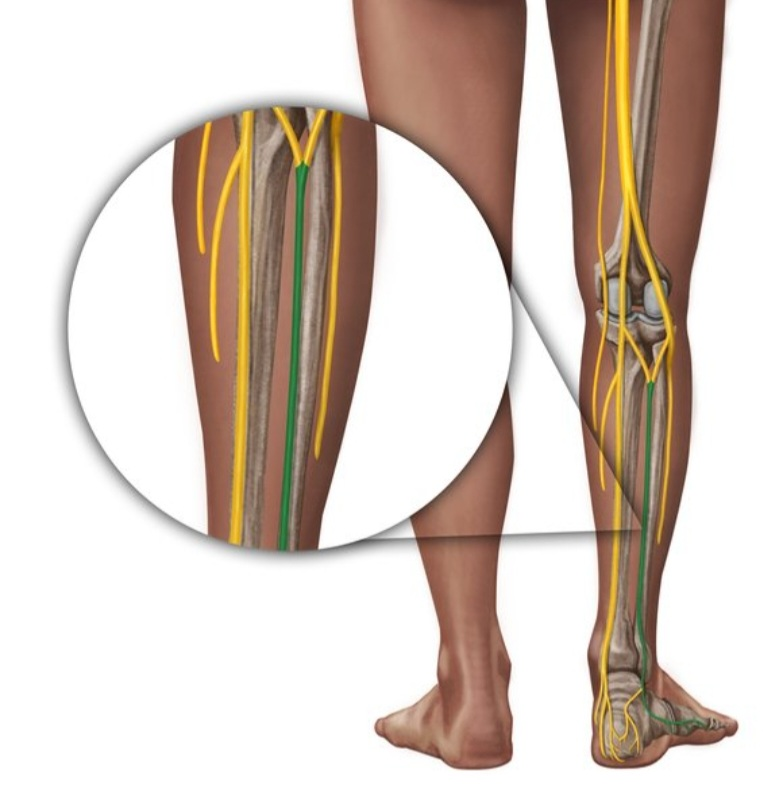
SURAL NERVE
By : Safa QusayIntroduction
The nerve arises superiorly in the poplitealous fossal(or popliteal fossa) , or inferiorly near to the heel (it has not been in the upper part of the thigh like other nerves)
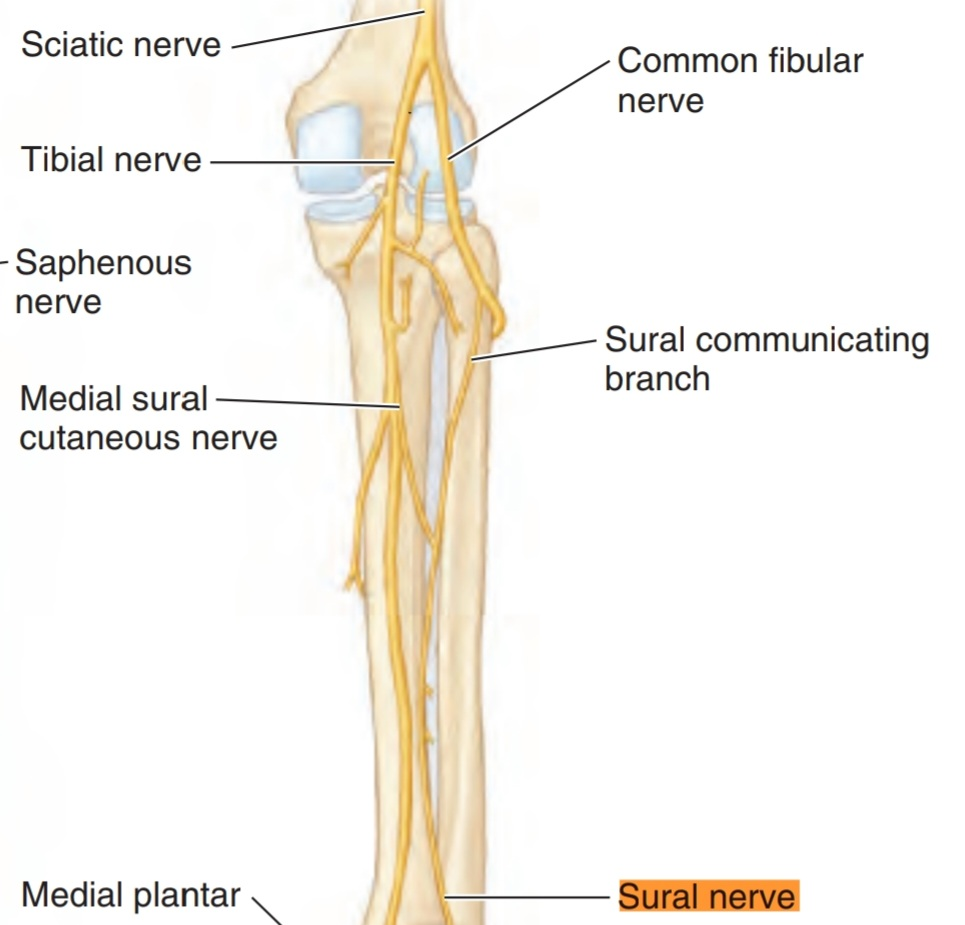
It is formed by the connecting or the union of :
1. Laterally: the sural communicating nerve (branch of the common fibular nerve).
2.Medially:the medial sural cutaneous nerve ( branch from the tibial nerve).
It is formed by the connecting or the union of :
1. Laterally: the sural communicating nerve (branch of the common fibular nerve).
2.Medially:the medial sural cutaneous nerve ( branch from the tibial nerve).
IMPORTANT NOTES
• In some people there is no union between these two branches, so in this case the sural nerve is not formed and supplied by the medial and lateral sural cutaneous branches.
• The small saphenous vein accompanies the sural nerve in the leg.
• In some people there is no union between these two branches, so in this case the sural nerve is not formed and supplied by the medial and lateral sural cutaneous branches.
• The small saphenous vein accompanies the sural nerve in the leg.
Course of the nerve:
The sural nerve arises from ( S1 , S2 ) in the posterior compartment of the leg in the calf.
Note
(it is called also the sural area) It is a muscles area formed by 3 muscles: 1. gastrocnemius muscle 2. soleus muscle 3. plantaris muscle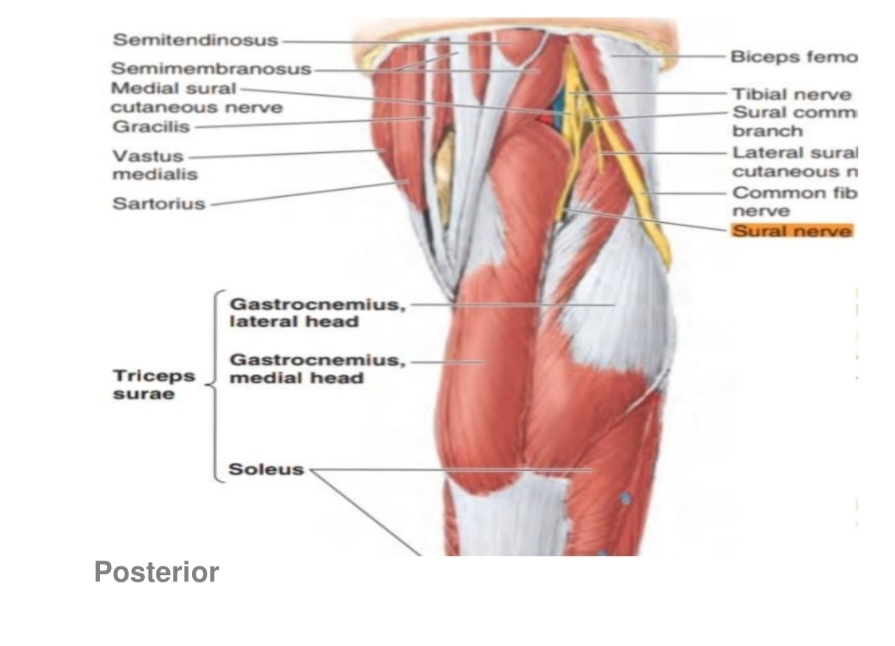
Sural nerve
By the union of the :
1. Laterally: the sural communicating nerve (branch of the common fibular nerve).
2.Medially:the medial sural cutaneous nerve ( branch from the tibial nerve)
In the popliteal fossa or beneath it when they connect.
1. Laterally: the sural communicating nerve (branch of the common fibular nerve).
2.Medially:the medial sural cutaneous nerve ( branch from the tibial nerve)
In the popliteal fossa or beneath it when they connect.
Then, the sural nerve runs between the two heads of gastrocnemius muscle. When it arrives one-third of the leg , it runs lateral to the calcaneus tendon with the small saphenous vein .
Note
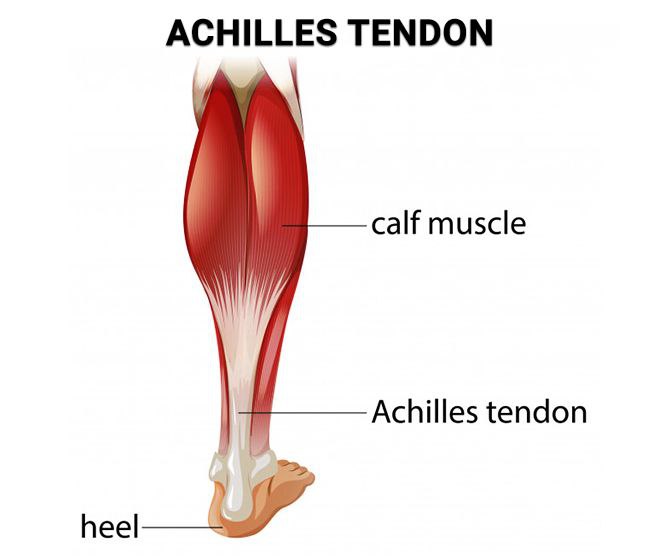
(Achilles tendon ) It is a strong band we can found in the back of leg ,it connects the calf muscles to the calcaneus bone. 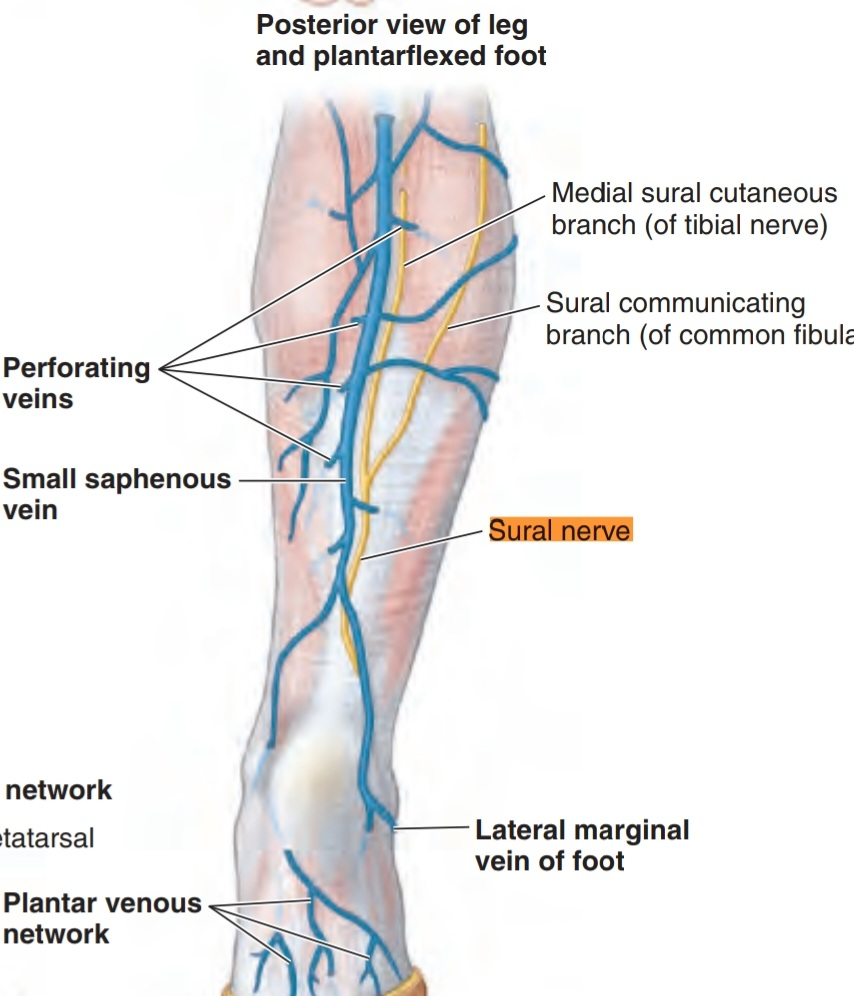
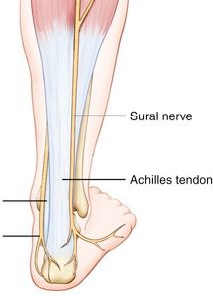
The sural nerve continues running in this way with the vein to reach the ankle and pass between the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus bone to enter the foot.
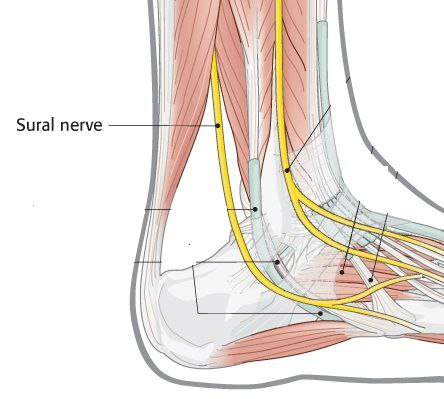
In the foot, it run lateral in the lateral aspect of the foot and it divides to form the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve.
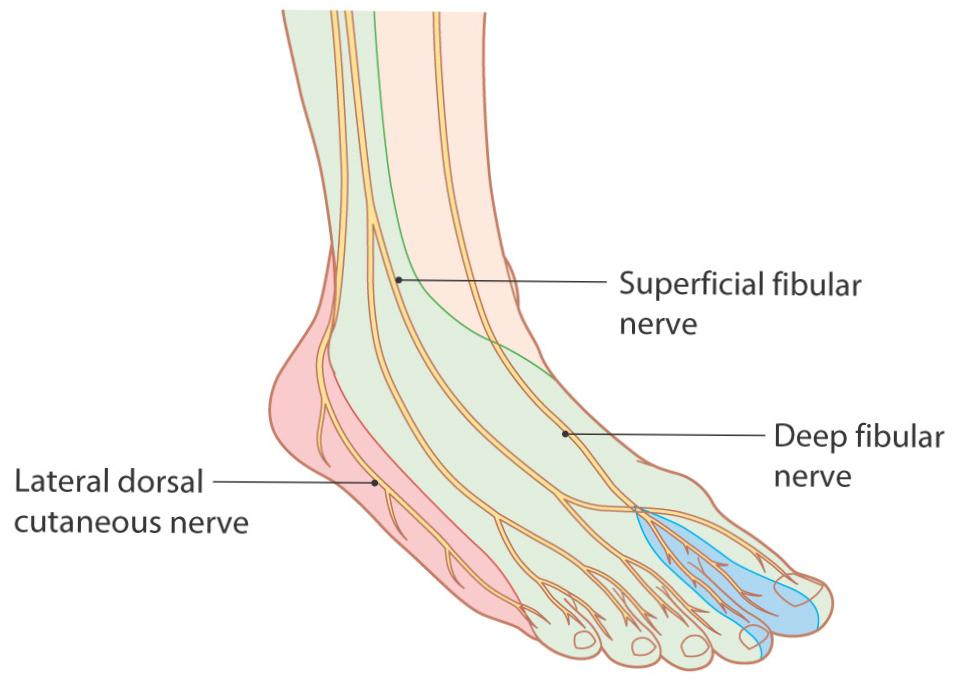
In foot
Motor or Sensory?
The sural nerve has a sensory function only, and has no motor function.
The branches of the sural nerve:
In the leg, the nerve doesn’t give any branches, but when it arrives to the foot it gives two branches:
1. Lateral calcaneal branch , which supplies the skin of the lateral portion of the heel .
2. Lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve of foot , it supplies the lateral side of the dorsum of the foot )this nerve ends as digital nerve to supply the lateral aspect of fifth toe).
1. Lateral calcaneal branch , which supplies the skin of the lateral portion of the heel .
2. Lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve of foot , it supplies the lateral side of the dorsum of the foot )this nerve ends as digital nerve to supply the lateral aspect of fifth toe).
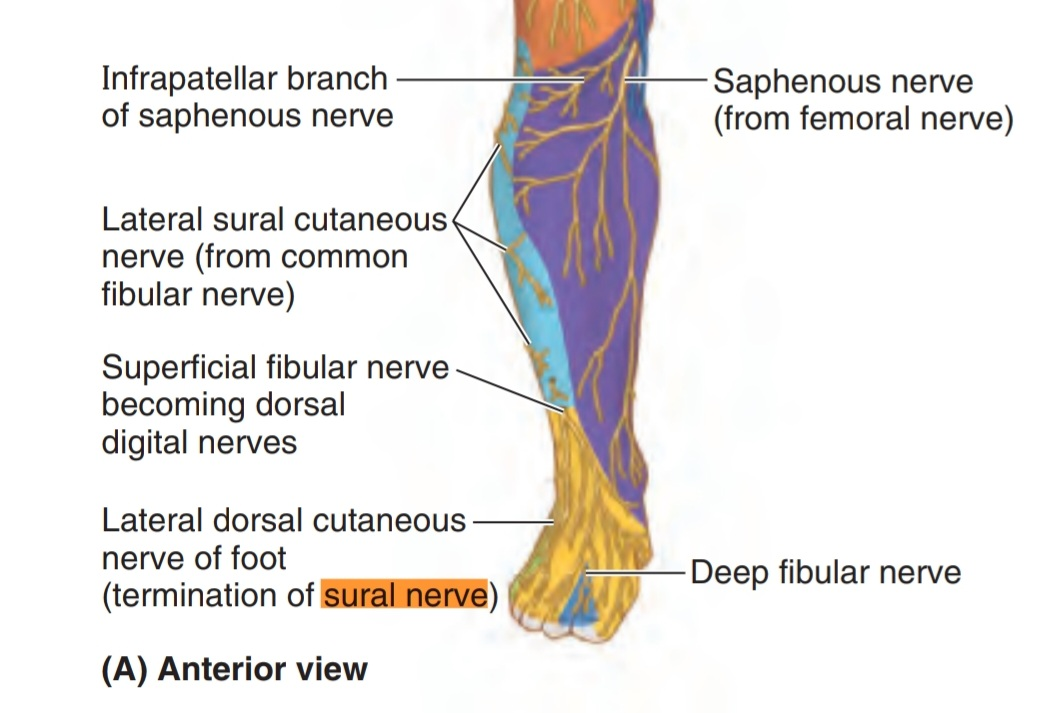
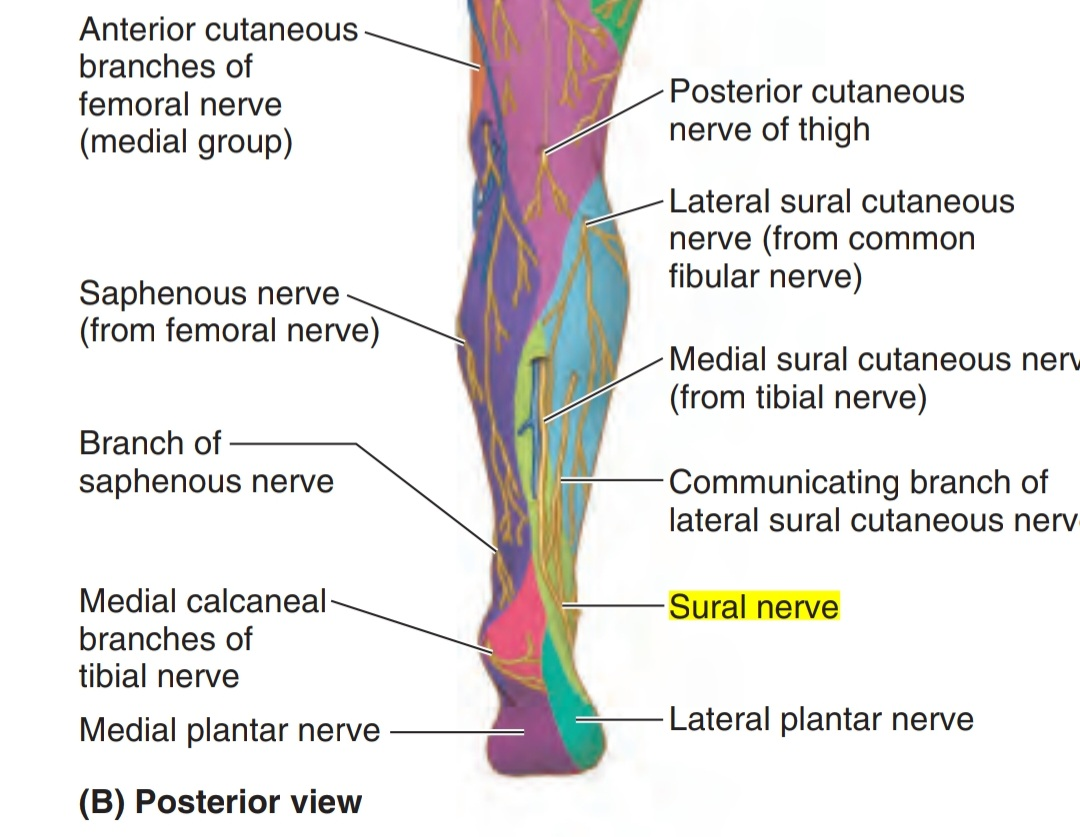
Cutaneous area
Lateral side of leg and foot
Refernces:
• MOORE Clinically Oriented ANATOMY Keith L. Moore Arthur F. Dalley Anne M.R. Agur 619,624,596
• Peripheral Nerve Injury ,JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE
https://www-hopkinsmedicine-org.cdn.ampp
• Sural nerve, Cleveland Clinic
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22323-sural-nerve
• Anatomy , Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb , Sural Nerve Miniato MA , Nedeff N. Books;
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546638/
Figures are:
1. From kenhub
2. From ankle, foot and orthoric centre
3. From basicmedicalkey.com
4. From Mayo clinic
5. From Jons Hopkins medicine
6. From Moore Clinically Oriented ANATOMY FIGURE 5.50. 5.61.,5.15. ,5.16.,5.74.,5.60A_E ,
• MOORE Clinically Oriented ANATOMY Keith L. Moore Arthur F. Dalley Anne M.R. Agur 619,624,596
• Peripheral Nerve Injury ,JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE
https://www-hopkinsmedicine-org.cdn.ampp
• Sural nerve, Cleveland Clinic
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22323-sural-nerve
• Anatomy , Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb , Sural Nerve Miniato MA , Nedeff N. Books;
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546638/
Figures are:
1. From kenhub
2. From ankle, foot and orthoric centre
3. From basicmedicalkey.com
4. From Mayo clinic
5. From Jons Hopkins medicine
6. From Moore Clinically Oriented ANATOMY FIGURE 5.50. 5.61.,5.15. ,5.16.,5.74.,5.60A_E ,
