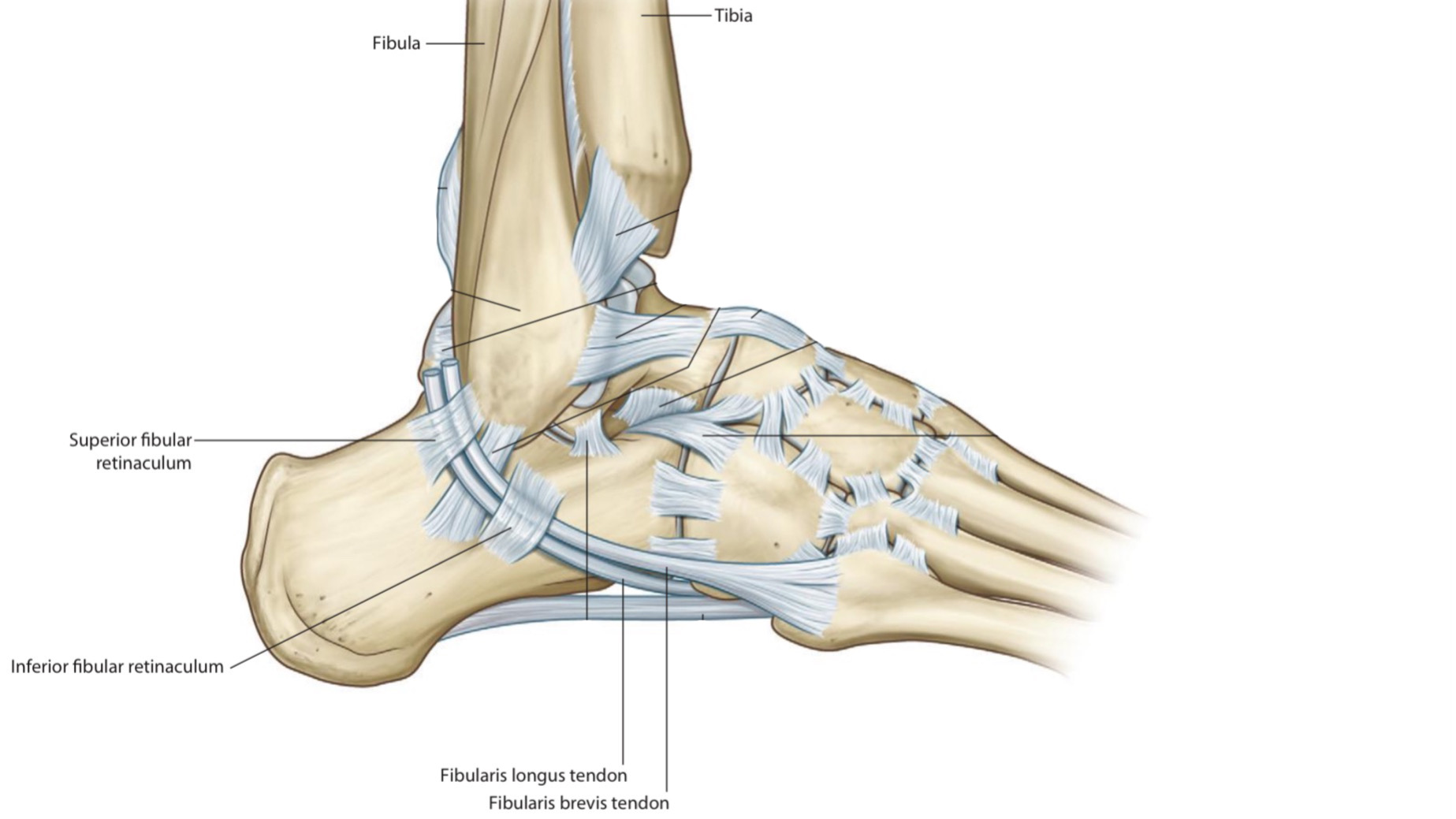
Structures That Pass Behind Lateral Malleolus Below Superficial Peroneal Retinaculum
By : Amna Mohammed1. Fibularis Longus tendon
Fibularis Longus muscle belongs to the lateral group of leg muscles.
Its tendon enters the sole of the foot under the peroneal retinaculum behind lateral malleolus and continues its course to attach to the base of the 1st metatarsal bone.
Its tendon enters the sole of the foot under the peroneal retinaculum behind lateral malleolus and continues its course to attach to the base of the 1st metatarsal bone.
2. Fibularis Brevis tendon
Fibularis Brevis belongs to the lateral group of leg muscles.
Its tendon enters the sole of the foot under the peroneal retinaculum behind the lateral malleolus. It continues its course to attach to the tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal bone.
Note: the fibularis longus and the fibularis brevis tendons share a common synovial sheath. Beneath the inferior peroneal retinaculum, the synovial sheath separates and each tendon has its synovial sheath after this level.
Its tendon enters the sole of the foot under the peroneal retinaculum behind the lateral malleolus. It continues its course to attach to the tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal bone.
Note: the fibularis longus and the fibularis brevis tendons share a common synovial sheath. Beneath the inferior peroneal retinaculum, the synovial sheath separates and each tendon has its synovial sheath after this level.
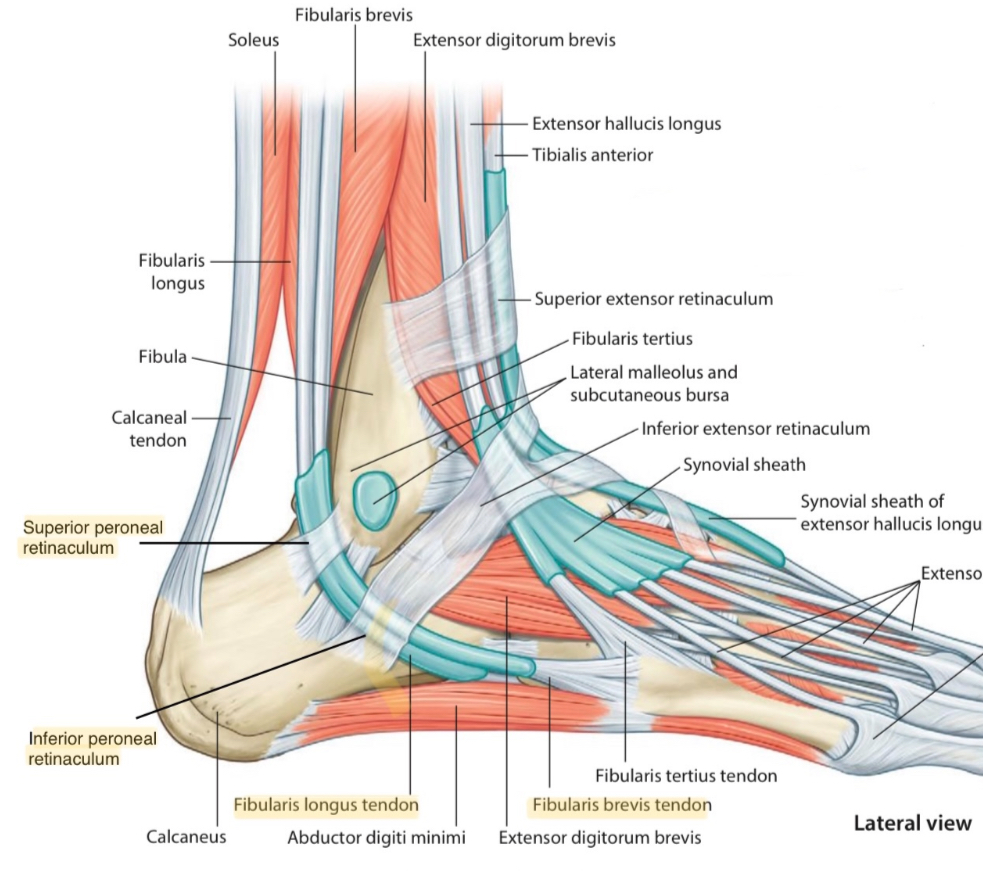
Lateral view.
Right foot.
Clinical Note
The FL & FB tendons & their synovial sheaths are prone to inflammation. This condition is called Tenosynovit is .
The possible causes
1. Activities that require repeated jumping and changing the direction.
2. Acute ankle sprains.
3.Not suitable exercises.
4. Hitting directly.
Note: tenosynovitis of FL or FB is common in athletes as runners, dancers and ice skaters.
2. Acute ankle sprains.
3.Not suitable exercises.
4. Hitting directly.
Note: tenosynovitis of FL or FB is common in athletes as runners, dancers and ice skaters.
Symptoms:
Pain and swelling along the course of fibularis tendon.
The pain increases during foot eversion , inversion and walking
The pain increases during foot eversion , inversion and walking
Diagnosis
1.The specialist uses plain film radiographs to discriminate the case from arthritis and bone distortions.
2.MRI scan and ultrasound checkup are used to exhibit oedema if it is found.
3.MR images show a clear look at the fluid accumulations inside the fibularis synovial sheath.
2.MRI scan and ultrasound checkup are used to exhibit oedema if it is found.
3.MR images show a clear look at the fluid accumulations inside the fibularis synovial sheath.
Treatment
The treatment method depends on how much the condition is acute .
There is more than one method to treat tenosynovitis:
1.Using non-steroid anti-inflammatory medications.
2.Physical Therapy includes ultrasound electric stimulation.
3. If the condition is acute, the only method for the treatment may be the tendon resect.
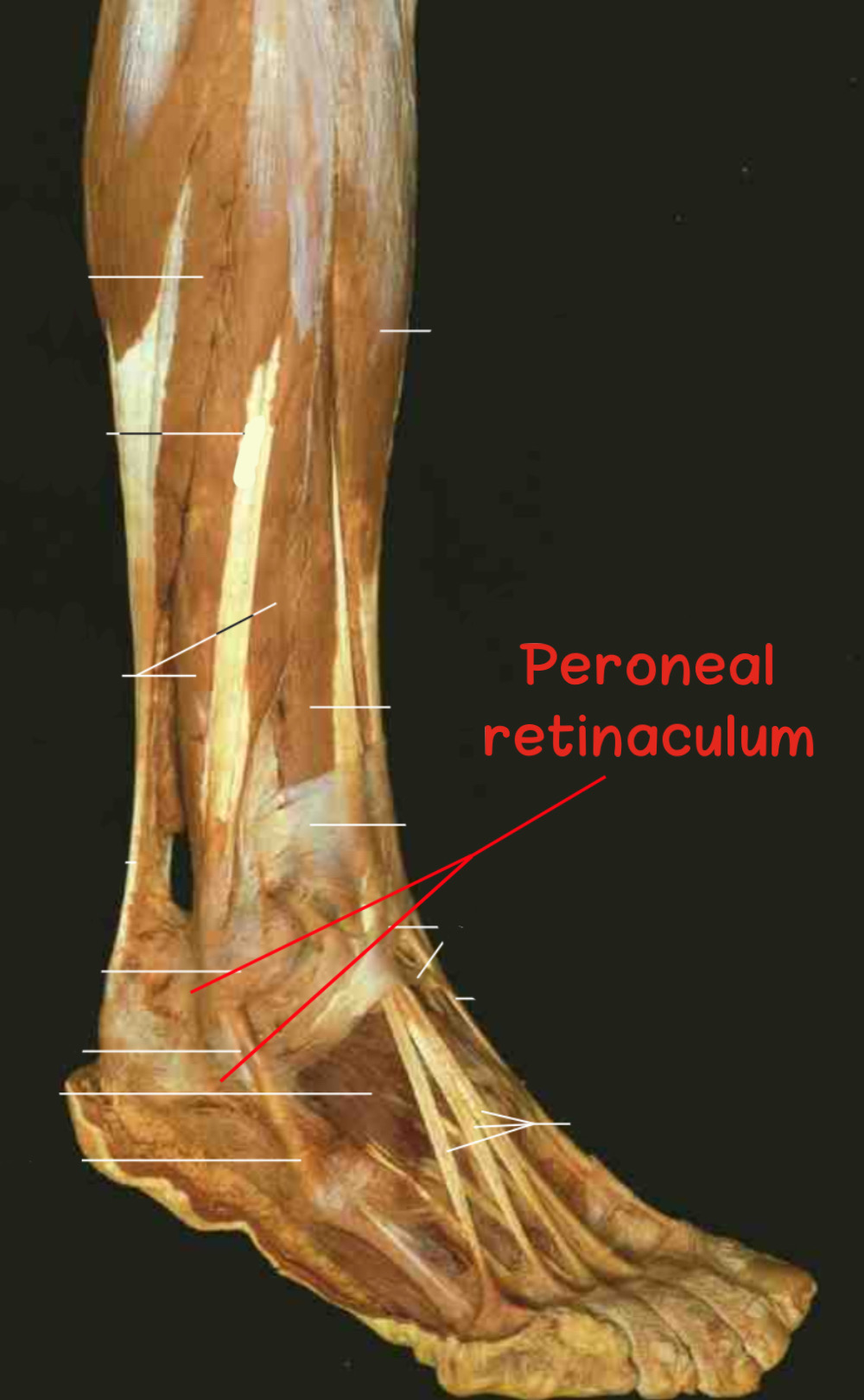
Antrolateral view
Right foot.
References
SNELL'S CLINICAL ANATOMY BY REGIONS (10th Edition)-1346,1354,1363,1379
PERONEAL TENDINOSIS-FootCareMD-https:// www.footcaremd.org/conditions-treatments/ankle/peroneal- tendinosis
Aging and tenosynovitis of the peroneal tendons: the cause and management-MedCrave-https://medcraveonline.com/
MOJAP/aging-and-tenosynovitis-of-the-peroneal-tendons-the- cause-and-management.html
Peroneal tendinopathy-physiopedia-https://www.physio-pedia.com/Peroneal_Tendinopathy
Gray’s Atlas Of Anatomy (2nd Edition)-363,366.
Color Atlas Of Anatomy (7th Edition)-459.
PERONEAL TENDINOSIS-FootCareMD-https:// www.footcaremd.org/conditions-treatments/ankle/peroneal- tendinosis
Aging and tenosynovitis of the peroneal tendons: the cause and management-MedCrave-https://medcraveonline.com/
MOJAP/aging-and-tenosynovitis-of-the-peroneal-tendons-the- cause-and-management.html
Peroneal tendinopathy-physiopedia-https://www.physio-pedia.com/Peroneal_Tendinopathy
Gray’s Atlas Of Anatomy (2nd Edition)-363,366.
Color Atlas Of Anatomy (7th Edition)-459.
