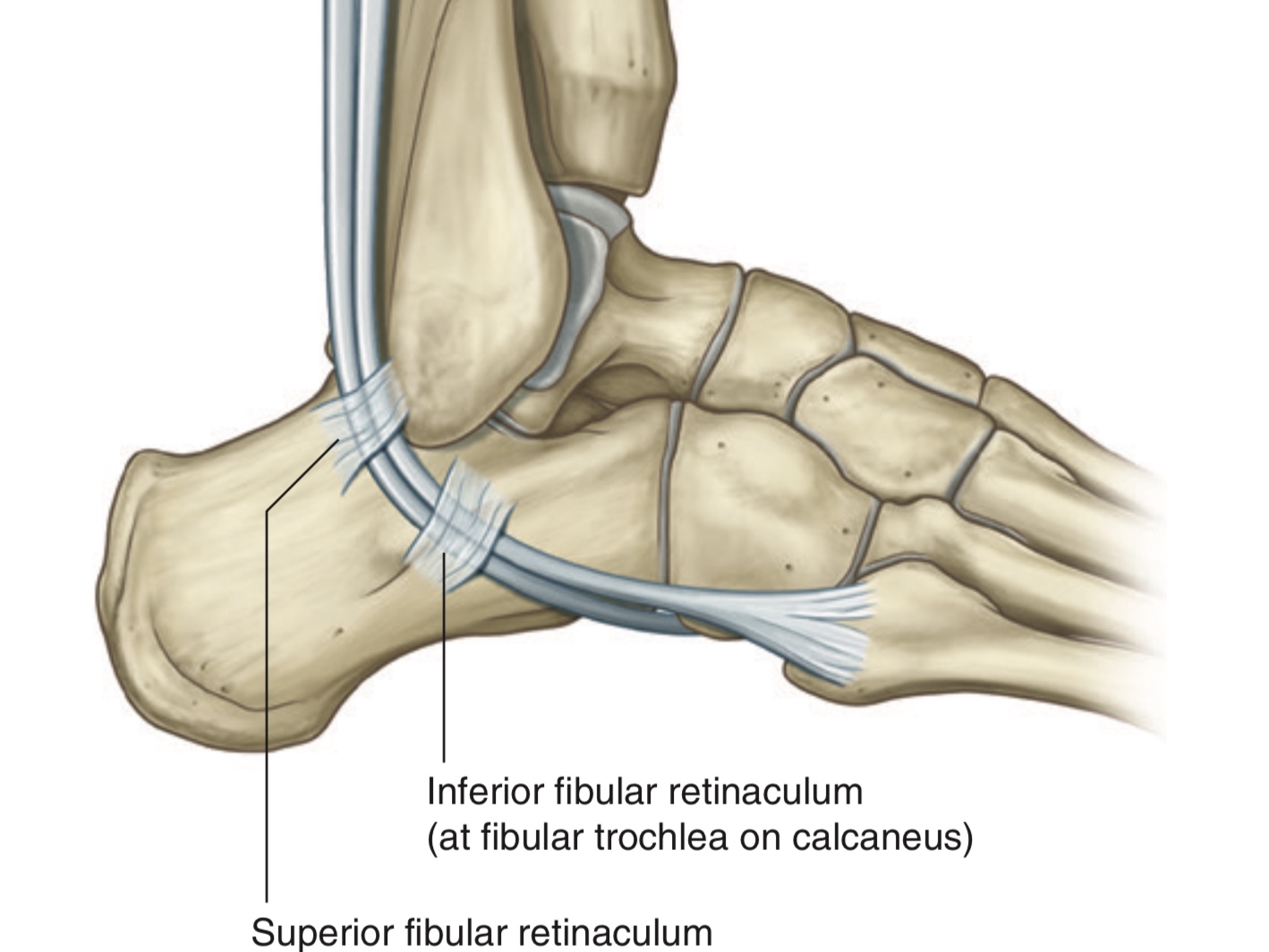
Peroneal (Fibular) Retinaculum
By : Hafsa OmarDefinition
It is a thickened band of the deep fascia at the lateral aspect of the foot, that holds the tendons of peroneus (fibularis) longus and peroneus (fibularis) brevis muscles in place.
Note: these tendons play role in stability of the ankle joint and the foot.
There are two peroneal retinacula:
1.Superior peroneal retinaculum
2.Inferior peroneal retinaculum
Note: these tendons play role in stability of the ankle joint and the foot.
There are two peroneal retinacula:
1.Superior peroneal retinaculum
2.Inferior peroneal retinaculum
A)Superior Peroneal (Fibular) Retinaculum
It is also called external annular ligament.
It extends between the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus.
This retinaculum holds the tendons of the peroneus longus and the peroneus brevis muscles in the retromalleolar groove to prevent them from subluxation or dislocation
Note: here, the tendons of the peroneus longus and brevis muscles are enclosed in a common synovial sheath (they share the same one synovial sheath) where the tendon of peroneus longus m. is superficial to the tendon of peroneus brevis m.
It extends between the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus.
This retinaculum holds the tendons of the peroneus longus and the peroneus brevis muscles in the retromalleolar groove
Note
(which is a groove located behind the lateral malleolus of fibula) Note
(prevent the tendon from getting out of place)Note: here, the tendons of the peroneus longus and brevis muscles are enclosed in a common synovial sheath (they share the same one synovial sheath) where the tendon of peroneus longus m. is superficial to the tendon of peroneus brevis m.
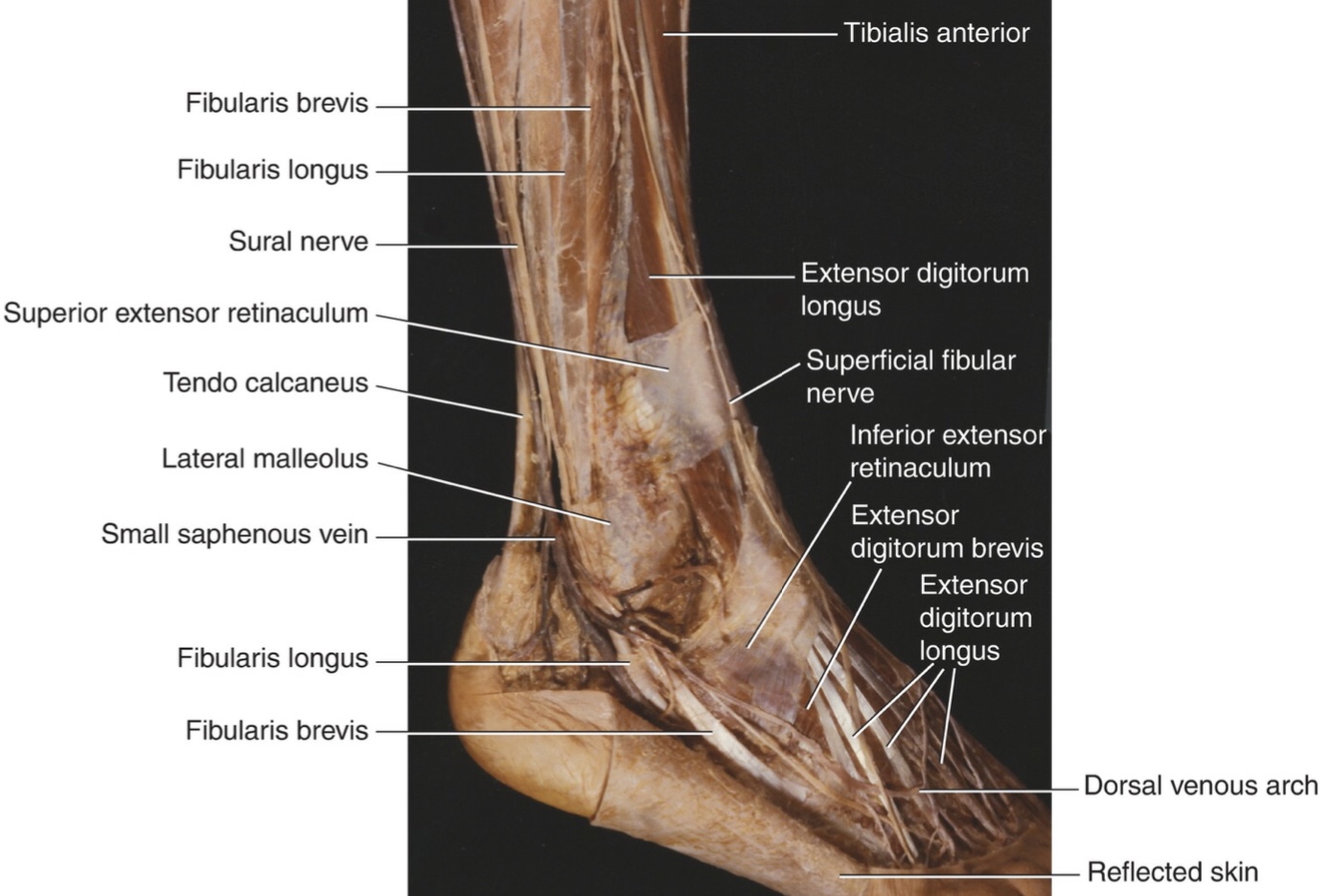
Structures that pass behind the lateral malleolus and deep to the superior fibular retinaculum
The fibularis longus and brevis tendons.
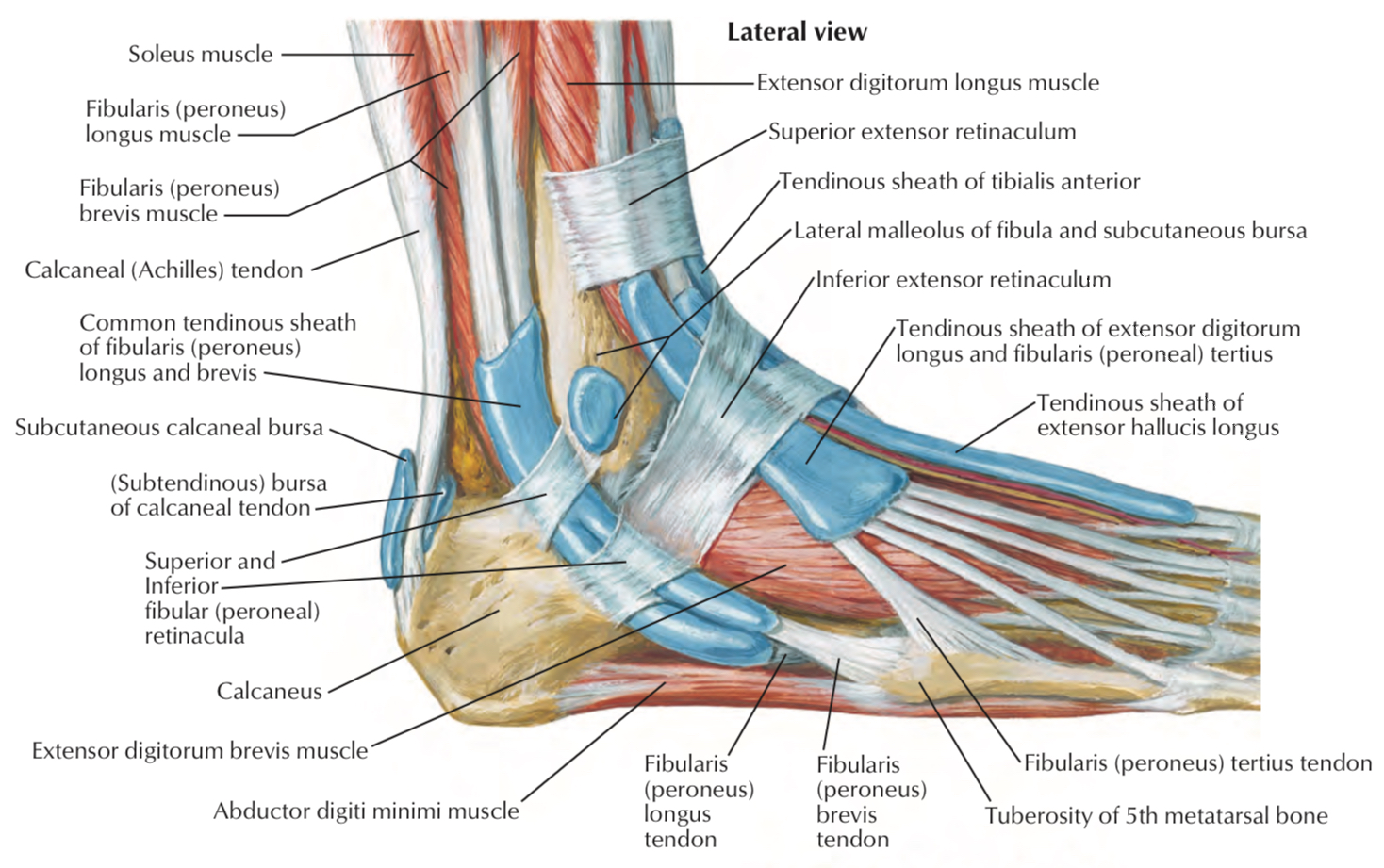
Structures pass deep to the superficial fibular retinaculum
Structures that pass behind the lateral malleolus and superficial to the superior fibular retinaculum
1- The sural nerve
2- Small saphenous vein
2- Small saphenous vein
Structures pass superficial to the superior fibular
Superior Peroneal (Fibular) Retinaculum Injury
Injury in superior peroneal retinaculum occurs with subluxation or dislocation of the tendons of peroneus longus and peroneus brevis in which these tendons get out from retromalleolar groove when the ankle is sprained severe.
Symptoms
1.Swelling
2.Pain at the lateral aspect of the ankle
3.Ankle instability
Symptoms
1.Swelling
2.Pain at the lateral aspect of the ankle
3.Ankle instability
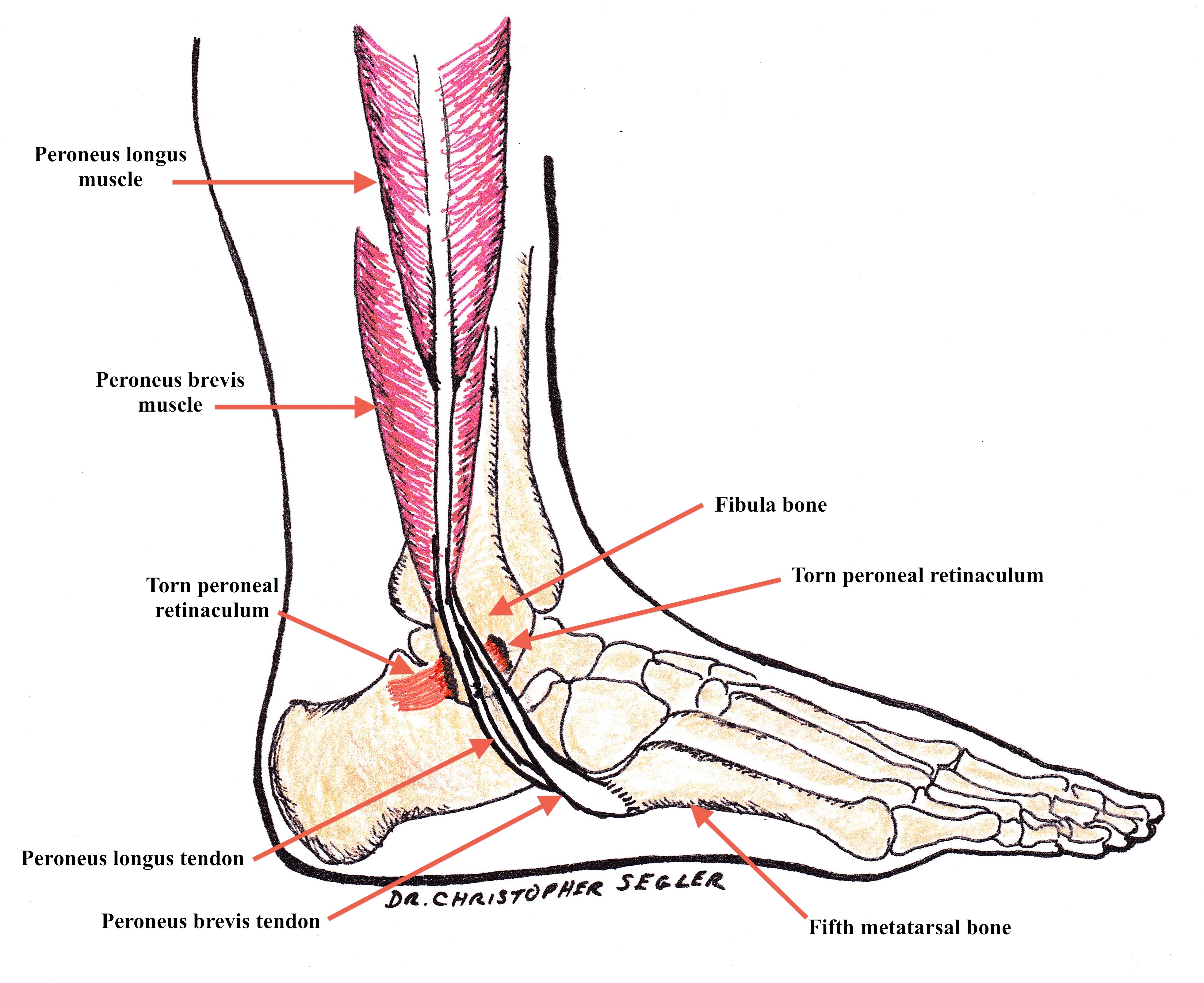
torn peroneal retinaculum allowing the peroneal tendons to slide forward and out of the retromalleolar groove
The injury is common with people who do sports activities, especially snow skiing and football.
The superior peroneal (fibular) retinaculum injury is classified into four grades:
Grade 1: the retinaculum is stripped off from the fibula.
Grade 2: the fibrous rim of the posterolateral aspect of the
fibula is avulsed along with the superior peroneal retinaculum.
Grade 3: bony avulsion of the posterolateral part of the fibula by the superior peroneal retinaculum.
Grade 4: the retinaculum is torn at its calcaneal side.
Treatment
The duration and type of treatment depend upon the condition.
In simple cases, the patient needs to rest and can put ice to reduce the swelling.
In some cases, the patient needs to put plaster bandage.
Severe cases require surgical intervention.
The superior peroneal (fibular) retinaculum injury is classified into four grades:
Grade 1: the retinaculum is stripped off from the fibula.
Grade 2: the fibrous rim of the posterolateral aspect of the
fibula is avulsed along with the superior peroneal retinaculum.
Grade 3: bony avulsion of the posterolateral part of the fibula by the superior peroneal retinaculum.
Grade 4: the retinaculum is torn at its calcaneal side.
Treatment
The duration and type of treatment depend upon the condition.
In simple cases, the patient needs to rest and can put ice to reduce the swelling.
In some cases, the patient needs to put plaster bandage.
Severe cases require surgical intervention.
B)Inferior Peroneal (Fibular) Retinaculum
It is a continuation of inferior extensor retinaculum.
It attaches to the lateral surface of the calcaneus around the fibular trochlea of calcaneus.
Note: each tendon has its own common synovial sheath, where the tendon of peroneus brevis m. is above the tendon of peroneus longus m.
Note: the injury to inferior peroneal retinaculum is rare.
It attaches to the lateral surface of the calcaneus around the fibular trochlea of calcaneus.
Note: each tendon has its own common synovial sheath, where the tendon of peroneus brevis m. is above the tendon of peroneus longus m.
Note: the injury to inferior peroneal retinaculum is rare.
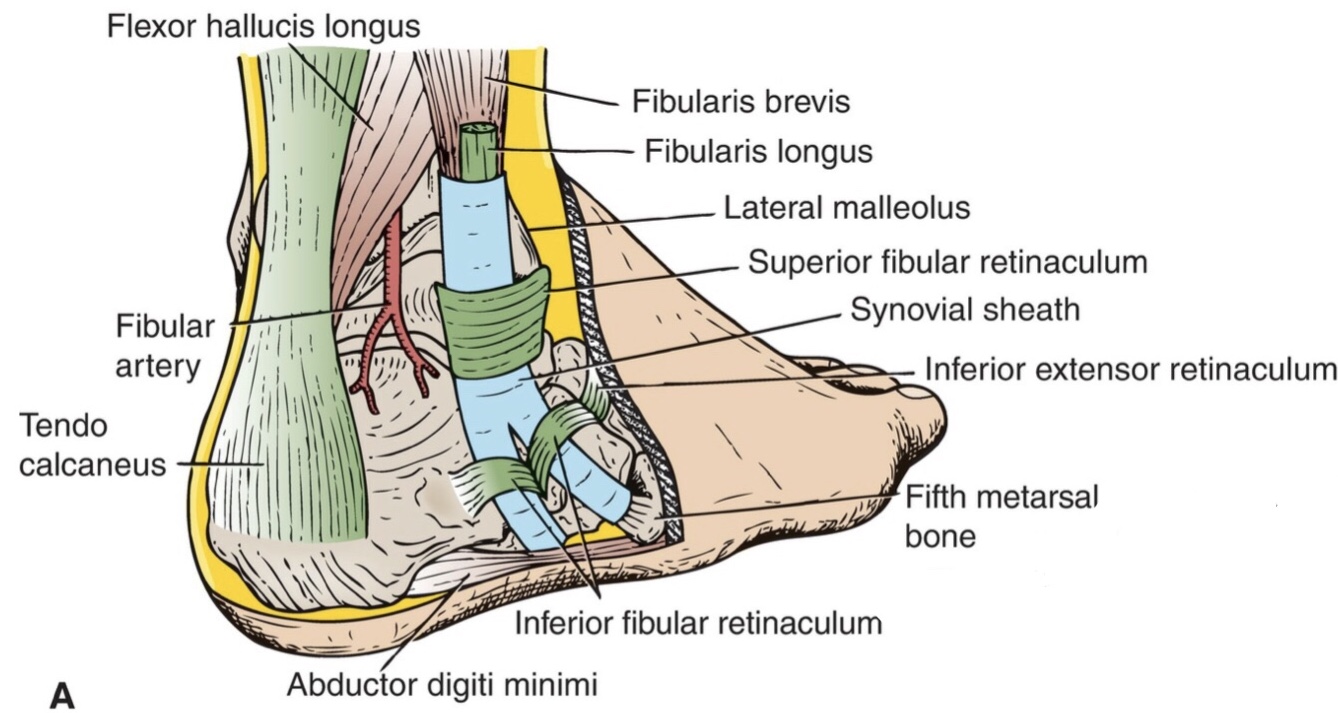
Inferior peroneal (fibular) retinaculum
References
1- Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl, Adam W. Mitchell, Gray’s Anatomy for Students (2019), 4th edition/ p.(643)
2- LAWRENCE E. WINESKI, SNELL'S CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS (2018), 10th edition/ p.(553-554, 563)
3- Endoscopic Superior Peroneal Retinaculum Reconstruction, ScienceDirect,
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212628717303183
4- SUPERIOR PERONEAL RETINACULUM, Earth's Lab,
https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/superior-peroneal-retinaculum/
2- LAWRENCE E. WINESKI, SNELL'S CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS (2018), 10th edition/ p.(553-554, 563)
3- Endoscopic Superior Peroneal Retinaculum Reconstruction, ScienceDirect,
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212628717303183
4- SUPERIOR PERONEAL RETINACULUM, Earth's Lab,
https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/superior-peroneal-retinaculum/
References of images
Cover image: Gray’s Anatomy for Students, Fig. 6.112
Fig 1: Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy, Plate516
Fig 2: Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions, Figure 11.42
Fig 3: A torn peroneal retinaculum allowing the peroneal tendons to slide forward and out of the retromalleolar groove, Dr.CHRISTOPHER SEGLER, DOC - on the run
https://www.docontherun.com/peroneal-tendon-subluxation/
Fig 4: Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions, Figure 11.44 A
Fig 1: Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy, Plate516
Fig 2: Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions, Figure 11.42
Fig 3: A torn peroneal retinaculum allowing the peroneal tendons to slide forward and out of the retromalleolar groove, Dr.CHRISTOPHER SEGLER, DOC - on the run
https://www.docontherun.com/peroneal-tendon-subluxation/
Fig 4: Snell's Clinical Anatomy by Regions, Figure 11.44 A
