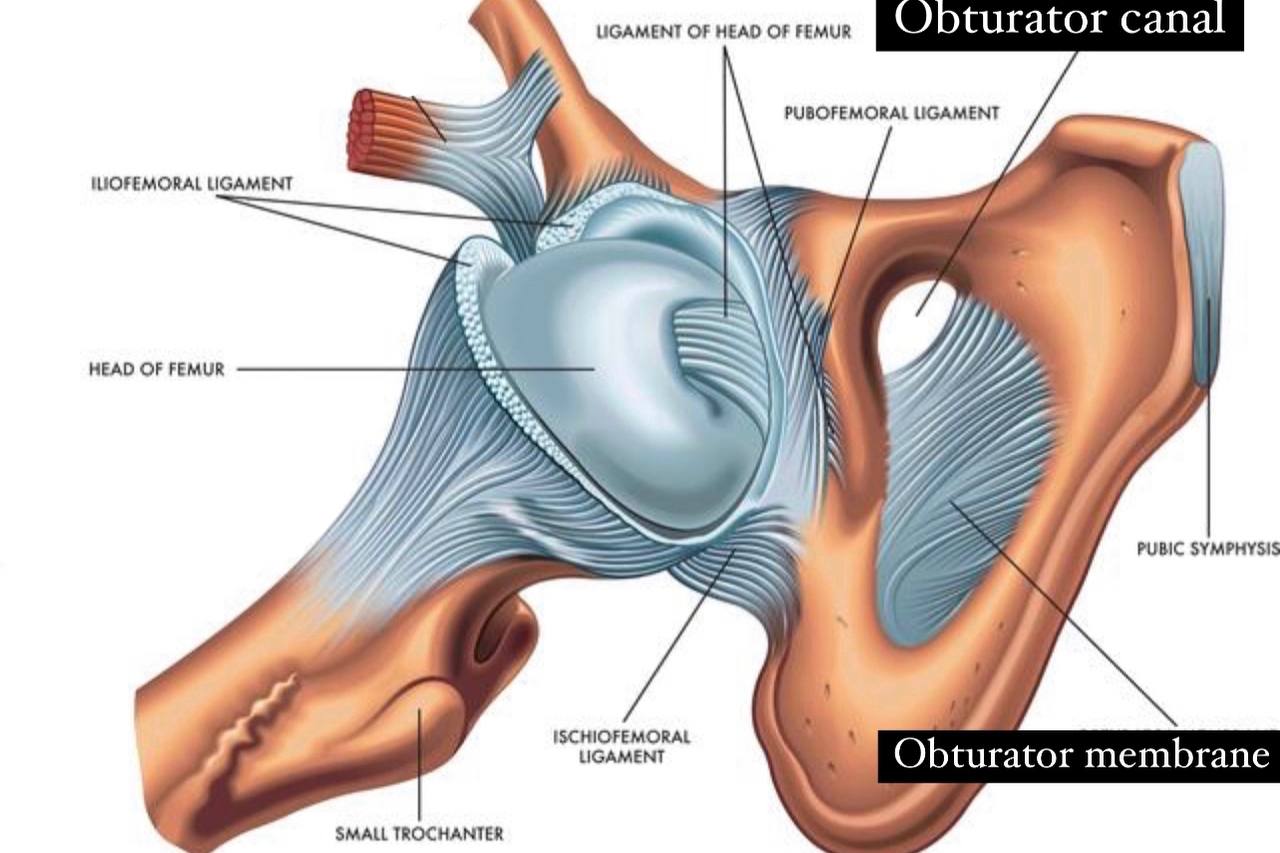
Obturator canal
By : Banan AlzubaidiDefinition :
. Obturator canal : it is a small opening in the pubic bone (part of
the hip bone ).
. It is formed in the posterolateral aspect of the
obturator foramen by:
. 1) obturator membrane and obturator internus and externus
muscles.
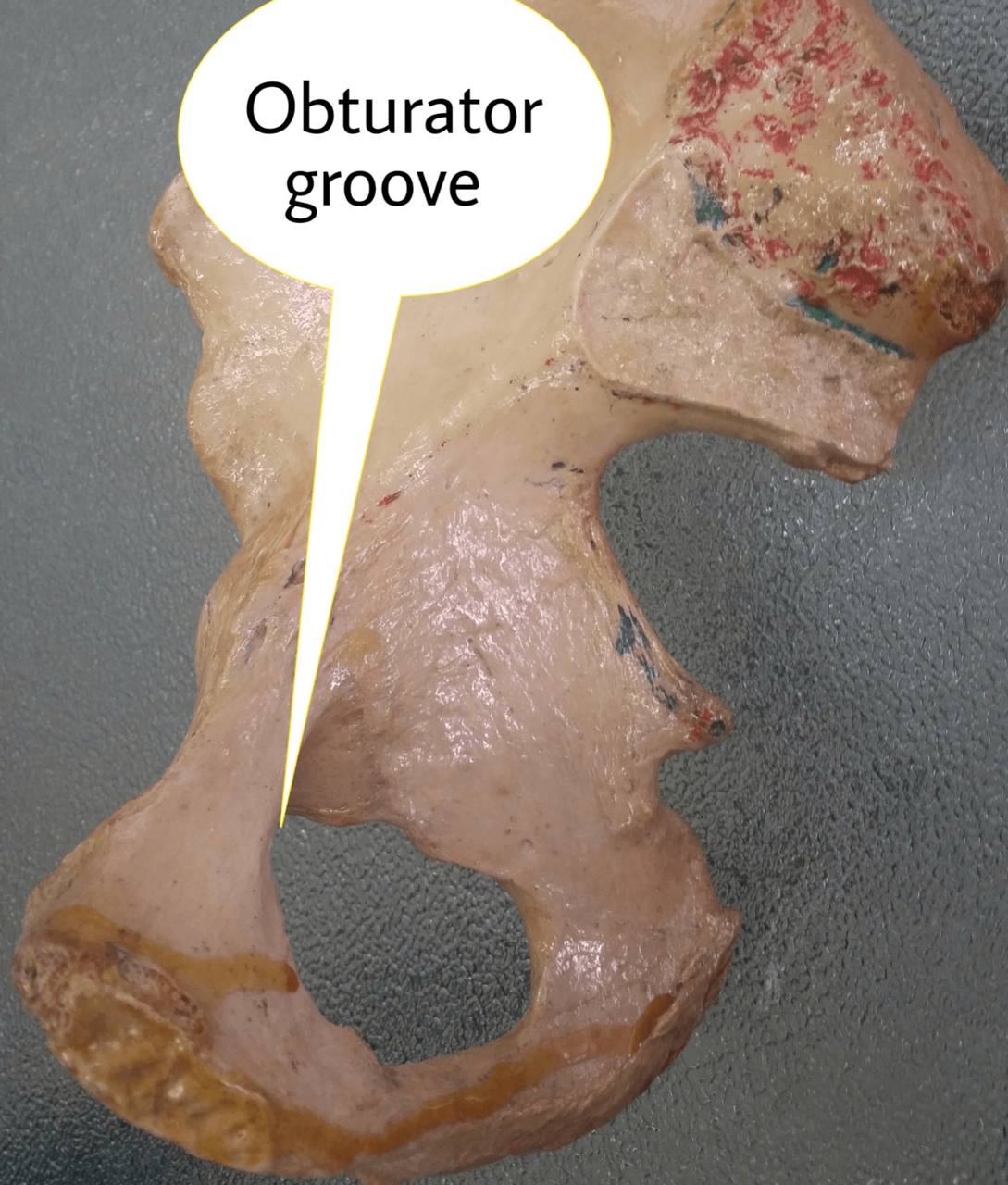
. 2) the obturator groove in the hip bone (in the pelvis).
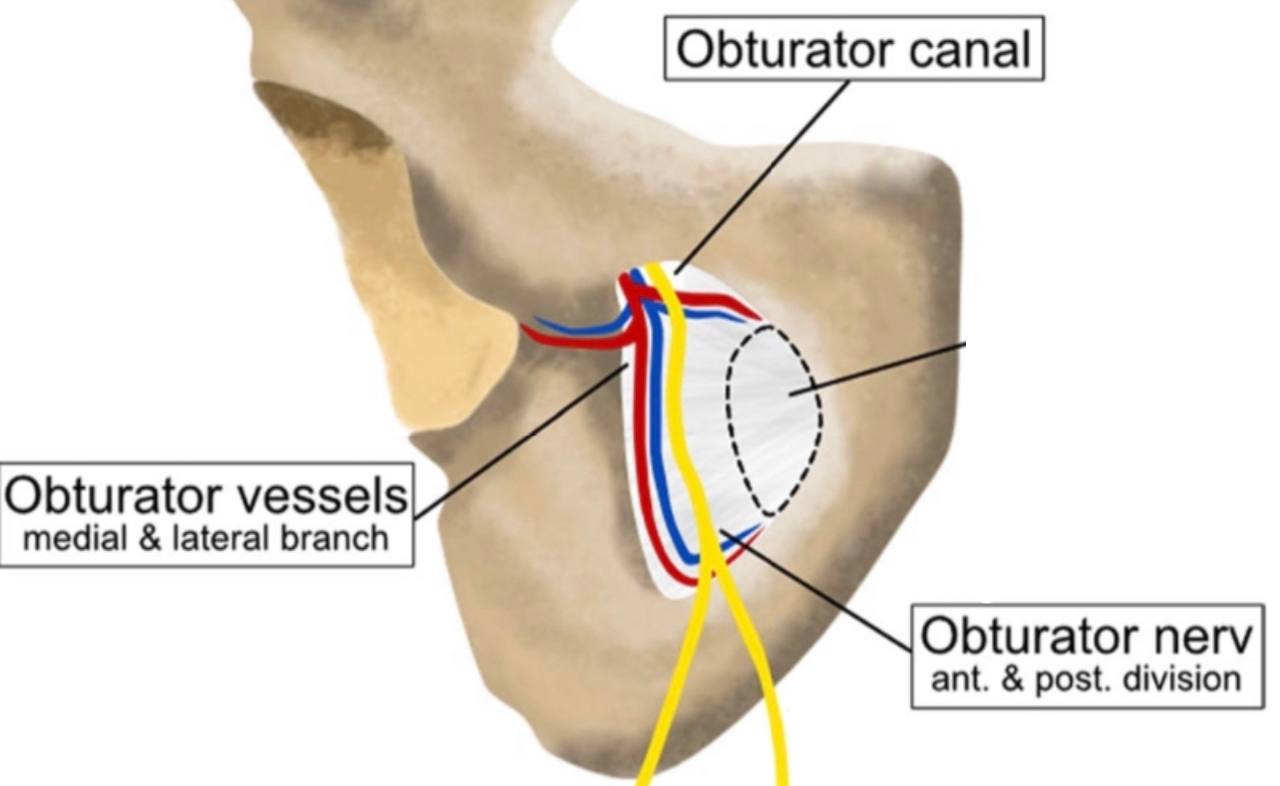
. It is considered a passageway of the obturator nerve and vessels
from the pelvis to the medial (adductor )compartment of the thigh
It is connects between the pelvis and the thigh.
. wide of the obturator canal :about 0.2-0.5 cm.
. length of the obturator canal : about 2 to 3 cm .
the hip bone ).
. It is formed in the posterolateral aspect of the
obturator foramen
Note
it is a large opening in the hip bone closed by the obturator membrane except a small opening in the upper part of the obturator foramen called (obturator canal)..provides extensive surface area on the both sides for muscle attachment ..it is formed between pubic bone and ischium bone (parts of the hip bone)..It is bounded by the pubic and ischium and their rami...the obturator foramen is oval in males and wider ..more triangular in females.. 1) obturator membrane
Note
it is thin, strong fibrous sheet ..completely closes the obturator foramen except a small opening in the upper part called (obturator canal)..it is attached to the sharp margin of the obturator forearm except at the inferolateral angle where it is attached to the pelvis surface of the inferior ramus of the ischium bone (part of the hip bone ) ..it separates the internus obturator muscle (that attached in the endopelvis surface )from the external obturator muscle (that attached in the exopelvis surface)..these muscles are connected to it .muscles.
. 2) the obturator groove in the hip bone (in the pelvis).
. It is considered a passageway of the obturator nerve and vessels
from the pelvis to the medial (adductor )compartment of the thigh
It is connects between the pelvis and the thigh.
. wide of the obturator canal :about 0.2-0.5 cm.
. length of the obturator canal : about 2 to 3 cm .
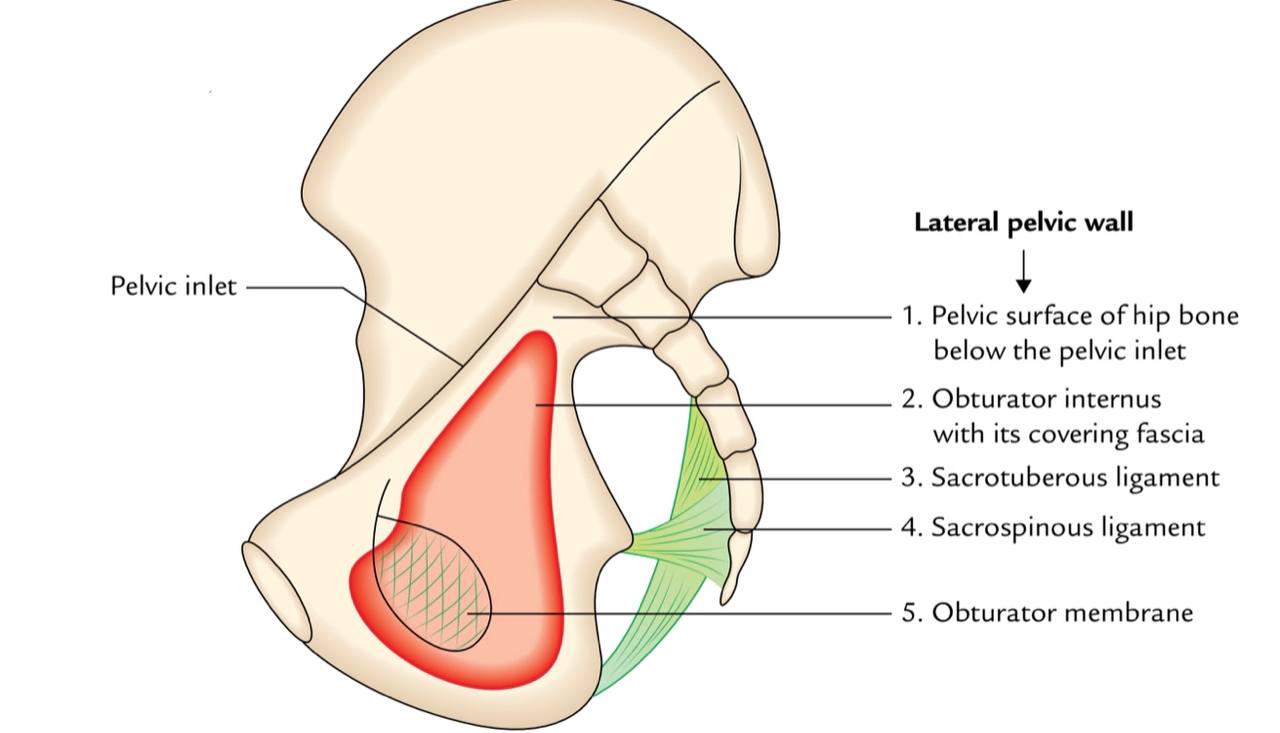
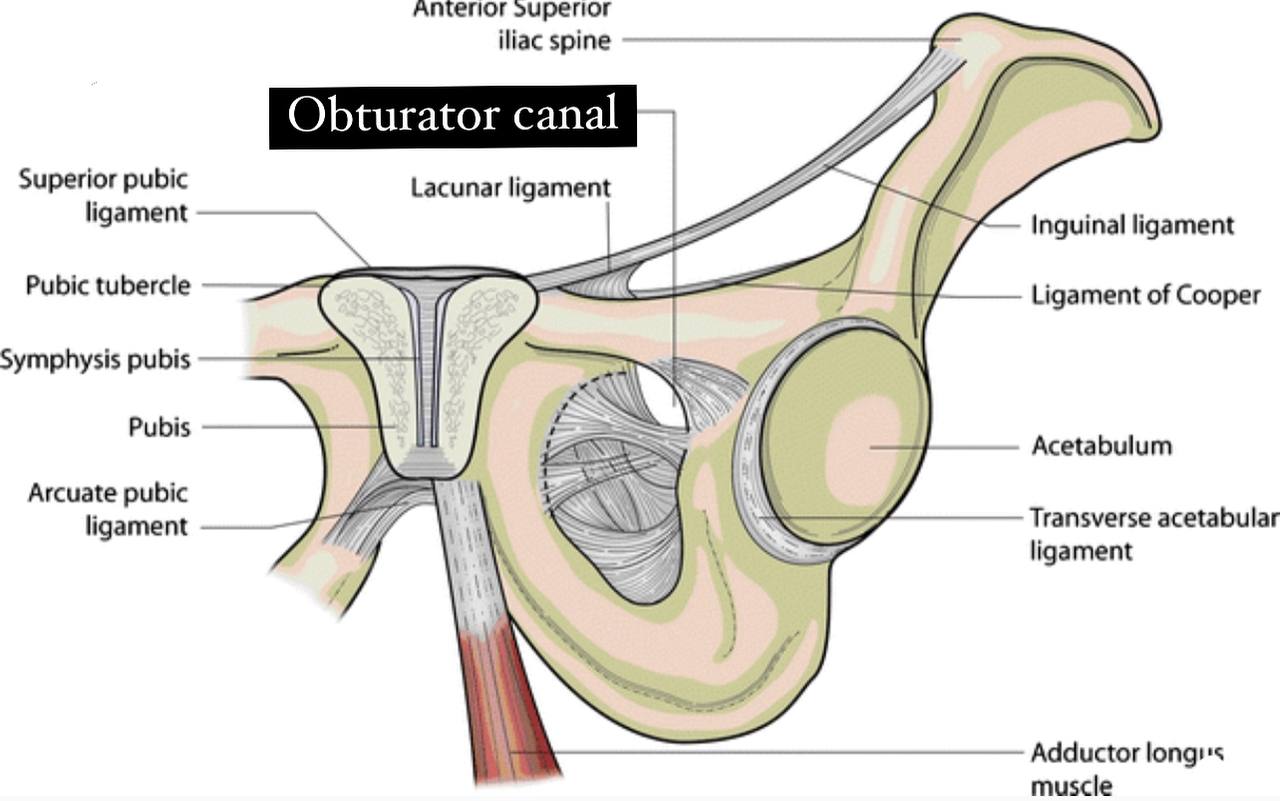
The Borders :
. Superior and lateral : obturator groove of the pubic bone
(part of the hip bone).
. Inferior : internal and external obturator muscles and free
edge of the obturator membrane.
(part of the hip bone).
. Inferior : internal and external obturator muscles and free
edge of the obturator membrane.
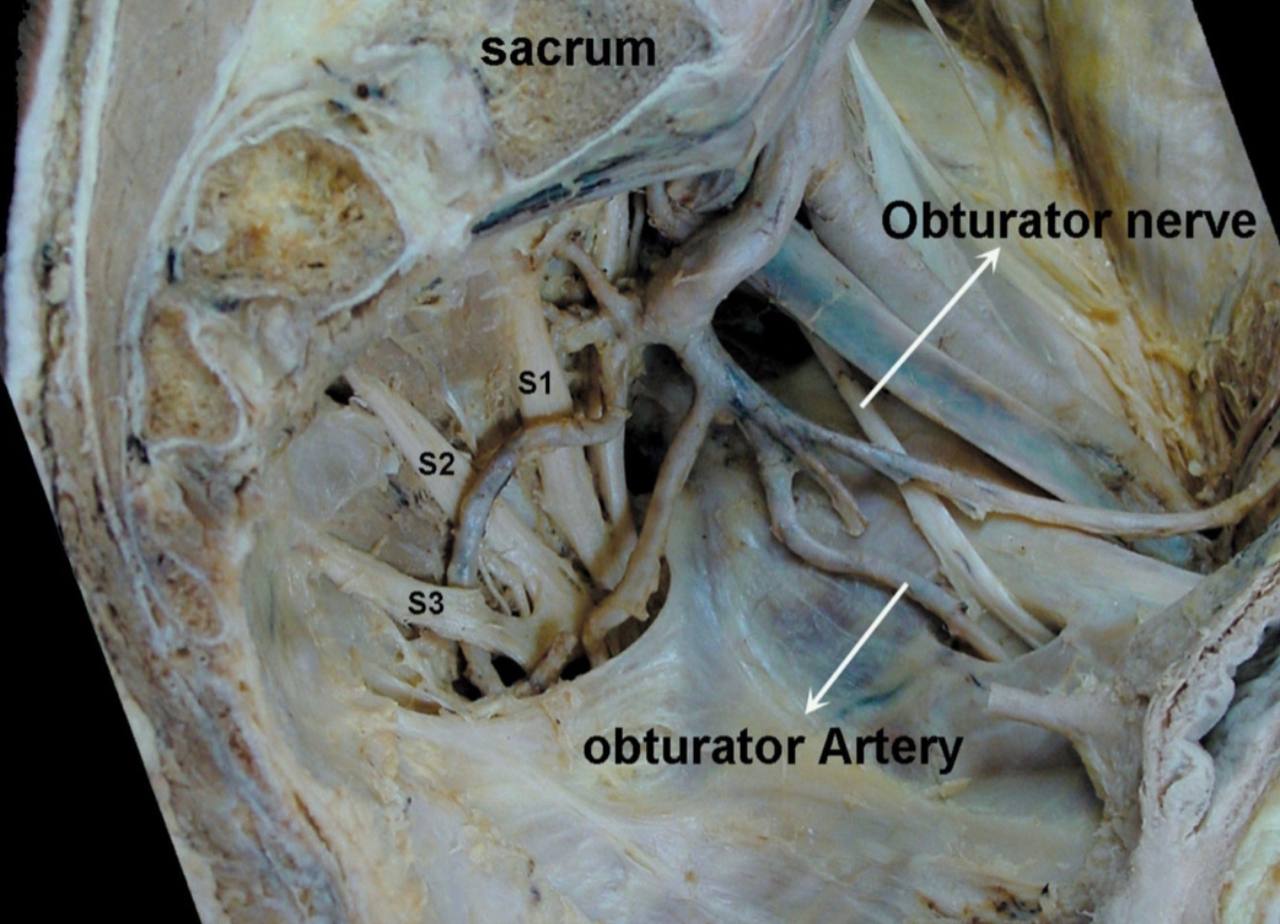
The contents :
1) Obturator nerve.
2) Obturator vessels (artery and vein).
2) Obturator vessels (artery and vein).


Clinical notes :
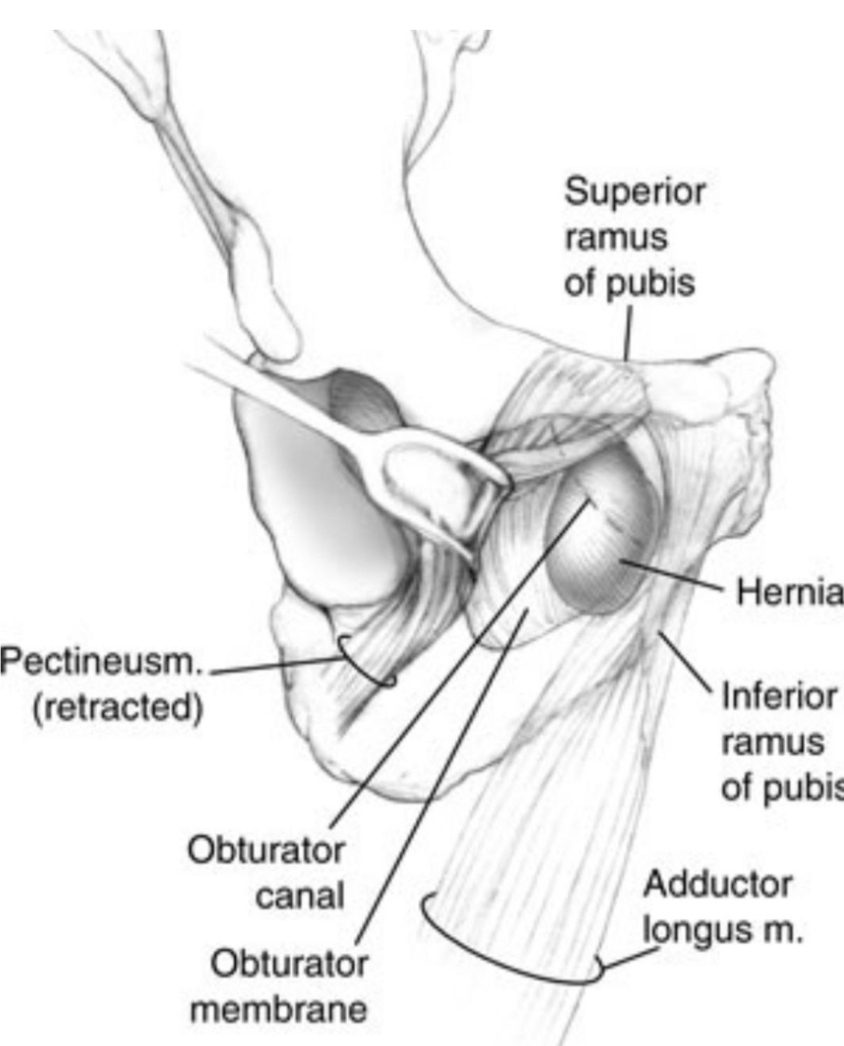
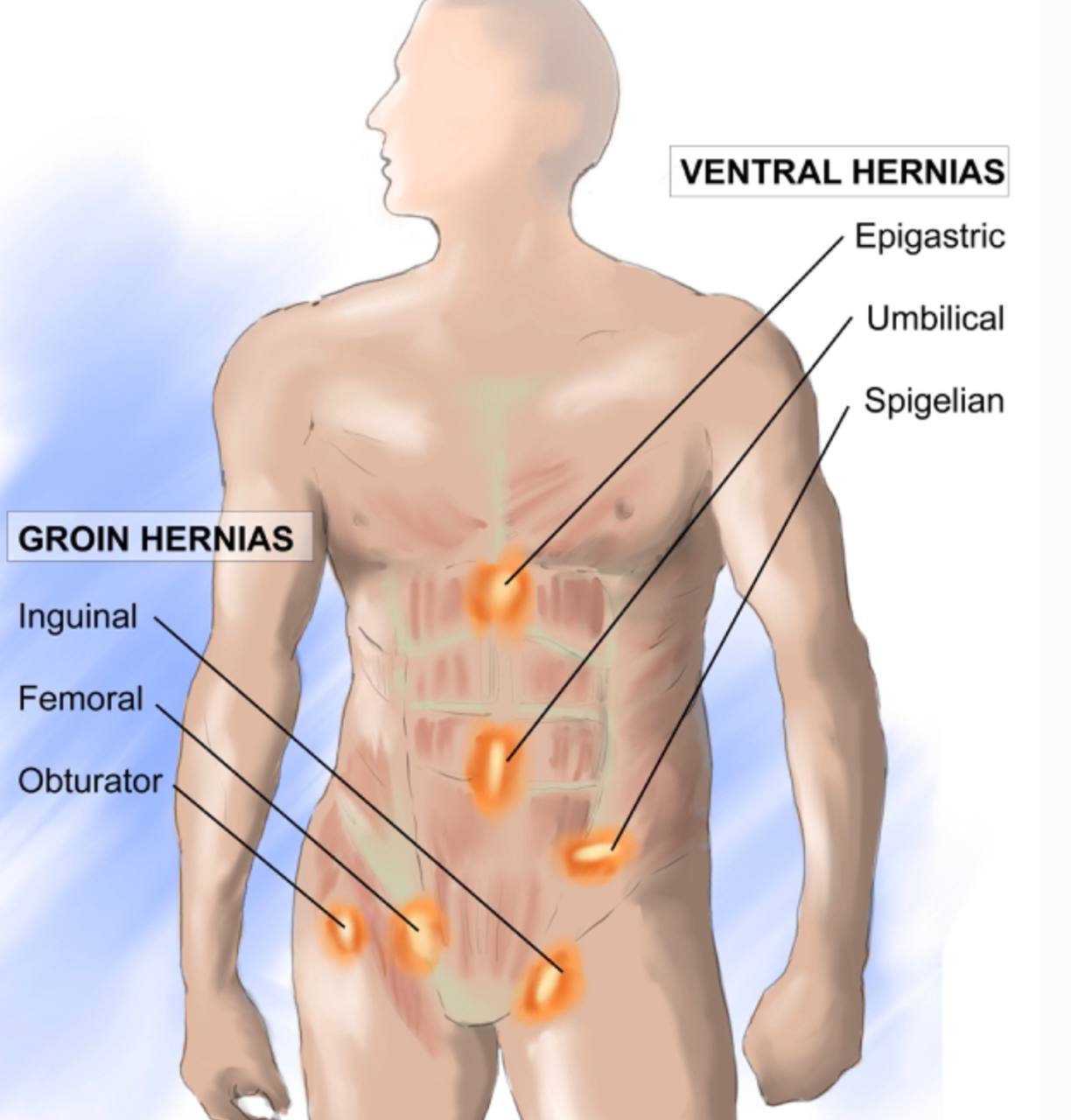
. Obturator hernia(the skinny old woman hernia) : It is a rare clinical condition
happens in the pelvis (in the obturator canal).
. It is about 1% from the abdominal hernia.
. Often, it is accompanied by severe intestinal obstruction
Early diagnosis of this disease for doctors is a challenge because its
symptoms are not specific.
.NOTE/ This disease is more common in women than men Because of the
anatomical difference between the sexes, where the pelvis of a woman is
wider ( It allows the contents of the hernia to pass easily )than that of a
man.
.NOTE/ the obturator hernia it is common in the (older woman's..multiparous..People
with chronic diseases and thin women(who have recently lost much weight))
.NOTE/ It is more common on the right side of the body.
.NOTE/ In this disease ..there is a protrusion of the content of the pelvis or
abdomen through the obturator canal( in the most cases protrudes small
intestine through the obturator canal )...The cyst may also include:
1) appendix.
2)omentum.
3)fallopian tubes.
4)or meckel's diverticulum.
. NOTE/ Obturator hernia has have the highest mortality rate compared to other abdominal
hernias .
happens in the pelvis (in the obturator canal).
. It is about 1% from the abdominal hernia.
. Often, it is accompanied by severe intestinal obstruction
Early diagnosis of this disease for doctors is a challenge because its
symptoms are not specific.
.NOTE/ This disease is more common in women than men Because of the
anatomical difference between the sexes, where the pelvis of a woman is
wider ( It allows the contents of the hernia to pass easily )than that of a
man.
.NOTE/ the obturator hernia it is common in the (older woman's..multiparous..People
with chronic diseases and thin women(who have recently lost much weight))
.NOTE/ It is more common on the right side of the body.
.NOTE/ In this disease ..there is a protrusion of the content of the pelvis or
abdomen through the obturator canal( in the most cases protrudes small
intestine through the obturator canal )...The cyst may also include:
1) appendix.
2)omentum.
3)fallopian tubes.
4)or meckel's diverticulum.
. NOTE/ Obturator hernia has have the highest mortality rate compared to other abdominal
hernias .
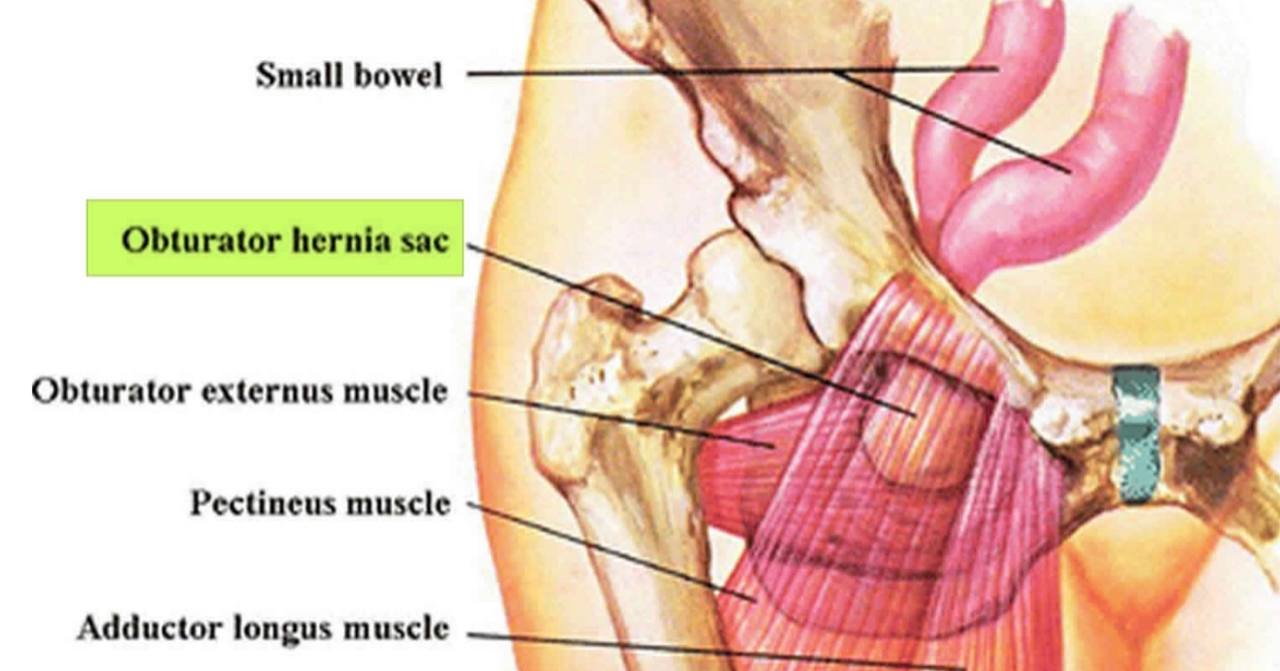
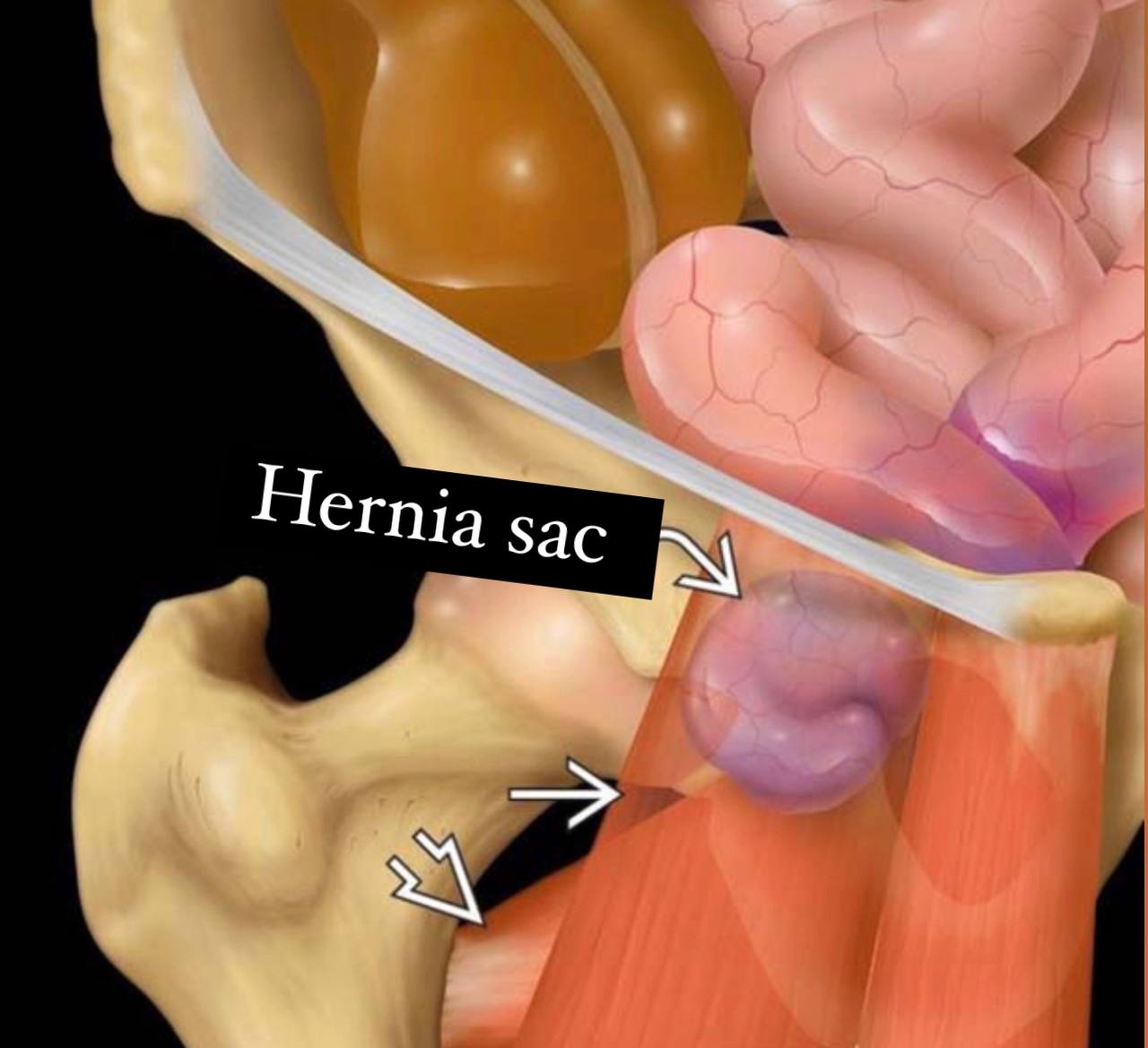
The normal position of the hernia sac:
1) Deep and inferior to the pectinuse muscle.
2) Superficial to the obturator externus.
3) Rarely, the position of the hernia sac is between the obturator externus
and obturator internus.
In general, the hernia sac is imperceptible(deep) .
2) Superficial to the obturator externus.
3) Rarely, the position of the hernia sac is between the obturator externus
and obturator internus.
In general, the hernia sac is imperceptible(deep) .
The causes :
1) It could be caused because of the expansion of the protective membrane of the
obturator canal, and thus allows the movement of tissues outside the
peritoneum ,or abdominal contents(especially the small intestine)through the
obturator canal.
2) One of the causes of the disease is also high intra-abdominal pressure (such as
ascites - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - chronic cough).
3) It also occurs due to the expansion of the pelvic peritoneum.
obturator canal, and thus allows the movement of tissues outside the
peritoneum ,or abdominal contents(especially the small intestine)through the
obturator canal.
2) One of the causes of the disease is also high intra-abdominal pressure (such as
ascites - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - chronic cough).
3) It also occurs due to the expansion of the pelvic peritoneum.
The symptoms :
. Symptoms are usually nonspecific, but the most common:
1) intestinal obstruction (more common ) Approximately 50% of patients suffer
from this symptom.
2) Abdominal pain - vomiting - nausea – fever.
3) sometimes it happens acute dilatation of the stomach.
4) In severe cases, necrosis or intestinal perforation may occur, which leads to
peritonitis.
1) intestinal obstruction (more common ) Approximately 50% of patients suffer
from this symptom.
2) Abdominal pain - vomiting - nausea – fever.
3) sometimes it happens acute dilatation of the stomach.
4) In severe cases, necrosis or intestinal perforation may occur, which leads to
peritonitis.
Signs of this disease:
1)Howship –Romberg sign (25-50% of patients suffer from this
symptom) it happens because of the compression of the obturator
nerve by the obturator hernia sac. This leads to the inner pain in the
medial side of the thigh extends to the knee(on internal rotation of
the hip)(along distribution of the obturator nerve ) and appearance of
a palpable mass at the medial aspect of the thigh.
2)Hannington-Kiff sign : in which the adductor reflex is absent in the
thigh, in the presence of a positive patellar reflex occur by the
compression of the obturator nerve by the obturator hernia sac.
symptom) it happens because of the compression of the obturator
nerve by the obturator hernia sac. This leads to the inner pain in the
medial side of the thigh extends to the knee(on internal rotation of
the hip)(along distribution of the obturator nerve ) and appearance of
a palpable mass at the medial aspect of the thigh.
2)Hannington-Kiff sign : in which the adductor reflex is absent in the
thigh, in the presence of a positive patellar reflex occur by the
compression of the obturator nerve by the obturator hernia sac.
The Diagnosis :
. Doctors consider it difficult to diagnose this disease because of its differentt
symptoms (The patient is often diagnosed after suffering from intestinal
obstruction) but it can be detected before surgery using some medical devices
such as:
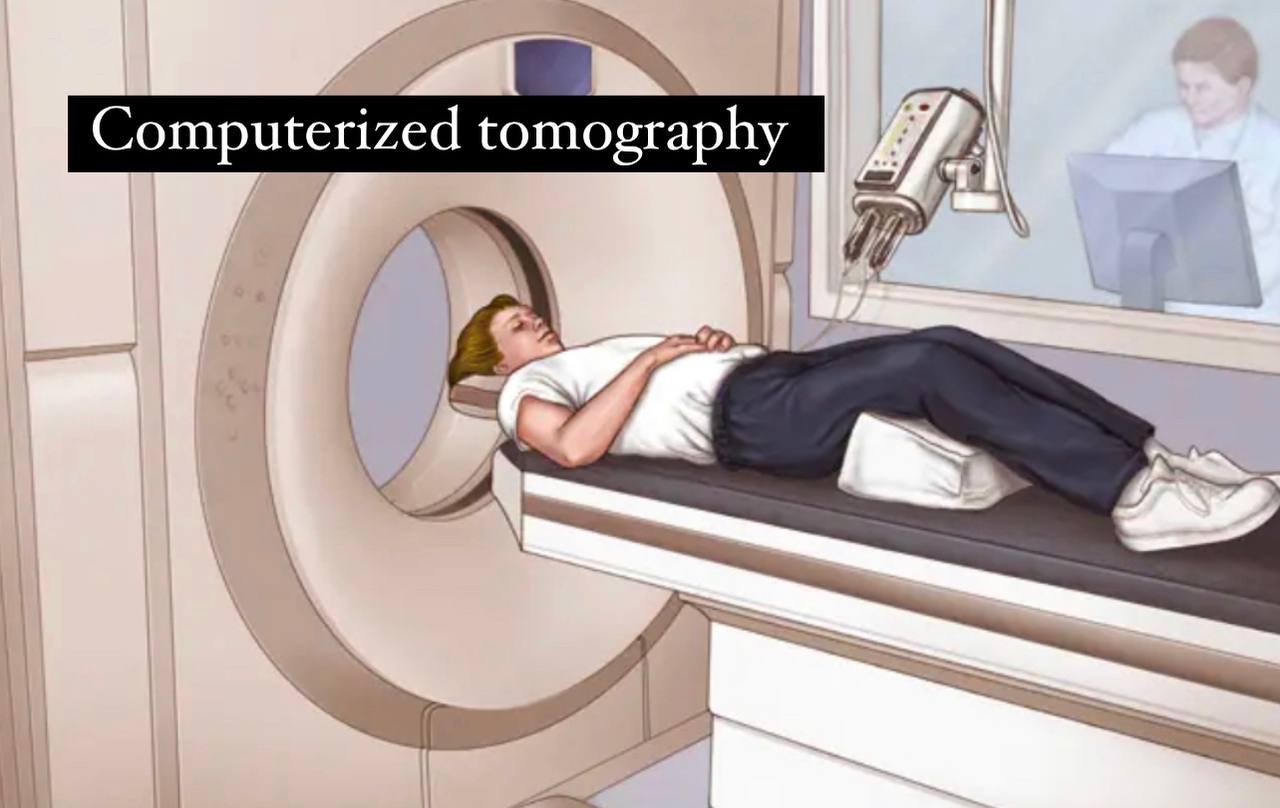
1)computerized tomography (CT): this device is important to detect the obturator
hernia before the surgery beginning.
2) By the usage of Ultrasound.
symptoms (The patient is often diagnosed after suffering from intestinal
obstruction) but it can be detected before surgery using some medical devices
such as:
1)computerized tomography (CT): this device is important to detect the obturator
hernia before the surgery beginning.
2) By the usage of Ultrasound.
The treatment :
. the only effective treatment is the surgical treatment or by the laparoscopic
treatment :
1) By surgery :( An appropriate surgical method must be chosen that suits the
patient’s condition, such as choosing an incision and a surgical procedure, and
whether a mesh should be placed or not).
. The mechanics of the surgery :
1) A low abdominal incision in the midline with attention to locating the
hernia.
2) Examination of the contents of the cyst (may require excision part of
the small intestine if it is within the components of the cyst).
3) Hernia repairs either with an initial thread or by placing a mesh.
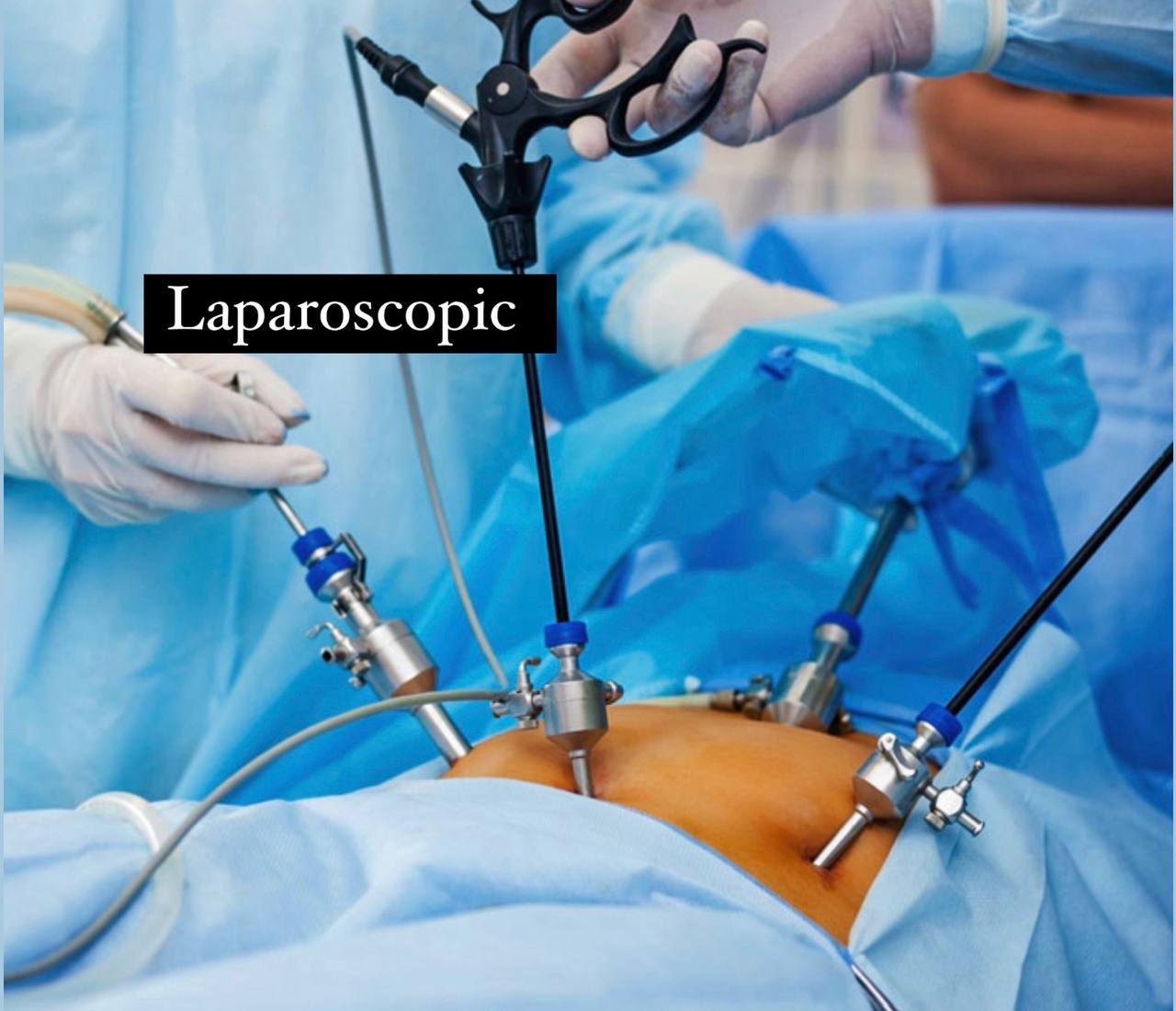
4) Abdominal defect repairs laparoscopic ally.
2)by the laparoscopic (Doctors prefer this method).
treatment :
1) By surgery :( An appropriate surgical method must be chosen that suits the
patient’s condition, such as choosing an incision and a surgical procedure, and
whether a mesh should be placed or not).
. The mechanics of the surgery :
1) A low abdominal incision in the midline with attention to locating the
hernia.
2) Examination of the contents of the cyst (may require excision part of
the small intestine if it is within the components of the cyst).
3) Hernia repairs either with an initial thread or by placing a mesh.
4) Abdominal defect repairs laparoscopic ally.
2)by the laparoscopic (Doctors prefer this method).

References of images :
Cover image/Obturator canal/Adobe stock /https://stock.adobe.com/search?k=obturator
Fig. 1/Obturator canal and obturator membrane /Earth's lab/https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/obturator-membrane/
Fig. 2/Obturator canal /Bonepit/http://www.bonepit.com/Lectures/Pubalgia%20Catherina%20Fu.pdf
Fig. 3/Obturator artery and nerve/NYSORA/https://www.nysora.com/topics/regional-anesthesia-for-specific-surgical-procedures/lower-extremity-regional-anesthesia-for-specific-surgical-procedures/obturator-nerve-block/
Fig. 4/Obturator canal/Nature/https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-92755-2
Fig. 5/lumen learning/https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap1/chapter/the-pelvic-girdle-and-pelvis/
Fig. 6/Obturator groove /http://www.eatlas-anatomy.ir/obturator-groove/
Fig. 7/Obturator membrane/https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Slide2DAD.JPG
Fig. 8/Obturator hernia/health jade /https://healthjade.net/obturator-hernia/
Fig. 9/Obturator hernia/Springer link /https://link.springer.com/10.1007%2F978-1-84628-833-3_127
Fig. 10/Obturator hernia/Radiology key /https://radiologykey.com/obturator-hernia-2/
Fig. 11/Computerized tomography/Mayo clinic /https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-scan/about/pac-20393675
Fig. 12/Laparoscopic/Asian hospital Faridabad/https://www.aimsindia.com/blog/advantages-of-laparoscopic-surgery/
Fig. 13/Laparoscopic/Healthdirect /https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/laparoscopy
Fig. 14/Hernia in the body /https://drandrewkiu.com.au/hernia-adelaide/
Fig. 1/Obturator canal and obturator membrane /Earth's lab/https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/obturator-membrane/
Fig. 2/Obturator canal /Bonepit/http://www.bonepit.com/Lectures/Pubalgia%20Catherina%20Fu.pdf
Fig. 3/Obturator artery and nerve/NYSORA/https://www.nysora.com/topics/regional-anesthesia-for-specific-surgical-procedures/lower-extremity-regional-anesthesia-for-specific-surgical-procedures/obturator-nerve-block/
Fig. 4/Obturator canal/Nature/https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-92755-2
Fig. 5/lumen learning/https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap1/chapter/the-pelvic-girdle-and-pelvis/
Fig. 6/Obturator groove /http://www.eatlas-anatomy.ir/obturator-groove/
Fig. 7/Obturator membrane/https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Slide2DAD.JPG
Fig. 8/Obturator hernia/health jade /https://healthjade.net/obturator-hernia/
Fig. 9/Obturator hernia/Springer link /https://link.springer.com/10.1007%2F978-1-84628-833-3_127
Fig. 10/Obturator hernia/Radiology key /https://radiologykey.com/obturator-hernia-2/
Fig. 11/Computerized tomography/Mayo clinic /https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-scan/about/pac-20393675
Fig. 12/Laparoscopic/Asian hospital Faridabad/https://www.aimsindia.com/blog/advantages-of-laparoscopic-surgery/
Fig. 13/Laparoscopic/Healthdirect /https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/laparoscopy
Fig. 14/Hernia in the body /https://drandrewkiu.com.au/hernia-adelaide/
Reference of the videoe:
1)VO60 Laparoscopic Obturator hernia repair in the setting of incarceration and obstruction/society of American gastrointestinal and endoscopic surgeins(Sages) /https://youtu.be/nrsggeebm8E
