.jpg)
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
By : Yaser MohammedLocation and Articulation
Proximal radioulnar joint: is a joint in the upper limb, especially in the forearm distal to the elbow joint lying between the proximal heads of radius and ulna bones.
the Proximal radioulnar joint formed from the articulation of the head of the radius (it's circular and convex) and the radial fossa of ulna (which is reciprocally concave). Both surfaces are lined with hyaline cartilage.
the Proximal radioulnar joint formed from the articulation of the head of the radius (it's circular and convex) and the radial fossa of ulna (which is reciprocally concave). Both surfaces are lined with hyaline cartilage.
Joint Type and Its Movement
Proximal radioulnar joint: is a joint in the upper limb, especially in the forearm distal to the elbow joint lying between the proximal heads of radius and ulna bones.
the Proximal radioulnar joint formed from the articulation of the head of radius (it's circular and convex) and the radial fossa of ulna (which is reciprocally concave). Both surfaces are lined with hyaline cartilage. [see fig 1]
the Proximal radioulnar joint formed from the articulation of the head of radius (it's circular and convex) and the radial fossa of ulna (which is reciprocally concave). Both surfaces are lined with hyaline cartilage. [see fig 1]
.jpg)
Articulation of the Proximal Radioulnar joint
Proximal radioulnar joint acts with the distal radioulnar joint to form two movements in the forearm:
Pronation: (range of motion is 61–66° ) When the palm or forearm faces down, it's pronated. the muscles that work to form pronation at this joint are pronator quadratus and pronator teres. The first is for slight movements, while the second is included in fast movements and movements against resistance.
Supination: (range of motion is 70–77° ) When the palm or forearm faces up, it's supinated. when the forearm is extended, supination is formed by contraction of supinator muscle, while when it's extended, and for the movement against resistance, the biceps brachii muscle acts as an accessory supinator.[see fig 2]
Pronation: (range of motion is 61–66° ) When the palm or forearm faces down, it's pronated. the muscles that work to form pronation at this joint are pronator quadratus and pronator teres. The first is for slight movements, while the second is included in fast movements and movements against resistance.
Supination: (range of motion is 70–77° ) When the palm or forearm faces up, it's supinated. when the forearm is extended, supination is formed by contraction of supinator muscle, while when it's extended, and for the movement against resistance, the biceps brachii muscle acts as an accessory supinator.[see fig 2]

Movements of the Joint
Blood Supply
The Blood supply to the proximal radioulnar joint comes from the radial collateral branch of deep brachial artery, radial and recurrent branches of the radial and common interosseous arteries which form a periarticular network. [see fig 3]
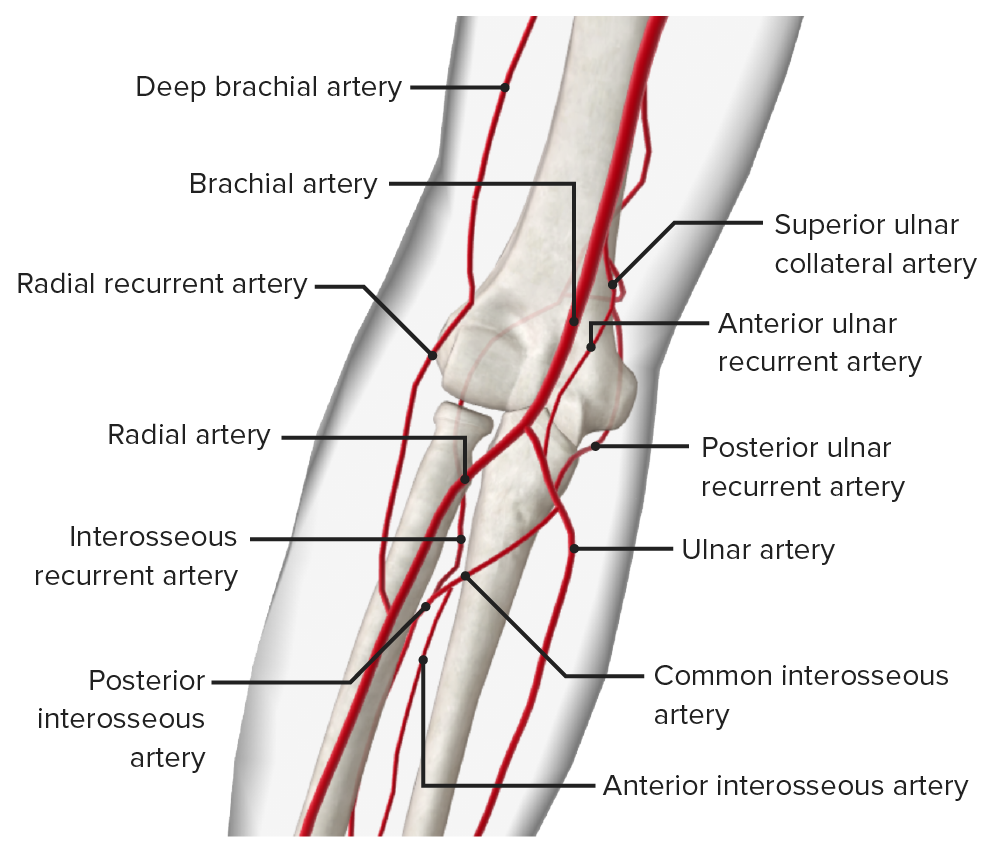
The Blood supply to the proximal radioulnar joint
Nerve Innervation
While the Nerve innervation of this joint is supplied by the branches of median, musculocutaneous, radial and ulnar nerves. [see fig 4]
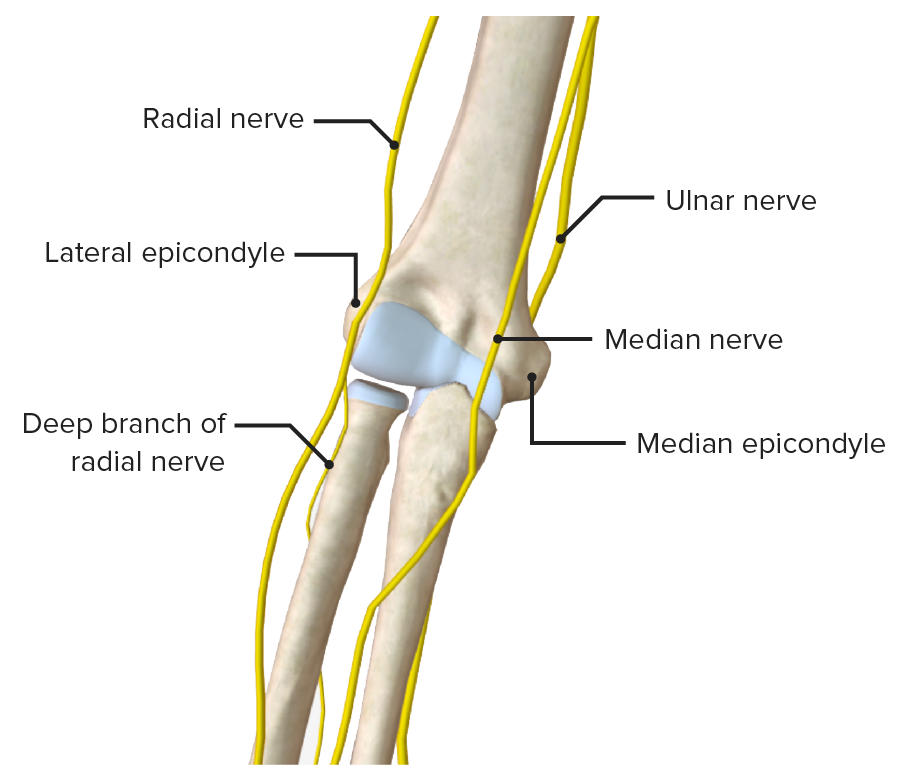
The Nerve innervation of the joint
Capsule and Ligaments
It has a fibrous capsule surrounding the joint which attaches to the annular ligament distally, and it is continuous with the capsule of the elbow joint proximally.
The proximal radioulnar joint is reinforced by the annular and quadrate ligaments and provide stability to it.
The annular ligament: extends from the anterior margin of radial fossa of ulna, encircles the radial head and attaches to the posterior margin of the radial fossa.
The quadrate ligament: is a short fibrous band that spans from the superior part of the supinator fossa of ulna to the neck of radius, just proximal to the radial tuberosity.
[see fig 5,6]
The proximal radioulnar joint is reinforced by the annular and quadrate ligaments and provide stability to it.
The annular ligament: extends from the anterior margin of radial fossa of ulna, encircles the radial head and attaches to the posterior margin of the radial fossa.
The quadrate ligament: is a short fibrous band that spans from the superior part of the supinator fossa of ulna to the neck of radius, just proximal to the radial tuberosity.
[see fig 5,6]
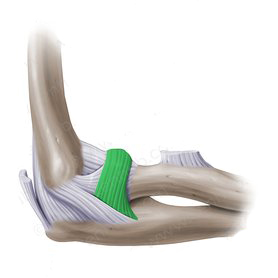
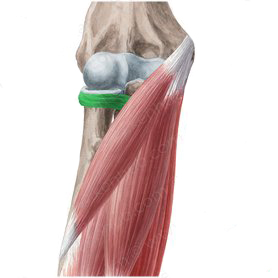
The Ligaments of the Joint (Annular ligament)
