Structures That Pass Above and Below Pectineus Muscle
By : Amna MohammedPectineus muscle
Pectineus muscle is one of the medial compartment muscles of the thigh.
Anterior view
right lower limb.
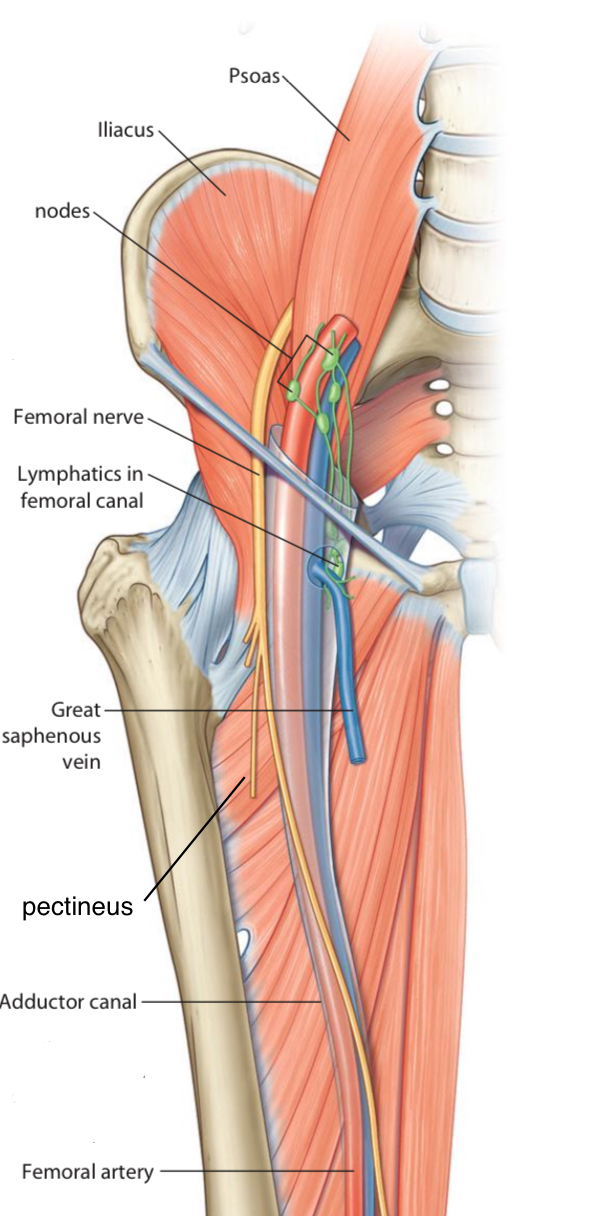
Structures that pass above pectineus muscle:
1. Femoral sheath contain three structures (From medial to lateral):
a) Deep inguinal lymph node(croquet node)
It pass through a canal called the Femoral canal.
pectineus.
b) Femoral vein
Is the middle structure in the femoral sheath, continues as external iliac vein after passing beneath inguinal ligament.
c) Femoral artery
is a complement of the external iliac artery-goes down anterior to the pectineus m. border & its two branchs superficial & deep external pudendal artery which go out from femoral sheath.
a) Deep inguinal lymph node(croquet node)
It pass through a canal called the Femoral canal.
pectineus.
b) Femoral vein
Is the middle structure in the femoral sheath, continues as external iliac vein after passing beneath inguinal ligament.
c) Femoral artery
is a complement of the external iliac artery-goes down anterior to the pectineus m. border & its two branchs superficial & deep external pudendal artery which go out from femoral sheath.
2. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
There are two parts of superficial lymph nodes: a horizontal & a vertical parts which located in the superficial fascia in the thigh.
3. Saphenous opening
An aperture in the deep fascia, its importance is that the Great saphenous vein ends at the femoral vein through it & allows to passage way for a small branches of femoral artery & a lymph vessels through it.
There are two parts of superficial lymph nodes: a horizontal & a vertical parts which located in the superficial fascia in the thigh.
3. Saphenous opening
An aperture in the deep fascia, its importance is that the Great saphenous vein ends at the femoral vein through it & allows to passage way for a small branches of femoral artery & a lymph vessels through it.
Anterior view
Right lower limb.
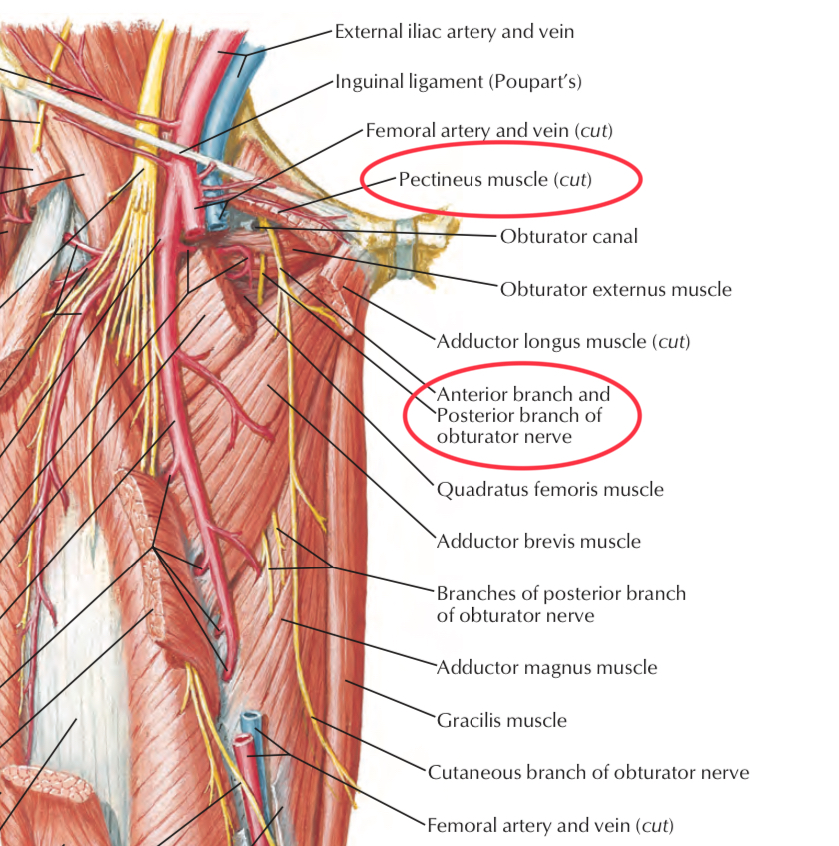
Structures that pass below pectineus muscle
1. Obturator Nerve (the anterior branch)
It descends behind the pectineus m. and innervates most of the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
2. Obturator Artery (the anterior and posterior branches)
It is a branch of the internal iliac artery. It is accompanied with the obturator nerve during its passage through the obturator canal.
3. Obturator Vein
It is corresponding to the obturator artery and drains into the internal iliac vein.
It descends behind the pectineus m. and innervates most of the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
2. Obturator Artery (the anterior and posterior branches)
It is a branch of the internal iliac artery. It is accompanied with the obturator nerve during its passage through the obturator canal.
3. Obturator Vein
It is corresponding to the obturator artery and drains into the internal iliac vein.
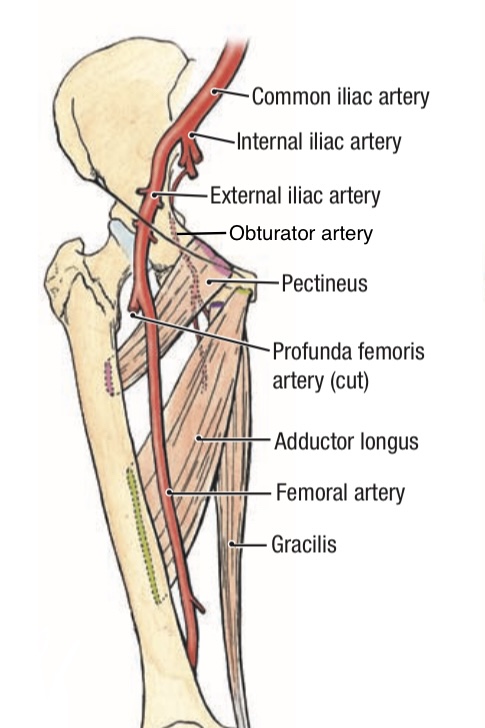
Anterior view.
Right lower limb.
References
Moore - Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th Edition) -554-555
Snell’s Clinical Anatomy By Regions (10th Edition) -1289, 1298,1321,1323
Pectineus Muscle - physio-pedia - https://www.physio- pedia.com/Pectineus_Muscle
Gray’s Atlas of Anatomy(2nd Edition)-310-374
Grant’s Atlas Of Anatomy(15th Edition)-6.23
Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy(6th Edition)-488
Snell’s Clinical Anatomy By Regions (10th Edition) -1289, 1298,1321,1323
Pectineus Muscle - physio-pedia - https://www.physio- pedia.com/Pectineus_Muscle
Gray’s Atlas of Anatomy(2nd Edition)-310-374
Grant’s Atlas Of Anatomy(15th Edition)-6.23
Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy(6th Edition)-488
