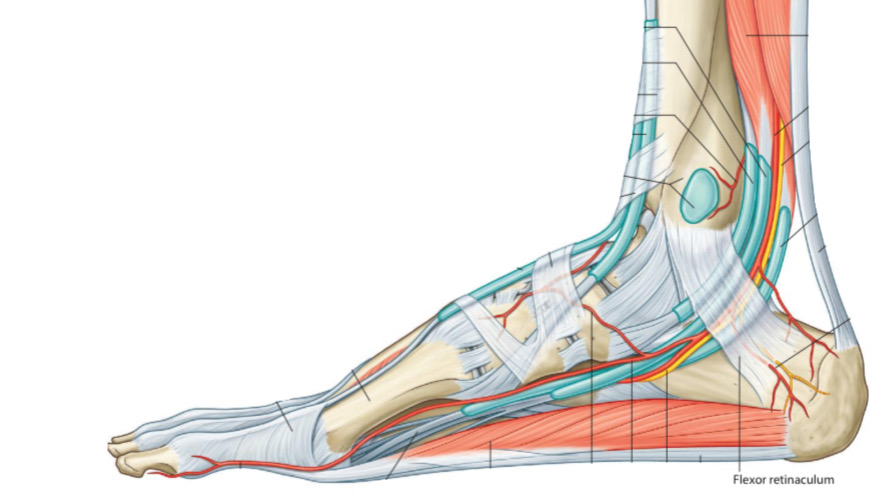
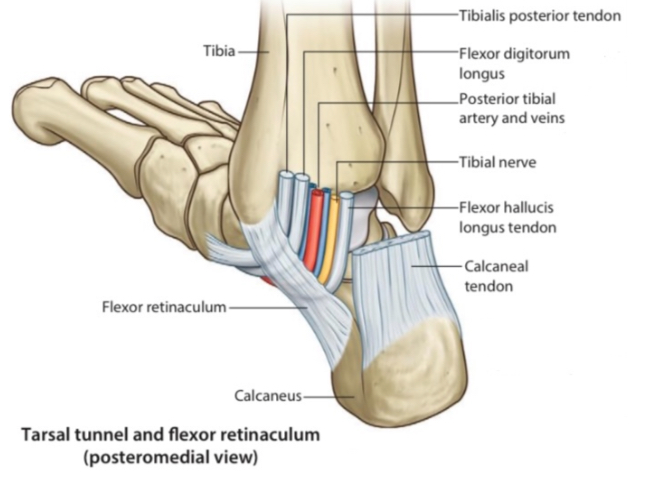
Structures That Pass Behind Medial Malleolus Below Flexor Retinaculum
By : Amna Mohammed1.Tibialis posterior tendon
Tibialis posterior muscle is one of the deep group muscles of the leg. It belongs to the fourth layer of foot muscle layers.
Its tendon passes posterior to the medial malleolus under the flexor retinaculum and continues superior to the sustentaculum tali. Then, it is divided into two divisions:
1.The mainly part attaches to the navicular bone tuberosity on the inferomedial side of it.
2.The other part is a small tendinous pieces pass to attach to the cuboid and the cuneiforms and the bases of the 2nd , 3rd, and 4th metatarsals.
Its tendon passes posterior to the medial malleolus under the flexor retinaculum and continues superior to the sustentaculum tali. Then, it is divided into two divisions:
1.The mainly part attaches to the navicular bone tuberosity on the inferomedial side of it.
2.The other part is a small tendinous pieces pass to attach to the cuboid and the cuneiforms and the bases of the 2nd , 3rd, and 4th metatarsals.

Posterior view.
Right leg.
2.Flexor digitorum longus tendon
Flexor digitorum longus is one of the deep group muscles of the leg. It belongs to the second layer of foot muscle layers.
Its tendon after passing under the flexor retinaculum continues to the medial side of the sustentaculum tali and then divides into four tendons. Each one of these four tendons attaches distally at the distal phalanx of four lateral toes.
It belongs to the second layer of foot muscle layers.
Its tendon after passing under the flexor retinaculum continues to the medial side of the sustentaculum tali and then divides into four tendons. Each one of these four tendons attaches distally at the distal phalanx of four lateral toes.
It belongs to the second layer of foot muscle layers.
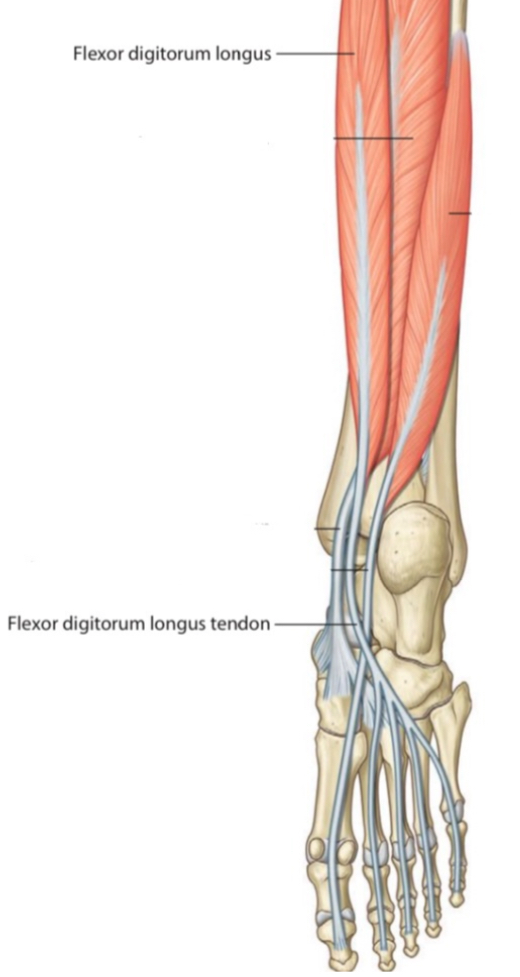
Posterior view.
Right leg.
3. Posterior tibial artery with its venae comitantes
It is a branch of the popliteal artery .
It enters the sole of the foot under the flexor retinaculum behind the medial malleolus, then it divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries to supply the two sides of the foot.
It has two veins that accompany it through its course.
It enters the sole of the foot under the flexor retinaculum behind the medial malleolus, then it divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries to supply the two sides of the foot.
It
Note
the artery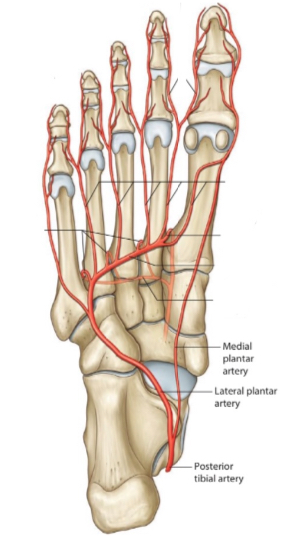
Inferior view.
Right foot.
4. Tibial nerve
It is a branch of the sciatic nerve .
It enters the sole of the foot under the flexor retinaculum behind the medial malleolus & divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves.
It enters the sole of the foot under the flexor retinaculum behind the medial malleolus & divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves.
5.Flexor hallucis longus tendon
Flexor hallucis longus is one of the deep group muscles of the leg. It belongs to the second layer of foot muscle layers.
Its tendon after passing under flexor retinaculum continues beneath sustentaculum tali and passes deep to FDL, then attaches distally to the distal phalanx of the big toe.
Note: the muscle tendons are surround by a synovial sheath during its passage under the flexor retinaculum.
Its tendon after passing under flexor retinaculum continues beneath sustentaculum tali and passes deep to FDL, then attaches distally to the distal phalanx of the big toe.
Note: the muscle tendons are surround by a synovial sheath during its passage under the flexor retinaculum.
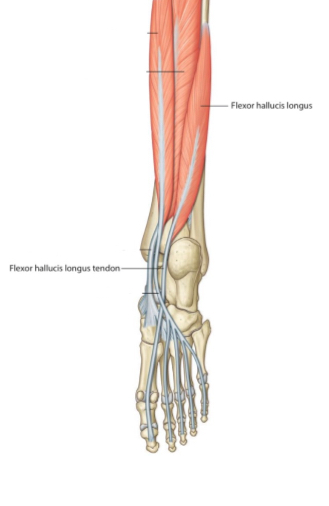
Posterior view.
Right leg.
Clinical Note
1. The Flexor Retinaculum with the structures that pass beneath it creates a canal called the tarsal tunnel , this tunnel is likely to have a tarsal tunnel syndrome .
2. This region has an important role to test the action of the tibialis posterior m. if the muscle is acting normally. The tendon of the tibialis posterior m. can be palpated posterior to the medial malleolus when the foot is inverted with a slight plantar flexion.
3. This region has an important role in the palpation of the posterior tibial artery pulse at the midway between the medial malleolus and the heel.
2. This region has an important role to test the action of the tibialis posterior m. if the muscle is acting normally. The tendon of the tibialis posterior m. can be palpated posterior to the medial malleolus when the foot is inverted with a slight plantar flexion.
3. This region has an important role in the palpation of the posterior tibial artery pulse at the midway between the medial malleolus and the heel.
References
Snell’s Clinical Anatomy By Regions (10th Edition) 1345,1358,1362,1366,1378-1379,1382,1456
Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) 622,666
Gray’s-Atlas Of Anatomy(2nd Edition) 341,362-363
Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) 622,666
Gray’s-Atlas Of Anatomy(2nd Edition) 341,362-363
