resembles the 2nd and the 3rd metacarpals in there features, except in:
1. It's a little smaller than them.
2. Its base has two essential articular facets( with the capitate & hamate bones) and a small articular region on its two sides to articulate with the 3rd and the 5th metacarpals.
Its spherical head forms a joint with the proximal phalanx of the ring finger.
The main attachment is:
1. The interossei m. only.
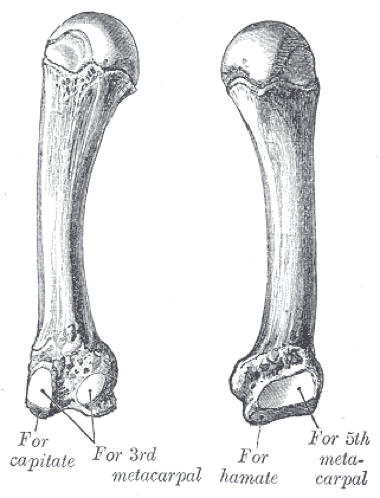
5. Metacarpal of the little finger (5th)
It has the same features as the other metacarpals, but It's the thinnest one between the metacarpals.
Its base shows some difference, which it has two articular facets to form a joint with:
1.The hamate bone on the lateral side
2.The 4th metacarpal bone on the lateral side
Its base doesn't have an articular facet on the medial side.
It forms a joint by its head with the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
The main attachments are:
1. The extensor carpi ulnaris m.
2. The opponens digiti minimi m.
It has the same features as the other metacarpals, but It's the thinnest one between the metacarpals.
Its base shows some difference, which it has two articular facets to form a joint with:
1.The hamate bone on the lateral side
2.The 4th metacarpal bone on the lateral side
Its base doesn't have an articular facet on the medial side.
It forms a joint by its head with the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
The main attachments are:
1. The extensor carpi ulnaris m.
2. The opponens digiti minimi m.
Clinical importance
These bones are easy to get fractured, especially the athletes, and exactly the 1st and the 5th metacarpals.
A) The first metacarpal fracture “Bennett’s Fracture”
This condition refers to the 1st metacarpal base fracture that leads to the split of the thumb from the medial side of the hand.
The possible causes of the fracture:
1. The main cause of the fracture is the applied force on it during thumb flexion.
2. The other causes are related to the trapezium fracture & the neighboring ligament injuries.
2. The other causes are related to the trapezium fracture & the neighboring ligament injuries.

Dorsal view, right hand
The symptoms
1. Pain & tenderness on the thumb base.
2. Limited movement of the thumb.
3. Reduced ability to grasp the pinch.
2. Limited movement of the thumb.
3. Reduced ability to grasp the pinch.
The diagnosis
1. The diagnosis includes radiographs of the hand & the thumb especially in certain movements, to show the fracture type and its location.
2. The diagnosis also includes CT scans to show the fracture details and how much damage has occurred.
2. The diagnosis also includes CT scans to show the fracture details and how much damage has occurred.
The treatment
1. The treatment includes a suitable splint for the fracture condition.
2. It is possible to resort to the use of screw and wire fixation techniques to fix the bone.
3. The treatment also includes physical therapy under the supervision of a specialist and for a certain period with splint treatment or surgery.
2. It is possible to resort to the use of screw and wire fixation techniques to fix the bone.
3. The treatment also includes physical therapy under the supervision of a specialist and for a certain period with splint treatment or surgery.
B) The fifth metacarpal fracture (Boxer’s fracture)
This condition refers to the 5th metacarpal neck fracture.
It's common among
1. Males more than females.
2. 10-29 years old people.
3. Boxer players.
It's common among
1. Males more than females.
2. 10-29 years old people.
3. Boxer players.
The possible causes of the fracture
1. The main cause of this fracture is the direct hit on a clenched grip that targets the metacarpals.
2. Uncommonly, this bone can be fractured in motorcycle accidents.
2. Uncommonly, this bone can be fractured in motorcycle accidents.
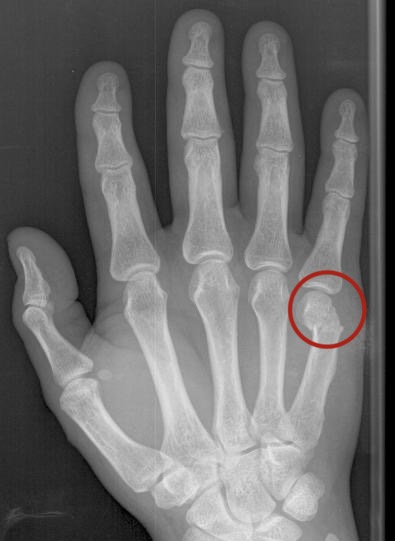
Dorsal view, right hand
The symptoms
1. Pain at the hand dorsal exactly at the location of the 5th metacarpal.
2. Swelling & distortion on the trauma point.
2. Swelling & distortion on the trauma point.
The diagnosis
1. The diagnosis includes a physical examination to evaluate the structures damage degree.
2. It includes also radiographs & CT scans to find out how much the fracture is acute and to be ensured of other bones and structures condition.
2. It includes also radiographs & CT scans to find out how much the fracture is acute and to be ensured of other bones and structures condition.
The treatment
The treatment includes a suitable splint for the fracture condition and putting in mind the amount of the damage caused to adjacent structures and their treatment.
References
Snell’s Clinical Anatomy By Regions (10th Edition) 238-239
Moore-Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition)680,687
Last’s Anatomy -Regional& Applied (9th Edition)140
BD_Chaurasia’s_Human_Anatomy, Volume 1 - Upper Limb Thorax (6th Edition) 26,28,29
Surgical Anatomy of the Hand & Upper Extermity 63-77
Metacarpal bones- radiopedia- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/metacarpal-bones-1
Bennett fracture- radiopedia- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/bennett- fracture
Bennett Fracture- Carter KR, Nallamothu SV- Books- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500035/
Bennett's fracture- physiopedia- https://www.physio- pedia.com/Bennett%27s_fracture#cite_note-6
Base of Thumb Fractures- orthobullets- https://www.orthobullets.com/hand/6036/base-of-thumb-fractures
Metacarpal Fractures- orthobullets- https://www.orthobullets.com/hand/6037/metacarpal-fractures
Fifth Metacarpal Fractures- Malik S, Herron T, Rosenberg N- Books- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470428/
Fractures of the metacarpals. A retrospective analysis of incidence and
aetiology and a review of the English-language literature- pinned-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8045639/
Fig cover-Pinterest- https://pin.it/6KqL2cz
Fig1-2- Netter- Atlas Of Human Anatomy (6th Edition)443
Fig 3-4-5-6-7- Bartleby.com https://www.bartleby.com/107/55.html
Fig8- life in the fast lane- https://litfl.com/bennett-fracture- eponymictionary/
Fig9- https://step1.medbullets.com/msk/107089/boxer-fracture-fifth- metacarpal-neck-fracture
Moore-Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition)680,687
Last’s Anatomy -Regional& Applied (9th Edition)140
BD_Chaurasia’s_Human_Anatomy, Volume 1 - Upper Limb Thorax (6th Edition) 26,28,29
Surgical Anatomy of the Hand & Upper Extermity 63-77
Metacarpal bones- radiopedia- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/metacarpal-bones-1
Bennett fracture- radiopedia- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/bennett- fracture
Bennett Fracture- Carter KR, Nallamothu SV- Books- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500035/
Bennett's fracture- physiopedia- https://www.physio- pedia.com/Bennett%27s_fracture#cite_note-6
Base of Thumb Fractures- orthobullets- https://www.orthobullets.com/hand/6036/base-of-thumb-fractures
Metacarpal Fractures- orthobullets- https://www.orthobullets.com/hand/6037/metacarpal-fractures
Fifth Metacarpal Fractures- Malik S, Herron T, Rosenberg N- Books- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470428/
Fractures of the metacarpals. A retrospective analysis of incidence and
aetiology and a review of the English-language literature- pinned-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8045639/
Fig cover-Pinterest- https://pin.it/6KqL2cz
Fig1-2- Netter- Atlas Of Human Anatomy (6th Edition)443
Fig 3-4-5-6-7- Bartleby.com https://www.bartleby.com/107/55.html
Fig8- life in the fast lane- https://litfl.com/bennett-fracture- eponymictionary/
Fig9- https://step1.medbullets.com/msk/107089/boxer-fracture-fifth- metacarpal-neck-fracture
