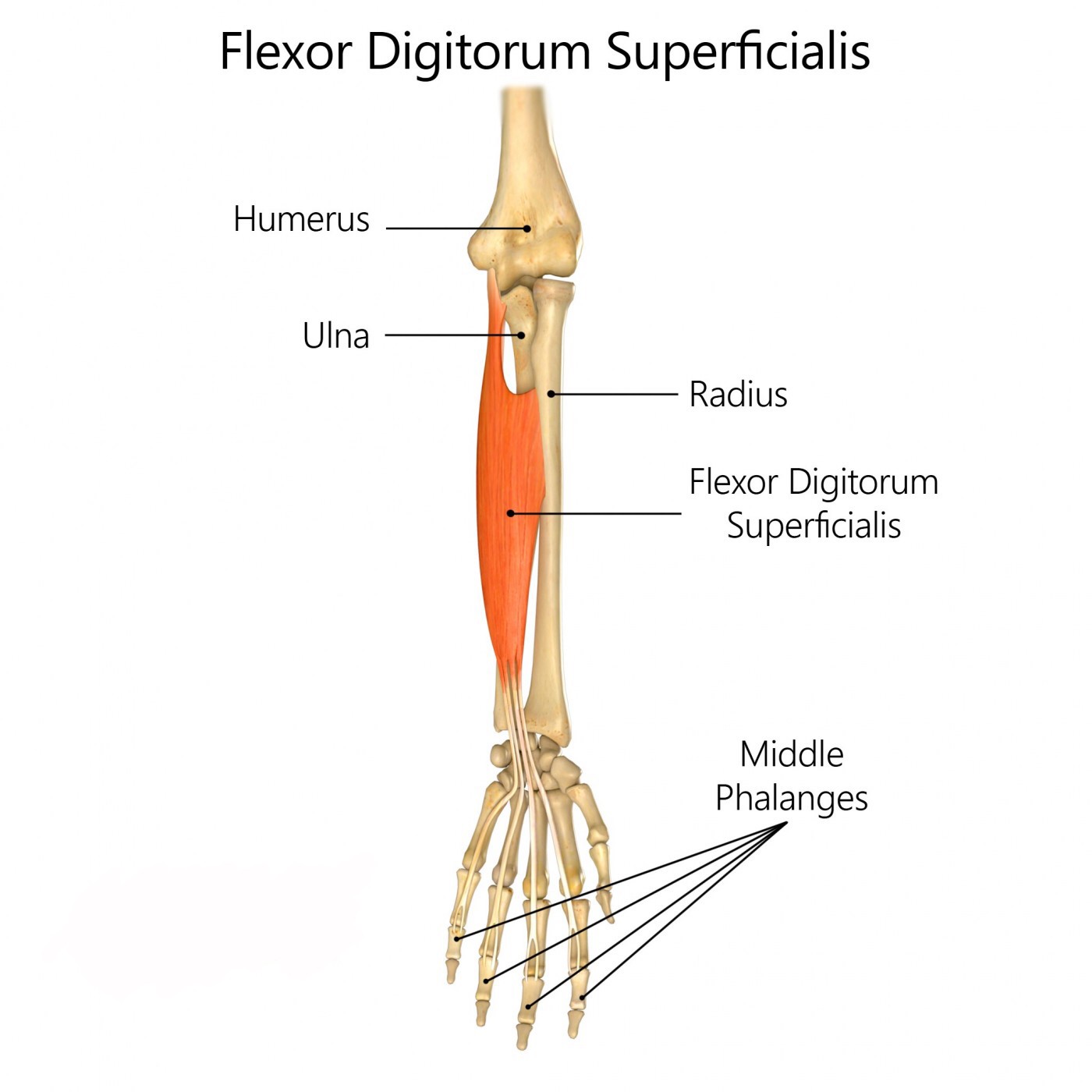
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
By : Mustafa AhmedName
The name, flexor digitorum superficialis, tells us that this muscle flexes the digits (i.e., fingers) and is
superficial (superficial to the flexor digitorum profundus).
Derivation :
flexor: L. a muscle that flexes a body part
digitorum: L. refers to a digit (finger)
superficialis: L. superficial (near the surface)
Pronunciation :
FLEKS-or
dij-i-TOE-rum
SOO-per-fish-ee-A-lis
superficial (superficial to the flexor digitorum profundus).
Derivation :
flexor: L. a muscle that flexes a body part
digitorum: L. refers to a digit (finger)
superficialis: L. superficial (near the surface)
Pronunciation :
FLEKS-or
dij-i-TOE-rum
SOO-per-fish-ee-A-lis
General
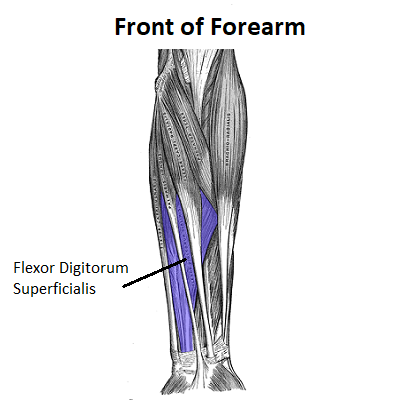
1. The flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) is also known as the flexor digitorum sublimis.
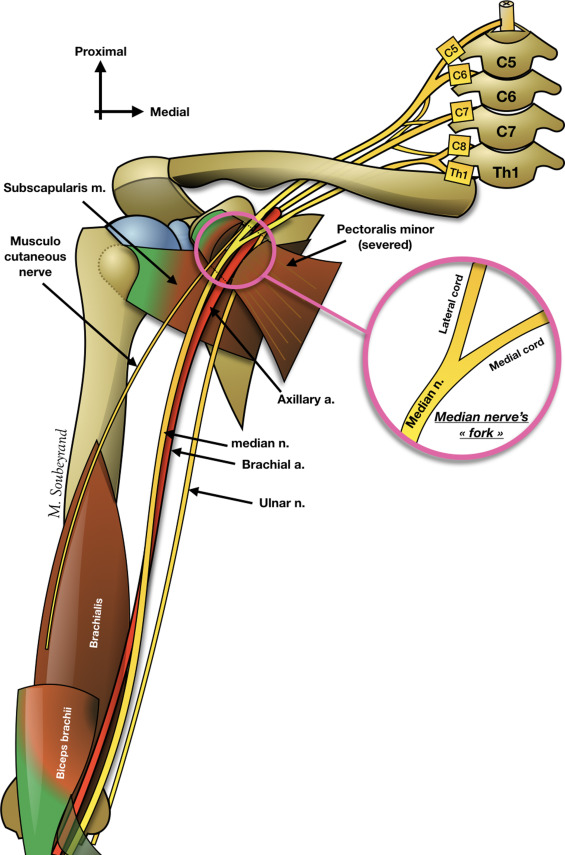
2. The median nerve and ulnar artery travel between the two heads of the FDS.
3.Is sometimes considered one of the superficial muscles of the forearm
2. The median nerve and ulnar artery travel between the two heads of the FDS.
3.Is sometimes considered one of the superficial muscles of the forearm
Supply
INNERVATION :
The Median Nerve
C7, C8, T1
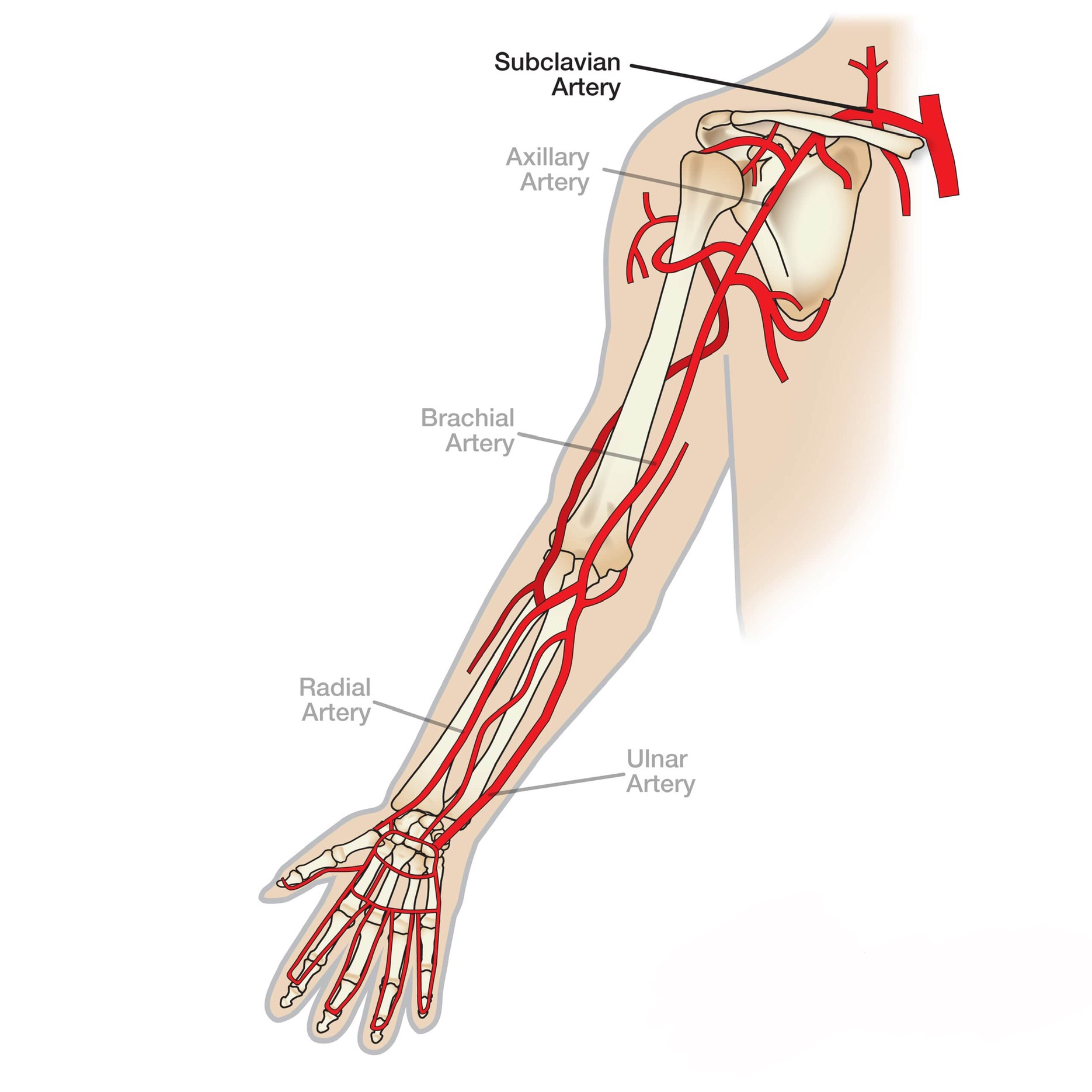
ARTERIAL SUPPLY :
The Ulnar and Radial Arteries (terminal branches of the Brachial Artery)
The Median Nerve
C7, C8, T1
ARTERIAL SUPPLY :
The Ulnar and Radial Arteries (terminal branches of the Brachial Artery)
Origin & insertion
Origin : Medial Epicondyle of the Humerus via the Common Flexor Belly/Tendon, and the Anterior Ulna and Radius
HUMEROULNAR HEAD:
medial epicondyle of the humerus (via the common flexor
belly/tendon) and the coronoid process of the ulna
RADIAL HEAD:
proximal 1/2 of the anterior shaft of the radius (starting just distal to the radial
tuberosity)
Insertion : Anterior Surfaces of Fingers Two through Five
*each of the four tendons divides into two slips that attach onto the sides of the anterior surface
of the middle phalanx.
HUMEROULNAR HEAD:
medial epicondyle of the humerus (via the common flexor
belly/tendon) and the coronoid process of the ulna
RADIAL HEAD:
proximal 1/2 of the anterior shaft of the radius (starting just distal to the radial
tuberosity)
Insertion : Anterior Surfaces of Fingers Two through Five
*each of the four tendons divides into two slips that attach onto the sides of the anterior surface
of the middle phalanx.
Movement & Action
1. Flexes fingers two through five at the MCP and PIP joints
2. Flexes the hand at the wrist joint
3. Flexes the forearm at the elbow joint
MCP joints = metacarpophalangeal joints; PIP joints = proximal interphalangeal joints
2. Flexes the hand at the wrist joint
3. Flexes the forearm at the elbow joint
MCP joints = metacarpophalangeal joints; PIP joints = proximal interphalangeal joints
Notes
The FDS actually forms an intermediate layer between the superfi cial and the deep groups
of forearm muscles.
Near the wrist, the FDS gives rise to four tendons, which pass deep to
the flexor retinaculum through the carpal tunnel to the fingers.
To test the flexor digitorum superficialis, one finger is
flexed at the proximal interphalangeal joint against resistance
and the other three fingers are held in an extended position
to in activate the flexor digitorum profundus.
of forearm muscles.
Near the wrist, the FDS gives rise to four tendons, which pass deep to
the flexor retinaculum through the carpal tunnel to the fingers.
To test the flexor digitorum superficialis, one finger is
flexed at the proximal interphalangeal joint against resistance
and the other three fingers are held in an extended position
to in activate the flexor digitorum profundus.
Clinical Notes
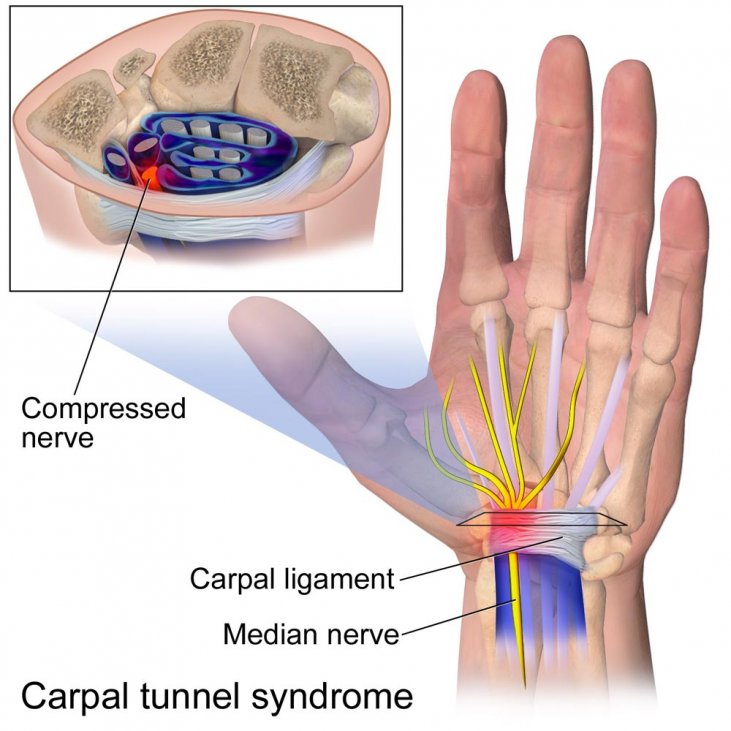
. Irritation of the synovial sheaths of the FDS and/or the flexor digitorum profundus in the carpal
tunnel can press on the median nerve and cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
tunnel can press on the median nerve and cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
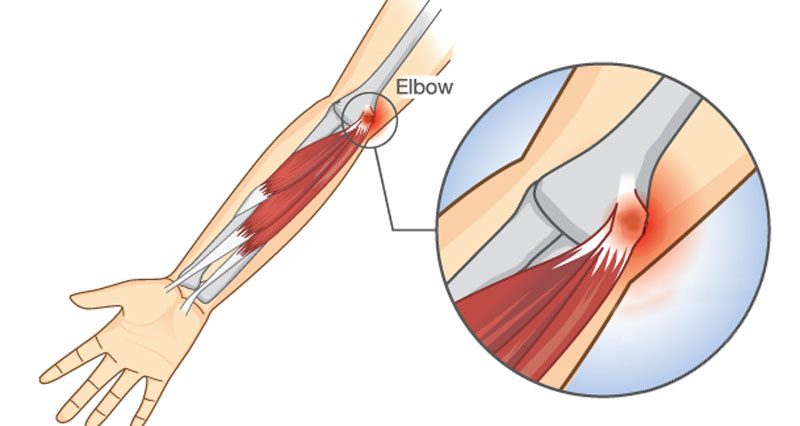
. Irritation and/or inflammation of the medial epicondyle and/or the common flexor belly/tendon is
known as medial epicondylitis, medial epicondylosis, or golfer’s elbow .
known as medial epicondylitis, medial epicondylosis, or golfer’s elbow .
Relations
The flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) is located in the anterior forearm, directly deep to the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris.
From the medial perspective, the FDS is deep to the ulnar head of the flexor carpi ulnaris.
Deep to the flexor FDS are the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus.
The four tendons of the FDS travel through the carpal tunnel medial to the median nerve and superficial to the four tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus.
The flexor digitorum superficialis is located within the superficial front arm line myofascial meridian.
From the medial perspective, the FDS is deep to the ulnar head of the flexor carpi ulnaris.
Deep to the flexor FDS are the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus.
The four tendons of the FDS travel through the carpal tunnel medial to the median nerve and superficial to the four tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus.
The flexor digitorum superficialis is located within the superficial front arm line myofascial meridian.
References
The Muscular system Manual - fourth edition
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition
https://images.app.goo.gl/FkBUgnfDrz7rqHEh8
https://images.app.goo.gl/AdBfspQ6KV3p56CD8
https://images.app.goo.gl/L4EcwkwZDfQqDUqA7
https://images.app.goo.gl/XjBMnbJ1p6P9ha3J9
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition
https://images.app.goo.gl/FkBUgnfDrz7rqHEh8
https://images.app.goo.gl/AdBfspQ6KV3p56CD8
https://images.app.goo.gl/L4EcwkwZDfQqDUqA7
https://images.app.goo.gl/XjBMnbJ1p6P9ha3J9
