
Flexor Retinaculum
By : zuhair Mohamed ammarDefinition
It’s a thickened band of deep fascia at the front of the wrist on the palm side of the hand and it has a retinaculum shape .
Note
(a thicker layer, that consists of a deep part of skin (deep fascia) under the skin)Shape
It’s not flat but slightly concave and it converts its concavity into a tunnel (near the hook of hamate) to be the carpal tunnel.
Note
It is a pathway for median nerve and flexor pollicis longus muscle 
Function
Is for stability-enhancing of long tendons of main flexor muscles, which fixes the tendons at the wrist to prevent them from getting out or being away from their position when they do their action.
Attachment
Medially (ulnar aspect ): hook of hamate and pisiform Laterally(radial aspect ) : scaphoid and trapezium tubercle.
Relations
There are structures which have superficial and deep relations to the flexor retinaculum .
A) Superficial Relations
1- Ulnar artery
2- Ulnar nerve
3- Palmar cutaneous branches of ulnar nerve
4- Palmar cutaneous branches of median nerve
B)Deep Relations ( inside the carpal tunnel)
1-Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons
2- Flexor digitorum profundus tendons
3-Flexor pollicis longus tendon
4-Median n.
5-Synovial sheath covering the long tendons
See the figure 3 below
A) Superficial Relations
1- Ulnar artery
Note
(it passes before its division into its branches (superficial and deep braches))2- Ulnar nerve
Note
(in the guyon's channel)3- Palmar cutaneous branches of ulnar nerve
Note
(which supply medial one and half fingers)4- Palmar cutaneous branches of median nerve
Note
( which supply lateral three and half fingers)B)Deep Relations ( inside the carpal tunnel)
1-Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons
2- Flexor digitorum profundus tendons
3-Flexor pollicis longus tendon
4-Median n.
5-Synovial sheath covering the long tendons
See the figure 3 below
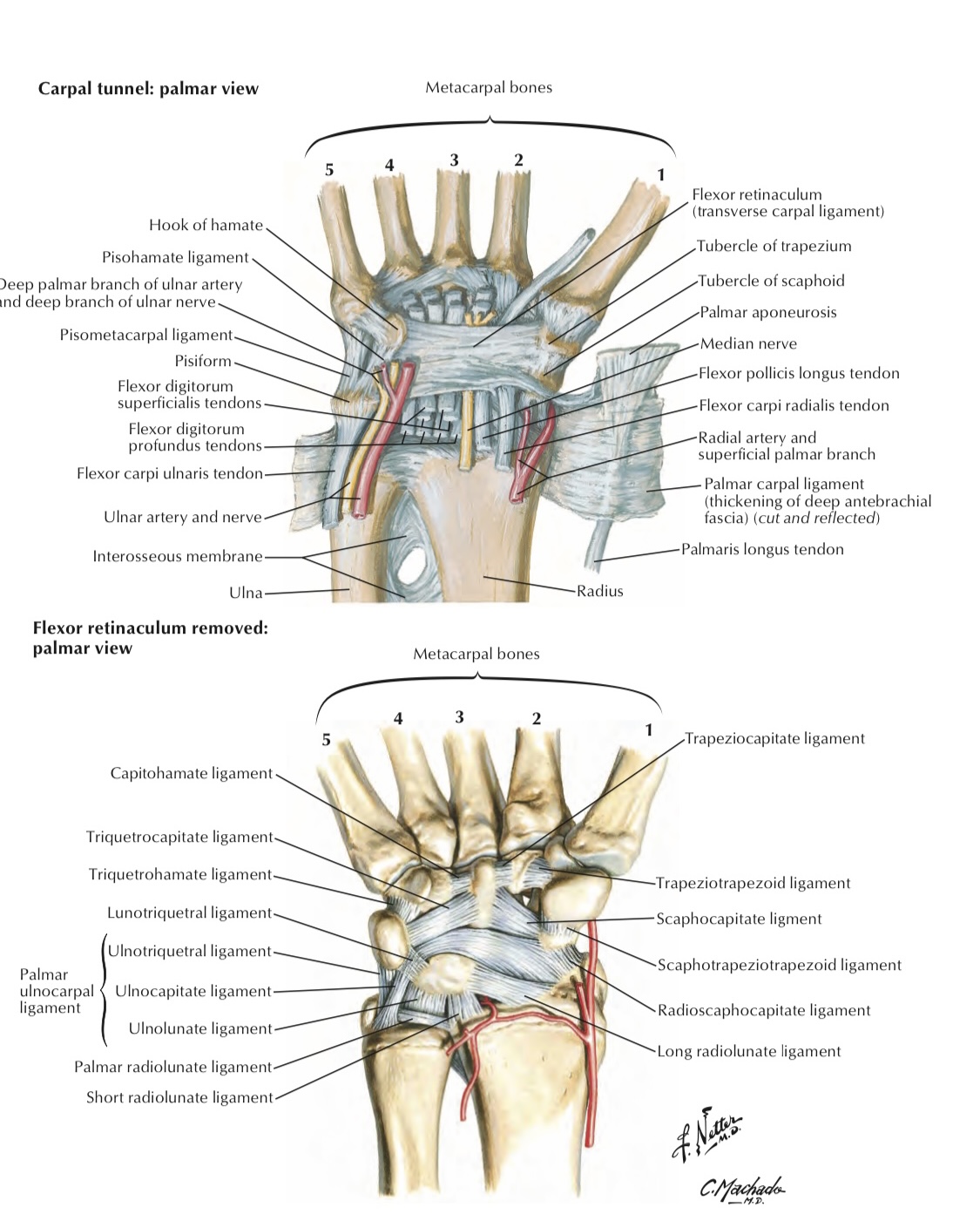
In this figure we can see the all superficial and deep sutures that will related to flexor retinaculum
General notes about flexor retinaculum
1- It forms the roof of carpal bones.
2- At the ulnar aspect it forms the floor of guyon's tunnel . See figure 4
3- It has two layers at radial aspect:
• Superficial layer
• Deep layer
Both of them surround the flexor carpi radialis tendon.
See figure 4
4- The flexor retinaculum has origin and insertion to some muscles:
• Origin of thenar muscles (includes flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis m.(muscles of thumb) and all of them are supplied by median nerve.
• Origin of flexor digiti minimi brevis & abductor digiti minimi and opponenes digiti minimi (muscles of little finger) supplied by ulnar nerve) see figure 5
• Insertion of palmaris longus muscle(it is inserted at the distal half of the flexor retinaculum)
See figure 6
2- At the ulnar aspect it forms the floor of guyon's tunnel
Note
( pathway of ulnar nerve and artery )3- It has two layers at radial aspect:
• Superficial layer
• Deep layer
Both of them surround the flexor carpi radialis tendon.
See figure 4
4- The flexor retinaculum has origin and insertion to some muscles:
• Origin of thenar muscles (includes flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis m.(muscles of thumb) and all of them are supplied by median nerve.
• Origin of flexor digiti minimi brevis & abductor digiti minimi and opponenes digiti minimi (muscles of little finger) supplied by ulnar nerve) see figure 5
• Insertion of palmaris longus muscle(it is inserted at the distal half of the flexor retinaculum)
See figure 6

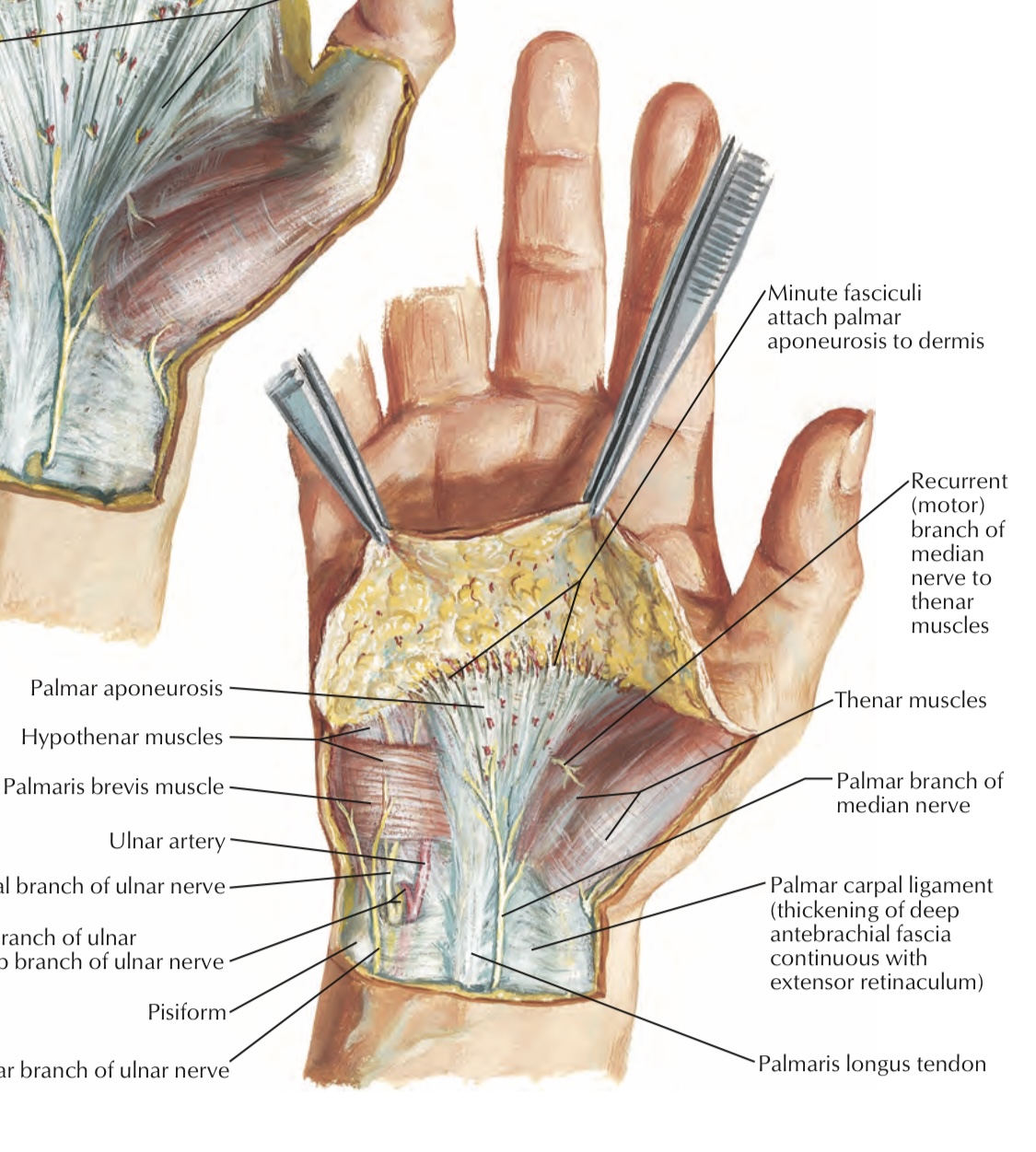
Clinical notes
Carpal tunnel syndrome:
This status due to swelling of synovial sheets of flexor tendon (Tenosynovitis) which leads to the compression of median nerve and may lead to the palsy of the nerve which means the loss of sensation of the lateral three and half fingers.
This status due to swelling of synovial sheets of flexor tendon (Tenosynovitis) which leads to the compression of median nerve and may lead to the palsy of the nerve which means the loss of sensation of the lateral three and half fingers.
References
1. Keith L. Moore , Arthur F. Dalley A. M. R. Agur; Moore clinically oriented anatomy 7th edition;ch.6,p.688
2. Dr. Lawrence E. Wineski,PhD;SNELLIS CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS 10th edition;ch3,pp.111-113
3. Sameh Doss, PhD; Flexor Retinaculum; ANATOMY HAND- OUT /UPPER LIM;p.57
4. Sameh Doss, PhD; Carpal Tunnel; ANATOMY HAND-OUT /UPPER LIM;p.58
2. Dr. Lawrence E. Wineski,PhD;SNELLIS CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS 10th edition;ch3,pp.111-113
3. Sameh Doss, PhD; Flexor Retinaculum; ANATOMY HAND- OUT /UPPER LIM;p.57
4. Sameh Doss, PhD; Carpal Tunnel; ANATOMY HAND-OUT /UPPER LIM;p.58
