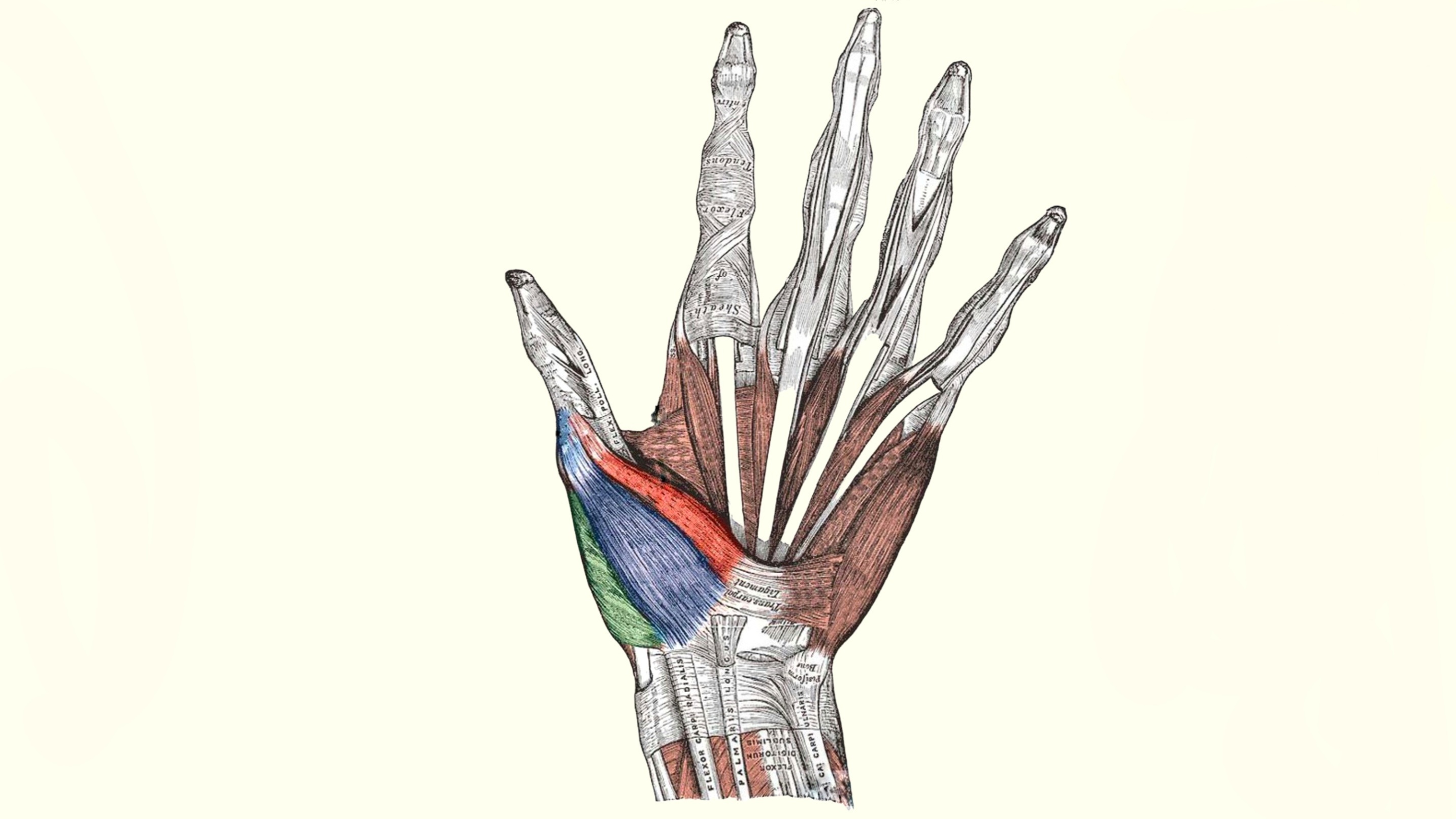
Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
By : Omar M. Subhi Altaie• NAME
The first part of the name indicates that this muscle flexes some body part, and the second part indicates that it applies that action to the thumb finger " pollicis ". the Latin word brevis means that it is shorter compared to the pollicis longus muscle in the forearm.
• GENERAL
Flexor pollicis brevis is one of three thenar muscle-group that Located laterally on the palm side of the hand, applies its actions on the thumb.
It is between the other two muscles of the group limiting the free-moving saddle joint of the thumb.
It passes over two joints of the thumb and they are:
• metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP)
• carpometacarpal joint (CMC)
It is between the other two muscles of the group limiting the free-moving saddle joint of the thumb.
It passes over two joints of the thumb and they are:
• metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP)
• carpometacarpal joint (CMC)
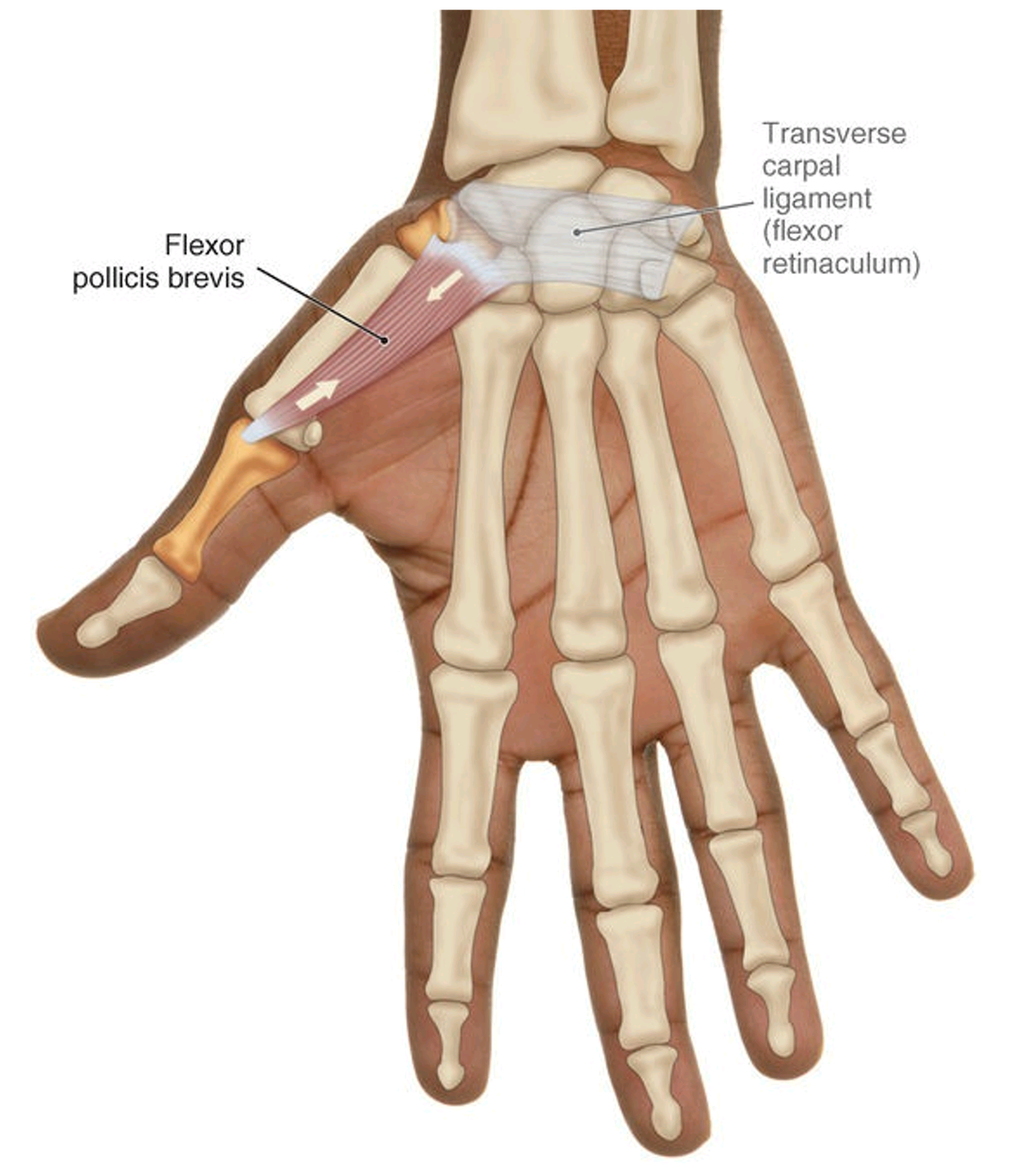
• SUPPLY
The nerve supply of the Flexor pollicis brevis muscle is divided into two parts :
• The superficial head of flexor pollicis muscle gets nerve supply from the recurrent branch of the median nerve,
• And the deep head gets nerve supply from the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
The blood supply of the Flexor pollicis brevis muscle is from the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery, branches of the princeps pollicis artery, and radialis indicis artery.
• The superficial head of flexor pollicis muscle gets nerve supply from the recurrent branch of the median nerve,
• And the deep head gets nerve supply from the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
The blood supply of the Flexor pollicis brevis muscle is from the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery, branches of the princeps pollicis artery, and radialis indicis artery.
● ORIGIN AND INSERTION
◇ Origin
The Flexor pollicis brevis muscle has two separated heads that arise from two different sites;
• Superficial head : arises from the border of the flexor retinaculum from the side of the metacarpal bones, and the distal part of the tubercle of trapezium bone (most lateral one of the carpal bones of the second row).
• Deep head : arises from the trapezoid (second lateral one of the carpal bones of the second row) and capitate (second medial of the carpal bones of the second row), and the palmar ligaments of the distal row of carpal bones.
◇ Insertion
The deep and superficial heads course obliquely and meet at the lateral side by a common short tendon of the base of the proximal phalanx of the first metacarpal bone of the thumb finger where they insert, and that tendon contains an embedded sesamoid bone which is the second sesamoid bones in the thumb.
The Flexor pollicis brevis muscle has two separated heads that arise from two different sites;
• Superficial head : arises from the border of the flexor retinaculum from the side of the metacarpal bones, and the distal part of the tubercle of trapezium bone (most lateral one of the carpal bones of the second row).
• Deep head : arises from the trapezoid (second lateral one of the carpal bones of the second row) and capitate (second medial of the carpal bones of the second row), and the palmar ligaments of the distal row of carpal bones.
◇ Insertion
The deep and superficial heads course obliquely and meet at the lateral side by a common short tendon of the base of the proximal phalanx of the first metacarpal bone of the thumb finger where they insert, and that tendon contains an embedded sesamoid bone which is the second sesamoid bones in the thumb.
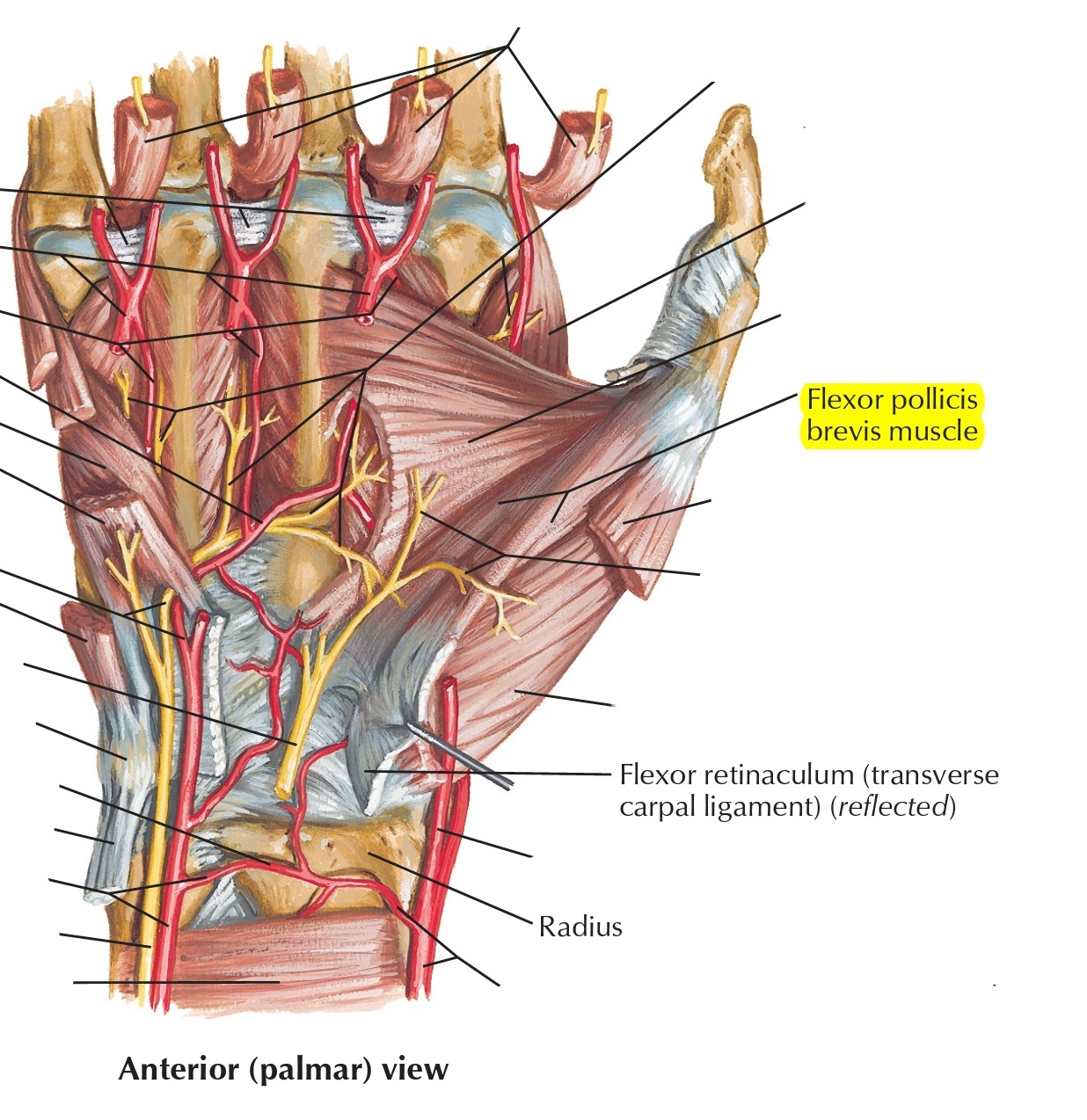
● MOVEMENT & ACTION
The main and basic action of the flexor pollicis bre-vis is simply Flexion; which can be seen when the metacarpal bone of the thumb is pulled medially to the anterior to the palm flexing the Carpometa-carpal joint of the thumb. And because it passes over the Metacarpophalgeal joint at the medial side so it flexes the proximal phalanx of the thumb too.
A good piece of information to add is that when the muscle is flexing at the latter joint it also medially rotating the thumb because of the morphology of the articular surface of the joint, so that is another action that (medial rotation) this muscle is capable of doing, the motion is coupled with the flexion; when moving the thumb toward the little finger with slightly changing its direction.
It also has another action which is ABduction; when the fibers that cross the joint anteriorly contract they pull the metacarpal bone of the thumb to move it to a position when it is vertical at a right angle with the surface of the palm, and the fibers also continue to reach the proximal interphalangeal joint, but the range of motion in this joint cannot be Ab-ducted.
The flexor pollicis brevis could be counted as a muscle that involves in the opposition of the thumb; because carpometacarpal joint opposition is composed of several actions like flexion, medial rotation, and abduction, as mentioned the flexor pollicis brevis does flexion and medial rotation of the thumb at that joint.
A good piece of information to add is that when the muscle is flexing at the latter joint it also medially rotating the thumb because of the morphology of the articular surface of the joint, so that is another action that (medial rotation) this muscle is capable of doing, the motion is coupled with the flexion; when moving the thumb toward the little finger with slightly changing its direction.
It also has another action which is ABduction; when the fibers that cross the joint anteriorly contract they pull the metacarpal bone of the thumb to move it to a position when it is vertical at a right angle with the surface of the palm, and the fibers also continue to reach the proximal interphalangeal joint, but the range of motion in this joint cannot be Ab-ducted.
The flexor pollicis brevis could be counted as a muscle that involves in the opposition of the thumb; because carpometacarpal joint opposition is composed of several actions like flexion, medial rotation, and abduction, as mentioned the flexor pollicis brevis does flexion and medial rotation of the thumb at that joint.
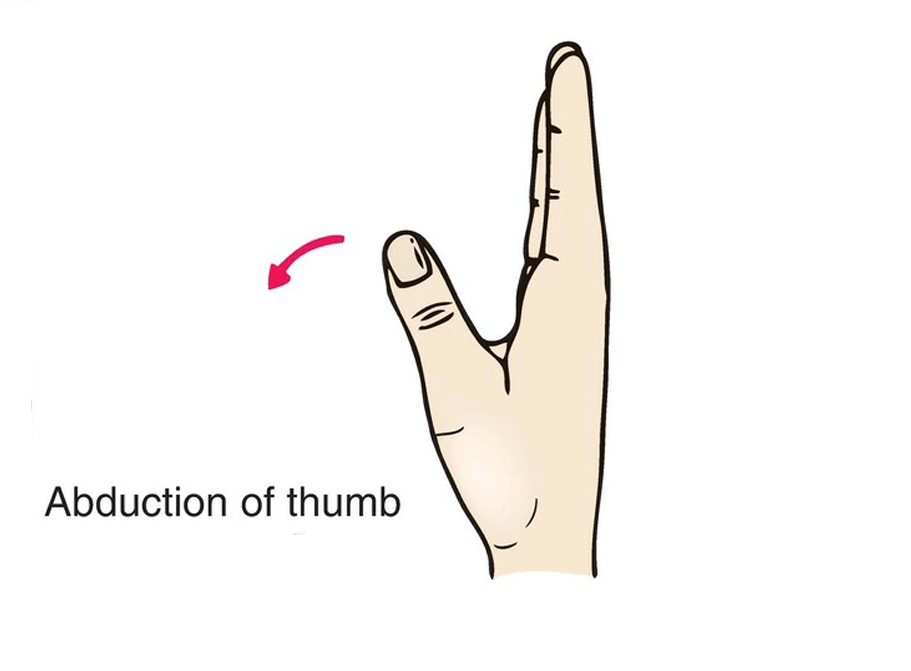
• REVERSE ACTION
As we know the normal action of any muscle is when the proximal attachment of the origin of that muscle is fixed and the distal attachment which is the insertion is the movable portion, but when the opposite of that happens we call it Reverse action
The Reverse action of this muscle is when the metacarpal bone of the thumb is fixed in place due to weight or something that the person is holding, thus the carpal bone of origin moves toward the metacarpal bone and makes the muscle contract at the same Metacarpophalangeal joint.
The metacarpal bone of the thumb moves toward the proximal phalanx making the muscle contract at the carpometacarpophalangeal joint.
We actually use this muscle in daily activities accompanied by other near muscles to help in Tip-pinch movements. like when turning a key to unlock something, or when opening a package.
The Reverse action of this muscle is when the metacarpal bone of the thumb is fixed in place due to weight or something that the person is holding, thus the carpal bone of origin moves toward the metacarpal bone and makes the muscle contract at the same Metacarpophalangeal joint.
The metacarpal bone of the thumb moves toward the proximal phalanx making the muscle contract at the carpometacarpophalangeal joint.
We actually use this muscle in daily activities accompanied by other near muscles to help in Tip-pinch movements. like when turning a key to unlock something, or when opening a package.
• ANTAGONIST FUNCTIONS
The flexor pollicis brevis restrains the extension of the muscles that extend at the metacarpo-phalangeal joint and interphalangeal joint, it also slows the ad-dution of the muscles that adduct the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
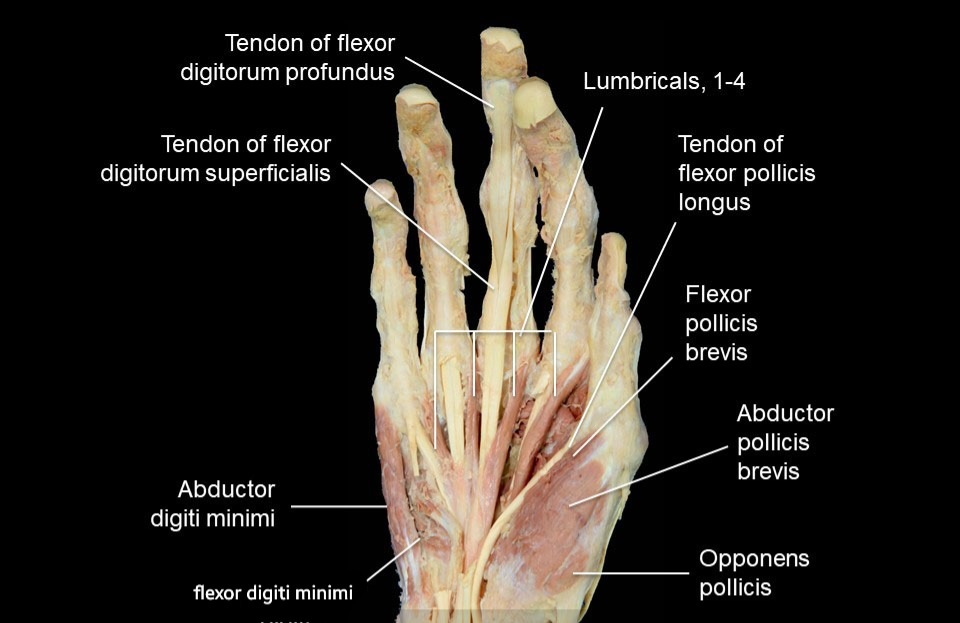
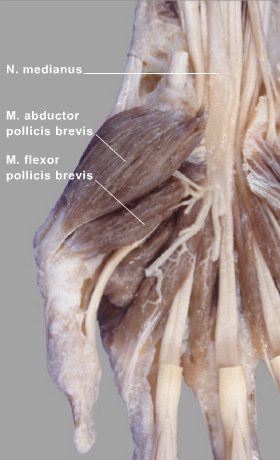
• Examination
With the patient seated and his palm facing upward, the doctor should apply resistance to the fleshy part at the base of his thumb and ask him to flex it against that resistance, if the muscle is intact, he should be able to flex it properly against that resistance .
At the same position of the hand. Bring the thumb to touch the base of the fifth little finger and apply more pressure on it. Hold the pressure for a few seconds and release it.
At the same position of the hand. Bring the thumb to touch the base of the fifth little finger and apply more pressure on it. Hold the pressure for a few seconds and release it.
• CLINICAL NOTES
Occurring of sensory weakness like numbness, paresthesias, and motor deficiency of the superficial head of the muscle, and the reason behind this is the blockage of the median nerve and compression which is occurred in carpal tunnel syndrome.
Circumduction and opposition actions require well-coordinated, simultaneous movements across each of the three thumb joints, because of Carpal tunnel syndrome this muscle does not have the ability to function as supposed to.
Circumduction and opposition actions require well-coordinated, simultaneous movements across each of the three thumb joints, because of Carpal tunnel syndrome this muscle does not have the ability to function as supposed to.
• RELATIONS
Flexor pollicis brevis one of the thenar eminence muscles group present on the lateral side of the hand, it is the most medial of this group.
Lateral and deep to it the abductor pollicis brevis, from the medial side of the opponens pollicis muscle, is located deep to the superficial head of the flexor pollicis brevis or something blended with it. The deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis is deep to the medial portion of the opponens pollicis muscle.
but from the medial side, there is adductor pollicis muscle with its two heads. the motor branch median nerve passes over the superficial surface of the muscle.
Lateral and deep to it the abductor pollicis brevis, from the medial side of the opponens pollicis muscle, is located deep to the superficial head of the flexor pollicis brevis or something blended with it. The deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis is deep to the medial portion of the opponens pollicis muscle.
but from the medial side, there is adductor pollicis muscle with its two heads. the motor branch median nerve passes over the superficial surface of the muscle.
● REFERENCES
• JOSEPH E. MUSCOLINO THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM MANUAL The Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body FOURTH EDITION pages 391, 398-401
• Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, Anne M. R Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) page 777
• Snell's clinical anatomy by Region's (10th edition) page 324
• flexor pollicis brevis, physiopedia website https://www.physio-pedia.com/Flexor_Pollicis_Brevis#:~:text=Flexor%20Pollicis%20Brevis(FPB)%20is,the%20outer%20and%20inner%20portions.
• Flexor pollicis brevis muscle Author: Gordana Sendić MD • Reviewer: Jana Vasković MD kenhub website: https://www.kenhub.com
• Flexor Pollicis Brevis Posted on 23rd Jul 2020 REHAB my patient website https://www.rehabmypatient.com/hand-fingers-thumb/flexor-pollicis-brevis
• Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle. Anatomical Study and Clinical Implications Edie Benedito Caetano et al. Open Orthop J. 2017 national library of medicine website: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29290870/
• Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, Anne M. R Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) page 777
• Snell's clinical anatomy by Region's (10th edition) page 324
• flexor pollicis brevis, physiopedia website https://www.physio-pedia.com/Flexor_Pollicis_Brevis#:~:text=Flexor%20Pollicis%20Brevis(FPB)%20is,the%20outer%20and%20inner%20portions.
• Flexor pollicis brevis muscle Author: Gordana Sendić MD • Reviewer: Jana Vasković MD kenhub website: https://www.kenhub.com
• Flexor Pollicis Brevis Posted on 23rd Jul 2020 REHAB my patient website https://www.rehabmypatient.com/hand-fingers-thumb/flexor-pollicis-brevis
• Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle. Anatomical Study and Clinical Implications Edie Benedito Caetano et al. Open Orthop J. 2017 national library of medicine website: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29290870/
● IMAGES REFERENCES
• Cover image from https://twitter.com/Radford_DPT/status/965657989691650051?t=EkP55hkCYQb8S7DURp_NdQ&s=19
• Fig1 Anterior view of the right flexor pollicis brevis FIGURE 9-7 .JOSEPH E. MUSCOLINO THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM MANUAL The Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body FOURTH EDITION PAGE 399
• Fig2 Frank H. Netter, Atlas of Human Anatomy (7th edition) plate 455
• Fig3 & Fig4 Various positions of the hand and movements of the thumb.(C) (F). Anterior views showing movements of the thumb Figure 3.81. Snell's clinical anatomy by Region's (10th edition) page 423
• Fig5 Prosection 1 – Muscles of the thenar and hypothenar eminences. Suárez-Quian & Vilensky. teach me anatomy website, https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/muscles/hand/
• Fig6 Hand muscles thenar muscles learn anatomy website: https://e-learn.anatomy.uzh.ch/anatomie/Bewegungsapparat/bewapp_HTML_eng/hand/handMlehr32.htm
• Fig1 Anterior view of the right flexor pollicis brevis FIGURE 9-7 .JOSEPH E. MUSCOLINO THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM MANUAL The Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body FOURTH EDITION PAGE 399
• Fig2 Frank H. Netter, Atlas of Human Anatomy (7th edition) plate 455
• Fig3 & Fig4 Various positions of the hand and movements of the thumb.(C) (F). Anterior views showing movements of the thumb Figure 3.81. Snell's clinical anatomy by Region's (10th edition) page 423
• Fig5 Prosection 1 – Muscles of the thenar and hypothenar eminences. Suárez-Quian & Vilensky. teach me anatomy website, https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/muscles/hand/
• Fig6 Hand muscles thenar muscles learn anatomy website: https://e-learn.anatomy.uzh.ch/anatomie/Bewegungsapparat/bewapp_HTML_eng/hand/handMlehr32.htm
