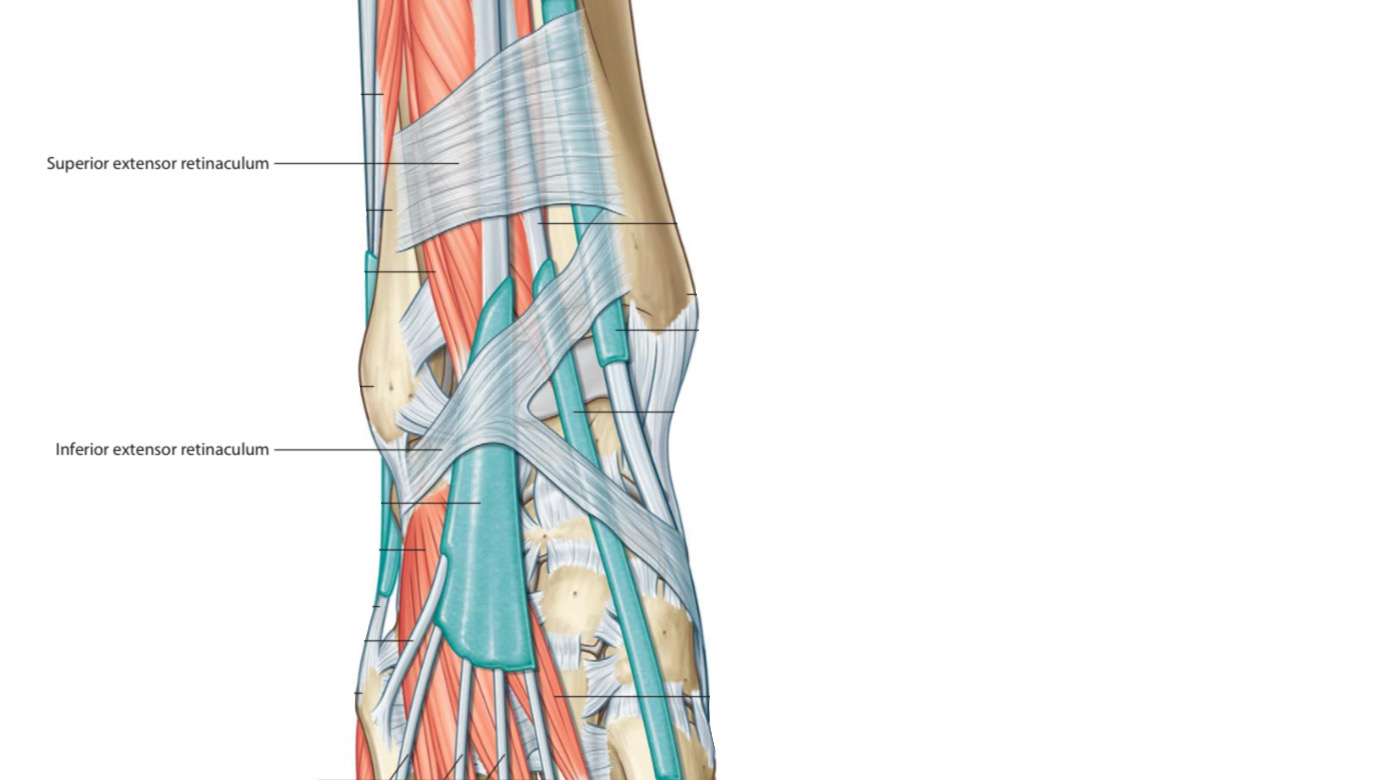
THE STRUCTURES THAT PASS BENEATH THE EXTENSOR RETINACULUM
By : Amna Mohammed
The extensor retinaculum keeps the structures that pass through it stable during dorsiflexion of the foot & prohibits the long tendons from bowstringing when the foot is dorsiflexed.
Note
bowstringing means egressing the tendon from the band that keeps it stable during joint movement.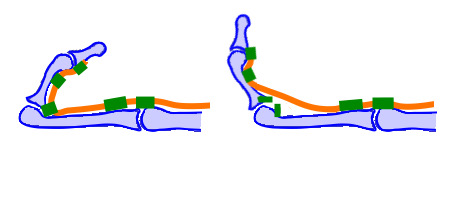
This fig. Shows the bowstring phenomenon of the finger tendon.
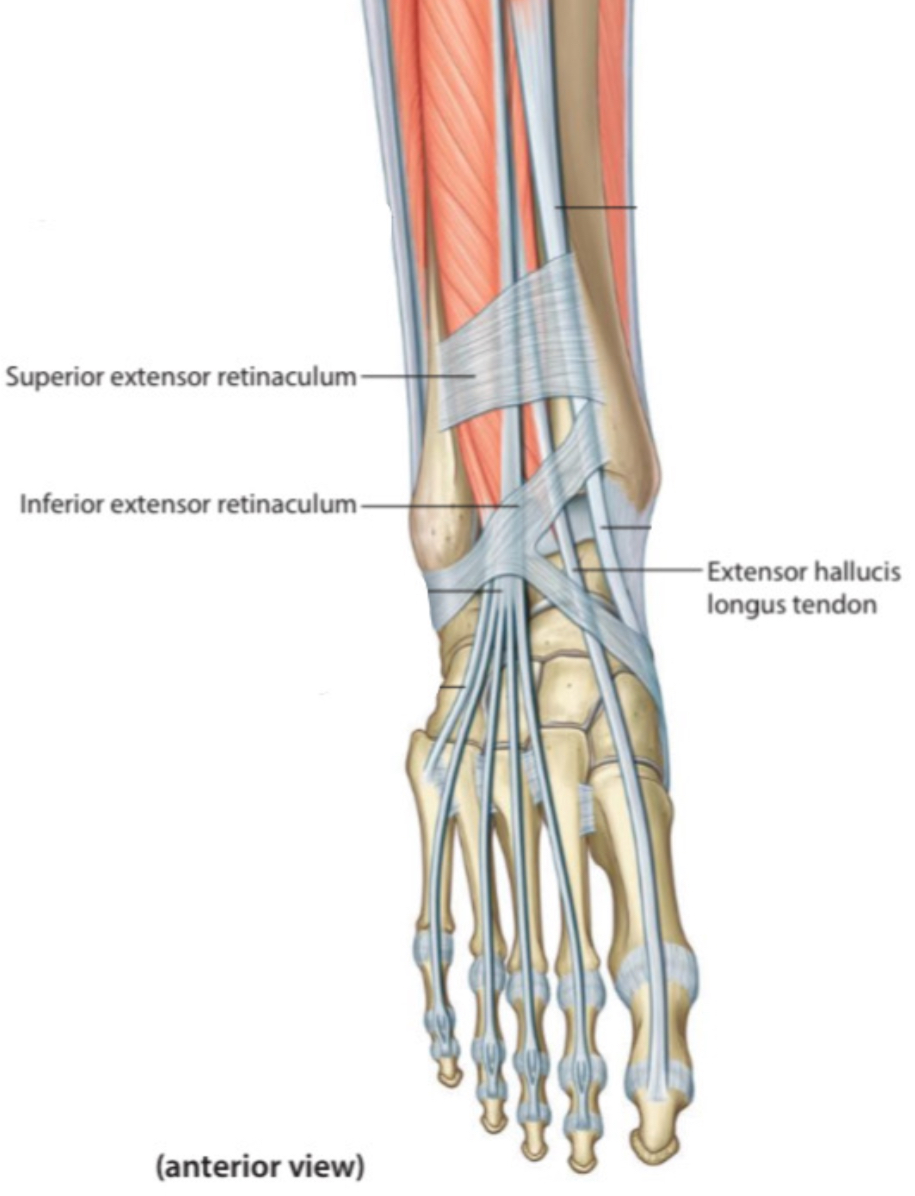
The structures that pass beneath the extensor retinaculum :
1. Tibialis anterior tendon
The tibialis anterior m. belongs to the anterior group of the leg muscles. Its tendon after passing under the extensor retinaculum, attaches distally at the medial and the inferior surfaces of the medial cuneiform and the base of 1st metatarsal.
The tibialis anterior m. belongs to the anterior group of the leg muscles. Its tendon after passing under the extensor retinaculum, attaches distally at the medial and the inferior surfaces of the medial cuneiform and the base of 1st metatarsal.

Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
2. Extensor hallucis longus tendon
Extensor hallucis longus m. belongs to the anterior group of the leg muscles. Its tendon after passing under the extensor retinaculum, attaches distally at the distal phalanx of the great toe.
Extensor hallucis longus m. belongs to the anterior group of the leg muscles. Its tendon after passing under the extensor retinaculum, attaches distally at the distal phalanx of the great toe.
Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
3. Anterior tibial artery with its venae comitantes
It is a branch of the popliteal artery . It enters the dorsum of the foot through the extensor retinaculum. At the midpoint between the two malleoli, it continues as the dorsal pedis artery that supplies the foot. It has two veins that accompany it through its course.
It is a branch of the popliteal artery . It enters the dorsum of the foot through the extensor retinaculum. At the midpoint between the two malleoli, it continues as the dorsal pedis artery that supplies the foot. It
Note
the artery
Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
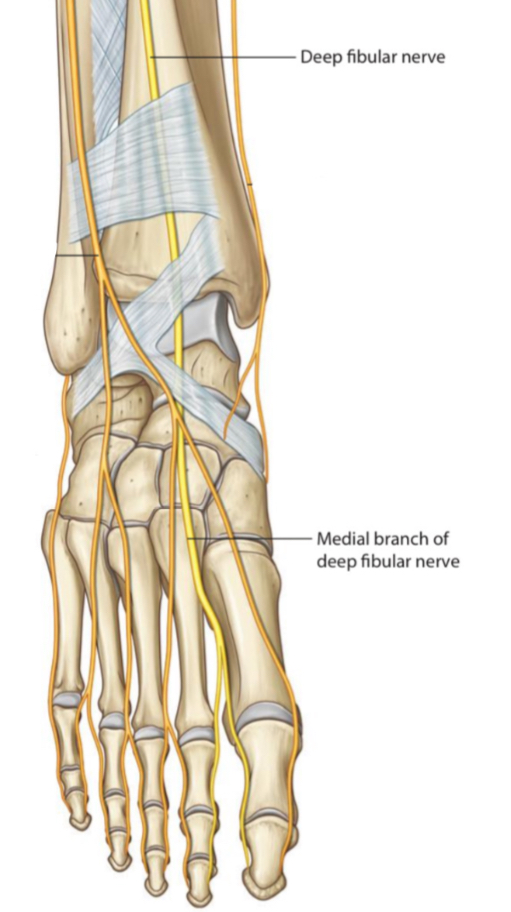
4.Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve
It is a branch of the common fibular (peroneal) nerve . It enters the dorsum of the foot through the extensor reticulum and innervates:
1. The foot dorsum muscles.
2. The skin over the area between the 1st and the 2nd toes.
It is a branch of the common fibular (peroneal) nerve . It enters the dorsum of the foot through the extensor reticulum and innervates:
1. The foot dorsum muscles.
2. The skin over the area between the 1st and the 2nd toes.
Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
5.Extensor digitorum longus tendon
The extensor digitorum longus m. belongs to the anterior group of the leg muscles. Its tendon after passing under the extensor retinaculum, is divided into four tendons for lateral four toes and attaches distally at the middle and the distal phalanges.
Note: the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus m., each of them is divided into 3 sections near the phalanges:
1.The central section is inserted at the middle phalanx
2.The two peripheral sections are inserted at the distal phalanx
This anatomical cut is called extensor expansion .
The extensor digitorum longus m. belongs to the anterior group of the leg muscles. Its tendon after passing under the extensor retinaculum, is divided into four tendons for lateral four toes and attaches distally at the middle and the distal phalanges.
Note: the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus m., each of them is divided into 3 sections near the phalanges:
1.The central section is inserted at the middle phalanx
2.The two peripheral sections are inserted at the distal phalanx
This anatomical cut is called extensor expansion .
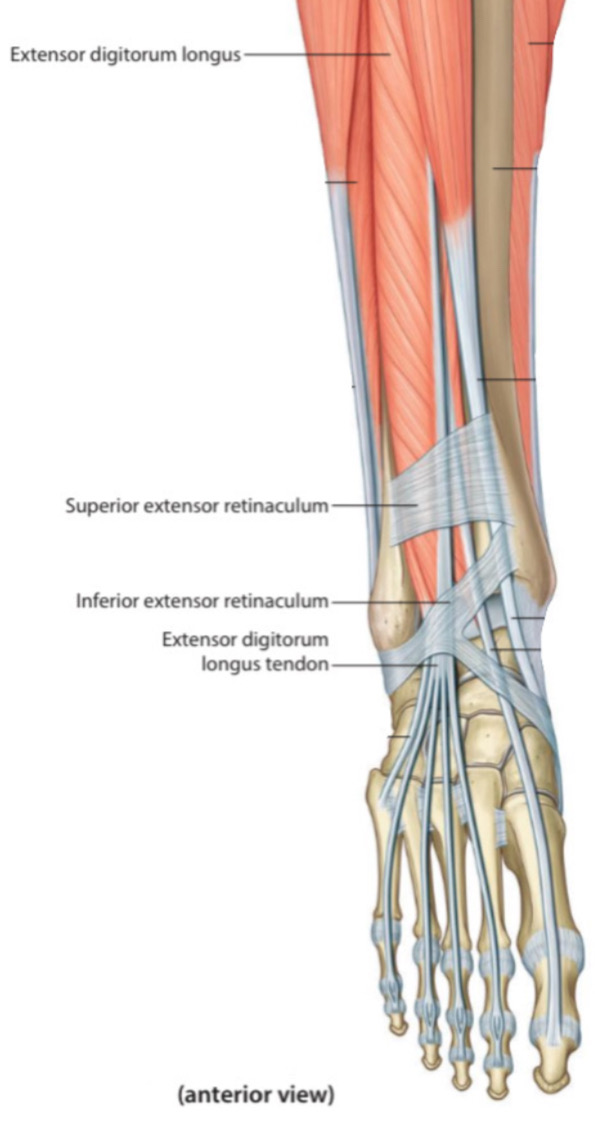
Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
6. Fibularis(Peroneus) tertius
The fibularis tertius m. is a part of the extensor digitorum longus muscle . Its tendon after splitting attaches distally at the 5th metatarsal.
Note: the fibularis tertius tendon shares the extensor digitorum longus tendon synovial sheath.
The fibularis tertius m. is a part of the extensor digitorum longus muscle . Its tendon after splitting attaches distally at the 5th metatarsal.
Note: the fibularis tertius tendon shares the extensor digitorum longus tendon synovial sheath.
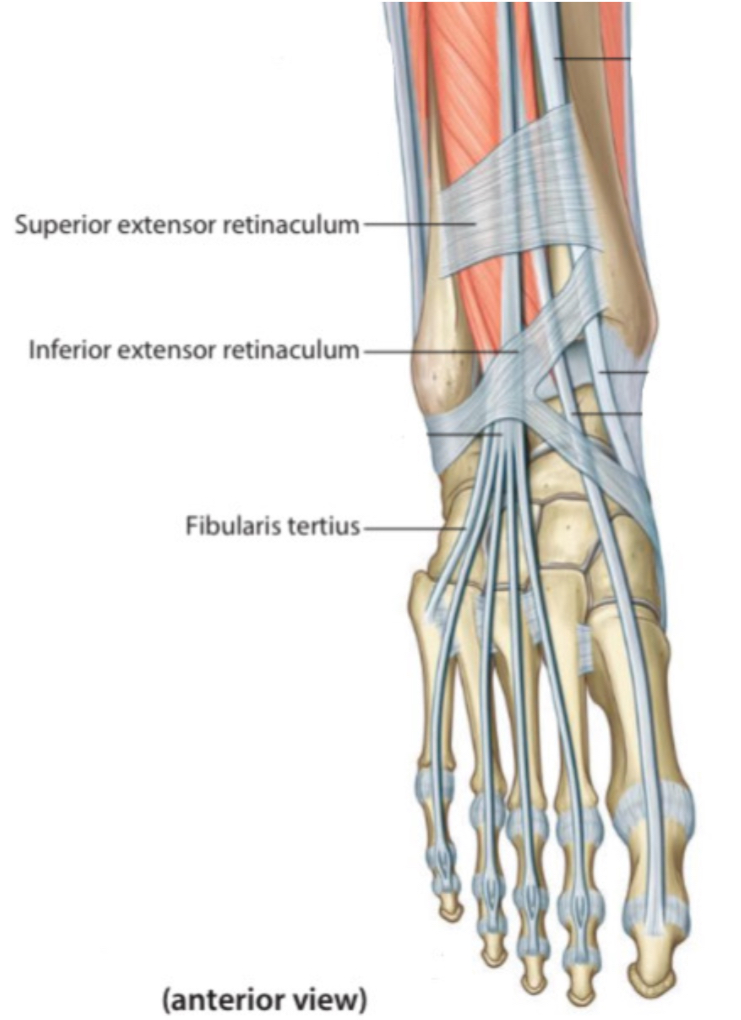
Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
References
SNELL'S CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS (10th Edition) 1338,1350-1351,1383,1385, Fig 11.40
Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) 589,591,594
Gray’s Atlas Of Anatomy (2nd Edition) 344,353-354.
bowstring phenomenon of the finger tendon - bone spine- https://boneandspine.com/flexor-tendon-pulley-system-of-hand/
Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) 589,591,594
Gray’s Atlas Of Anatomy (2nd Edition) 344,353-354.
bowstring phenomenon of the finger tendon - bone spine- https://boneandspine.com/flexor-tendon-pulley-system-of-hand/
