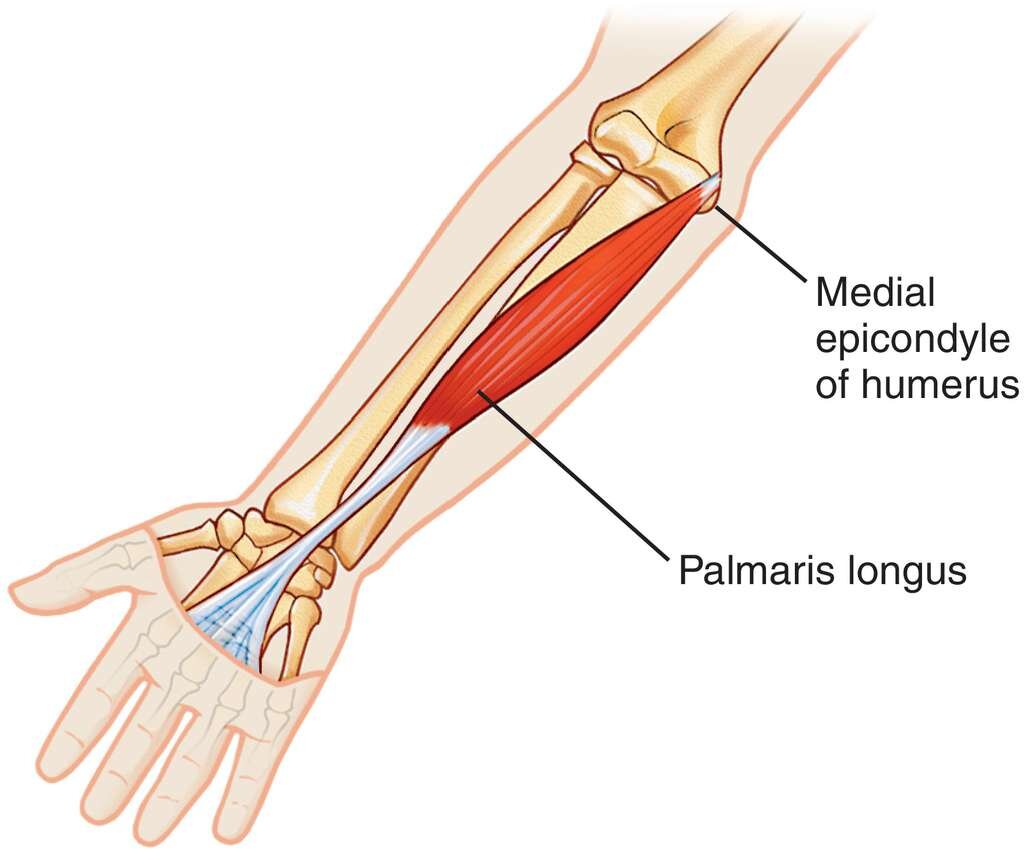
Palmaris Longus
By : Mustafa AhmedName
palmaris longus , tells us that this muscle attaches into the palm of the hand and is long (longer than the palmaris brevis).
Derivation :
palmaris: L. refers to the palm
longus: L. longer
Pronunciation :
pall-MA-ris
LONG-us
Derivation :
palmaris: L. refers to the palm
longus: L. longer
Pronunciation :
pall-MA-ris
LONG-us
general
1. The palmaris longus , is absent on one or both sides (usually the left) in approximately 14% of people, but its actions are not missed.
2. The flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris are often grouped together as
the wrist flexor group of the forearm.
3. The palmaris longus is the only muscle of the anterior forearm with a tendon that is superficial to the flexor retinaculum.
2. The flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris are often grouped together as
the wrist flexor group of the forearm.
3. The palmaris longus is the only muscle of the anterior forearm with a tendon that is superficial to the flexor retinaculum.
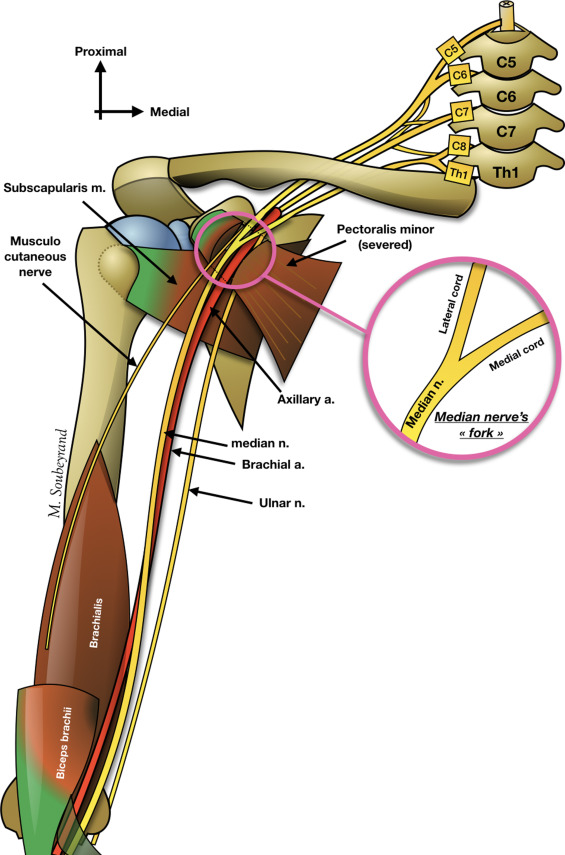
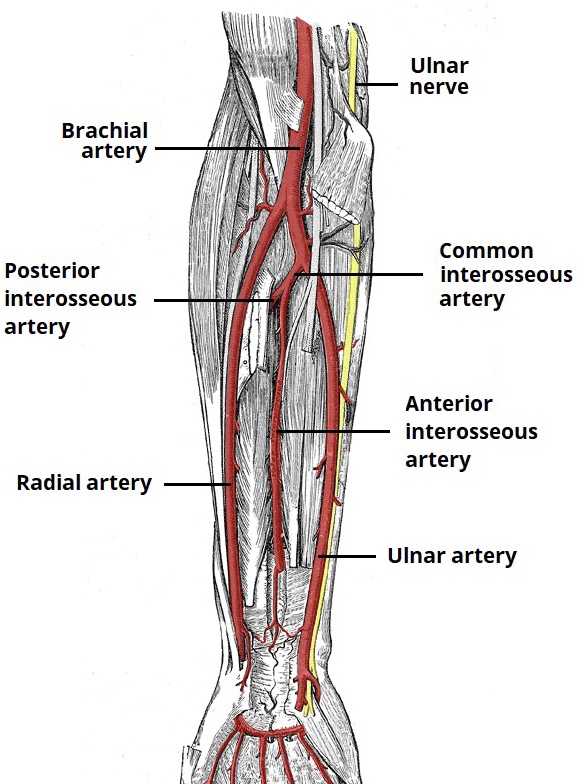
Supply
INNERVATION :
The Median Nerve
C7, C8
ARTERIAL SUPPLY :
The Ulnar Artery (a terminal branch of the Brachial Artery)
The Median Nerve
C7, C8
ARTERIAL SUPPLY :
The Ulnar Artery (a terminal branch of the Brachial Artery)
Origin & insertion
Origin : Medial Epicondyle of the Humerus via the Common Flexor Belly/Tendon
Insertion : Palm of the Hand(the palmar aponeurosis and the flexor retinaculum)
Insertion : Palm of the Hand(the palmar aponeurosis and the flexor retinaculum)
Movement & Actions
1. Flexes the hand at the
wrist joint.
2. Wrinkles the skin of the palm.
3. Flexes the forearm at the elbow joint.
4. Pronates the forearm at the RU joints.
5. Radially deviates the hand at
the wrist joint.
6. Ulnar deviates the hand at
the wrist joint.
RU joints = radioulnar joints; GH joint = glenohumeral joint
Notes
- The palmaris longus, a small fusi-form muscle.
- It has a short belly and a long, cord-like tendon that passes
superficial to the fl exor retinaculum and attaches to it and the
apex of the palmar aponeurosis.
- To test the palmaris longus, the wrist is fl exed and the pads
of the little fi nger and thumb are tightly pinched together. If
present and acting normally, the tendon can be easily seen
and palpated.
- It has a short belly and a long, cord-like tendon that passes
superficial to the fl exor retinaculum and attaches to it and the
apex of the palmar aponeurosis.
- To test the palmaris longus, the wrist is fl exed and the pads
of the little fi nger and thumb are tightly pinched together. If
present and acting normally, the tendon can be easily seen
and palpated.
Clinical Notes
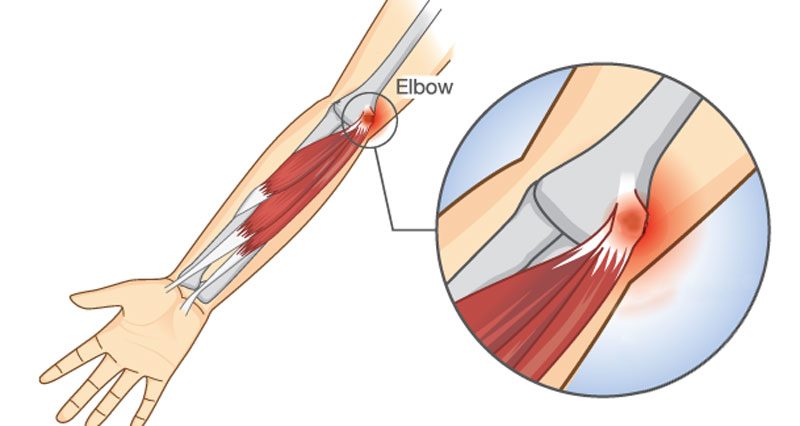
Irritation or inflammation of the medial epicondyle or the common flexor
belly/tendon is known as medial epicondylitis, medial epicondylosis, or golfer’s elbow.
belly/tendon is known as medial epicondylitis, medial epicondylosis, or golfer’s elbow.
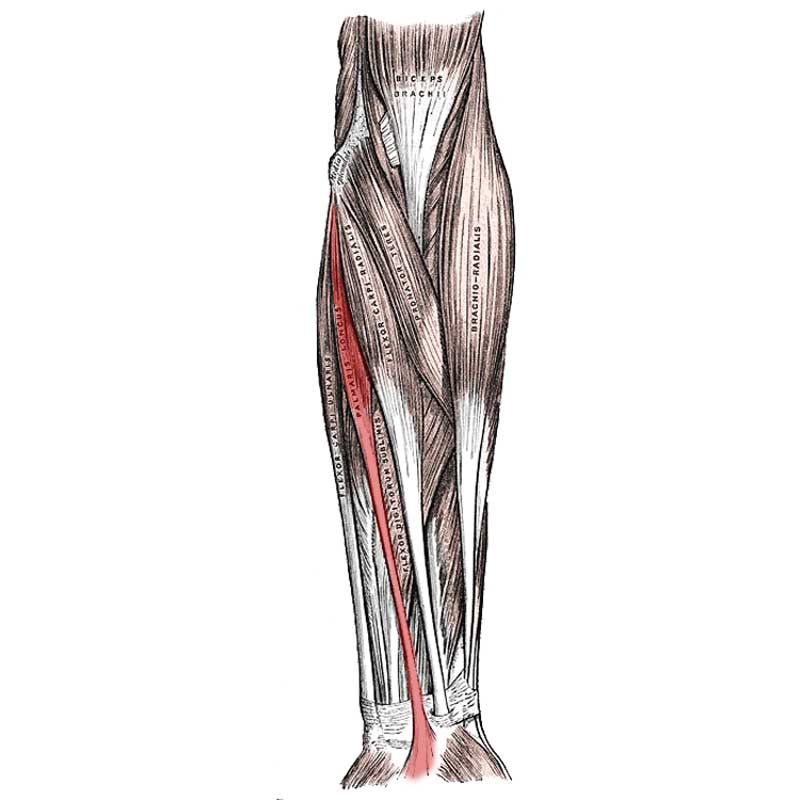
Relations
The palmaris longus is superficial in the anteromedial forearm.
The palmaris longus is medial to the flexor carpi radialis.
Proximally, the palmaris longus is lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris.
More distally, the palmaris longus is lateral to the flexor digitorum superficialis.
The palmaris longus is located within the superficial front arm line myofascial meridian
The palmaris longus is medial to the flexor carpi radialis.
Proximally, the palmaris longus is lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris.
More distally, the palmaris longus is lateral to the flexor digitorum superficialis.
The palmaris longus is located within the superficial front arm line myofascial meridian
References
The Muscular system Manual - fourth edition
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition
https://images.app.goo.gl/qXYe3FsroqD2s8kx9
https://images.app.goo.gl/VjC6r1r2EhGtheRL6
https://images.app.goo.gl/ehqKbShSRPo4Sx739
Moore-clinically oriented-Anatomy eighth edition
https://images.app.goo.gl/qXYe3FsroqD2s8kx9
https://images.app.goo.gl/VjC6r1r2EhGtheRL6
https://images.app.goo.gl/ehqKbShSRPo4Sx739
